Area information based quiescent voltage unstability prediction method
A static voltage and wide-area information technology, applied in the direction of measuring current/voltage, measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as difficult and predictable voltage instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
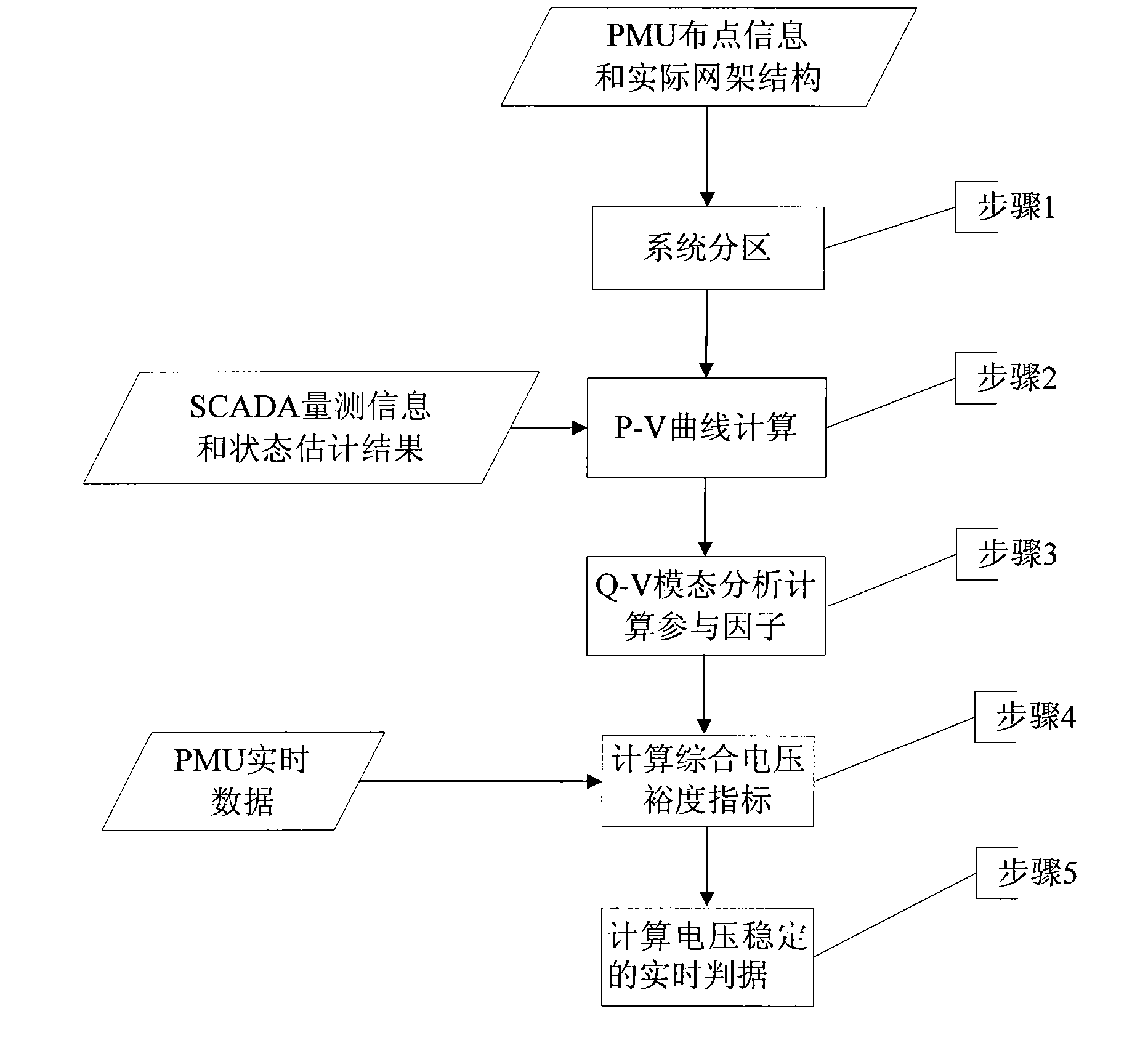
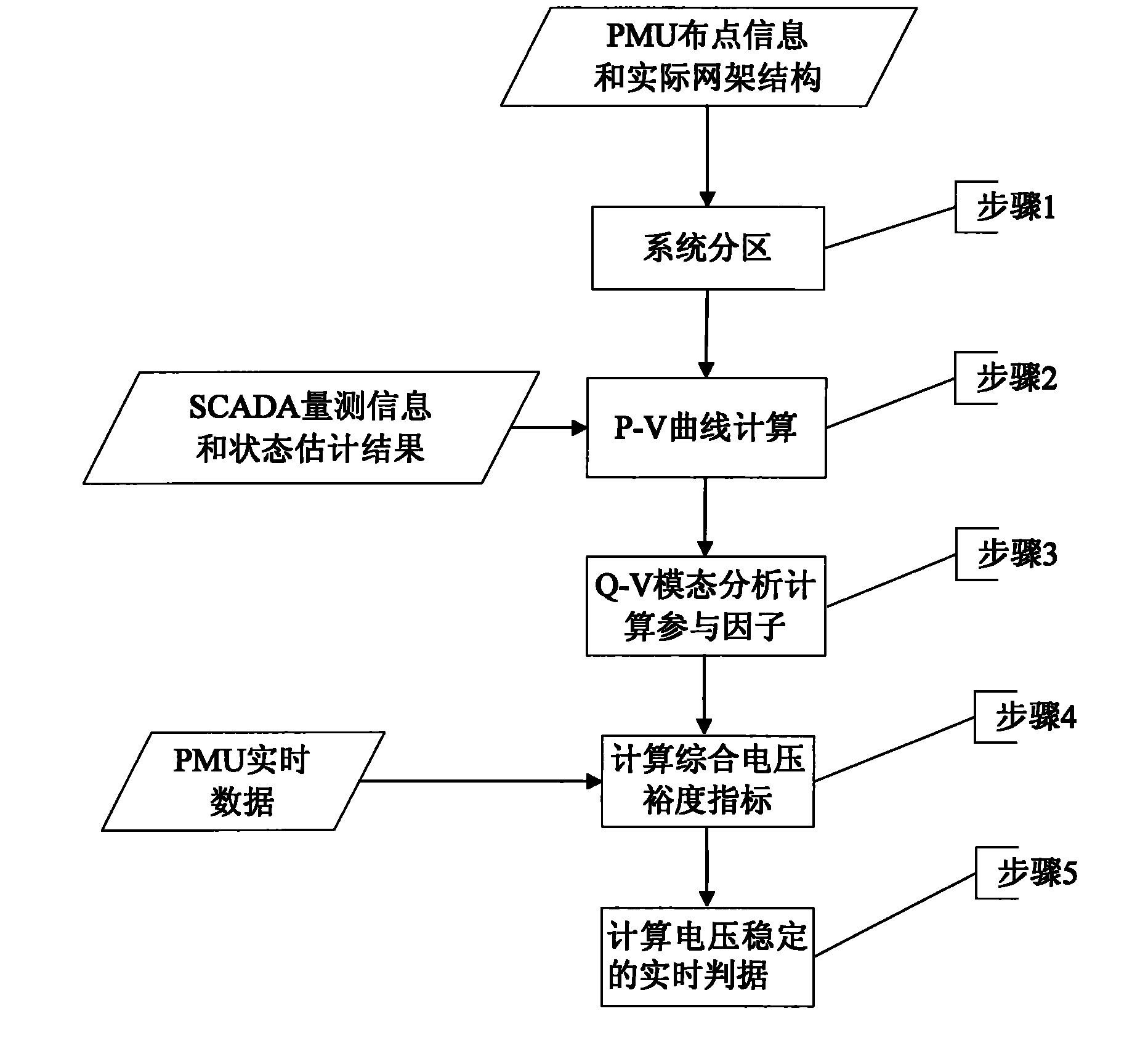
[0022] Attached below figure 1 , the method of the present invention is described in detail.
[0023] figure 1 Step 1 in the above describes the distribution information of PMUs in the integrated power grid and the actual grid structure. The power grid is divided into several power generation areas and load areas, and PMUs are installed on the important buses of the transmission channels and load areas.
[0024] figure 1 Step 2 in the above describes that once the state estimation refreshes the data, based on the SCADA measurement information and the state estimation results, the P-V curve calculation is performed for a certain power generation and load growth mode, and the critical voltage at each point when the voltage collapses is obtained. conditions and their anticipated post-accident conditions.
[0025] figure 1 Step 3 in the above describes the Q-V modal analysis and calculation of the power flow when the voltage is about to collapse, to obtain the participation fa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com