Interval propagation reasoning method of Ising graphical model
A reasoning method and graph model technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, character and pattern recognition, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problem of rarely considering variational reasoning methods, reducing computational complexity, and difficult to measure approximate belief propagation calculations Accuracy and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0066] Firstly, the reasoning method of the present invention will be introduced in detail below.
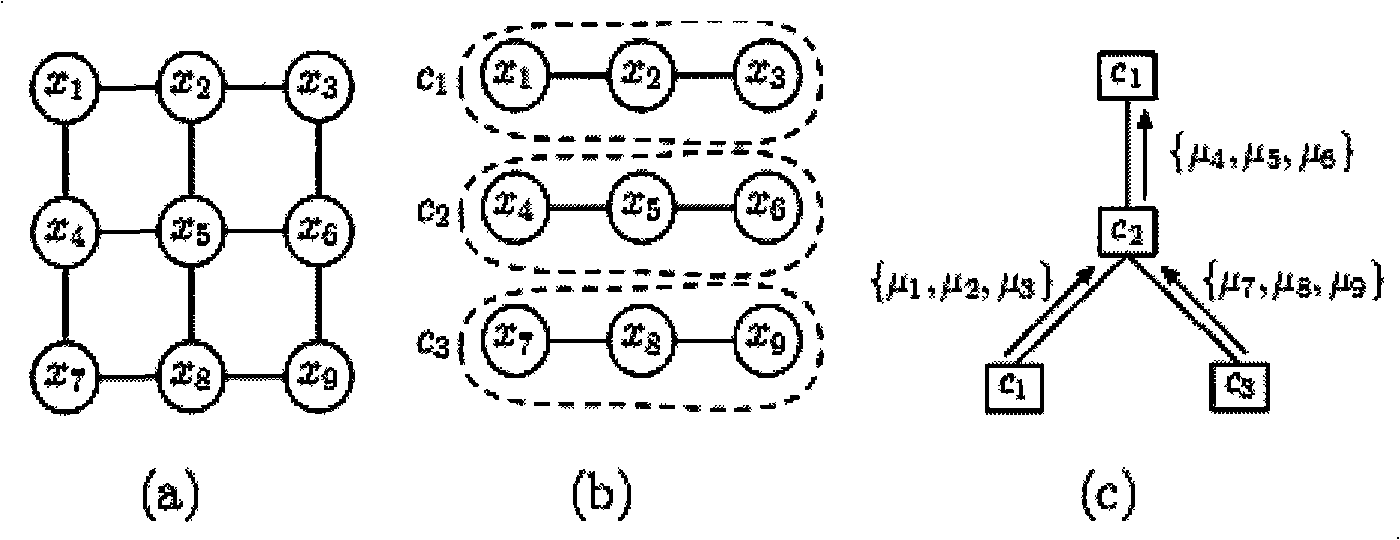
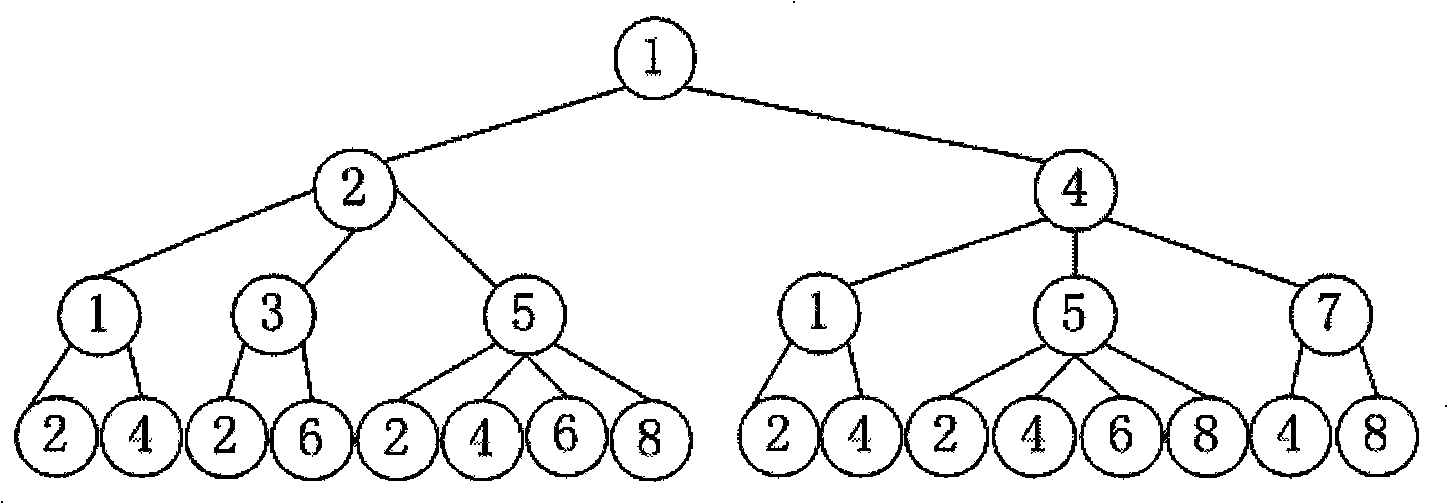
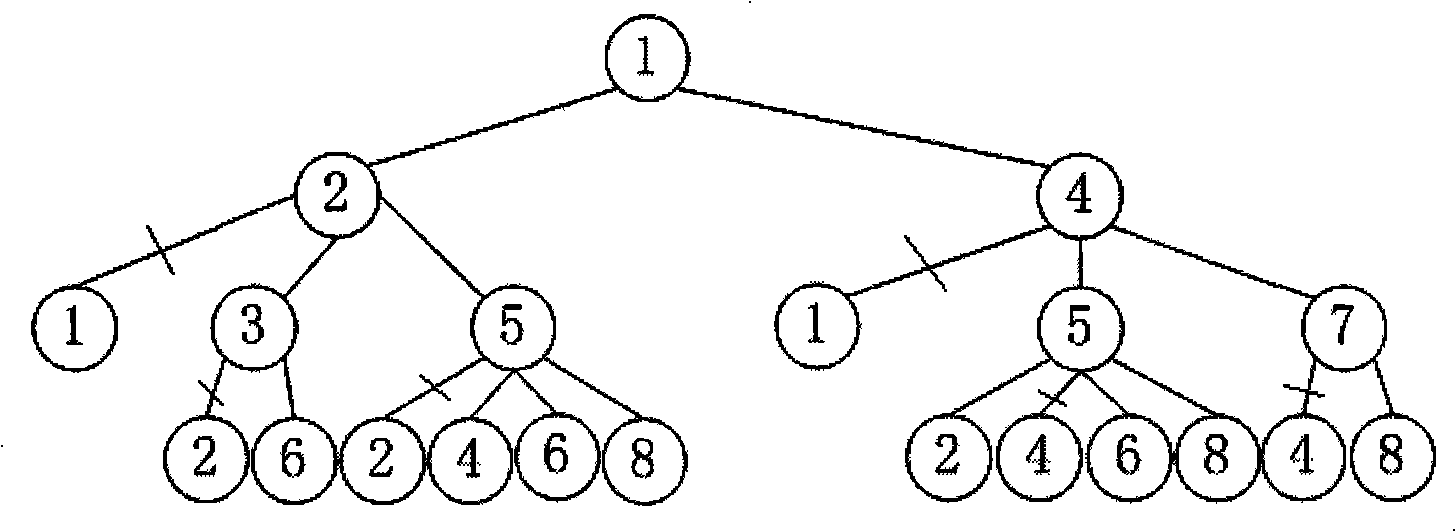
[0067] 1. Ising mean field calculation tree
[0068] The Ising mean field calculation tree is a tree structure to represent the iterative calculation process of the mean field on the Ising graphical model.
[0069] Definition 1: Under Ising mean field inference, the variable cluster c γ The computational tree model is a quadruple T(D γ , R, M, Q).
[0070] in:
[0071] 5)D γ : to c γ The variable cluster node set D which is the root node γ ={c γ}∪Ch(c γ )∪Ch(Ch(c γ ))∪….
[0072] Among them, Ch(c γ ) means c γ The child node set of Ch(c γ )={c β |x i ∈ c γ , x j ∈ c β , (i, j)∈E, γ≠β}, Ch(Ch(c γ )) represents the variable set Ch(c γ ) child node set: Ch ( Ch ( c γ ) ) = ∪ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com