Collision avoidance for traffic in a wireless network
A wireless network and business technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as extra delay of business data, transmission failure, and consumption of broadcast time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The word "exemplary" is used herein to mean "serving as an instance, instance, illustration". Any embodiment or design described herein as "exemplary" is not necessarily to be construed as preferred or advantageous over other embodiments or designs.
[0021] The collision avoidance techniques described herein can be used in various wireless networks, such as WLAN, WWAN, WMAN, WMAN, WPAN, etc. A WLAN may implement one or more standards in the IEEE 802.11 family of standards for WLANs developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
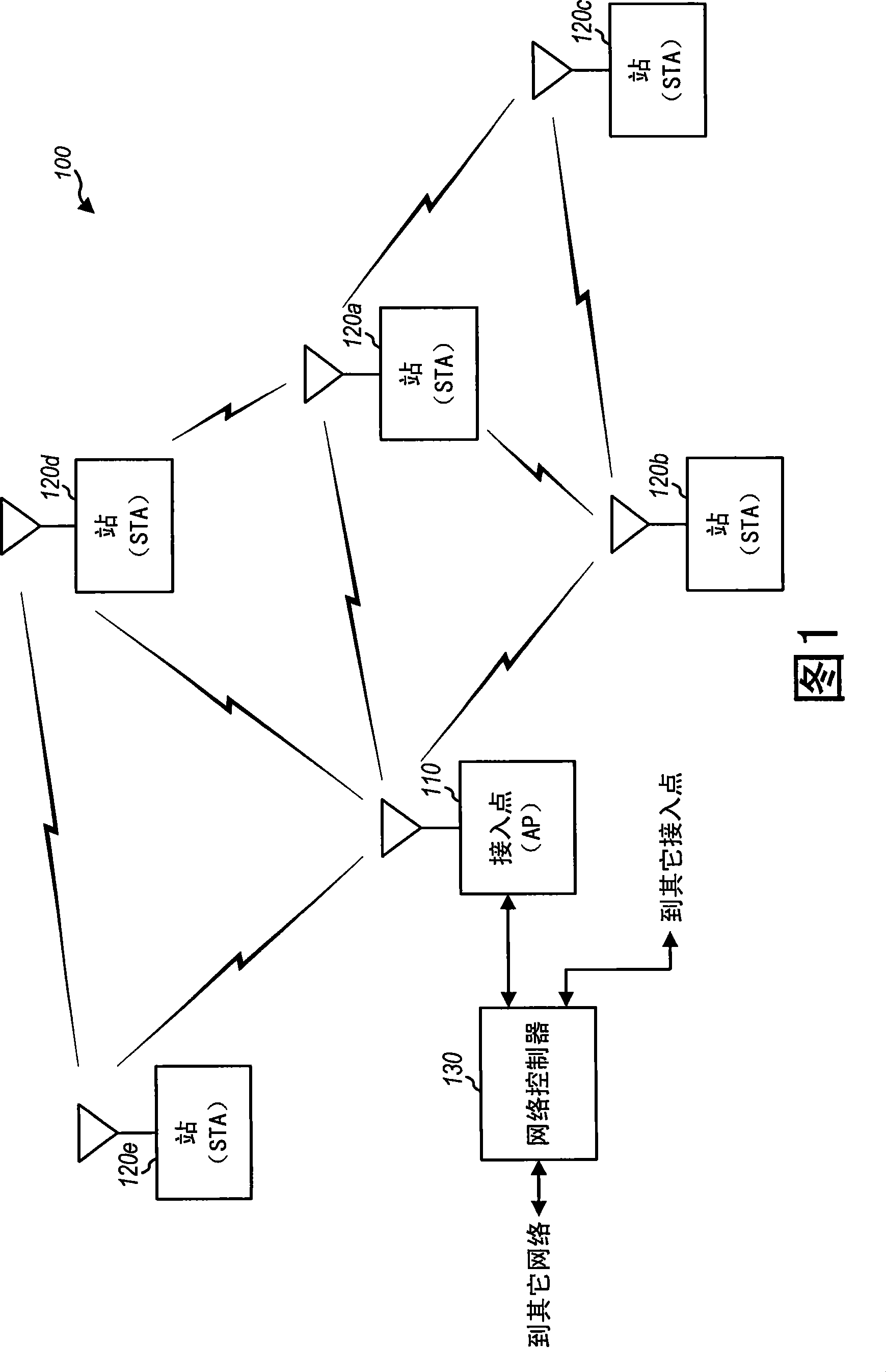
[0022] FIG. 1 shows a wireless network 100 having an access point (AP) 110 and a plurality of stations (SAT) 120 . In general, a wireless network can include any number of access points and any number of stations. A station is a device that can communicate with another station via a wireless medium. The terms "wireless medium," "wireless channel," and "channel" are often used interchangeably. A station may commu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com