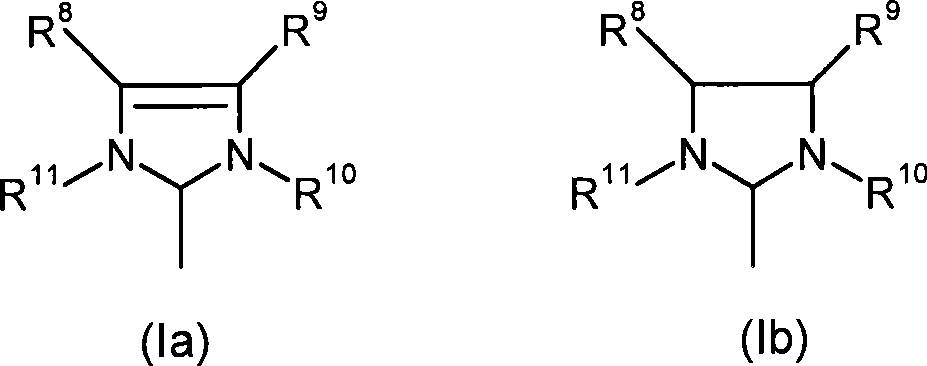
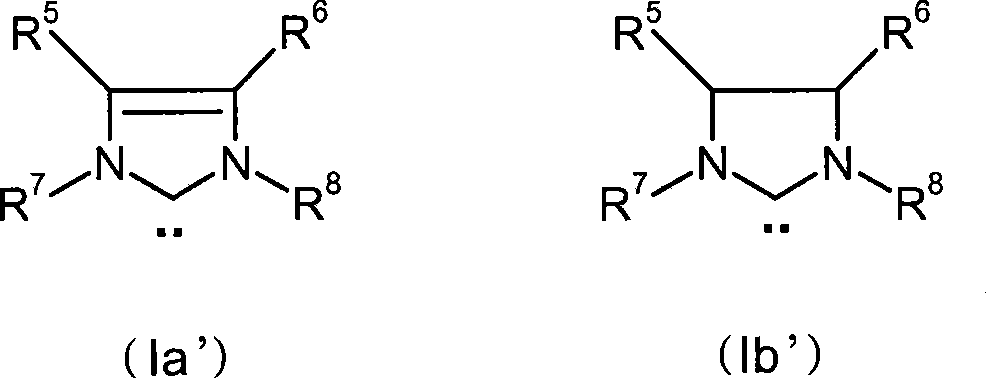
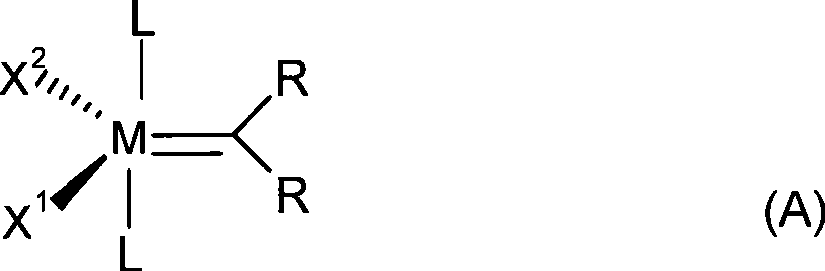A process for removing iron-residues, rhodium- and ruthenium-containing catalyst residues from optionally hydrogenated nitrile rubber
A nitrile rubber, ruthenium catalyst technology, applied in the field of removing iron residues, rhodium-containing and ruthenium-containing catalyst residues from optionally hydrogenated nitrile rubber, capable of solving the problem of catalyst removal, nitrile rubber solution is not an alternative, Cost and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1-3 and comparative example 4
[0160] A hydrogenated nitrile rubber containing 34% by weight of acrylonitrile, less than 0.9% of residual double bonds and a Mooney viscosity (ML 1+4 at 100°C) of 65 was used, produced by adding a Nitrile butadiene rubber (34% by weight acrylonitrile, 66% butadiene) in RhCl (PPh 3 ) 3 (Ph = phenyl) is prepared by subjecting it to hydrogenation in the presence of a catalyst.
[0161] A 6.0% by weight solution of this hydrogenated nitrile rubber in monochlorobenzene was used as a standard for the following examples, and the term "hydrogenated nitrile rubber", as used in the following examples, refers to this solution.
[0162] In Examples 1-3, 0.5 g of the specified resin (see Table 1) was added together with 180 g of the hydrogenated nitrile rubber solution in a 500 ml three-necked round bottom flask. Each reaction mixture was stirred at about 100°C under nitrogen for 66 hours. The resin was then removed from the mixture by filtration and the rubber recovered by evaporatin...
example 5
[0168] A hydrogenated nitrile rubber containing 34% by weight of acrylonitrile, having less than 0.9% residual double bonds and a Mooney viscosity (ML 1+4 at 100°C) of 40 was used by adding a Nitrile butadiene rubber (34% by weight acrylonitrile, 66% butadiene) undergoes a metathesis process using a ruthenium-containing catalyst of general formula (III) and additionally reacts in RhCl (PPh 3 ) 3 (Ph = phenyl) is prepared by subjecting it to a subsequent hydrogenation process in the presence of a catalyst.
[0169] A 6.0% by weight solution of this hydrogenated nitrile rubber in monochlorobenzene, which was subjected to a metathesis process before hydrogenation, and the term "hydrogenated nitrile rubber", as here As used herein, this solution is referred to.
[0170] In a 500 ml three-necked round bottom flask, 0.5 g of a specified resin (see Table 1) was added together with 180 g of the hydrogenated nitrile rubber solution. The reaction mixture was stirred at about 100°C un...
example 7
[0176] A hydrogenated nitrile rubber containing 34% by weight of acrylonitrile, having less than 0.9% residual double bonds and a Mooney viscosity (ML 1+4 at 100°C) of 65 was used by adding a Nitrile butadiene rubber (34% by weight acrylonitrile, 66% butadiene) in RhCl (PPh 3 ) 3 (Ph = phenyl) is prepared by subjecting it to hydrogenation in the presence of a catalyst.
[0177] A 6.0% (by weight) solution of this hydrogenated nitrile rubber in monochlorobenzene was used as the standard for the following examples. The term "hydrogenated nitrile rubber", as used in the following examples, refers to this solution.
[0178] In a 500 ml three-necked round bottom flask, 0.5 g of a specified resin (as shown in Table 1) was added together with 180 g of the hydrogenated nitrile rubber solution. The reaction mixture was stirred at approximately 100° C. under nitrogen for various time intervals (see Table 4). The resin was then removed from the mixture by filtration and the hydrogenate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com