Circular chromosome conformation capture (4c)
一种染色体、核苷酸序列的技术,应用在环状染色体构象捕获(4C)领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0567] and figure 2 , 13 , 14, 15, 16, 17, 19 matching materials and methods
[0568] 4C technology
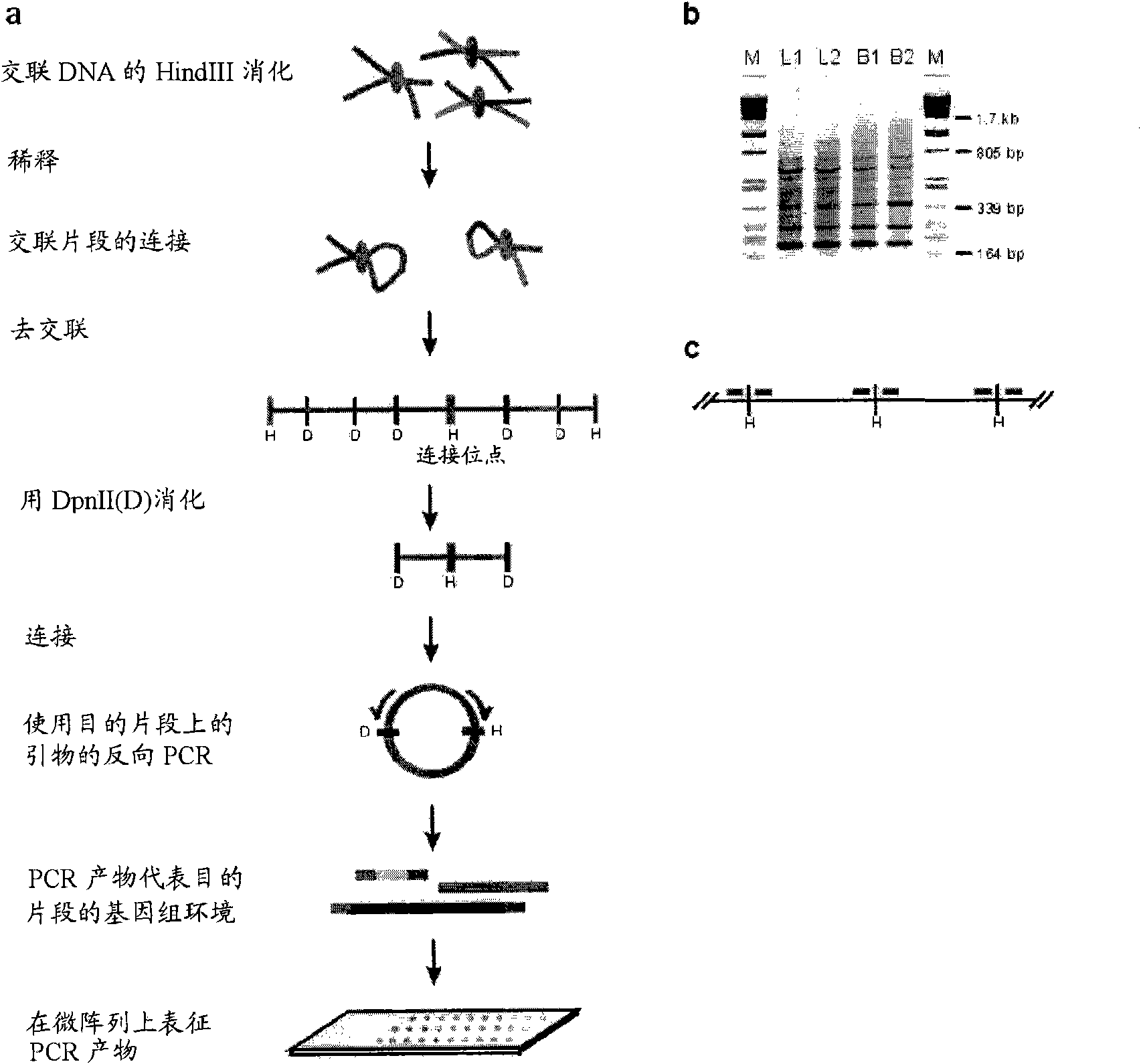
[0569]The initial steps of the 3C technology process were performed as described previously (Splinter et al. (2004). Methods Enzymol 375, 493-507 (2004)), generating ligation products between HindIII fragments. The HindIII-ligated 3C template (~50 μg) was digested overnight at 100 ng / μl with 50 U of the second, frequently cutting restriction enzyme, DpnII (HS2, Rad23A) or NlaIII (β-major). To avoid restriction of DNA loop formation (Rippe et al. (1995) Trends Biochem Sci 20, 500-6), care is taken to select a second restriction enzyme that is not at a distance from the HindIII restriction enzyme site demarcating the restriction fragment of interest (i.e. the 'bait') Point about 350-400bp within the cut. After digestion with the second restriction enzyme, the DNA was extracted with phenol, precipitated with ethanol, and then ligated at a low concentration (200 U ligase (R...
Embodiment 2
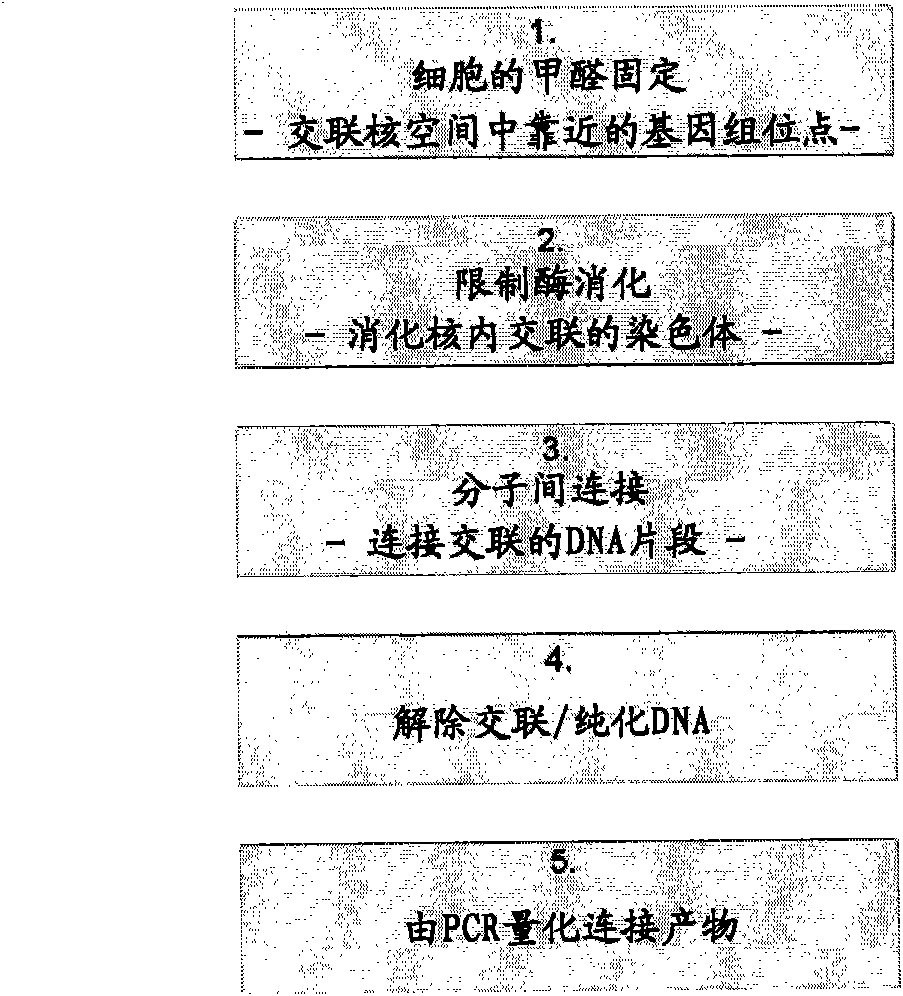
[0592] The 3C procedure (i.e. fixation with formaldehyde, digestion with (first) restriction enzyme, religation of cross-linked DNA fragments and DNA purification), resulting in a DNA mixture ('3C template') containing restriction fragments that were ligated due to their original proximity in the nuclear space.
[0593] Inverse PCR is performed to amplify all nucleotide sequences associated with a given restriction fragment ("bait"; as it contains a promoter, enhancer, insulator, matrix attachment region, origin of replication, or any other primary (target) nucleotide sequence while being picked) connected fragments.
[0594] To this end, the 3C template is generated by digesting the 3C template with a second restriction enzyme (preferably one that recognizes frequent cleavage of sequences of four or five nucleotides), followed by ligation under dilute conditions that favor intramolecular interactions. DNA circle. In order to minimize the bias in loop formation due to topolo...
Embodiment 3
[0609] Detecting translocations using 4C techniques
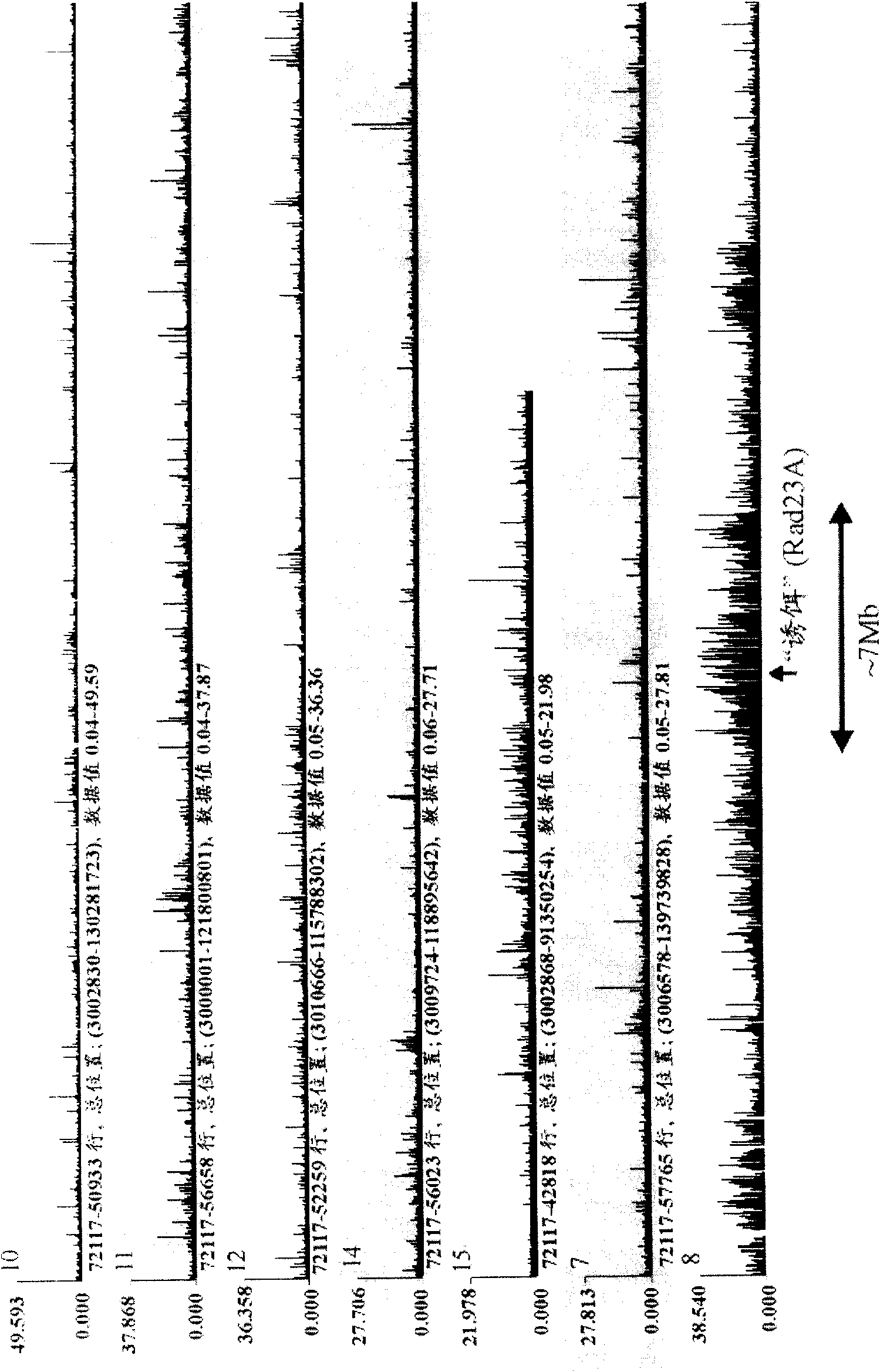
[0610] The frequency of interaction against a given sequence X occurring on a given chromosome A in cells from healthy subjects and in cells from patients with a single sequence between chromosomes A and B was measured using the 4C technique Reciprocal translocations in which the breakpoint is close to sequence X (eg Figure 8 shown).
[0611] In normal cells, this analysis revealed an enhanced hybridization signal (i.e., frequent interaction with X) for (almost) every probe located within 0.2-10 Mb of sequence X on chromosome A (showing strong cross-linking The actual size of the chromosomal region of the signal depends largely on the complexity of the sample hybridized to the array). Elsewhere on the same chromosome A, as well as on other chromosomes, no such large probe regions (on linear DNA templates) with increased hybridization signals were observed.
[0612] However, in patient cells, the hybridization signal was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com