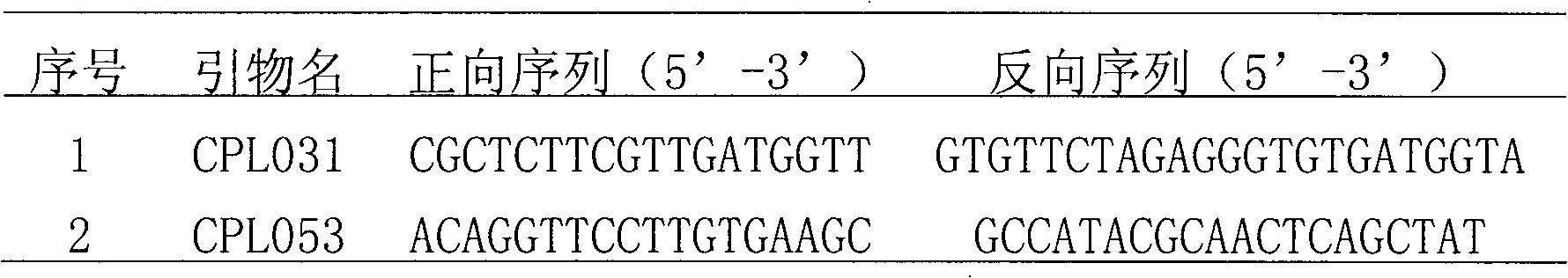Method for rapidly detecting seed purity of asparagus bean cultivars and reagent kit thereof
A cowpea and seed technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as long identification time, crops are easy to change with environmental conditions, etc., to achieve convenient operation, stable and reliable test results, and improved standardization. degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: (application kit is required to identify the target variety to be the detection of one of five main varieties to be tested) according to the following steps:
[0033] (1) DNA extraction: spread the seeds to be tested in a seedling tray equipped with a substrate (vermiculite:peat=1:2), place the seedlings at 25-30°C, and when the first pair of true leaves are flat, separate Take 0.1 g of the leaves of the plant, add liquid nitrogen and grind them into powder, and use the conventional CTAB method to extract DNA;
[0034] (2) SSR primer amplification and electrophoresis detection: use SSR10 provided in the kit for PCR analysis of diagnostic primers, the reaction volume is 12.5 μL; each PCR component is 1.25 μL of 10×buffer, 25 mM MgCl 20.75μL, 2.5mM dNTPs 1μL, Taq enzyme (5U / μL) 0.1μL, template DNA 10ng, add water to 12.5μL; SSR reaction program: 94°C pre-denaturation for 3min, 94°C denaturation for 30sec, 52°C annealing for 30sec, 72°C Extend for 50 sec, cy...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: (application kit is to the detection that requires identification target variety to be one of non-five main cultivars tested sample)
[0037] Follow these steps:
[0038] (1) DNA extraction: the seeds to be tested and the standard seeds required to identify the target species are spread respectively in seedling trays equipped with substrates (vermiculite: peat=1: 2), placed at 25-30°C for seedling cultivation, When the first pair of true leaves are flattened, take 0.1 g of leaves per plant, add liquid nitrogen and grind them into powder, and use CTAB method to extract DNA;
[0039] (2) SSR primer amplification and electrophoresis detection: same as Example 1;
[0040] (3) according to the PCR amplification and electrophoresis detection results of the seeds to be tested and the seeds of the standard variety respectively, construct the DNA fingerprints of the seeds to be tested and the seeds of the standard variety;
[0041] (4) DNA Fingerprint Comparison ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: (the contrast test of the present invention and traditional method identification seed purity)
[0043] The traditional identification method is carried out in the following steps:
[0044] 1. Sow the standard seeds of the variety to be tested and the target variety required to be identified in the field or greenhouse, with a row spacing of 70cm and a plant spacing of 30cm, 1 seed per hole, more than 100 holes for each variety, and the minimum environmental temperature requirement is higher than 15°C;
[0045] 2. Daily field management refers to conventional cultivation techniques.
[0046] 3, generally observe carefully the characteristic characteristic of this standard variety in the tender pod blooming period, compare the difference of the characteristic characteristic of the variety to be tested and the standard variety one by one, determine the authenticity of the seed, and use the formula after the detection is all completed: seed purity=(detected tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com