Transmission method of random access response, transmission base station and receiving terminal
A technology of random access response and random access preamble, applied in the field of communications, can solve problems such as wasting system resources, and achieve the effects of reducing resource waste, improving utilization, and avoiding excessive restrictions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
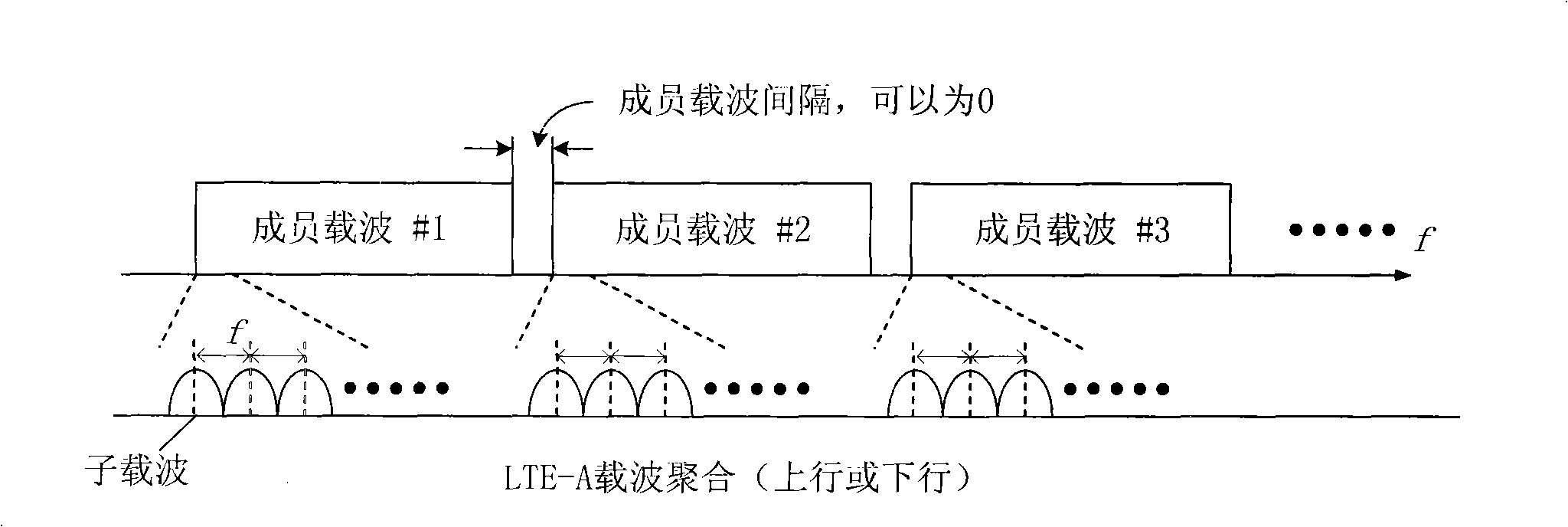
[0172] There are four 20MHz component carriers in the downlink, namely D1, D2, D3, and D4; there are two 20MHz component carriers in the uplink, namely U1 and U2.
[0173] The downlink component carriers are divided into two groups, that is, N=2. Such as Figure 4 As shown in the figure, Indicates the downlink synchronization signal, Indicates a broadcast channel. The first group contains {D1, D2}, which corresponds to U1; the second group contains {D3, D4}, which corresponds to U2. That is, a terminal whose downlink is synchronized to D1 or D2 sends a random access preamble on the uplink carrier U1; a terminal whose downlink is synchronized to D3 or D4 sends a random access preamble on the uplink carrier U2.
[0174] The base station notifies the terminal with broadcast signaling: the terminal with downlink synchronization in the first group of downlink component carriers receives a random access response on D1; the terminal with downlink synchronization in the second g...
Embodiment 2
[0178] There are four 20MHz component carriers in the downlink, namely D1, D2, D3, and D4; there are two 20MHz component carriers in the uplink, namely U1 and U2.
[0179] The downlink component carriers are divided into two groups, that is, N=2. Such as Figure 5 As shown in the figure, Indicates the downlink synchronization signal, Indicates a broadcast channel. The first group contains {D1, D2}, which corresponds to U1; the second group contains {D3, D4}, which corresponds to U2. That is, a terminal whose downlink is synchronized to D1 or D2 sends a random access preamble on the uplink carrier U1; a terminal whose downlink is synchronized to D3 or D4 sends a random access preamble on the uplink carrier U2.
[0180] In the first group, the random access response is always sent on D1, and in the second group, the random access response is always sent on D3
[0181] According to the uplink component carrier used by the terminal to send the preamble, the base station can...
Embodiment 3
[0183] There are four 20MHz component carriers in the downlink, namely D1, D2, D3, and D4; there are two 20MHz component carriers in the uplink, namely U1 and U2.
[0184] The downlink component carriers are divided into two groups, that is, N=2. Such as Figure 6 As shown in the figure, Indicates the downlink synchronization signal, Indicates the broadcast channel, □ indicates the random access preamble with an even number, Indicates a random access preamble with an odd sequence number. The first group contains {D1, D2}, which corresponds to U1; the second group contains {D3, D4}, which corresponds to U2. That is, a terminal whose downlink is synchronized to D1 or D2 sends a random access preamble on the uplink carrier U1; a terminal whose downlink is synchronized to D3 or D4 sends a random access preamble on the uplink carrier U2.
[0185] In the first group, the downlink synchronous terminals on D1 use random access preambles with even numbers, and the downlink sync...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com