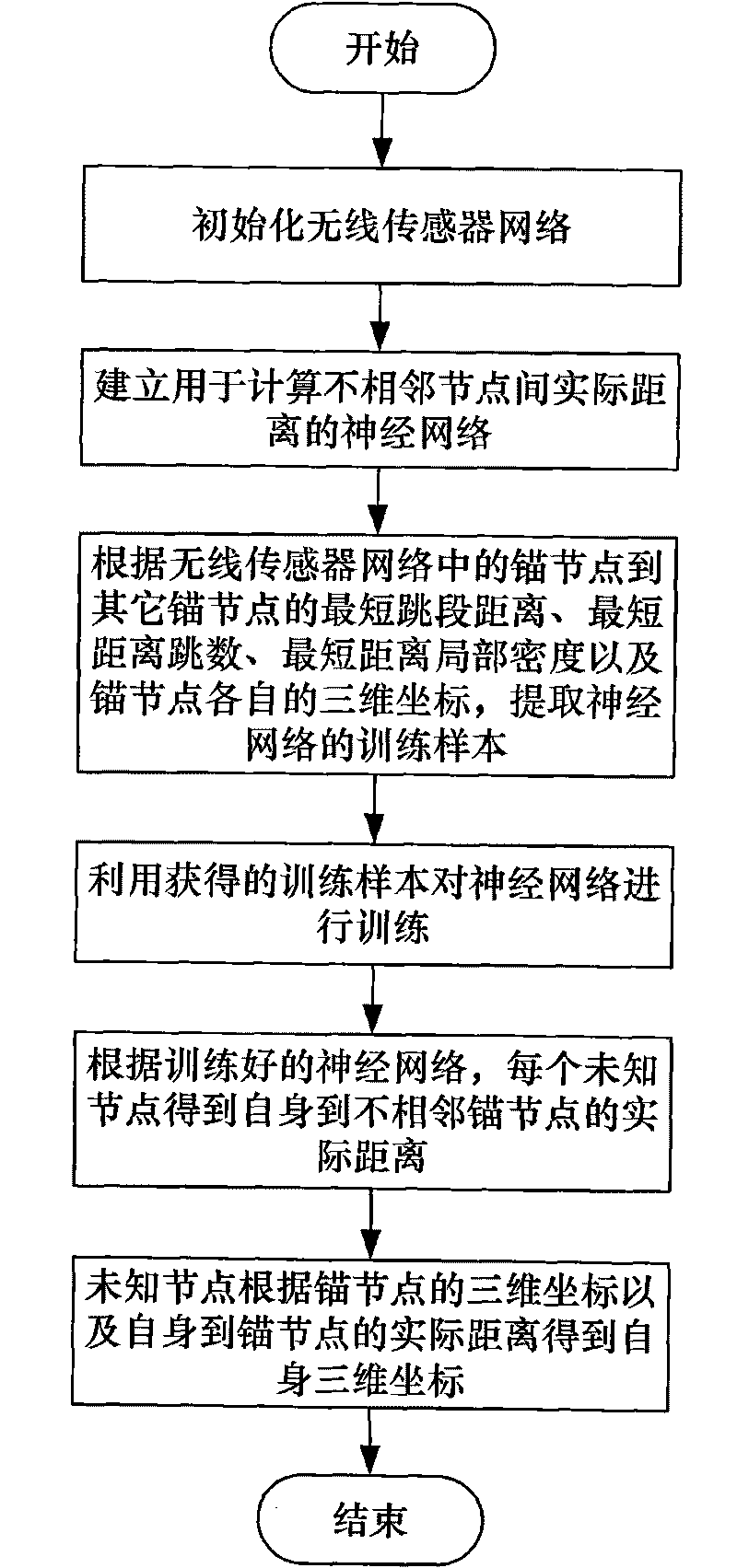
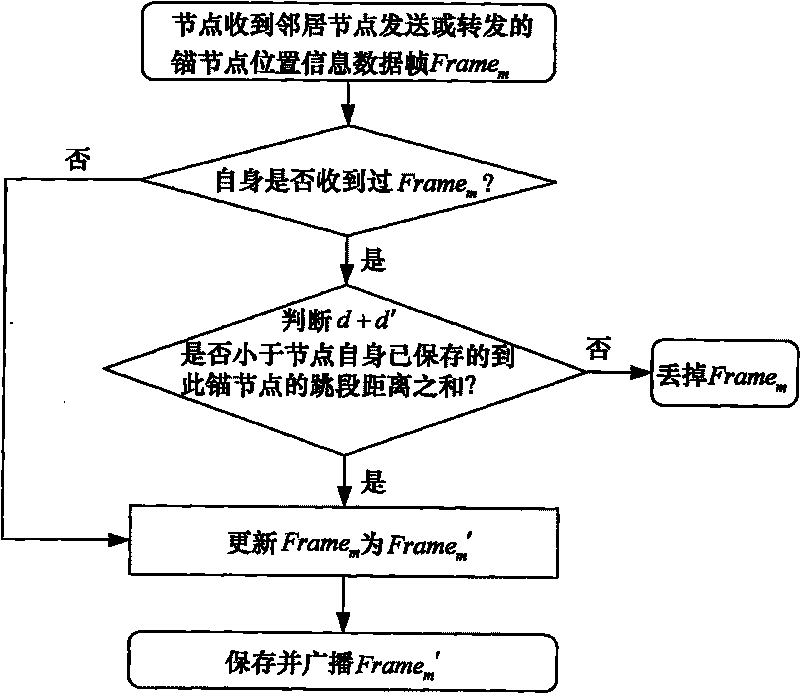
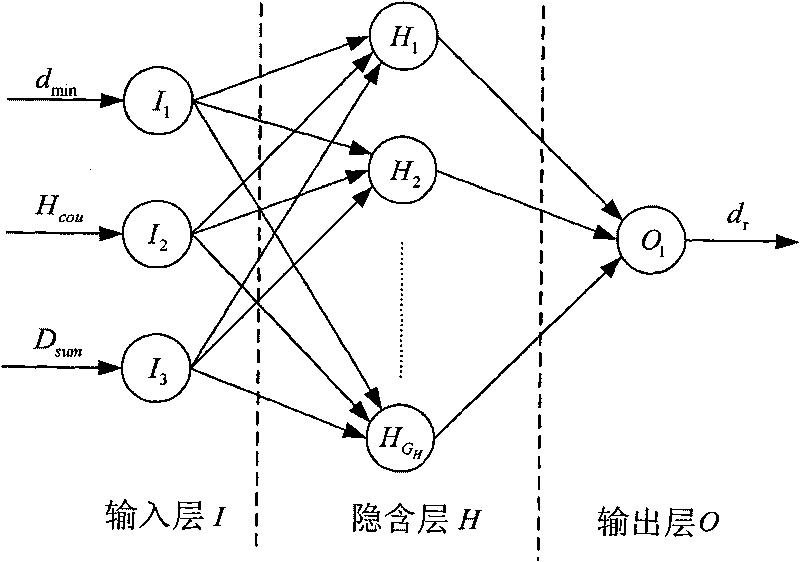
Three-dimensional wireless sensor network node self-locating method based on neural network
A wireless sensor and neural network technology, applied in the field of self-location of wireless sensor network nodes, can solve the problems of low representativeness of samples and failure to consider the impact of positioning performance, etc., achieve simple sample acquisition methods, strong sample representativeness, and reduce distance The effect of estimation error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0088] Such as Figure 5 As shown, 200 wireless sensor nodes are randomly deployed in a uniform distribution in a three-dimensional space area of 200m×200m×200m; in the figure, the anchor nodes are solid five-pointed stars, the proportion is 20%, and the ID is 1-40; unknown nodes are solid Dots with a scale of 80% and an ID of 41-200.
[0089] Using the node positioning method of the present invention and the distance vector method to perform node positioning respectively, the positioning error of each node obtained is as follows: Image 6 As shown, the solid line in the figure is the positioning error of each node obtained using the method of the present invention, and the average positioning error is 23.45%; the dotted line in the figure is the positioning error of each node obtained using the distance vector method, and the average positioning error is 43.67%; Compared with the distance vector method, the method of the present invention can improve the positioning accura...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com