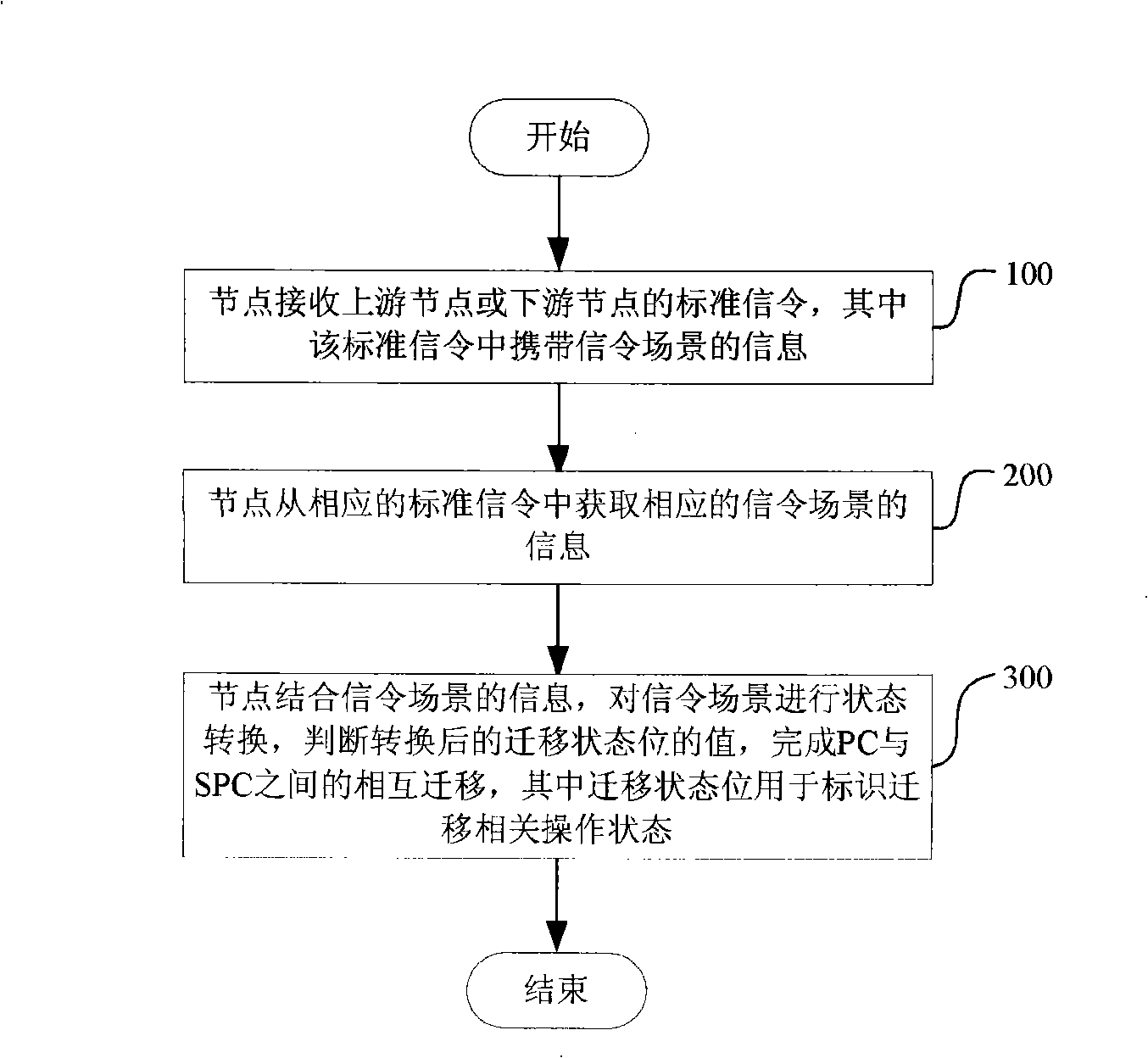
Method for automatically exchanging emigration based on status transition in optical network
A technology of state transition and automatic switching, applied in multiplexing system selection devices, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as service interruption, label and cross-connect release, and inability to ensure robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0058] Example 1: The normal signaling process of migrating the SPC to a PC.
[0059] Such as figure 2 As shown, the normal signaling process of migrating an SPC to a PC is consistent with the signaling process of graceful connection deletion described in RFC3473. combine Figure 7 , describing the processing under this signaling flow, the operation steps are as follows:
[0060] If the Path signaling from the upstream node is received, the corresponding signaling scenario is taken out from the private data of the Path. At this time, the signaling scenario should be the migration of SPC to PC; judge the value of the migration status bit, and combine the signaling scenario, Make corresponding conversions.
[0061] At this point, different values are handled as follows:
[0062] takes the value of PC migration to SPC success status, at this time, the SPC is successfully migrated from PC, and it is converted to start the migration from SPC to PC.
[0063] The value is t...
example 2
[0069] Example 2: An abnormal signaling process for migrating from an SPC to a PC.
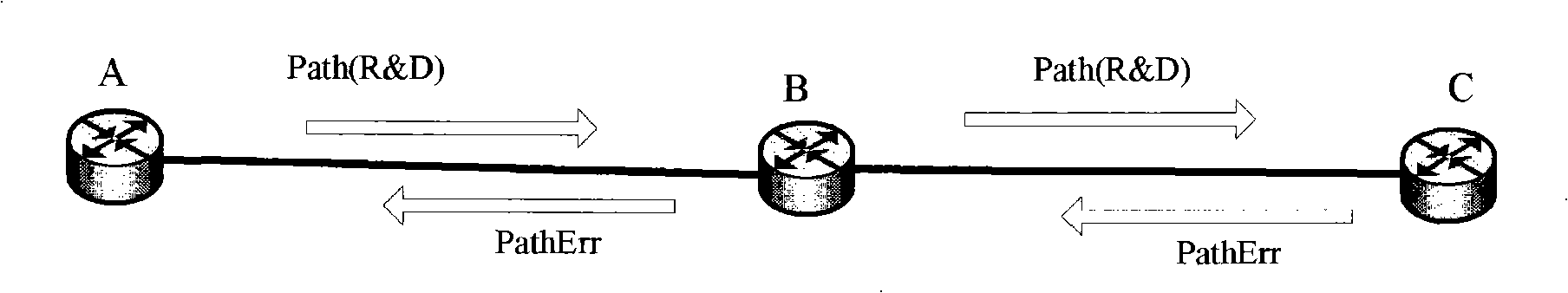
[0070] Such as image 3 As shown, the abnormal signaling process of migrating an SPC to a PC is consistent with the signaling process of forced connection deletion described in RFC3473. Image 6 In indicates that after the first node sends Path (R&D), it does not receive the downstream PathErr within a timeout (the timeout may be due to the failure of the downstream signaling control channel or the failure of the downstream node), and sends Pathtear to the downstream to implement forced migration from SPC to PC. combine Figure 7 , taking the intermediate node as an example to describe the implementation of migrating SPC to PC under this signaling process, the operation steps are as follows:
[0071] Step 201: Receive the Pathtear signaling from the upstream node, and take out the corresponding signaling scenario from the private data of Path according to the interface provided by the protoc...
example 3
[0077] Example 3: When a PC is migrated to an SPC, a PathErr from a downstream node is received.
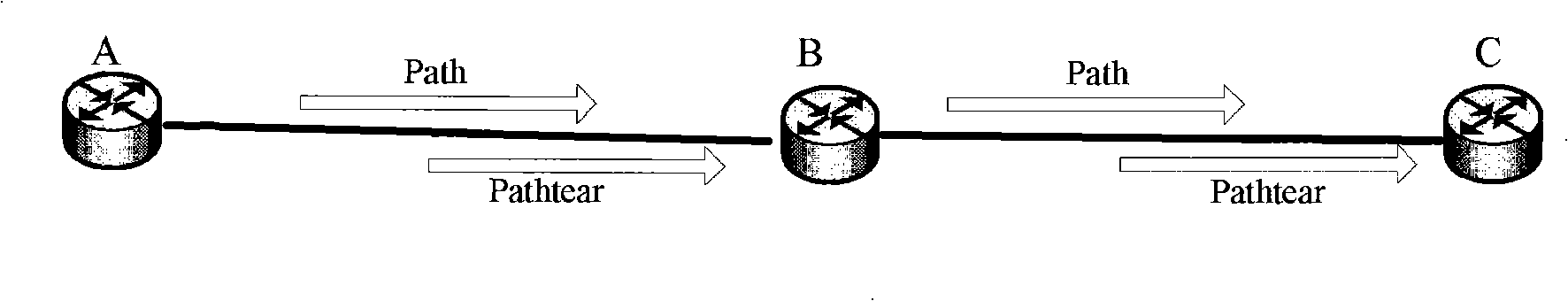
[0078] Such as Figure 4 As shown, when the PC is migrated to the SPC, the intermediate node fails to migrate the cross-connection after receiving the downstream Resv signaling. If it fails, it will respond to the failure of the protocol stack, thus sending Pathtear downstream and PathErr upstream.
[0079] Such as Figure 5 As shown, when the PC is migrated to the SPC, after the intermediate node sends the Path signaling, the intermediate node receives the PathErr returned by the tail node due to an error in the migration of the tail node.
[0080] combine Figure 7 , taking the middle node as an example, described in Figure 4 , Figure 5 The implementation of migrating from SPC to PC under the signaling process, the operation steps are as follows:
[0081] Step 301: Receive the PathErr message (for Figure 4 , the intermediate node is the origin of PathErr, for Figure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com