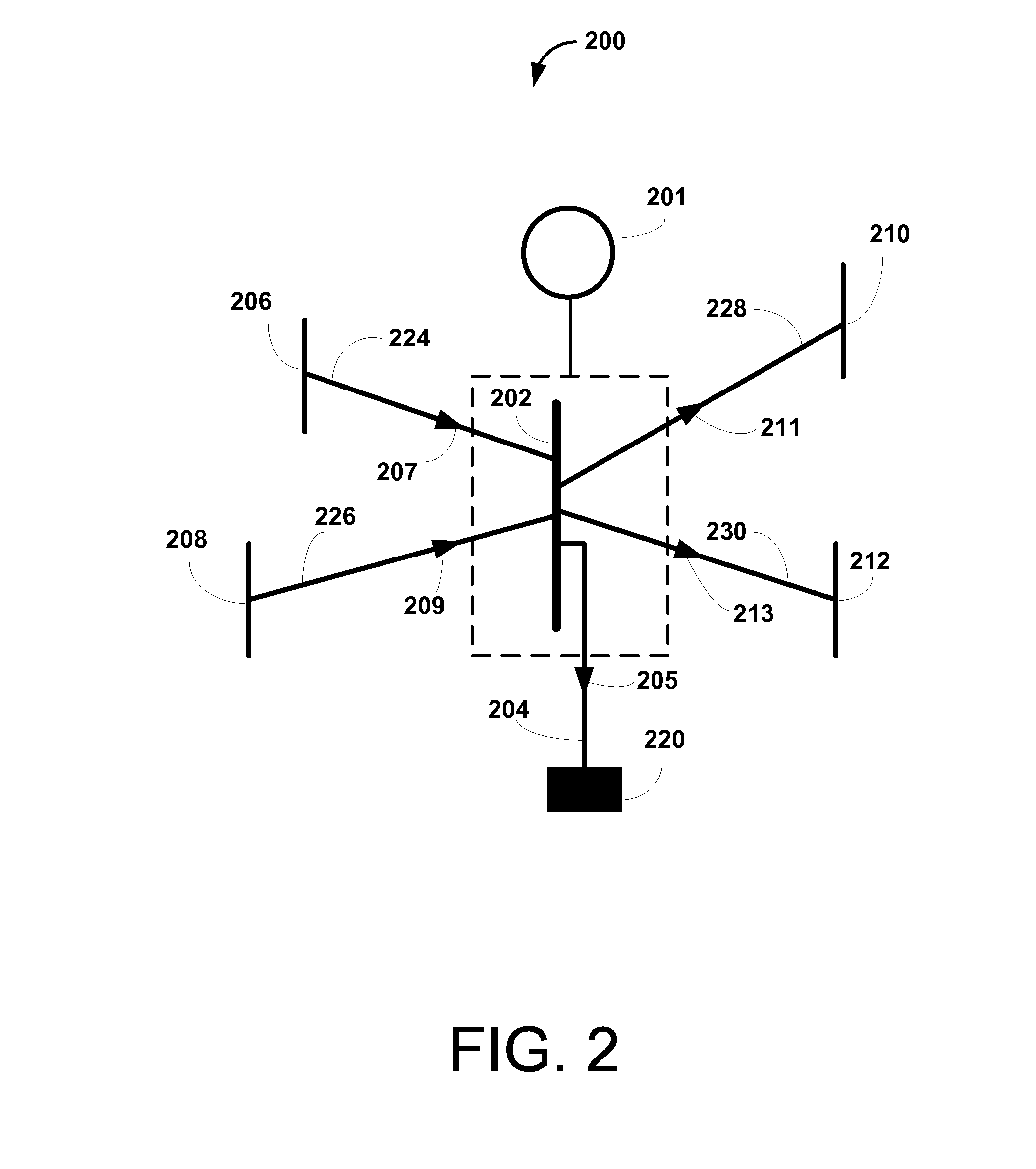
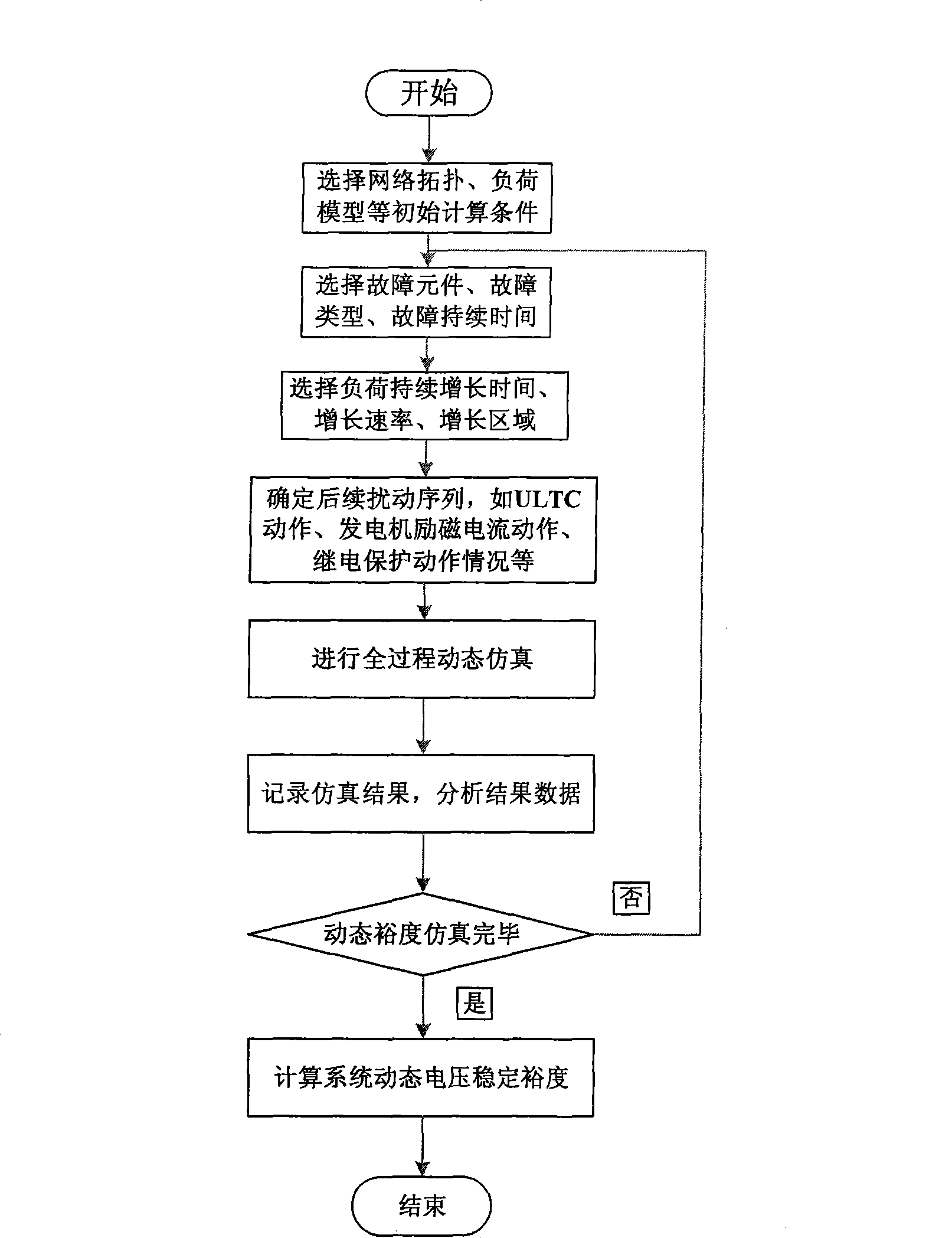
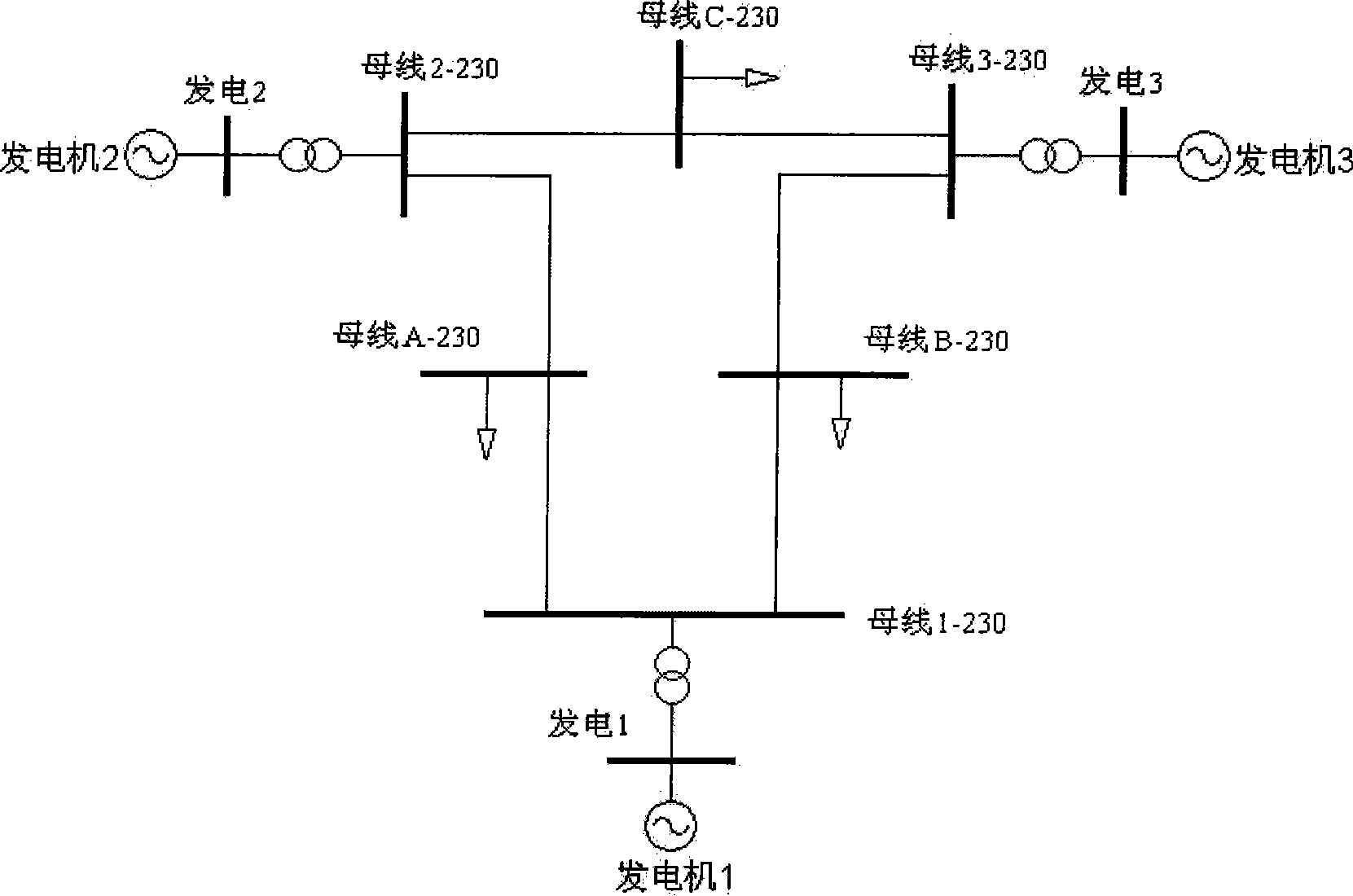
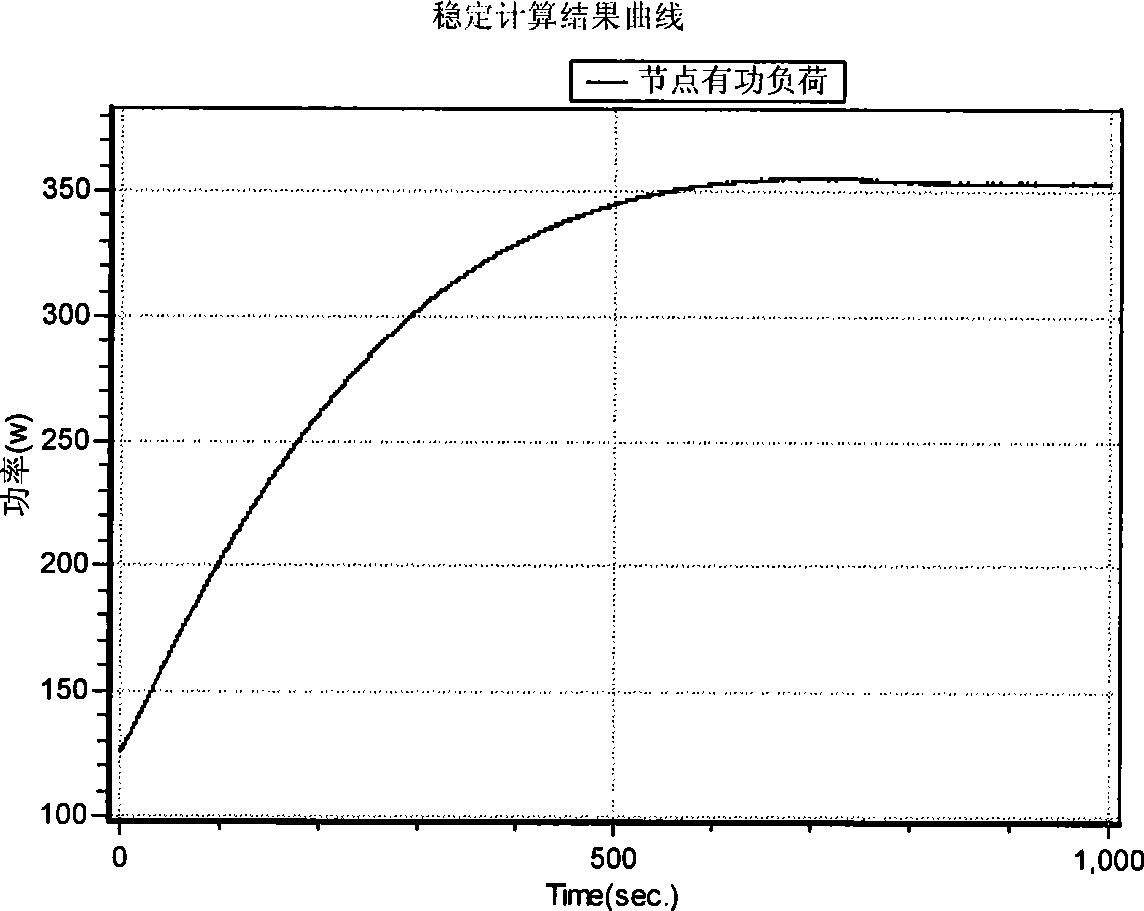
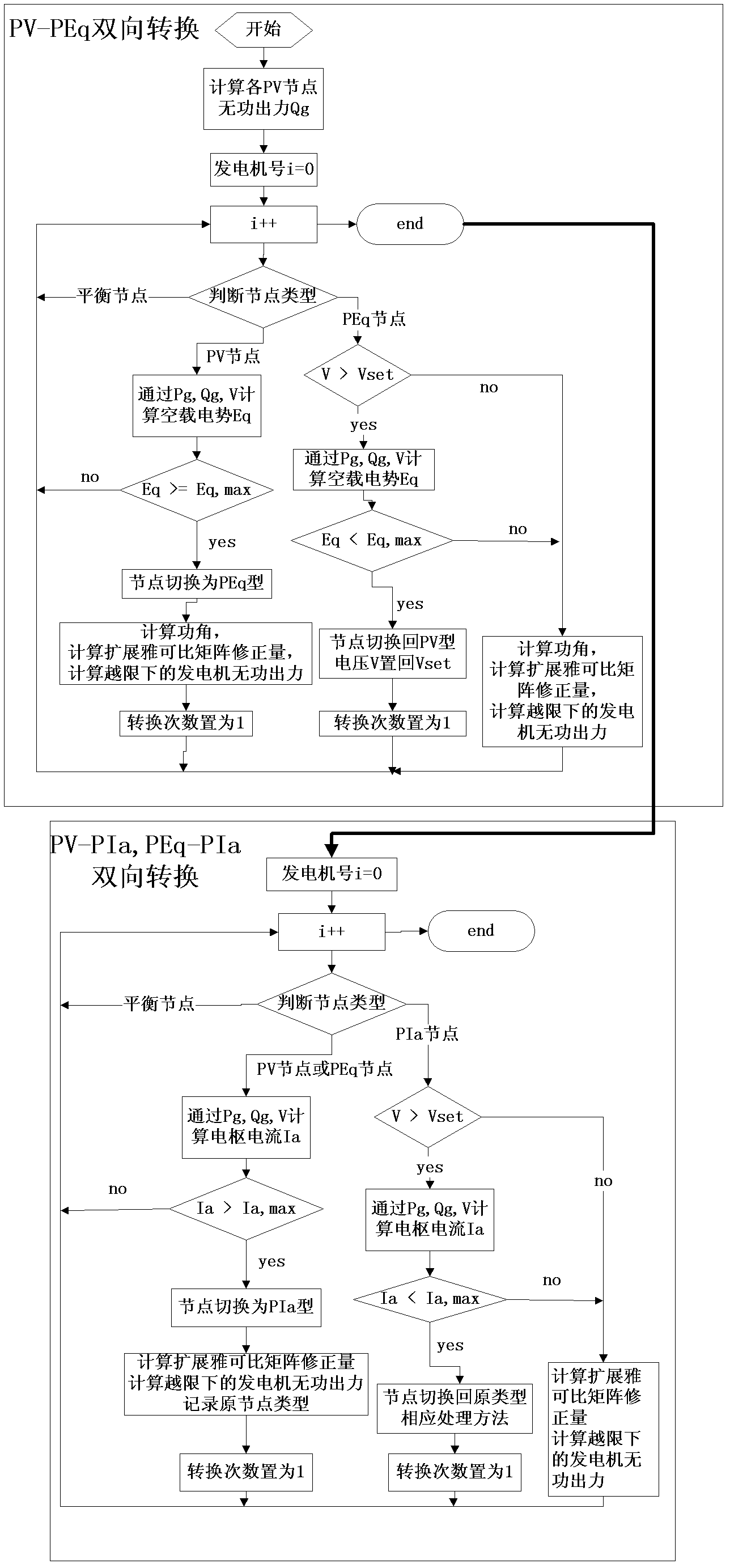
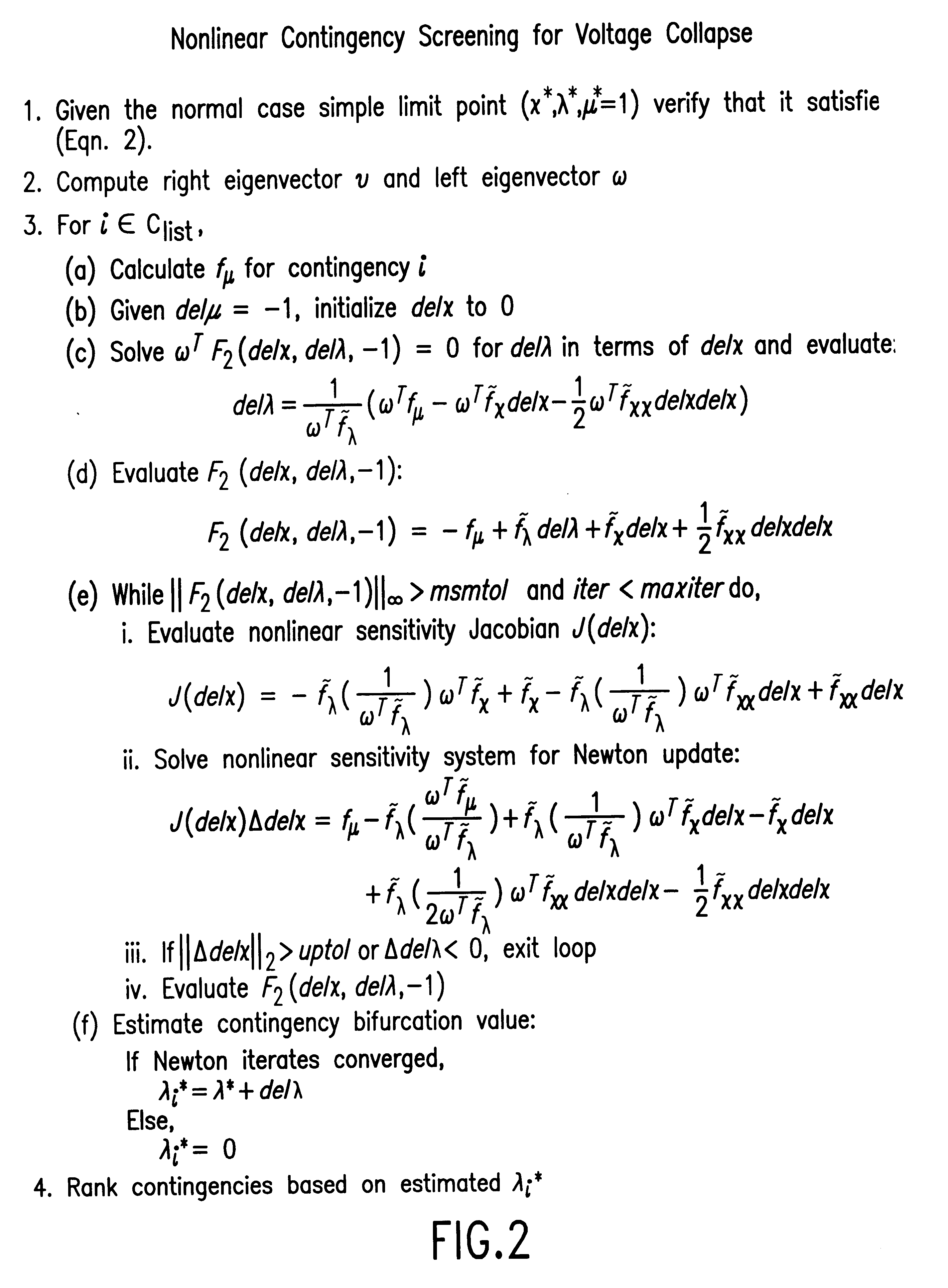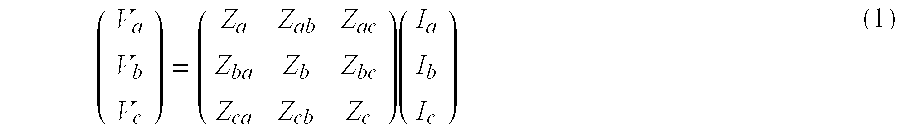Patents
Literature
133 results about "Voltage collapse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
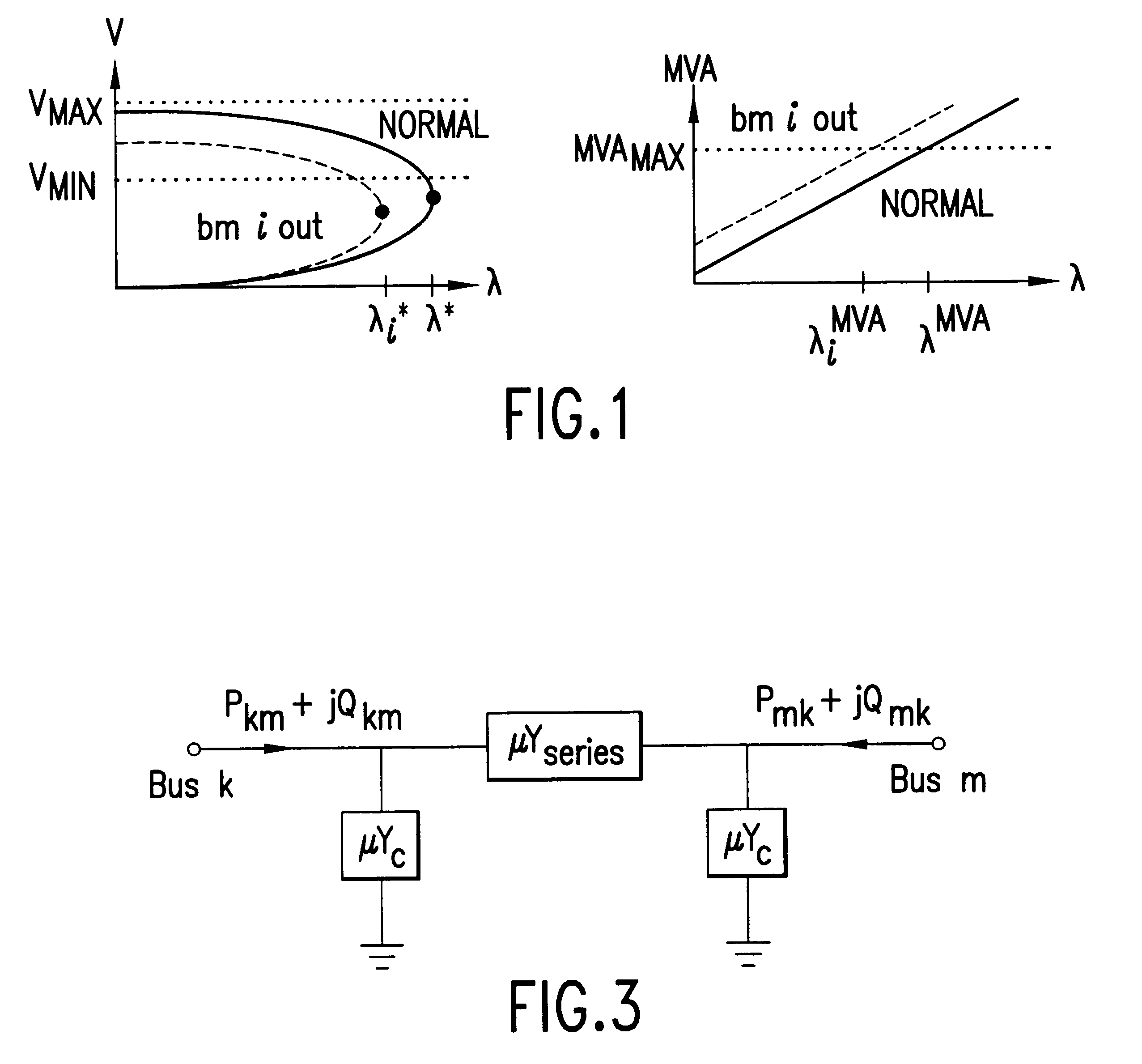
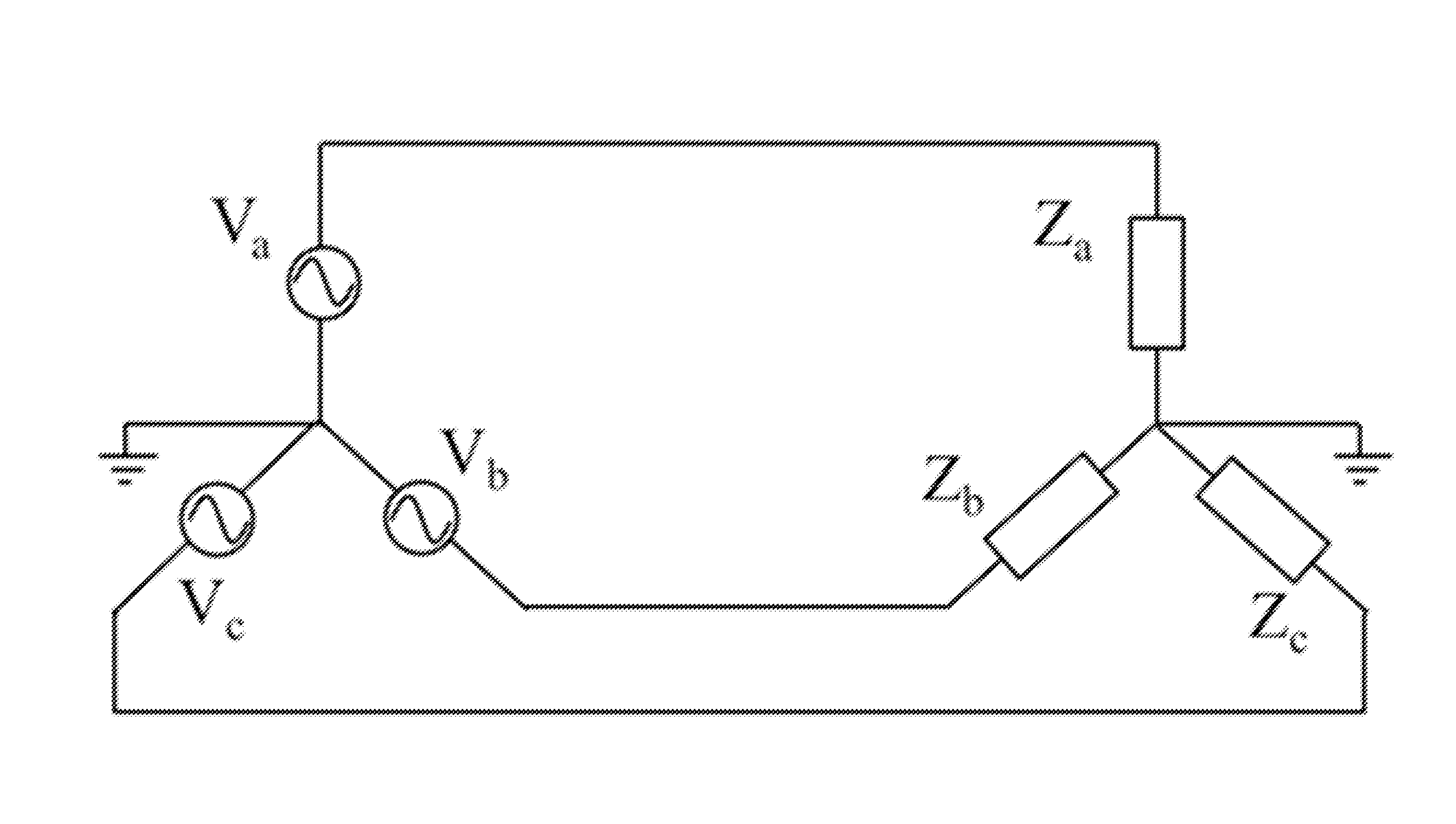
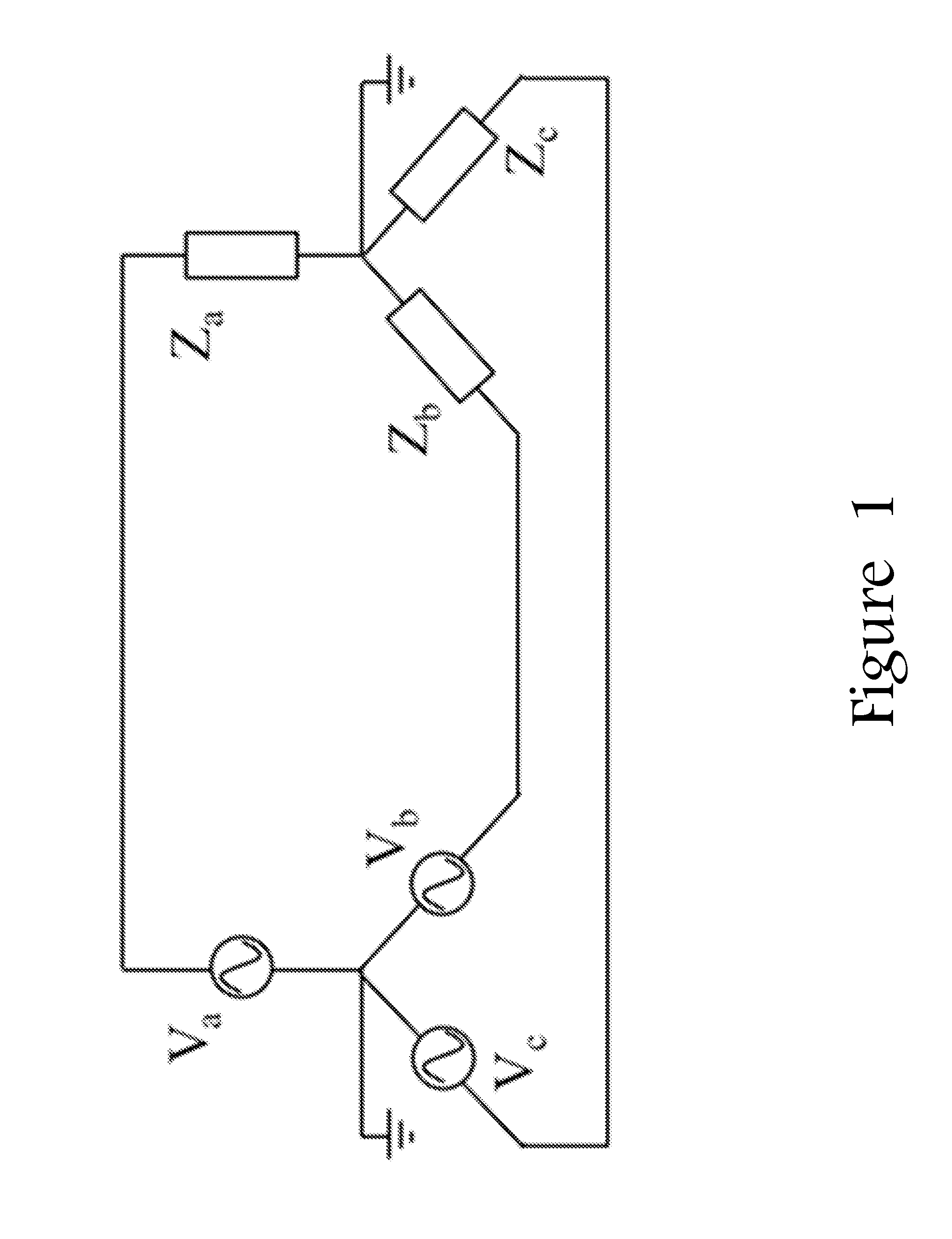
Voltage collapse is the process by which voltage instability leads to the loss of voltage in a significant part of the system. This condition results from reactive losses significantly exceeding the reactive resources available to supply them.
Safety level evaluation method of power grid
ActiveCN101800426AEasy to understandPractical applicationAc network circuit arrangementsStructure analysisTotal risk
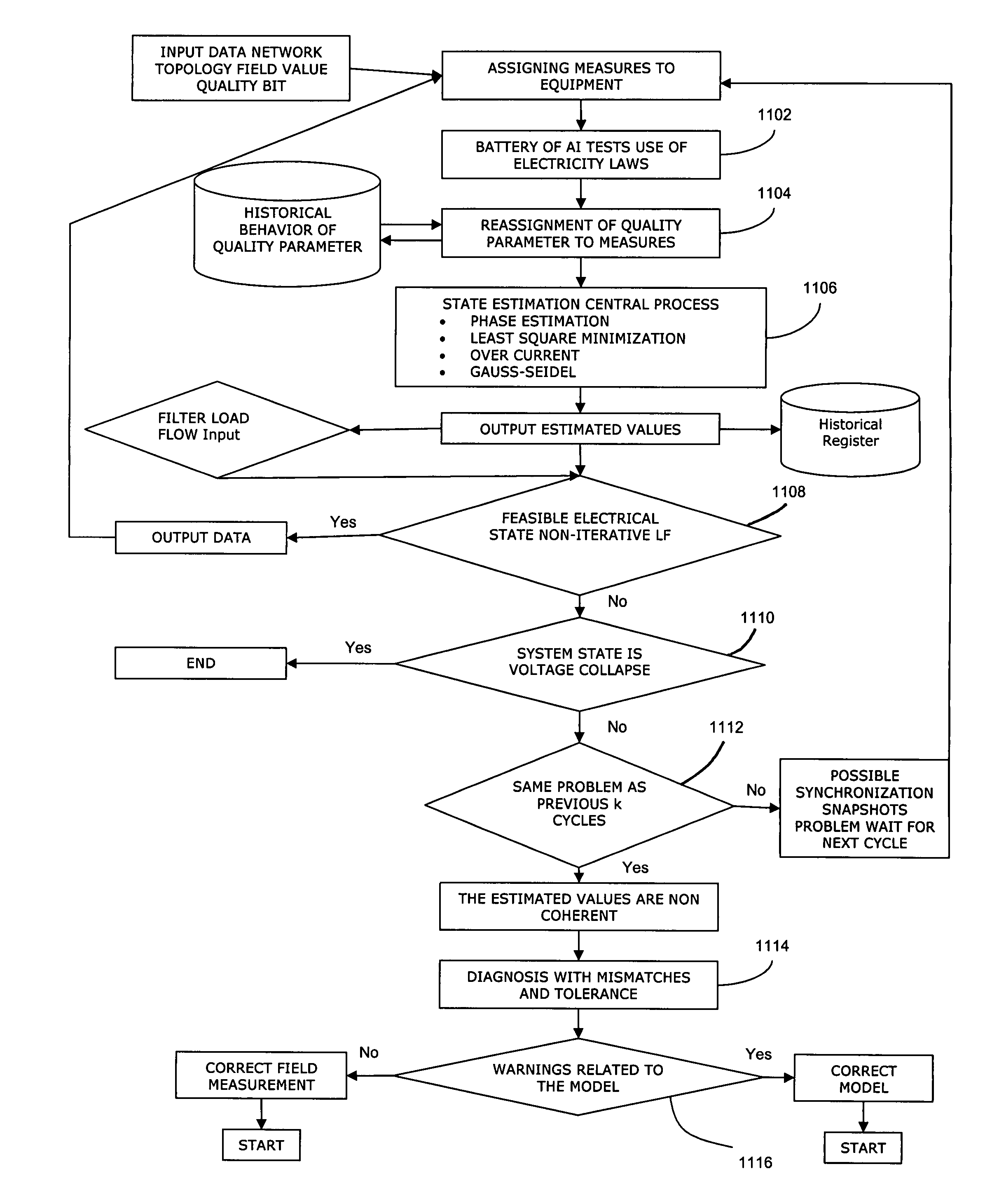
The invention relates to a safety level evaluation method a power grid, comprising the following steps of: firstly determining a supposed accident list, and sequentially disconnecting elements of the supposed accident list; after a certain element is disconnected, carrying out topological structure analysis and load flow calculation on a system, and then calculating a power grid loss load risk evaluation index, a power grid overload risk evaluation index, a power grid low voltage risk evaluation index and a power grid voltage collapse risk evaluation index; repeating the process till all the elements of the supposed accident list are completely calculated; and then calculating a system single-risk evaluation index and a system total-risk evaluation index. The invention introduces a risk theory and a utility theory to the safety evaluation of the power grid, separately diagnoses the safety of the system from different side surfaces, further obtains the risk evaluation index of the whole system by an analytic hierarchy process (AHP), obtains simple and clear results and has better discrimination and can reflect the occurrence possibility of different accidental accidents and severity degree of a consequence caused by the accidental accidents.
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +1
Nonlinear contingency screening for voltage collapse
InactiveUS6496757B1Screening contingencies fasterMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlSaddle-node bifurcationElectric power system
A method for estimating the severity of generator unit outage and multi-terminal branch outage contingencies with respect to voltage collapse in large-scale electric power systems which includes the steps of estimating a post-contingency saddle-node bifurcation induced voltage collapse point of an electric power system following a set of generator unit outages and / or a set of branch outages and calculating a distance to collapse of said power system. The post-contingency voltage collapse point is determined by application of a nonlinear contingency screening method.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
System and method for monitoring and managing electrical power transmission and distribution networks
ActiveUS20060111860A1Simple methodLevel controlTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesElectric power systemPower grid
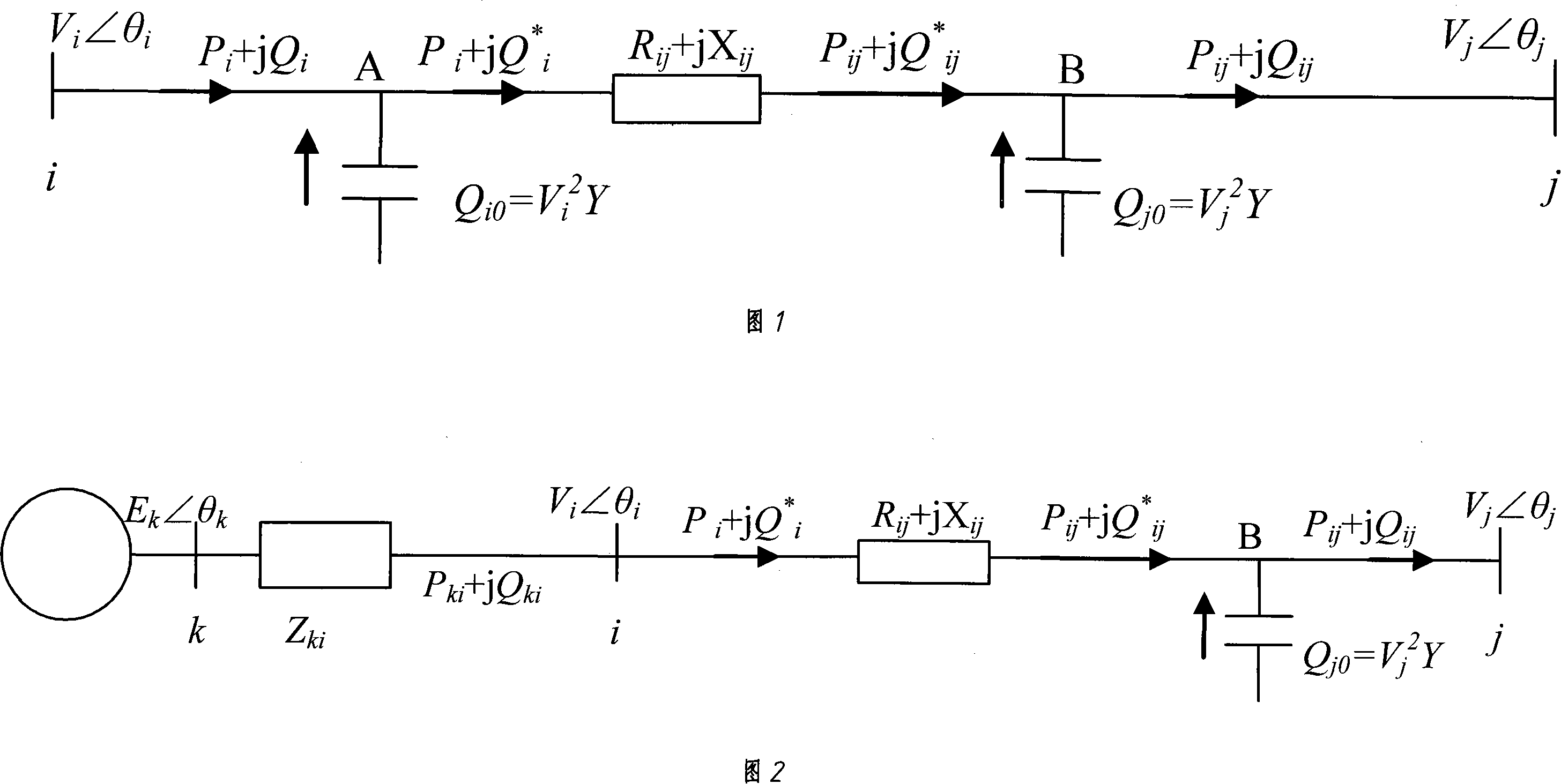
A system and method for monitoring and managing electrical power transmission and distribution networks through use of a deterministic, non-iterative method using an holomorphic embedding and algebraic approximants for determining the real-time load flow in a power generating system having an electrical grid. Such method may be employed for real-time or off-line applications for electric power systems reliability assessment, and is capable of determining whether or not a physical solution to the load flow problem exists, or if the system is in a state of voltage collapse.
Owner:APLICACIONES & INFORMATICA AVANZADA
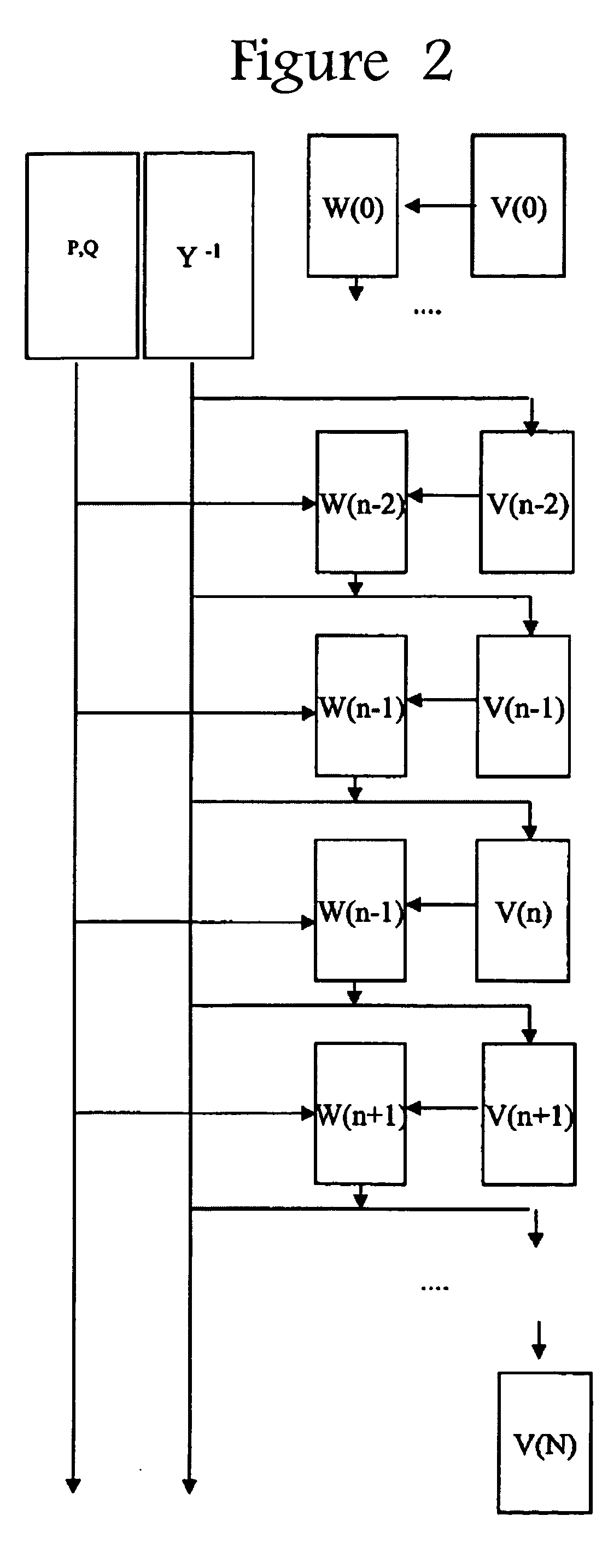
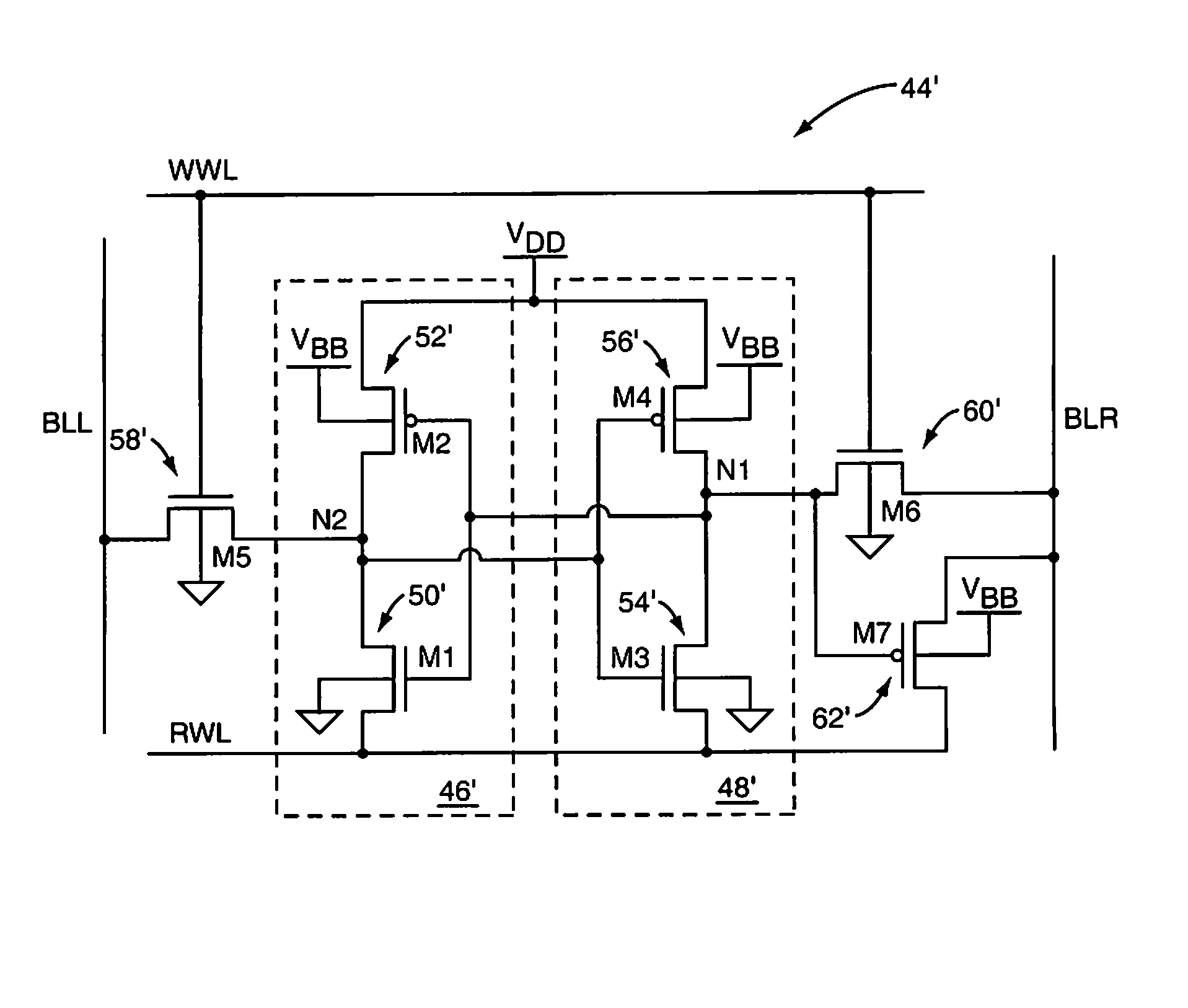
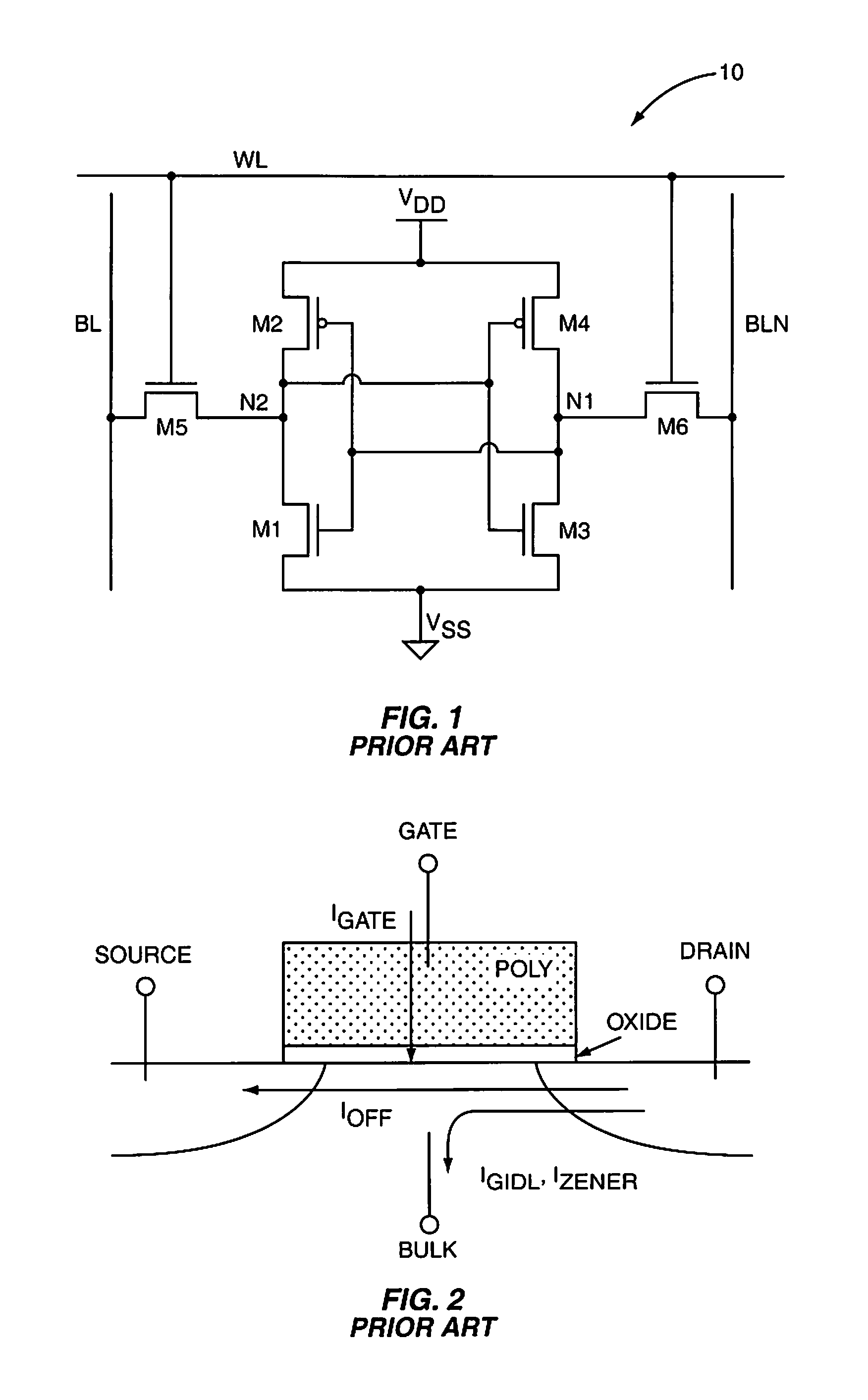
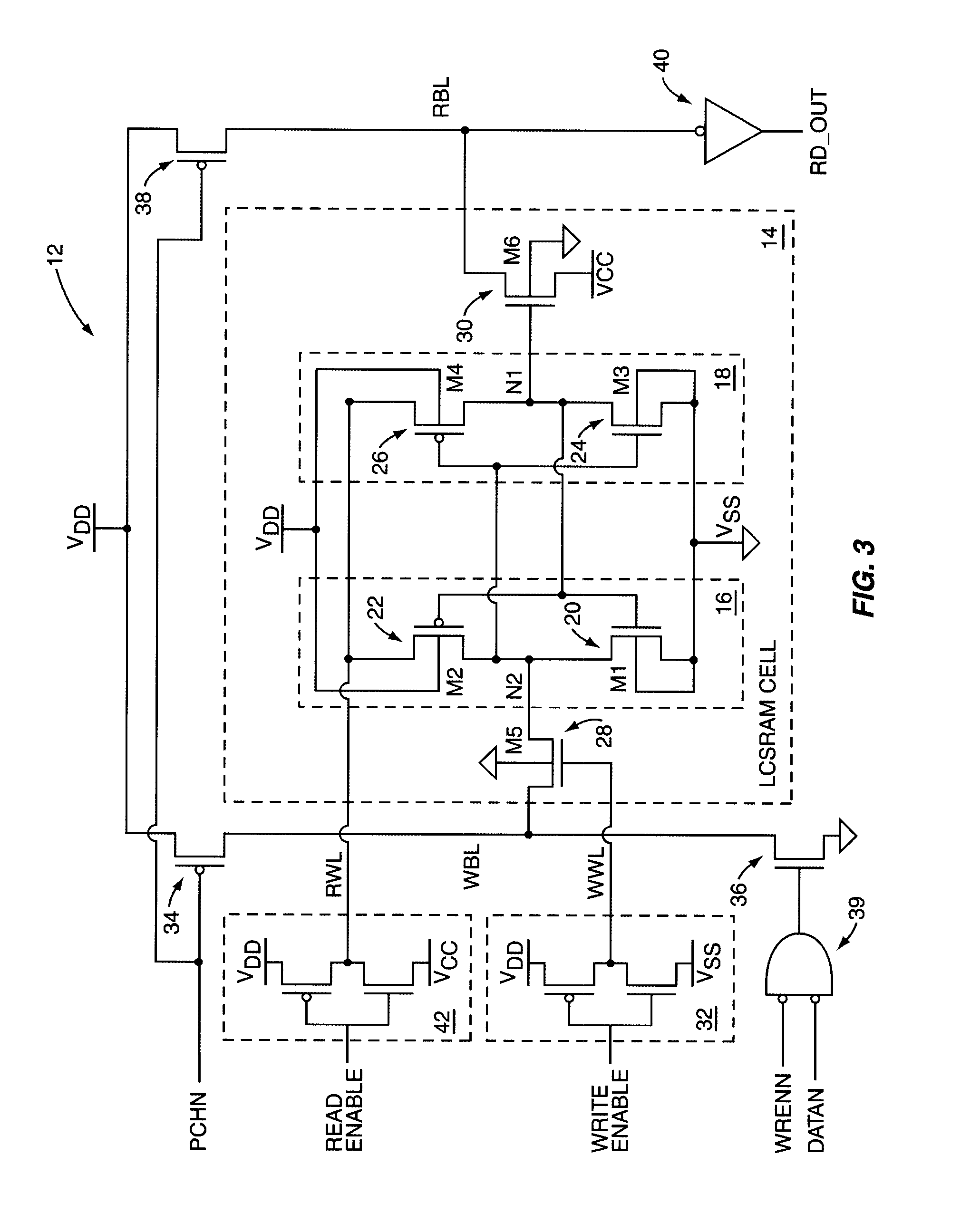
SRAM cell with intrinsically high stability and low leakage
InactiveUS7920409B1Improve stabilityReduce leakageDigital storageStatic random-access memoryControl signal
A Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) cell having high stability and low leakage is provided. The SRAM cell includes a pair of cross-coupled inverters providing differential storage of a data bit. Power to the SRAM cell is provided by a read word line (RWL) signal, which is also referred to herein as a read control signal. During read operations, the RWL signal is pulled to a voltage level that forces the SRAM cell to a full-voltage state. During standby, the RWL signal is pulled to a voltage level that forces the SRAM cell to a voltage collapsed state in order to reduce leakage current, or leakage power, of the SRAM cell. A read-transistor providing access to the bit stored by the SRAM cell is coupled to the SRAM cell via a gate of the read transistor, thereby decoupling the stability of the SRAM cell from the read operation.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Process for real time recognizing voltage stability of electrified wire netting trough recognizing weak links of electric network
InactiveCN101118265AQuick calculationReal-time identification of voltage instabilityElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringLoad following power plant
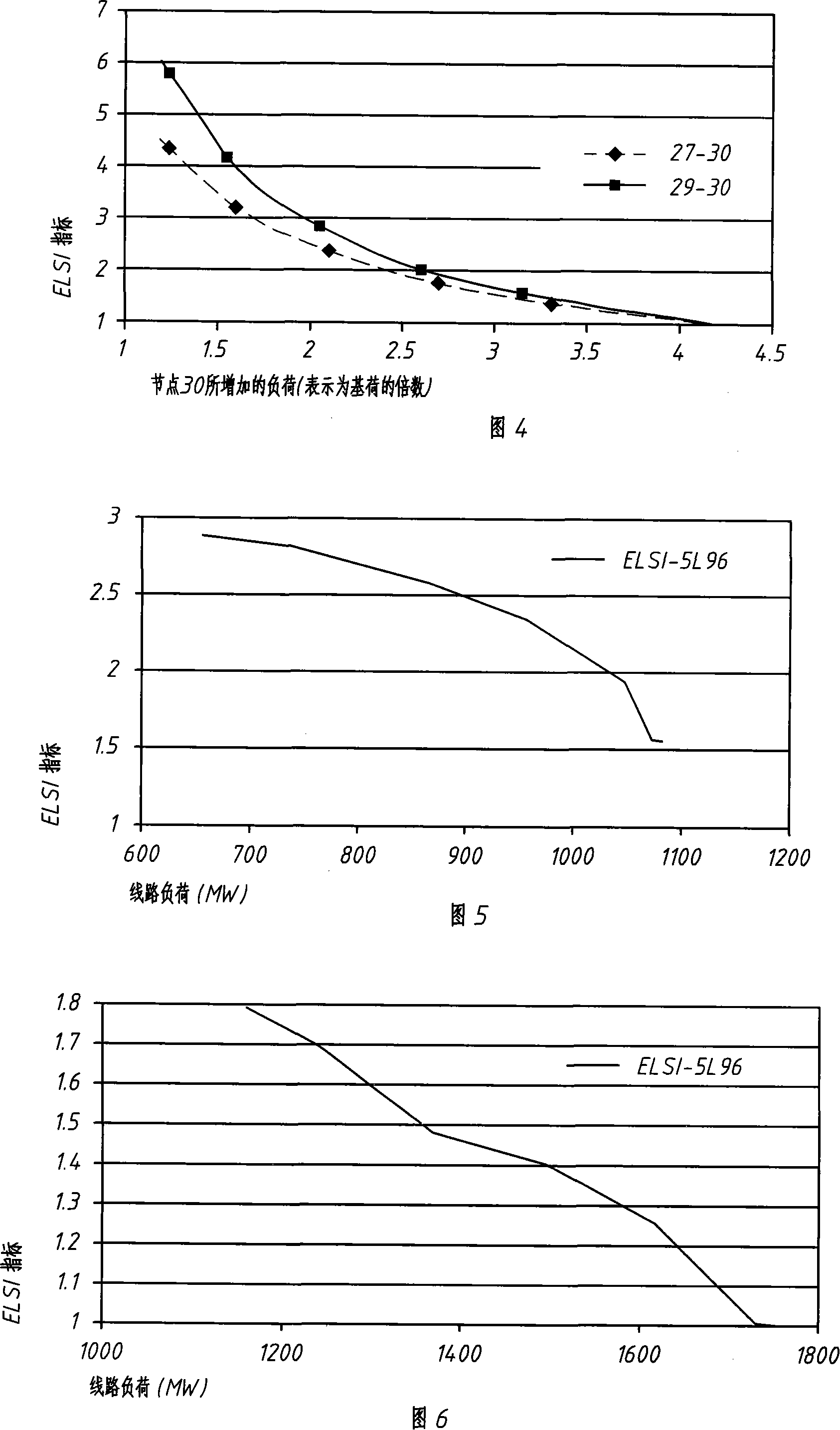
The present invention relates to a method of identifying the voltage stability of power grid in real time via figuring out the weak links of power grid; and uses a basic line voltage stability index BLSI or an extended line voltage stability index ELSI which is improved on the basis of the BLSI index to monitor, identify and judge power grid. The steps of identifying are as follows. Firstly, the requisite real-time date can be obtained via a PMU system or SCADA and EMS; Secondly, useless measurements get filtrated; thirdly, the parameters of the line are reassessed in real time if necessary in a given time interval; fourthly, a BLSI index or ELSI index is used to identify the weak links of the system; lastly, the system emergency protection control is started up to avoid the breakdown of system voltage at the BLSI value or ELSI value which is the weakest link that leads to voltage breakdown. The present invention has the advantages of identifying voltage invariability of the system in real time and weak lines and weak links that cause voltage breakdown of the system; and automatically dealing with actual loading properties relevant to voltage or frequency.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
System and method for monitoring and managing electrical power transmission and distribution networks
InactiveUS7519506B2Level controlTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesElectric power transmissionElectric power system
A system and method for monitoring and managing electrical power transmission and distribution networks through use of a deterministic, non-iterative method using an holomorphic embedding and algebraic approximants for determining the real-time load flow in a power generating system having an electrical grid. Such method may be employed for real-time or off-line applications for electric power systems reliability assessment, and is capable of determining whether or not a physical solution to the load flow problem exists, or if the system is in a state of voltage collapse.
Owner:APLICACIONES & INFORMATICA AVANZADA
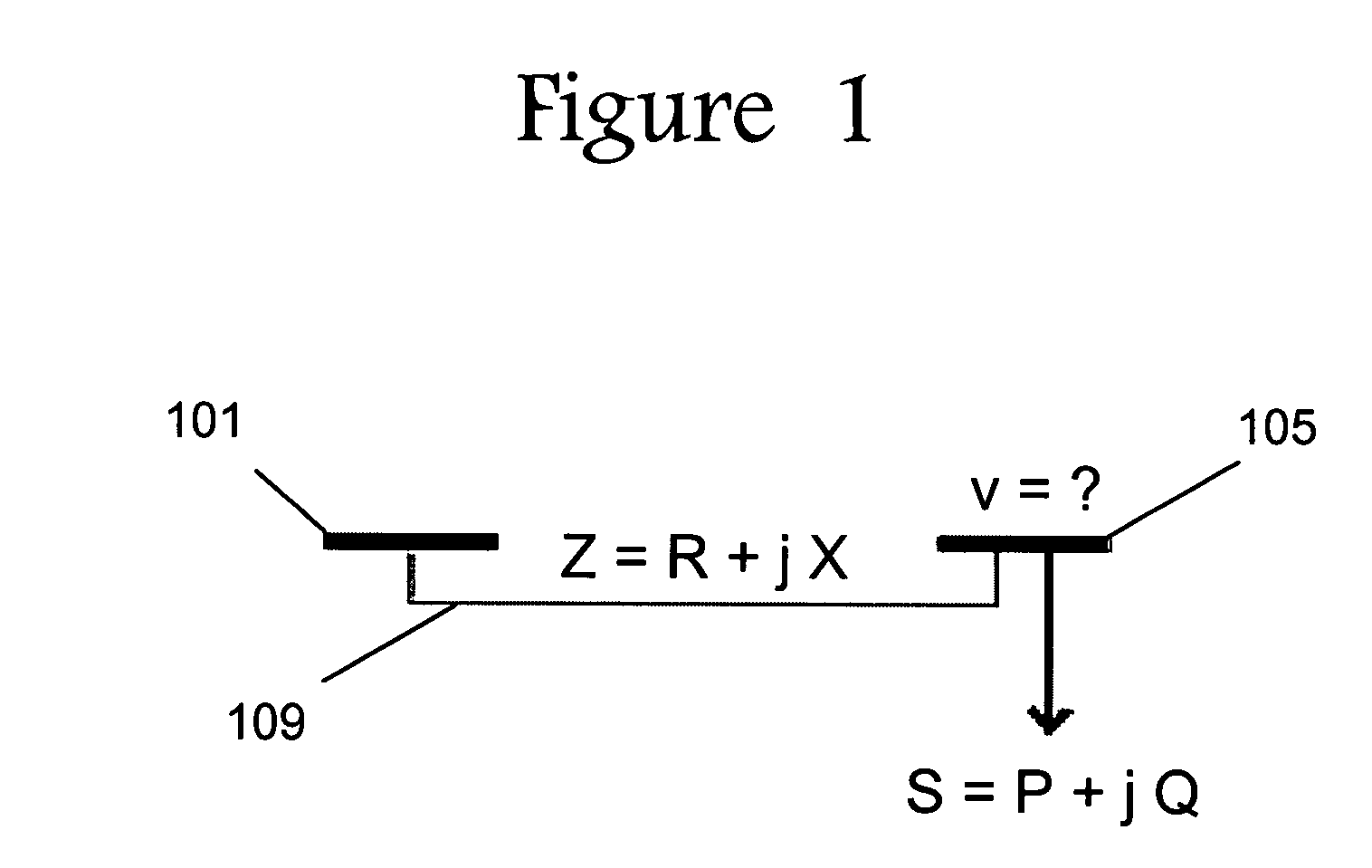
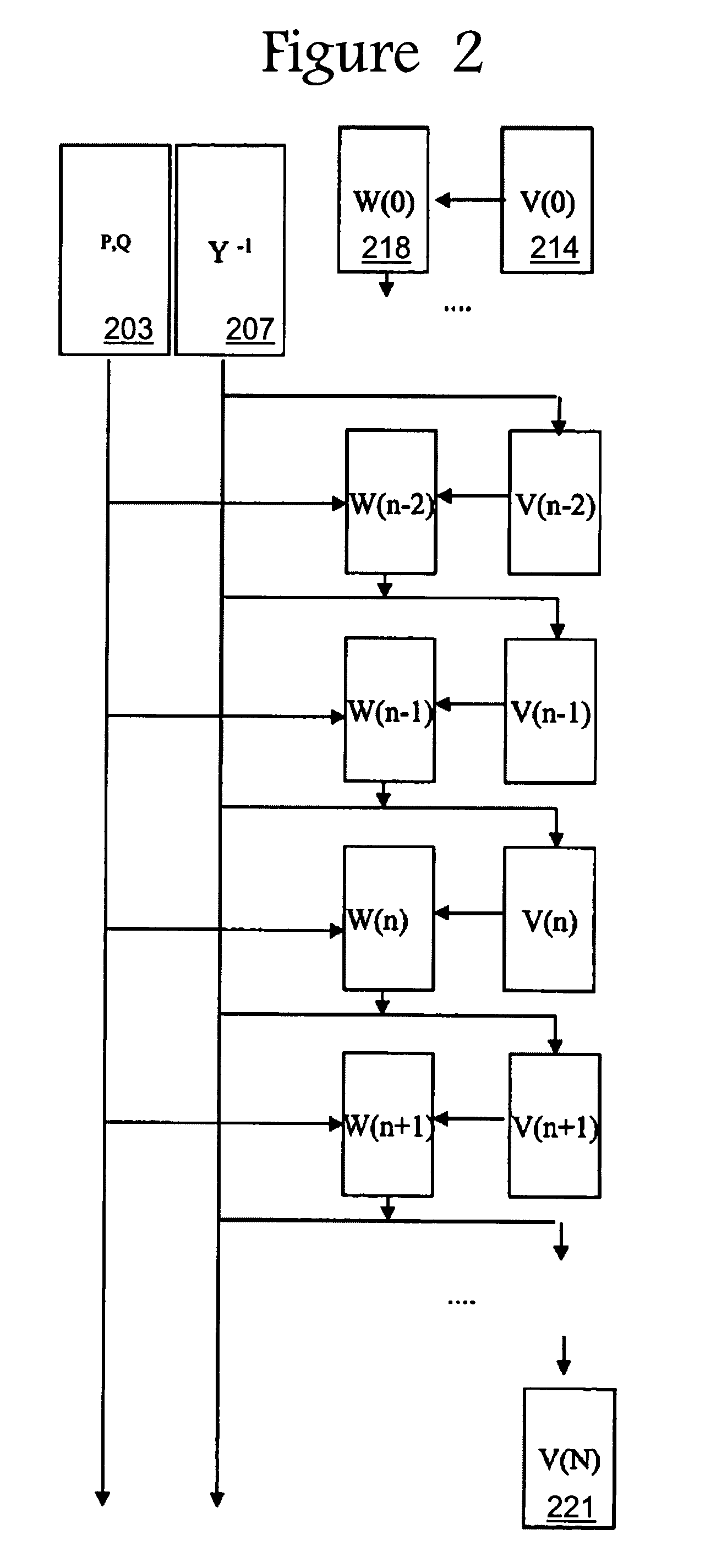
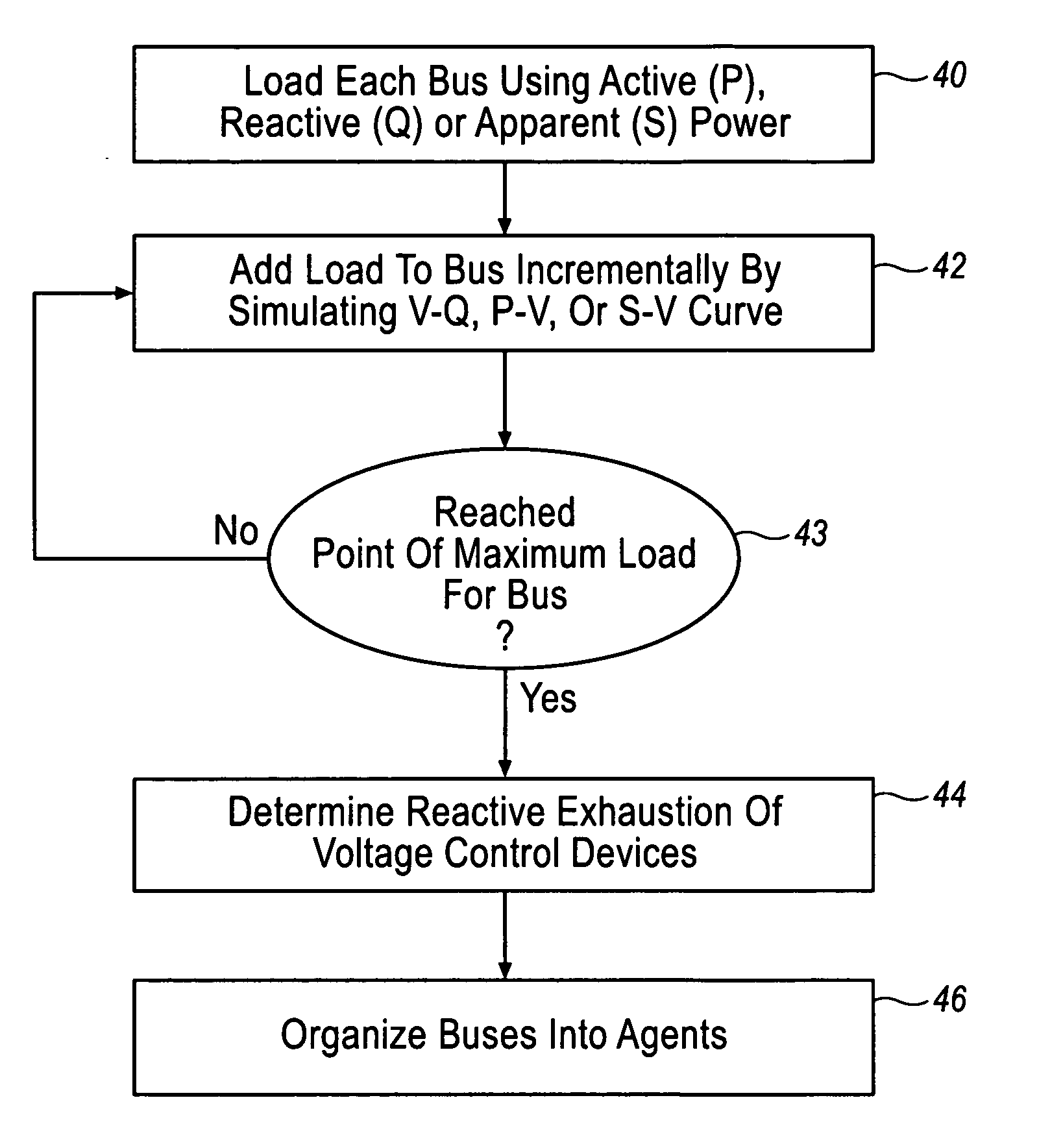
Voltage collapse diagnostic and ATC system
InactiveUS20060030972A1Improve and reduce reliabilityAvoid power outagesMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlLoad SheddingSystems design
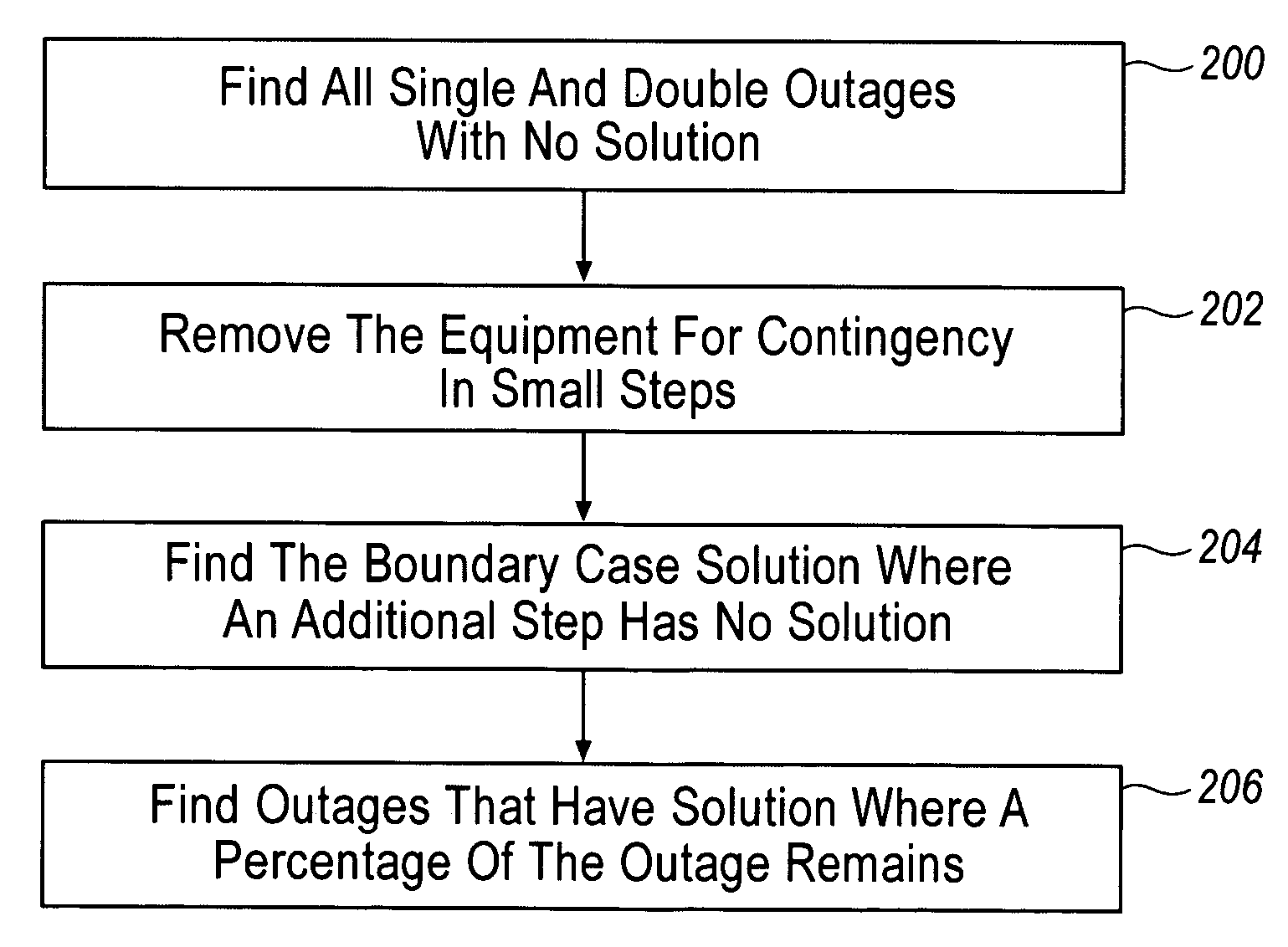
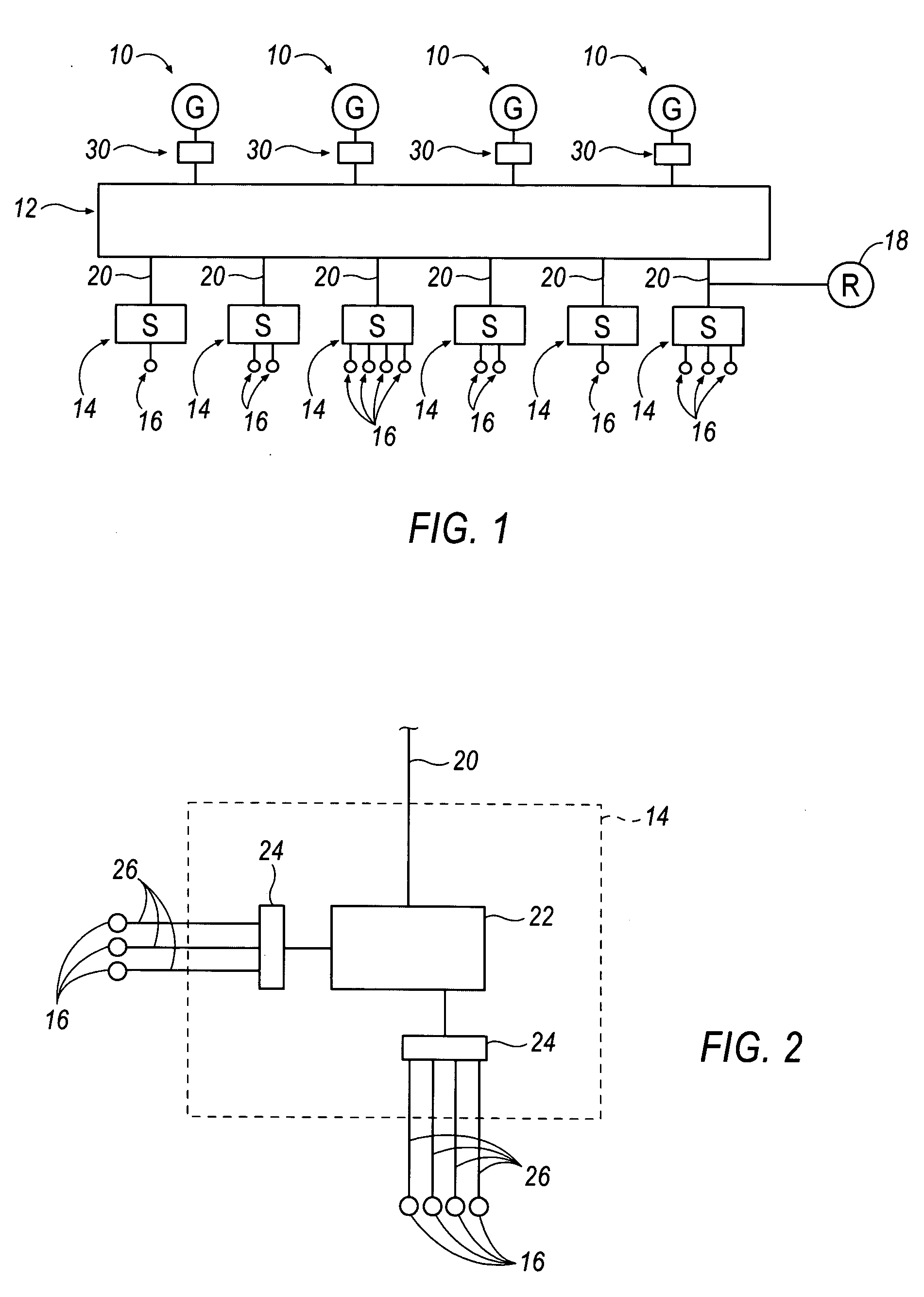
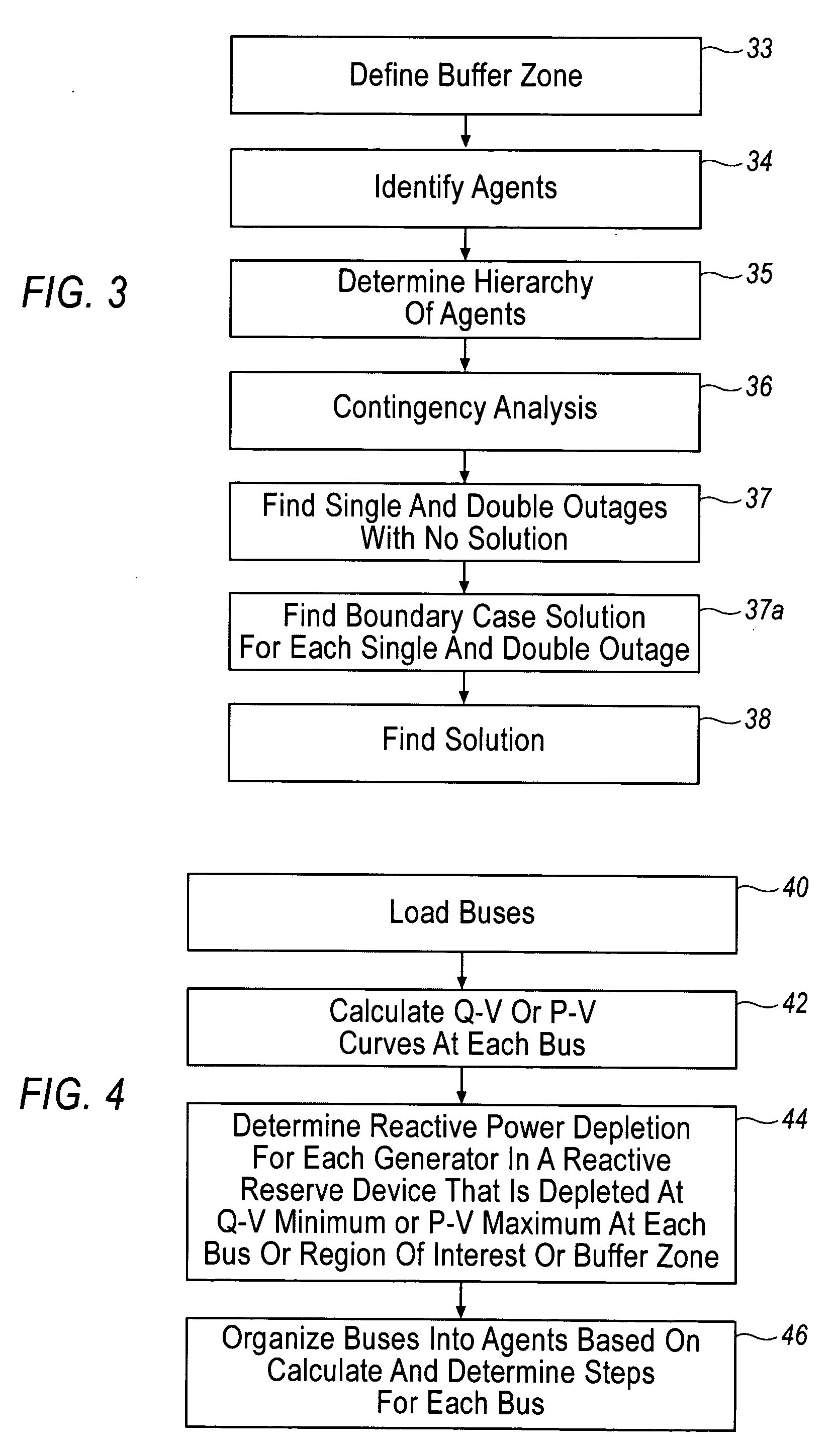
The present invention provides an analysis method for an electrical power system whereby the plurality of buses are grouped into agents, family lines of agents and families of agents based on the reactive reserves depleted when the buses are loaded. Contingencies are then applied to the electrical power system and the reactive reserves are monitored and an exhaustion factor is determined for one or more family lines in one or more families. A method for selecting double outage that have no solution for each outage that has no solution when the outage is removed in small steps and an additional step has no solution. The boundary case solution is used to assess where, why, and how the contingency causes voltage instability, voltage collapse, and local blackout. Based on this information, the design of voltage rescheduling, active rescheduling, unit commitment, load shedding is determined that can be used as preventive, corrective, or emergency controls in applications such as system design and planning, operation planning, reactive and voltage management, real time control, and Special Protection System Control. Based on this information, solutions can then be applied to the political power system.
Owner:INTELILCON
Static voltage stability margin analyzing and system fault ordering method of power system
ActiveCN103795058AEasy to operateClear stepsSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsPower compensationElectric power system
The invention provides a static voltage stability margin analyzing and system fault ordering method of a power system. The static voltage stability margin analyzing and system fault ordering method includes the following steps that the Newton iteration method based on the optimal multiplier is used for determining a static voltage collapse point; according to the characteristic of iteration convergence, the type of the voltage collapse point is judged; according to the requirement for stability margin, system fault danger conditions are checked and ordering of stability faults is performed; the faults are parameterized and the iteration method is used for giving out the order of seriousness degrees of instability faults. According to the static voltage stability margin analyzing and system fault ordering method of the power system, voltage stability margins of the power system can be rapidly given online, real-time effective monitoring is carried out on the voltage stability and the comprehensive order of the stability faults and the instability faults can be used for guiding a power generator to adjust online and switching reactive power compensation devices when the system encounters faults, can also guide sub-circuit parameter adjusting, line increasing and decreasing, configuration of an FACTS device and the like off line and have great significance in operation and planning of the power system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Method for Predicting a Voltage Collapse in a Micro-Grid Connected to a Power Distribution Network
ActiveUS20160274606A1Improve voltage stabilityLow costComputer controlKnowledge representationPower gridElectric distribution network
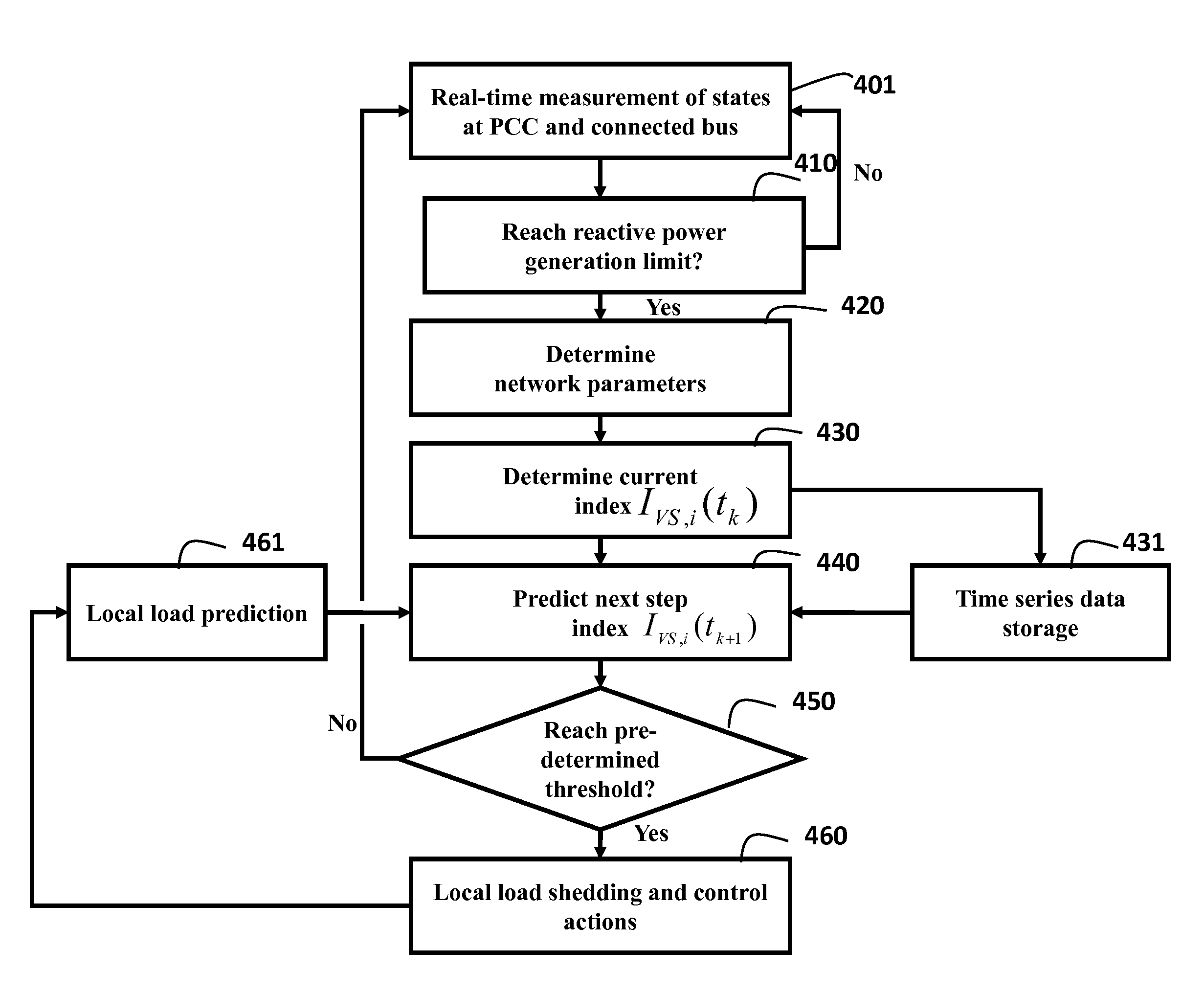
A method predicts a voltage collapse in a micro-grid connected to a power distribution network by measuring states at a point of common coupling of the micro-grid, and a connected bus of the power distribution network connected to the micro-grid through a connection link. Then, it is determined whether a reactive power generation limit of the micro-grid is reached based on the states, and if no, repeating the measuring, and otherwise determining parameters of the connection link using the measurements. A static voltage stability margin index is determined, and a voltage stability margin index is predicted using the static voltage stability margin index and a forecast of future load variations in the micro-grid. Then, it is determined whether the voltage stability margin index is smaller than a threshold, and if no, repeating the measuring, determining and predicting steps, and otherwise if yes, signaling a control action indicating the voltage collapse.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
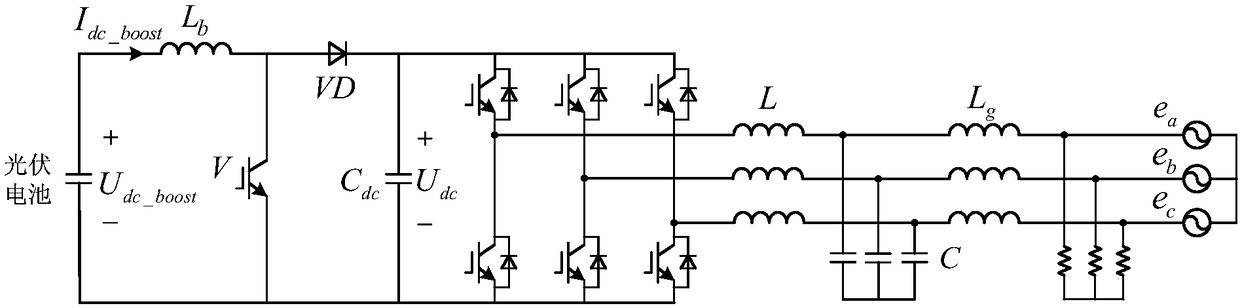
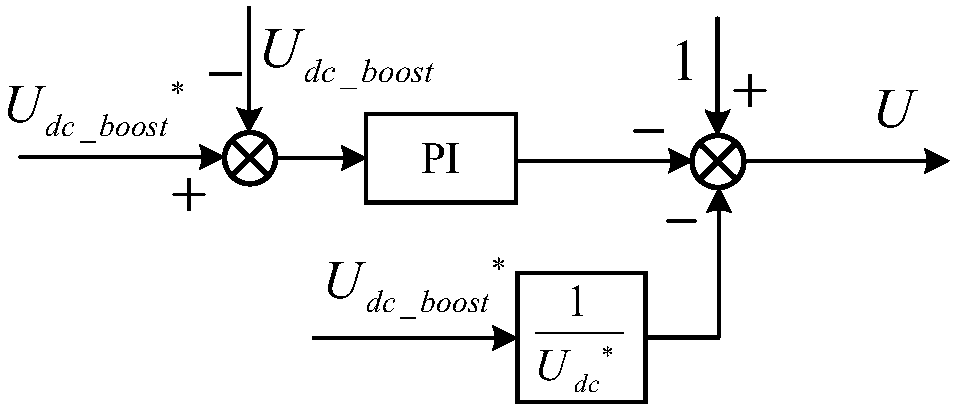
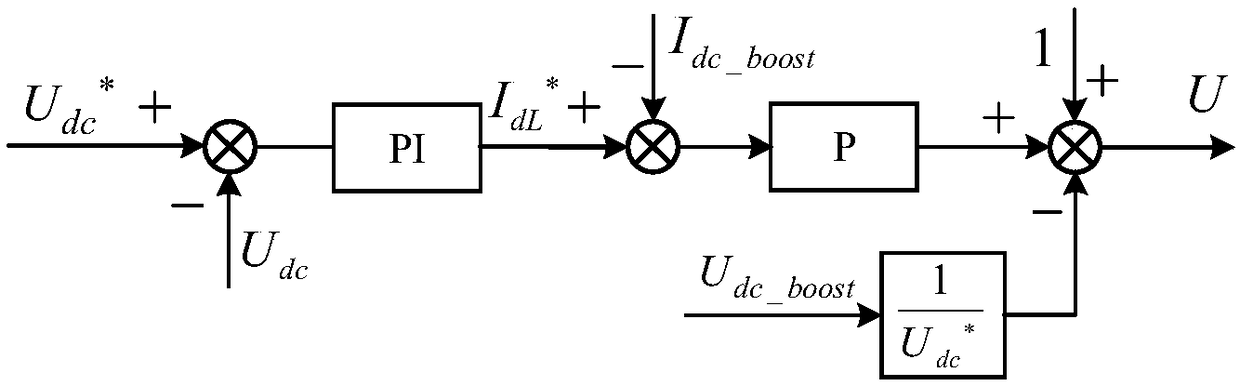
Method for controlling virtual synchronous generator of two-stage photovoltaic inverter
ActiveCN108233415AReduce shockReduce seamless switching timeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentCapacitanceVirtual synchronous generator
The invention discloses a method for controlling a virtual synchronous generator of a two-stage photovoltaic inverter. The method is characterized in that the procedure of logic judgment on the working area of a photovoltaic power curve is given, so as to solve the problems of power fluctuation and voltage stabilizing at the direct current side under two running modes of the virtual synchronous generator, such as grid connecting and grid disconnecting; the stability of the working area of a photovoltaic battery is represented by judging the positive and negative of the change rate dPdc_boost / dUdc_boost of input power along with the direct current voltage, and a pre-boost controller and a post-inverter power outer loop controller are switched, so as to effectively solve the problem of direct current voltage collapse during overload running; a combined feedback control method of post-inverter output frequency and power grid frequency is adopted, so that the sag coefficient is controlledby the power angle, and the virtual damping is independently adjusted; an inductance current and capacitance current weighting control method is used for balancing the output voltage dynamic responseof the photovoltaic inverter and the island parallel current equalizing characteristics, so as to realize the uniform control under two running modes of the two-stage photovoltaic inverter, such as grid connecting and grid disconnecting, thereby improving the whole property.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
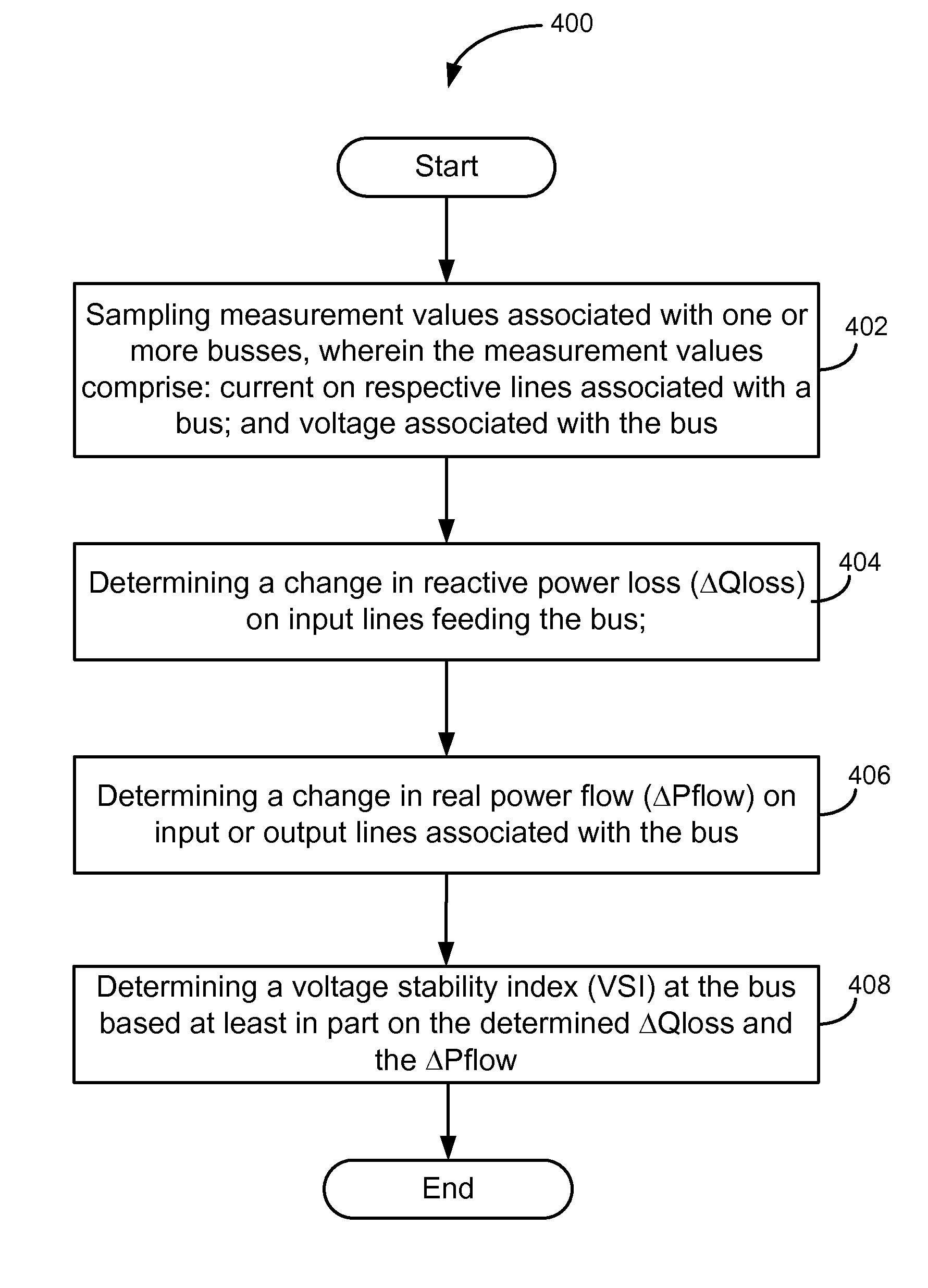
Systems and Methods for Predicting Power System Instability
Certain embodiments of the invention may include systems and methods for predicting power system instability. According to an example embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for predicting voltage collapse or instability in a power system. The method can include sampling measurement values associated with one or more busses, wherein the measurement values include current on respective lines associated with a bus; and voltage associated with the bus. The method can further include determining a change in reactive power loss (ΔQloss) on input lines feeding the bus; determining a change in real power flow (ΔPflow) on input or output lines associated with the bus; and determining a voltage stability index (VSI) at the bus based at least in part on the determined ΔQloss and the ΔPflow.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for weighting dynamic voltage stability margin index
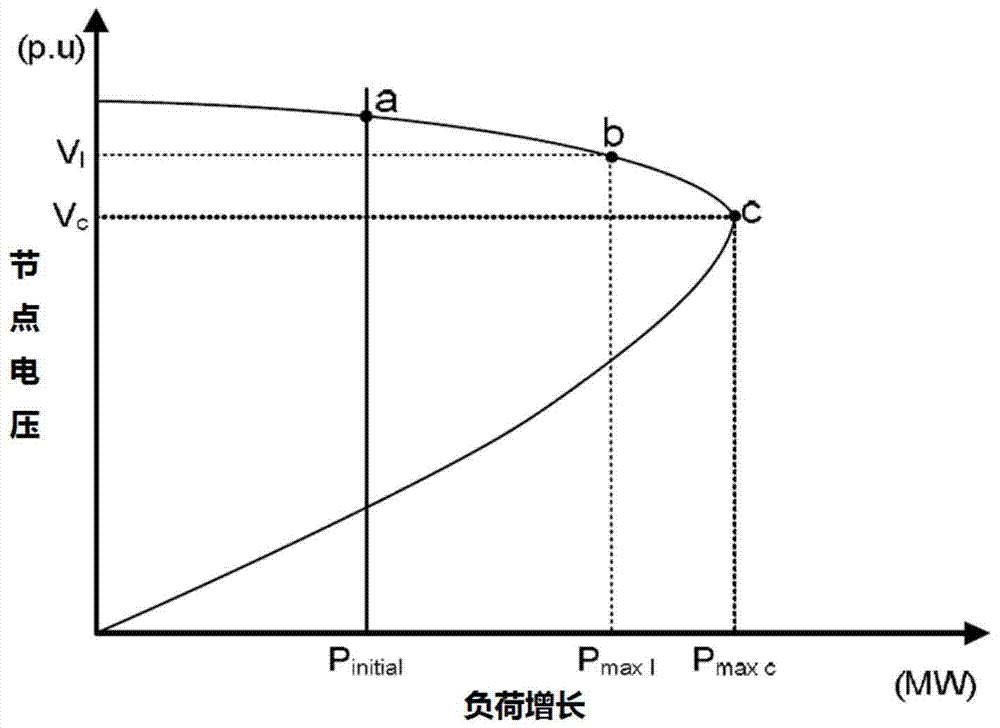
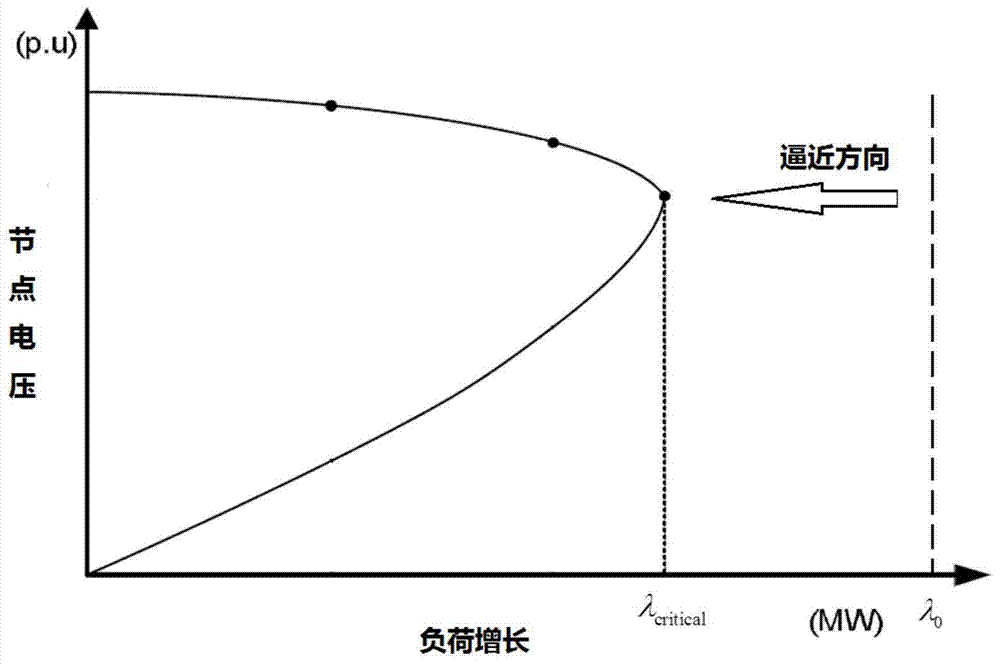
ActiveCN101387679AIncrease marginPhysical concepts are clearElectric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementElectric power systemLinear relationship
The invention provides a method for measuring dynamic voltage stability margin index, while the dynamic voltage stability margin index is the margin to the voltage collapse point of a power system which load increase slowly in a certain speed; the dynamic voltage stability margin index considers that the system is affected by the dynamic components such as the on-load tap changer (ULTC) and the over excitation limit of engines. The method can calculate the dynamic margins of the system which load increases in various types such as single node, regional or full-network type, to provide a visual measurement presenting the distance between the prior operation point of the system and the voltage collapse point, while the distance and the dynamic margin have linear relationship. Therefore, the dynamic margin index has high practical values.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Optimal configuration method for high-voltage distribution network dynamic reactive power compensation equipment capacity
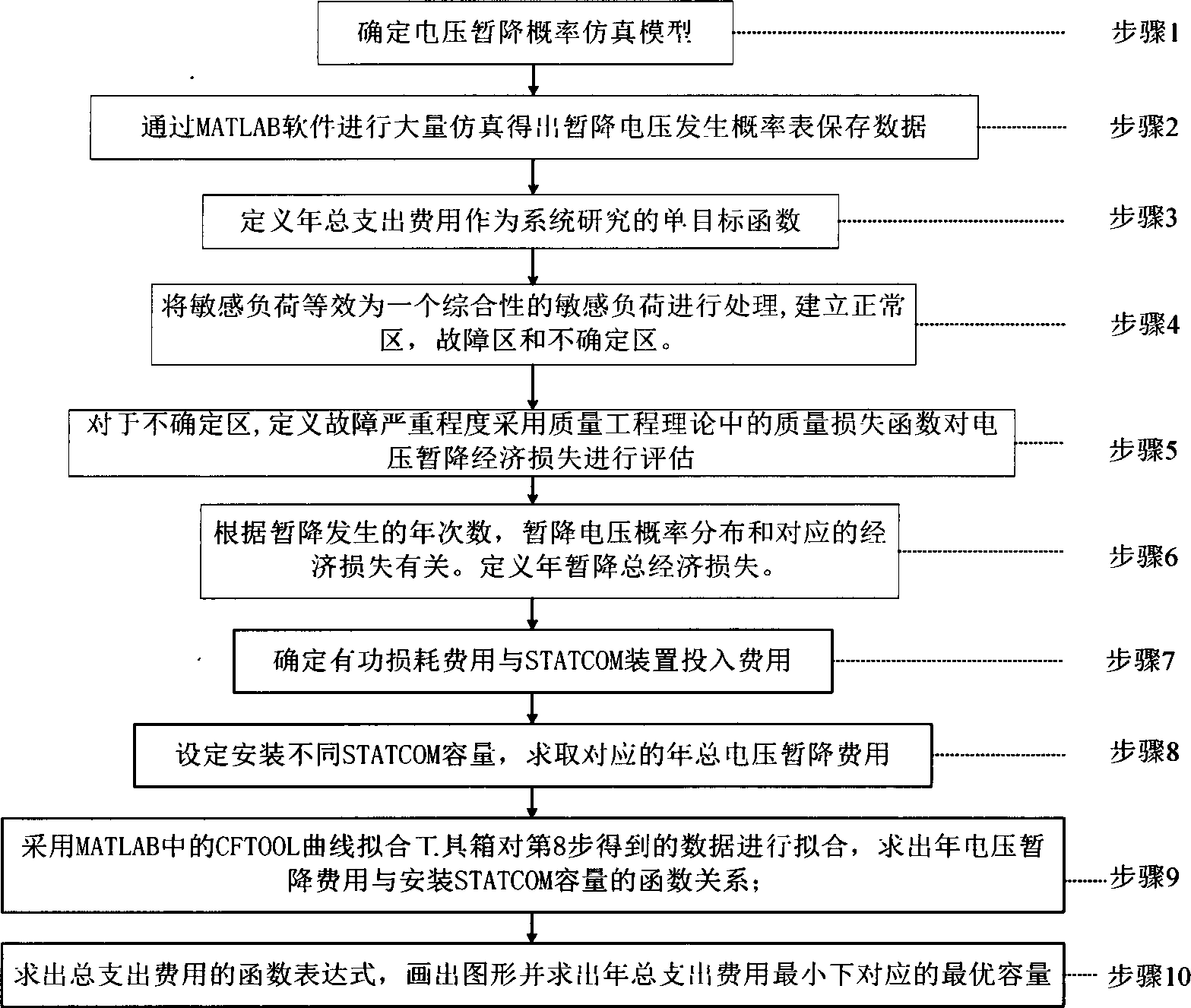
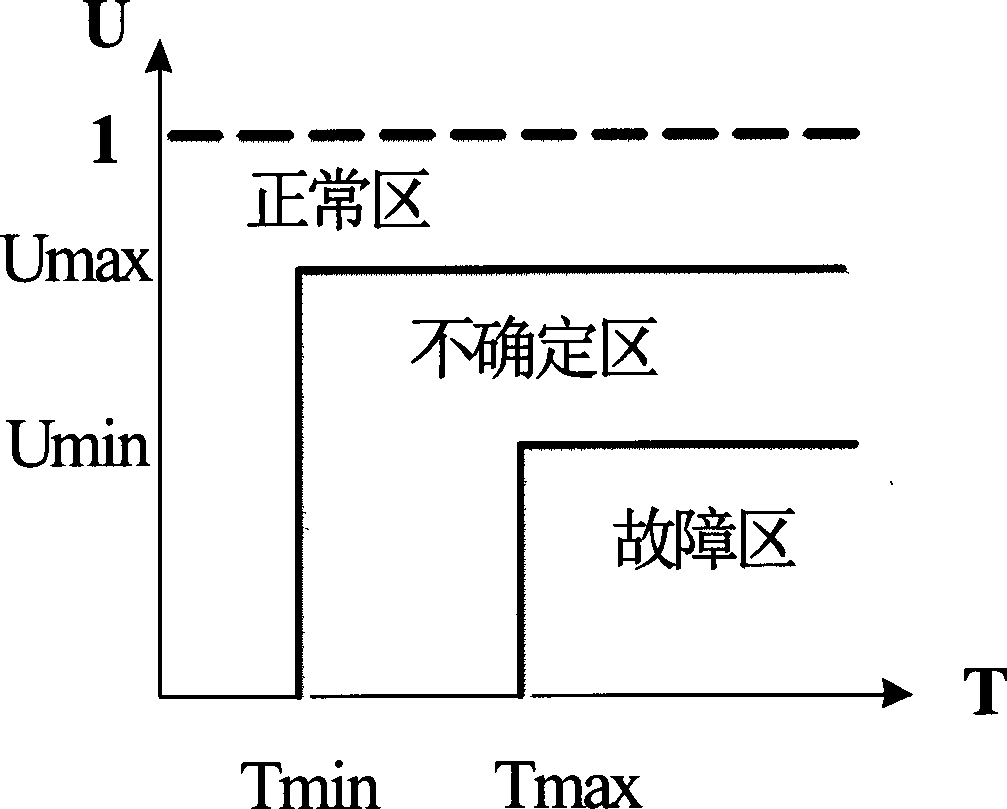
InactiveCN103795068AIncrease safety and stability marginUniversally applicableFlexible AC transmissionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPower compensationCurve fitting
The invention discloses an optimal configuration method for high-voltage distribution network dynamic reactive power compensation equipment capacity. The optimal configuration method of the high-voltage distribution network dynamic reactive power compensation equipment capacity includes the steps that in a high-voltage distribution network, by combination of sensitive load characteristics, a voltage dip risk is introduced to serve as a voltage stabilization consideration object; a reactive power optimization single objective function model is established, and voltage dip loss, line active loss and dynamic reactive compensation equipment cost are added in an economic measurement mode; multiple groups of reactive capacity are set and corresponding total expenditure cost is solved; curve fitting is carried out on the cost and the capacity by means of MATLAB software, so that optimal capacity is calculated. According to the method, the modern power grid characteristic that a high-voltage distribution network voltage sensitive load continuously increases currently, the fact that the probability of voltage dips of a power grid is much larger than the probability of voltage collapse or the probability of voltage unstability, the situation that dynamic reactive compensation equipment configuration cost is relatively high currently and other actual influence factors are considered, and superiority is reflected from the perspectives of theories and engineering. Therefore, the method has a good actual instruction meaning.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Voltage collapse diagnostic and ATC system
InactiveUS20050033480A1Improve and reduce reliabilityAvoid power outagesBatteries circuit arrangementsLevel controlLoad SheddingSystems design
The present invention provides an analysis method for an electrical power system whereby the plurality of buses are grouped into agents, family lines of agents and families of agents based on the reactive reserves depleted when the buses are loaded. Contingencies are then applied to the electrical power system and the reactive reserves are monitored and an exhaustion factor is determined for one or more family lines in one ore more families. A method for selecting double outage that have no solution for each outage that has no solution when the outage is removed in small steps and an additional step has no solution. The boundary case solution is used to assess where, why, and how the contingency causes voltage instability, voltage collapse, and local blackout. Based on this information, the design of voltage rescheduling, active rescheduling, unit commitment, load shedding is determined that can be used as preventive, corrective, or emergency controls in applications such as system design and planning, operation planning, reactive and voltage management, real time control, and Special Protection System Control. Based on this information, solutions can then be applied to the political power system.
Owner:INTELILCON
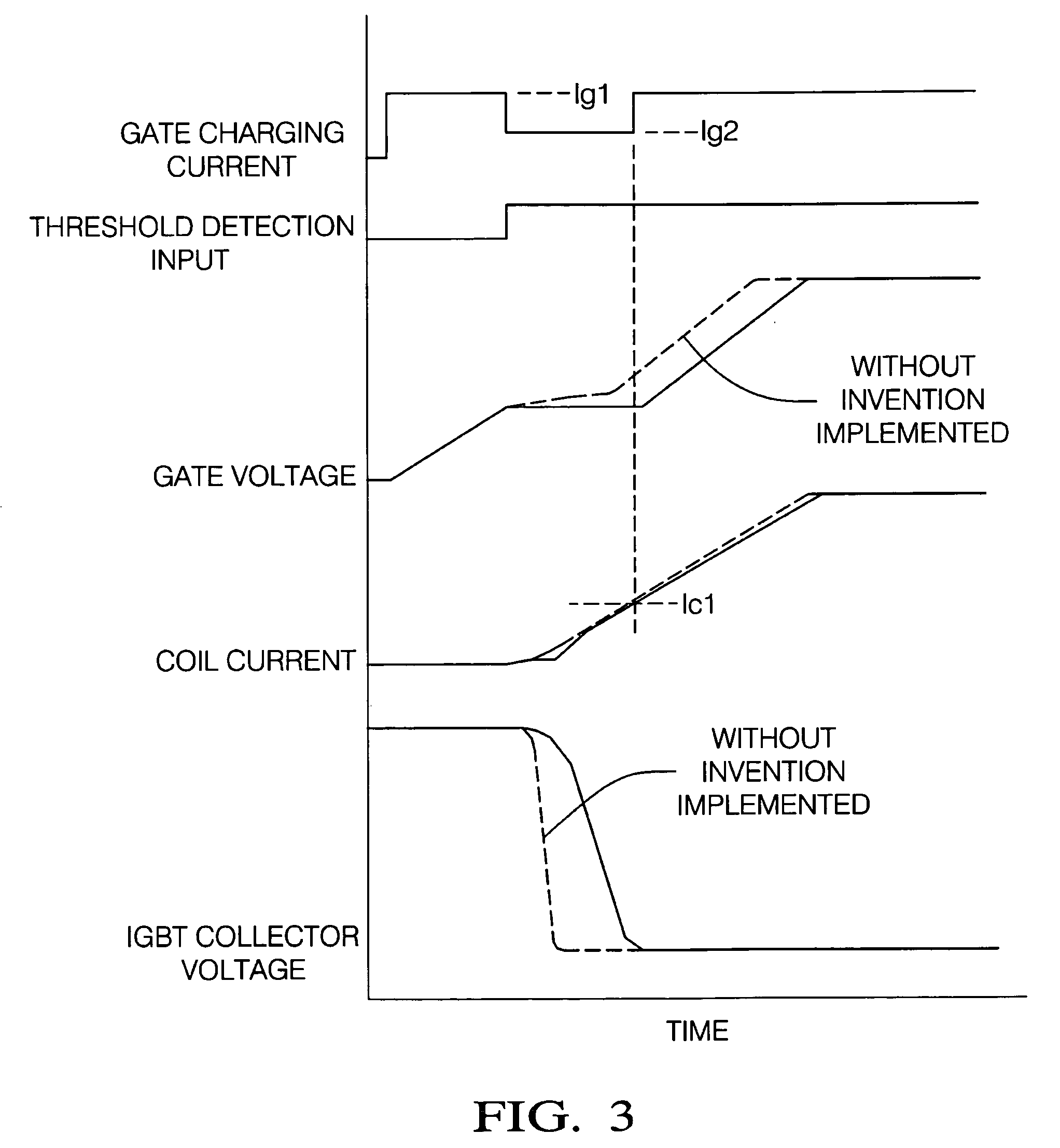
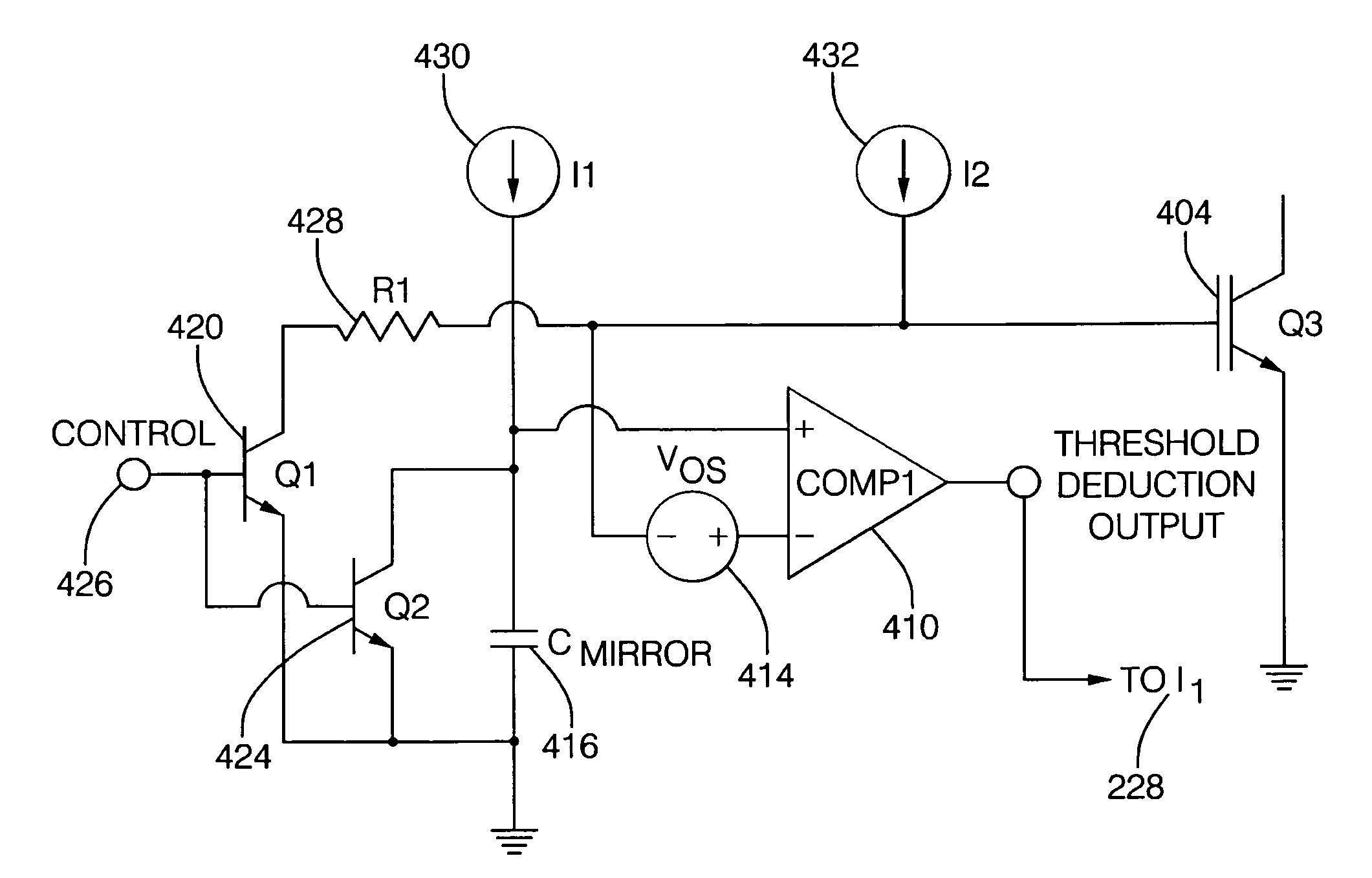
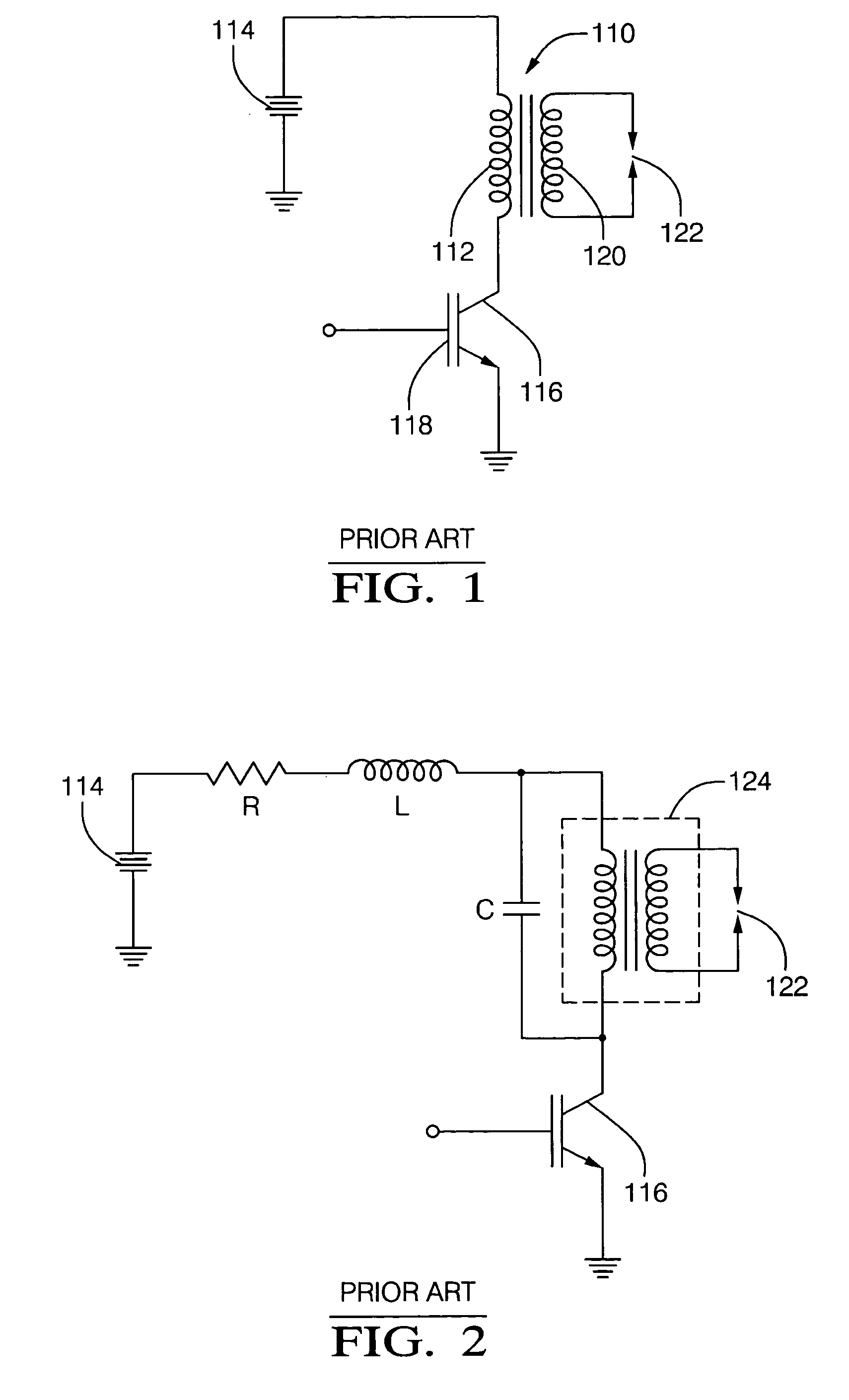
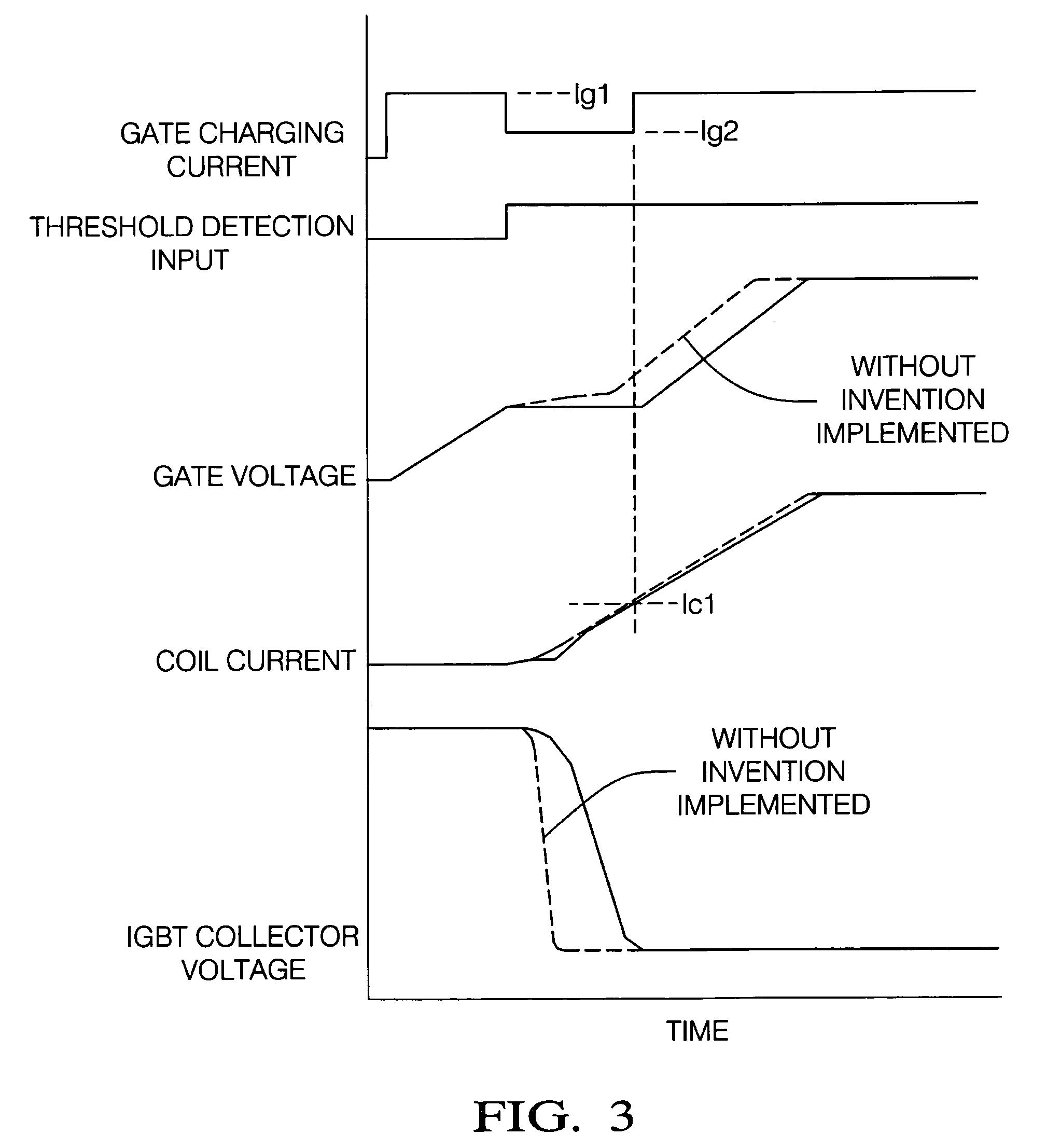
Switching control system to reduce coil output voltage when commencing coil charging
ActiveUS20080012041A1Eliminate errorsMinimize dwell timing errorThyristorElectronic switchingIgnition coilCapacitor voltage
A switching control system and method is provided that optimizes switching efficiencies for power switching applications including automotive ignition systems, solenoid drivers, motor drivers and power regulation systems. In an ignition system, a coil current switching magnitude is controlled at the start of ignition coil charging, thereby avoiding an untimely spark event. When the transistor threshold voltage is reached, the collapse rate of the ignition system transistor collector voltage is reduced by reducing the gate charging current. The reduced collector voltage slew rate results in a reduced primary and secondary coil output voltage. After the collector voltage collapses, a continued rapid charge is provided to place the transistor in a hard saturation bias condition. In an aspect, the present invention dynamically determines the threshold voltage of a power transistor. A mirror capacitor substantially matches a transistor gate voltage and a signal is generated when the mirror capacitor voltage proportionally exceeds the transistor gate voltage as a consequence of the transistor reaching a threshold voltage.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
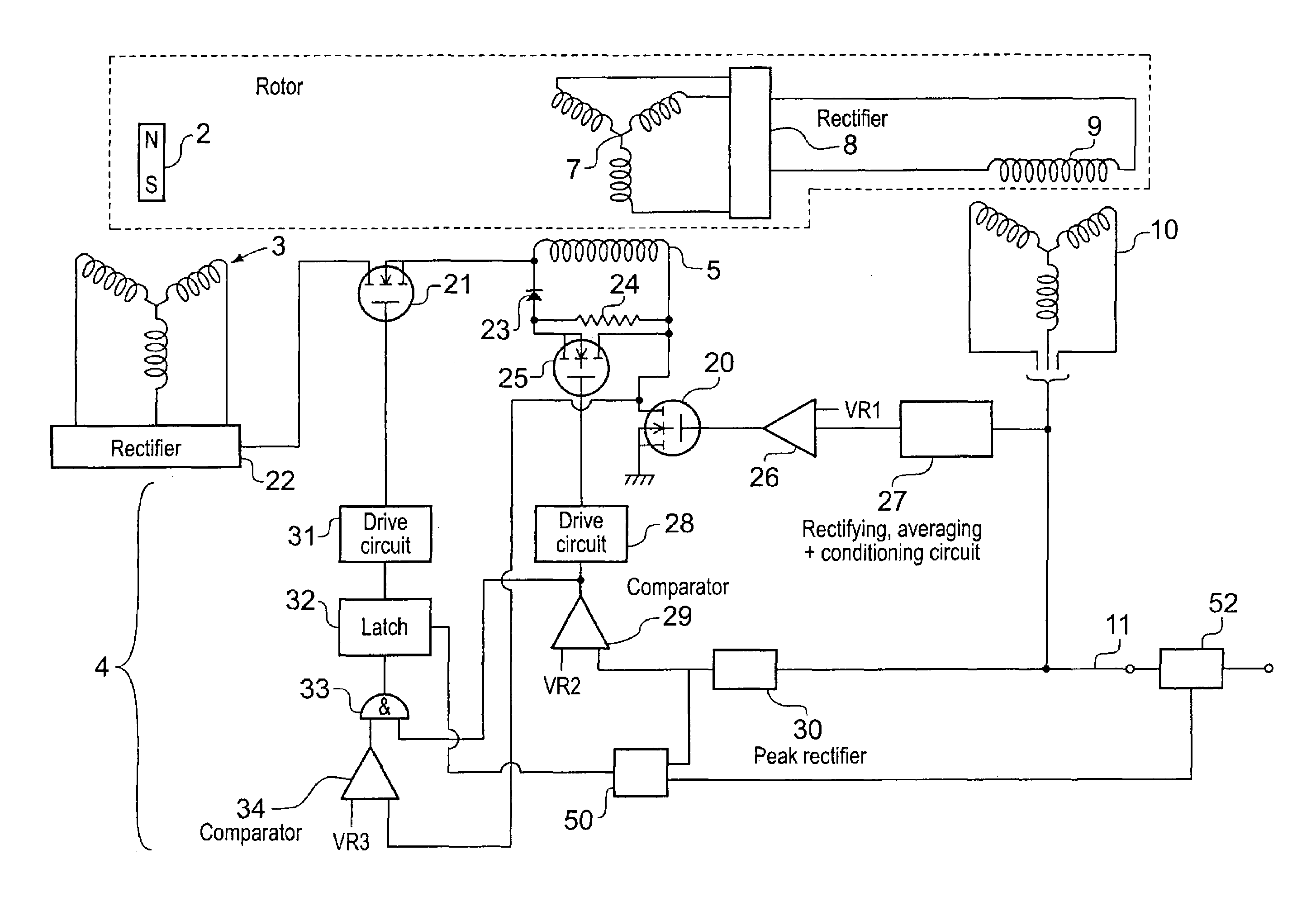
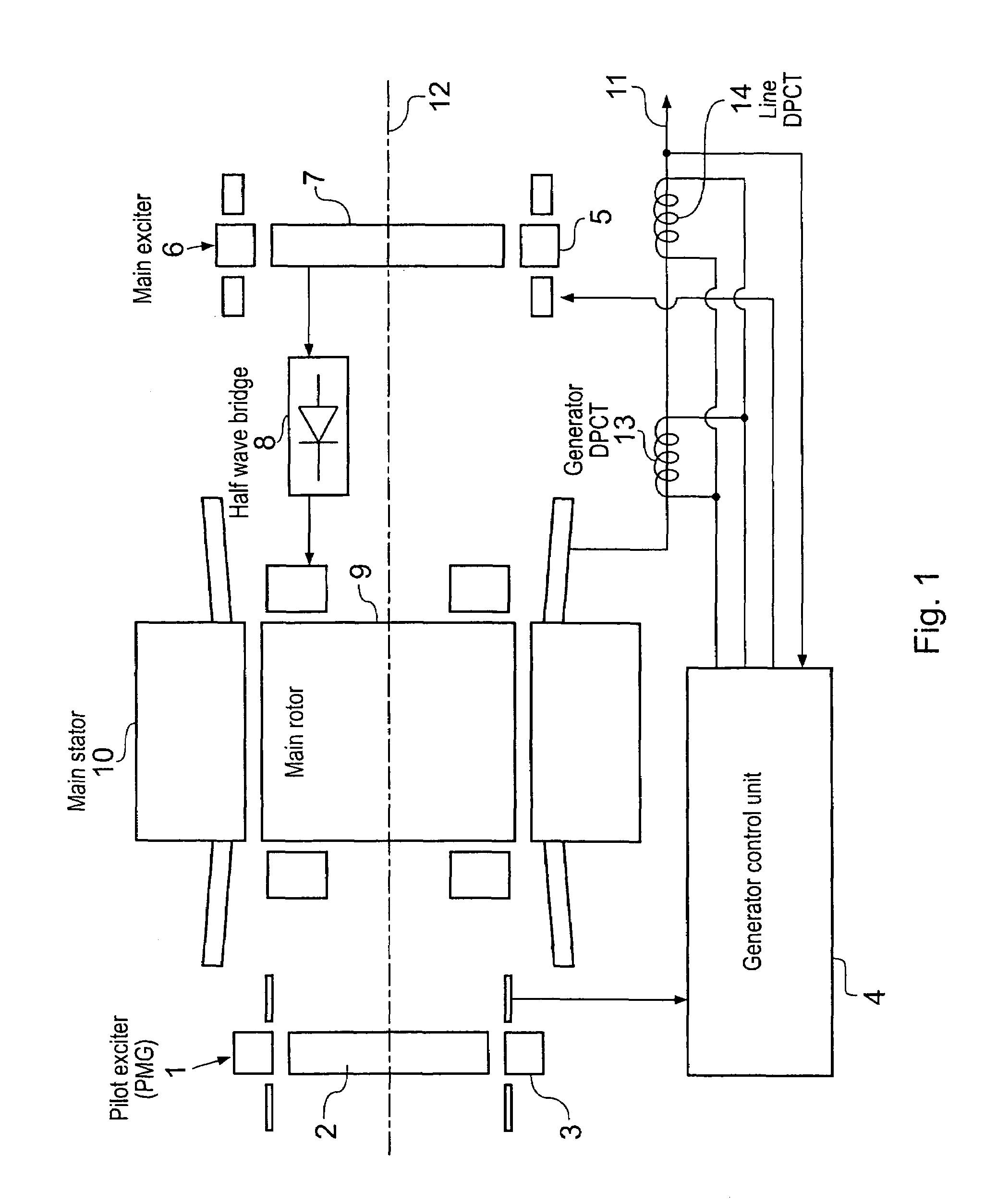
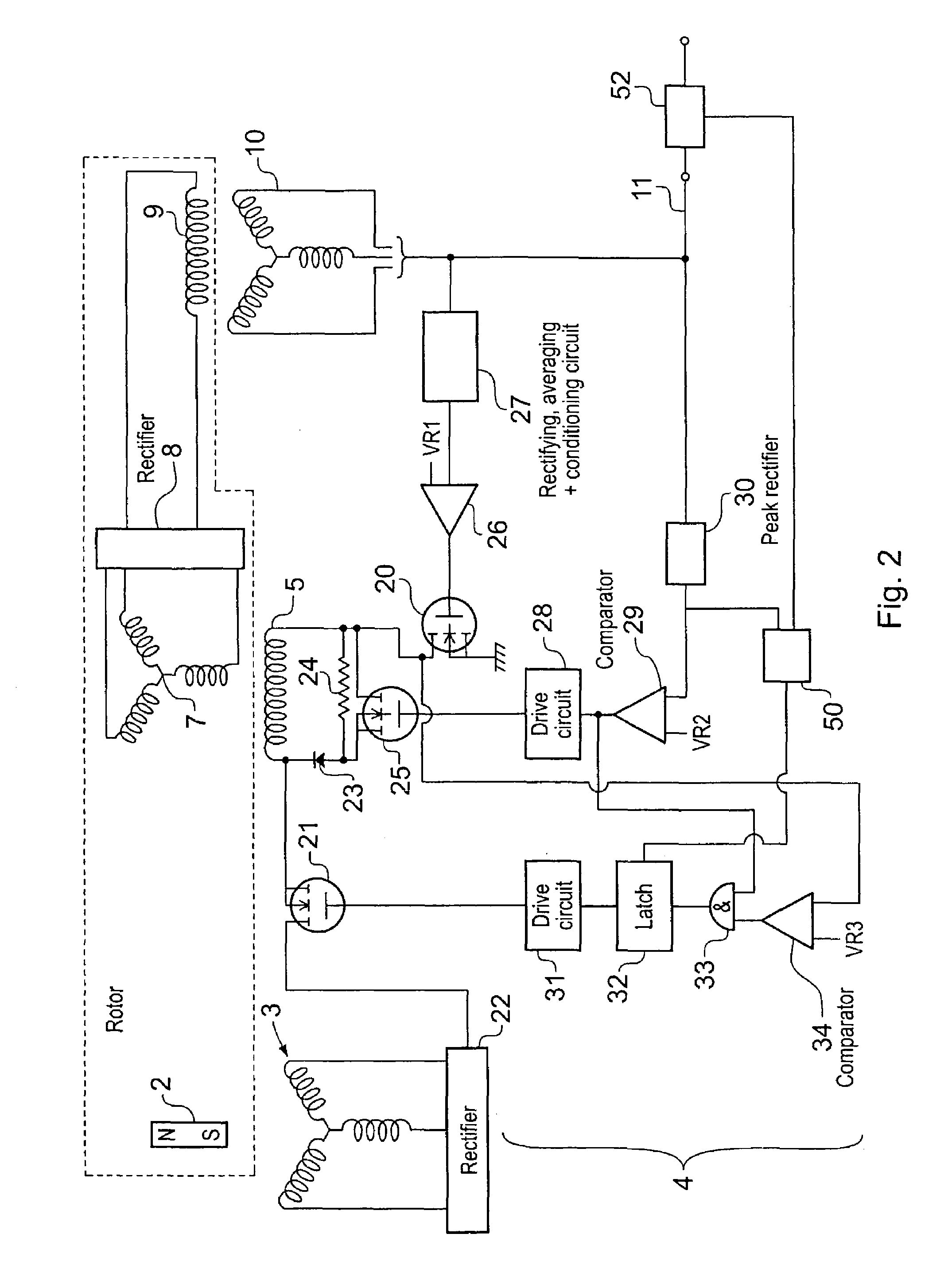
Method of and apparatus for detecting sensor loss in a generator control system
InactiveUS7005833B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlControl systemCurrent threshold
A generator controller (4) is provided which is able to detect and respond to failure of a generator output voltage sensor, whilst being able to distinguish voltage sensor failure from output voltage collapse due to the presence of an overload or short circuit condition. The presence of a voltage sensor failure is indicated by the measured output voltage being below a first voltage threshold whilst the output current is also below a current threshold.
Owner:SAFRAN POWER UK
System and method for monitoring and managing three-phase power flows in electrical transmission and distribution networks
ActiveUS20110257933A1Power network operation systems integrationDigital computer detailsPower flowPower grid
A system and method for monitoring and managing three-phase power flows in electrical transmission and distribution networks through the use of a deterministic, non-iterative method using an holomorphic embedding and algebraic approximants for determining the power flows in the three phases of a power generating system having an electrical grid. Such method is capable of determining whether or not a physical solution to the load flow problem exists, or if the system is in a state of voltage collapse. It may be employed in either real-time or off-line analytic applications for balanced or unbalanced electric power systems, in particular for monitoring and analyzing unbalanced conditions in three-phase electrical networks and for the accurate calculation of short-circuit conditions.
Owner:APLICACIONES & INFORMATICA AVANZADA
Perturbation and observation method for tracking maximum power point of photovoltaic grid-connected generating system
InactiveCN102591399AReduce hardware costsAccurate tracking of maximum power pointPhotovoltaic energy generationElectric variable regulationPerturbation and observationGrid connected inverter
The invention discloses a perturbation and observation method for tracking a maximum power point of a photovoltaic grid-connected generating system, which is characterized in that reference current amplitude value signals of a grid-connected inverter serve as alternative signals of output power of the grid-connected inverter, and a controller is used for perturbing photovoltaic array reference voltage in real time and determining the direction of perturbing photovoltaic array reference voltage for next time according to reference current amplitude value signal change before and after the photovoltaic array reference voltage is perturbed. By means of ring closure of a PI regulator, reference current amplitude value signals of the grid-connected inverter for next time can be also obtained while practical output voltage of a photovoltaic array tracks the reference voltage in real time. Repeatedly, a maximum power point tracking function of the photovoltaic array can be realized by perturbing the voltage, observing the reference current amplitude value signal change and regulating reference voltage of the photovoltaic array and the reference current amplitude value signals of the grid-connected inverter for next time. By the aid of the method, voltage collapse of a direct-current bus and incapability of correctly tracking in weak sunlight are avoided, hardware cost is reduced, and generating power of the photovoltaic array is improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Electric power system static voltage stability assessment method considering electric automobile charging characteristic and load fluctuation limit
ActiveCN106712037AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityAc network voltage adjustmentLoad SheddingPower grid
The invention particularly relates to an electric power system static voltage stability assessment method considering the electric automobile charging characteristic and the load fluctuation limit. The method comprises the steps of establishing of a power grid node injection power random mode, Sobol sequence construction in a QMC sampling method, electric power system static voltage stability critical state searching and establishing of a static voltage indictor assessment system. The defect that the conventional analysis method can only analyze the static voltage stability limit of the system under the single load growth mode can be improved, the influence of the charging characteristic and the load random fluctuation on the static voltage stability of the system after an electric automobile accesses to the power grid can be researched and considered and different static voltage instable states of the power grid can be searched. The operation process is rapid, efficient and accurate; and the analysis conclusion is that an electric power system static voltage stability weak area can act as the key monitoring object of actual power grid operation so that power grid operation personnel are enabled to timely take corresponding load shedding measures, the accident of whole grid voltage collapse can be avoided and the engineering practicality is high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Maximum power point tracking method based on disturbance observation
InactiveCN103455081AReduce the impactSteady state tracking error is smallPhotovoltaic energy generationElectric variable regulationDynamic modelsReference current
The invention discloses a maximum power point tracking method based on disturbance observation. The method comprises the steps of firstly, sampling a photovoltaic array voltage, a grid voltage and a grid-connected current signal; then, establishing a dynamic model of a single-stage photovoltaic grid-connected generation system; finally, carrying out maximum power point tracking on the single-stage photovoltaic grid-connected generation system. According to the method, only the photovoltaic array voltage is detected, and a grid-connected reference current amplitude signal Iref is taken as an equivalent signal of output power of a grid-connected inverter, so that the influence on a maximum power point tracking algorithm caused by sampling quantization errors is lowered effectively, and the problems of the traditional disturbance observation methods that in the single-stage photovoltaic grid-connected generation system, the stability of the control strategy is poor and the bus voltage collapses or the output power oscillates are solved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Coordinated emergency control method for near-region power grid voltage of phase modifier
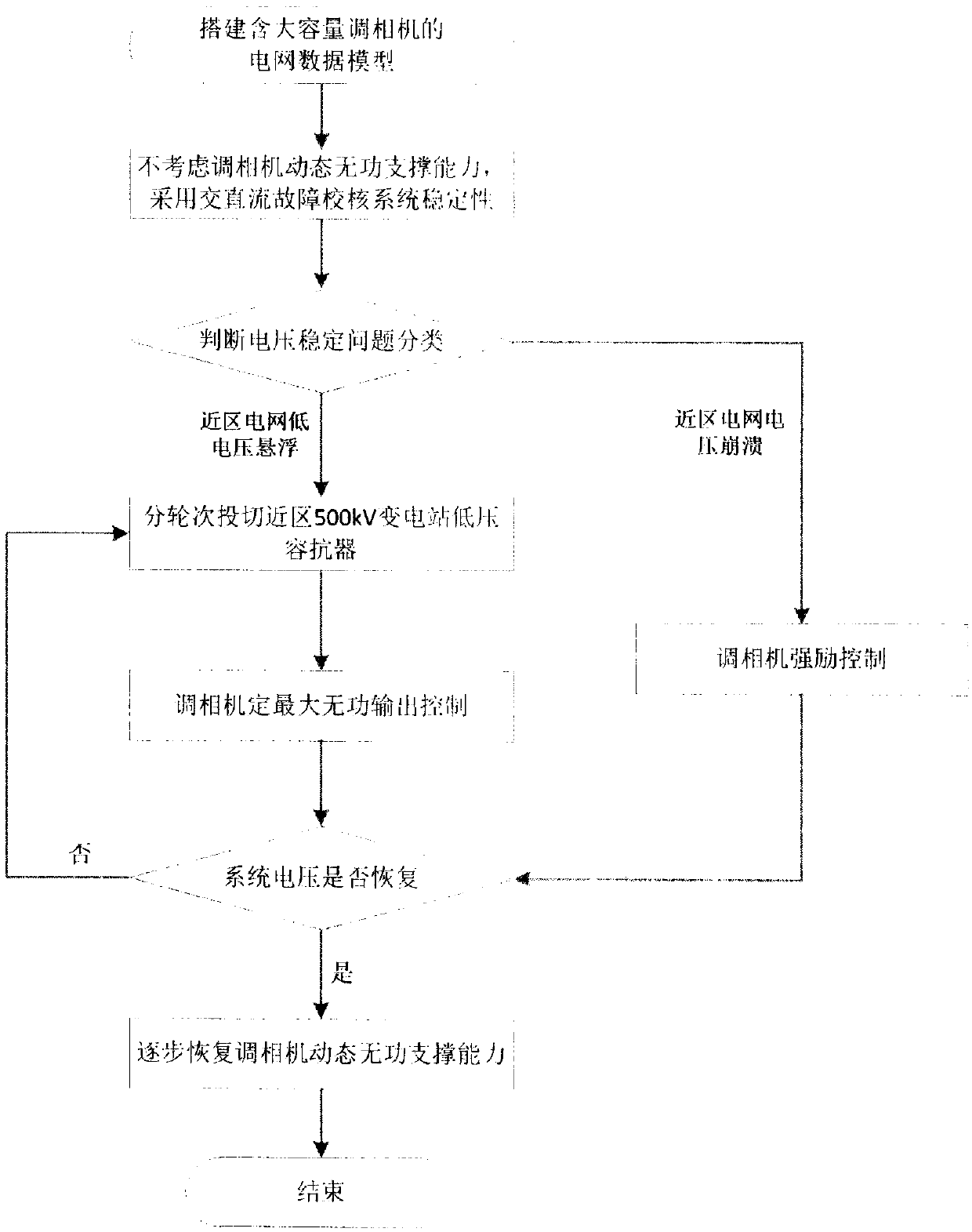
ActiveCN107749630AImprove adaptabilitySimple calculationContigency dealing ac circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLow voltagePower grid
The invention provides a coordinated emergency control method for near-region power grid voltage of a phase modifier. The coordinated emergency control method comprises the steps of building a data model of a power grid containing a phase modifier; checking the stability of the power grid by adopting an AC / DC system fault; distinguishing the type of a voltage stability problem caused by the fault;if the voltage stability problem is near-region power grid low-voltage suspension of the phase modifier, firstly switching a low-voltage capacitive reactor by turns, and then adopting fixed maximum reactive power output control for the phase modifier; if the voltage stability problem is near-region power grid voltage collapse, adopting fixed maximum reactive power output control for the phase modifier; then judging whether the system voltage recovers or not, if so, exiting, otherwise, firstly switching the low-voltage capacitive rector by turns, and then adopting fixed maximum reactive poweroutput control for the phase modifier. The method provided by the invention can provide emergency control and control indicators in allusion to the near-region power grid voltage of the phase modifier, thereby providing a technical reference for a new generation of phase modifiers to participate in coordinated emergency control for the near-region power grid voltage.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Continuous power flow based maximum transmission capacity calculation method for system containing power source converter (VSC)
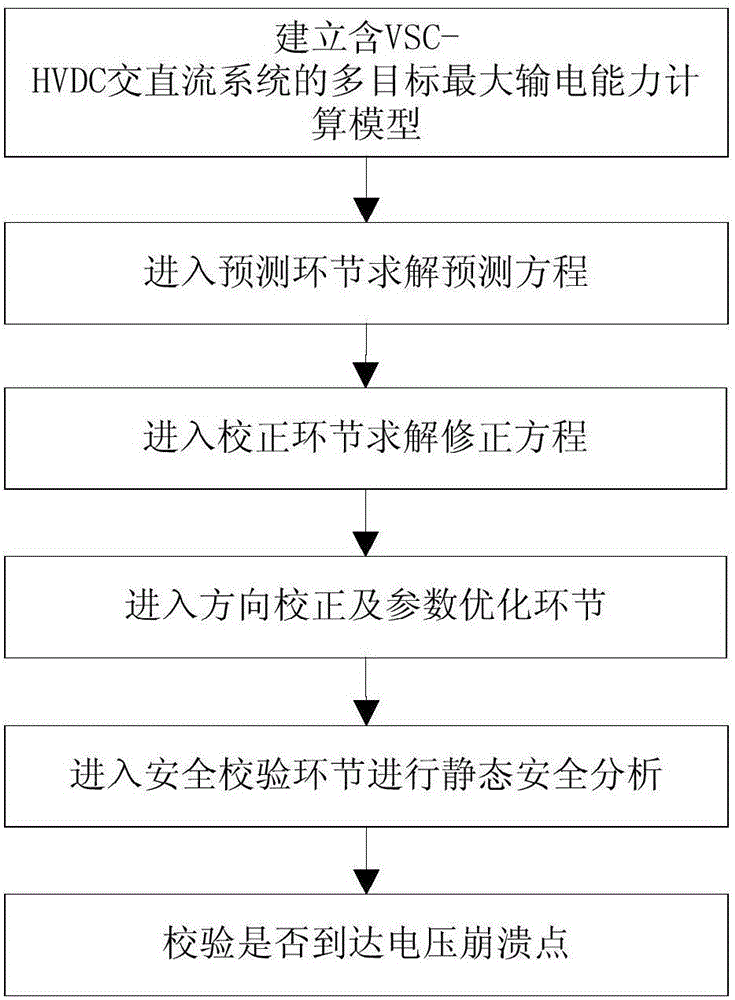
ActiveCN105958496ASolve the problem of calculating the maximum transmission capacityEffective guidance and adjustmentElectric power transfer ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower system schedulingHeat stability
The invention belongs to the field of dispatching automation of electric power systems, and particularly relates to a continuous power flow based maximum transmission capacity calculation method for a system containing a power source converter (VSC). The continuous power flow based maximum transmission capacity calculation method comprises the following steps: firstly establishing a multi-target maximum transmission capacity calculation model of an AC / DC system containing power source converter based high voltage direct current (VSC-HVDC); entering a predication link to solve a prediction equation based on the calculation model, then entering a correction link to solve a modified equation, entering a direction correction and parameter optimization link, and finally entering a safety verification ink to carry out static safety analysis so as to check voltage level and line heat stability; and simultaneously checking whether to reach a voltage collapse point. The static voltage stability, the static safety and the influence of system economy on transmission capacity can be taken into account comprehensively, so that the maximum transmission capacity calculation problem of the AC / DC system containing VSC-HVDC can be effectively solved, the electric generator economy output and VSC optimal control parameters are given out while the maximum transmission capacity is calculated, and the method has extremely good engineering application prospect.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
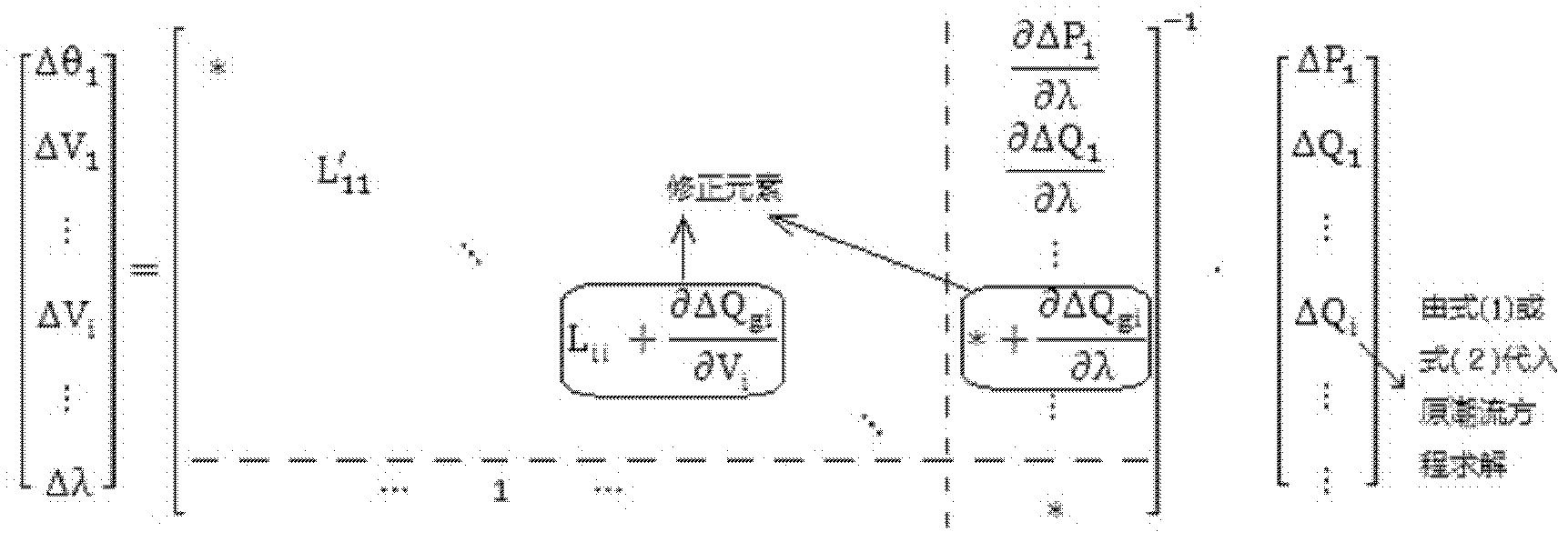
Area information based quiescent voltage unstability prediction method
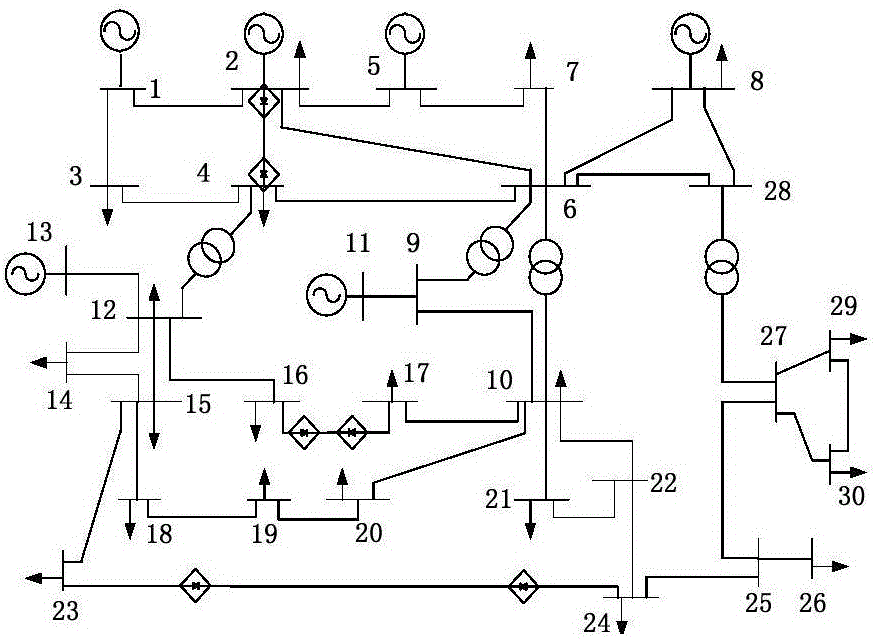
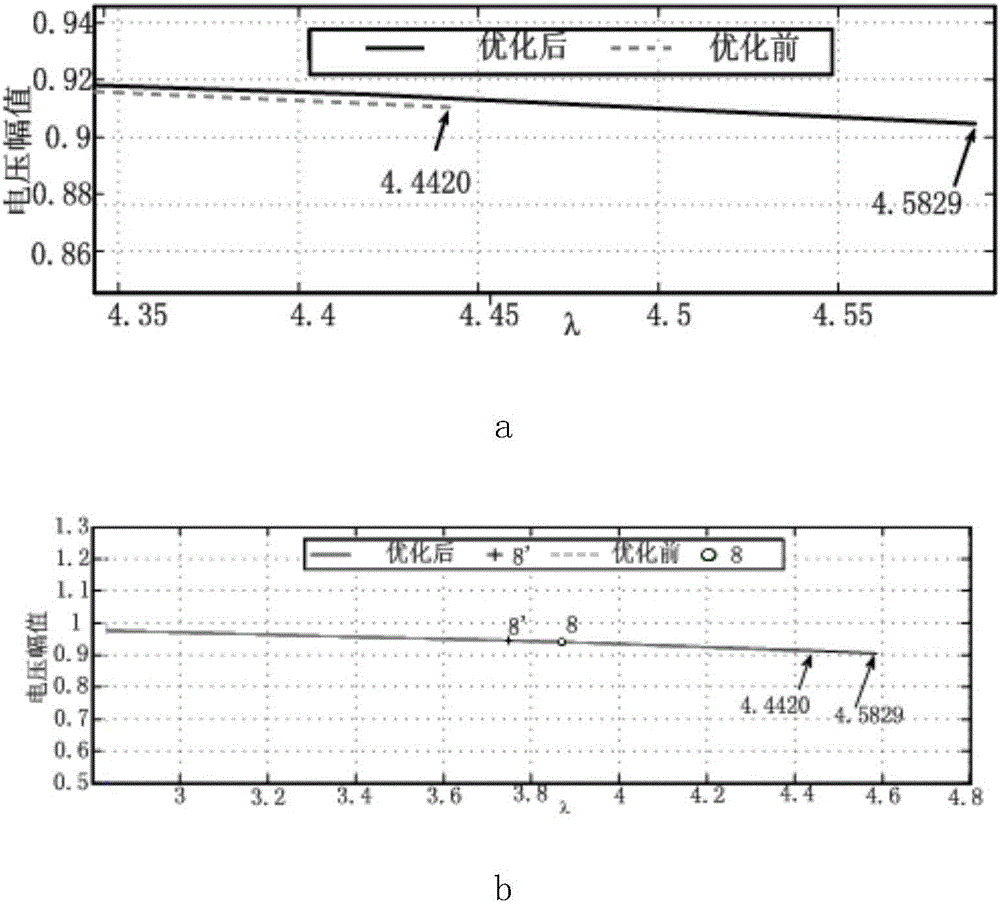
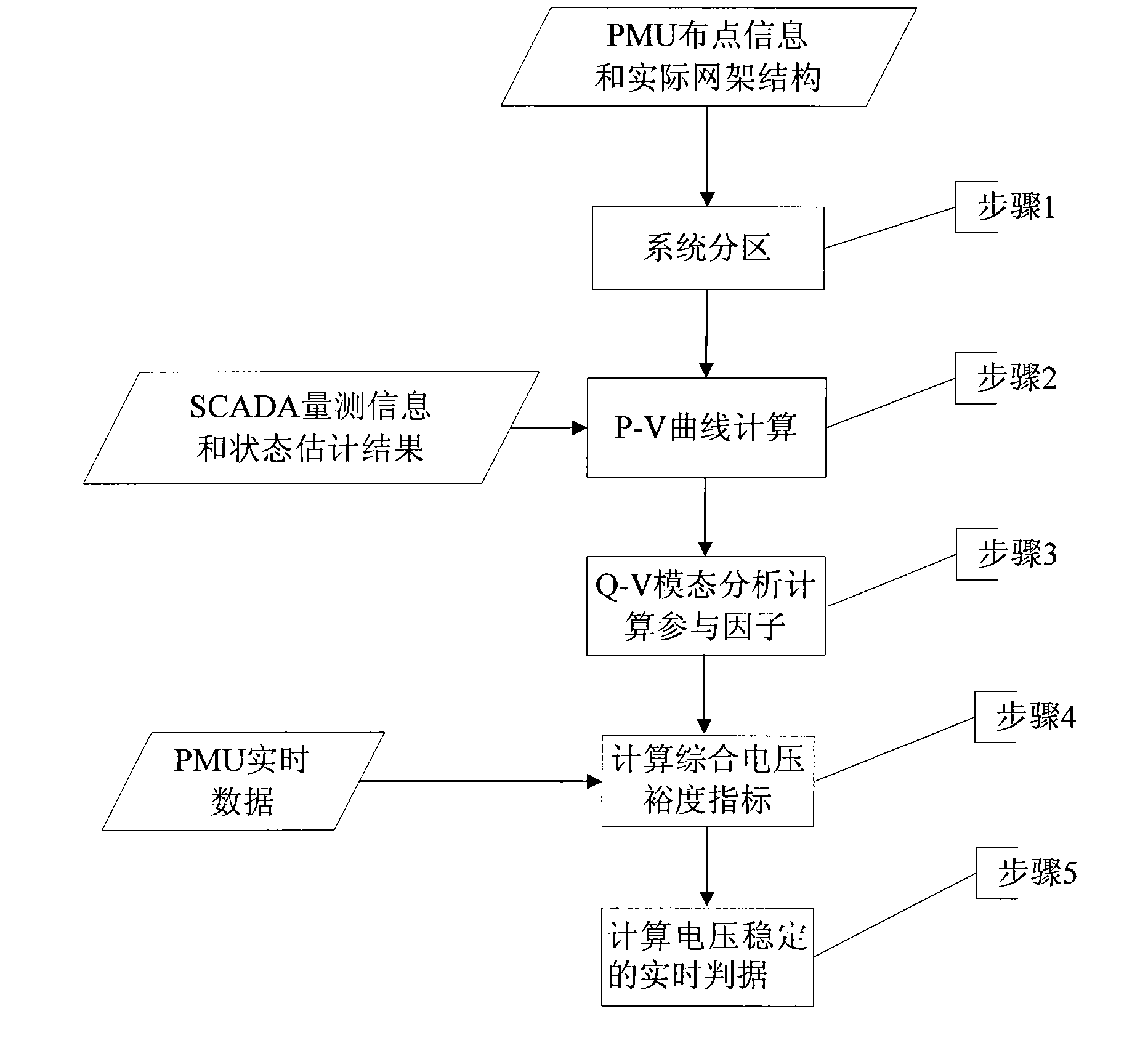
ActiveCN101819243ASafe and stable operationPrevent crashCurrent/voltage measurementFault locationElectric power systemData acquisition
The invention belongs to the field of a power supply system and automatics thereof and is applicable to wide area information based quiescent voltage unstability prediction of power grid real-time states and working conditions after a predicted accident. The method comprises the steps of: (1) integrating the PMU (Power Management Unit) node distribution information and actual grid structure of the power grid and dividing the power grid into a plurality of generating areas and load areas; (2) carrying out P-V curve computation on the basis of SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) measurement information and state estimation results to obtain critical voltage of each node at the moment of voltage breakdown; (3) carrying out Q-V model analysis computation on a trend the voltage ofwhich is close to breakdown to obtain all participation factors installed with PMU nodes; (4) weighting the voltage margin of each node in real time to be used as a compressive voltage margin index according to real voltage data detected by a PMU by taking the PMU node participation factors as weight; and (5) when the compressive voltage margin index is relatively small, using the sensitivity of the reactive power loss change of a receiving section in a load area to transmission active power as a real-time proof for calculating voltage unstability.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
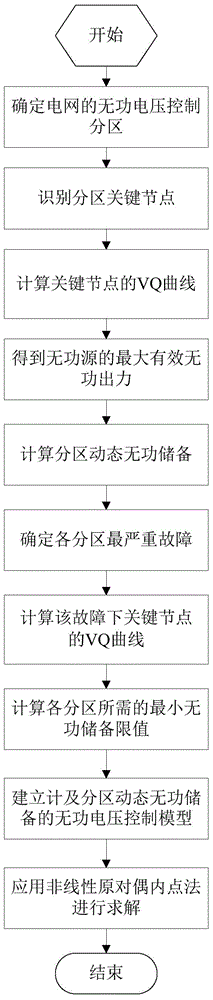
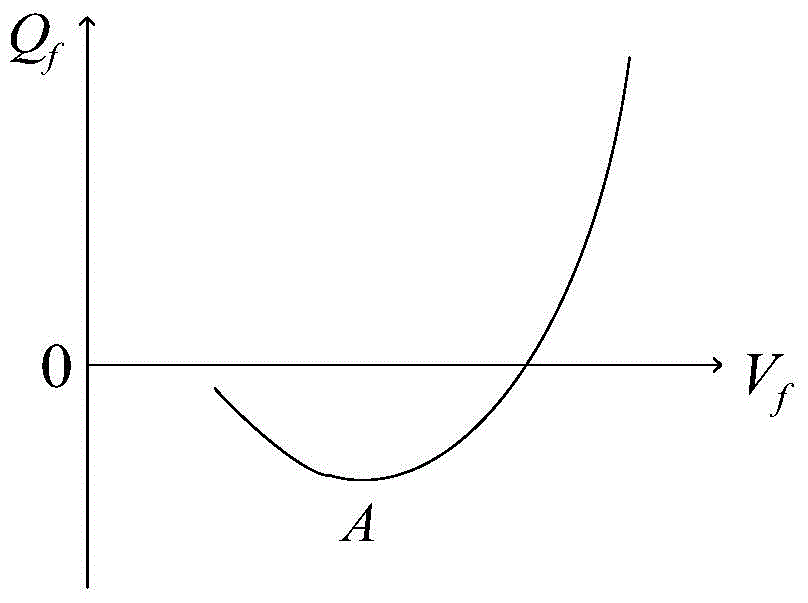
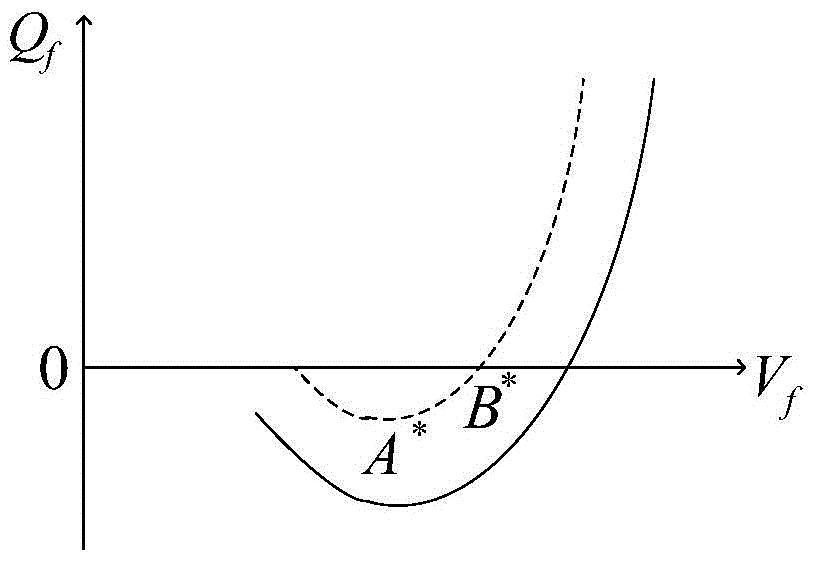
Reactive voltage control method considering dynamic reactive power reserves of partitions
InactiveCN104701858APrevent crashReduce active network lossAc network voltage adjustmentReactive power compensationElectric power systemPower grid
The invention discloses a reactive voltage control method considering dynamic reactive power reserves of partitions and belongs to the technical field of power system optimized operation. The method comprises the steps of determining the reactive voltage control partitions of the power grid and identifying the key node of each partition, calculating the VQ curve of the key nodes and the dynamic reactive power reserves of the partitions, calculating the minimum reactive power reserve limiting value needed by each partition under the most serious failure, establishing a reactive voltage control model with the total dynamic reactive power reserve of the system as an optimization goal and the minimum reactive power reserve limiting value needed by each partition under the most serious failure as a constraint condition, and solving the reactive voltage control model. According to the reactive voltage control method, the reactive voltage control model contains the system total dynamic reactive power reserve optimized item and the minimum reactive power reserve limiting value constraint of each partition is established to balance the distribution of the dynamic reactive power reserve of each partition, and therefore, the voltage collapse phenomenon is avoided, and meanwhile, the purposes of reducing the active grid loss of the system, improving the voltage quality and enhancing the system voltage stability are achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
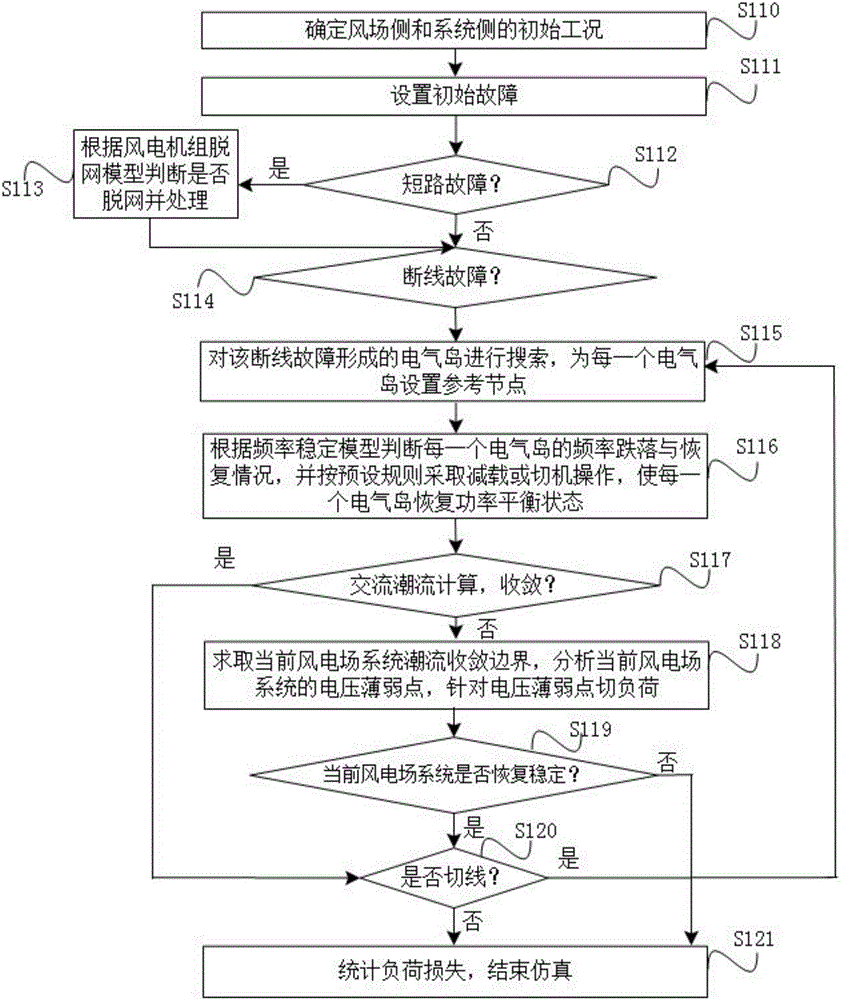
Power failure risk computing method for electric power system containing double-fed wind power plant
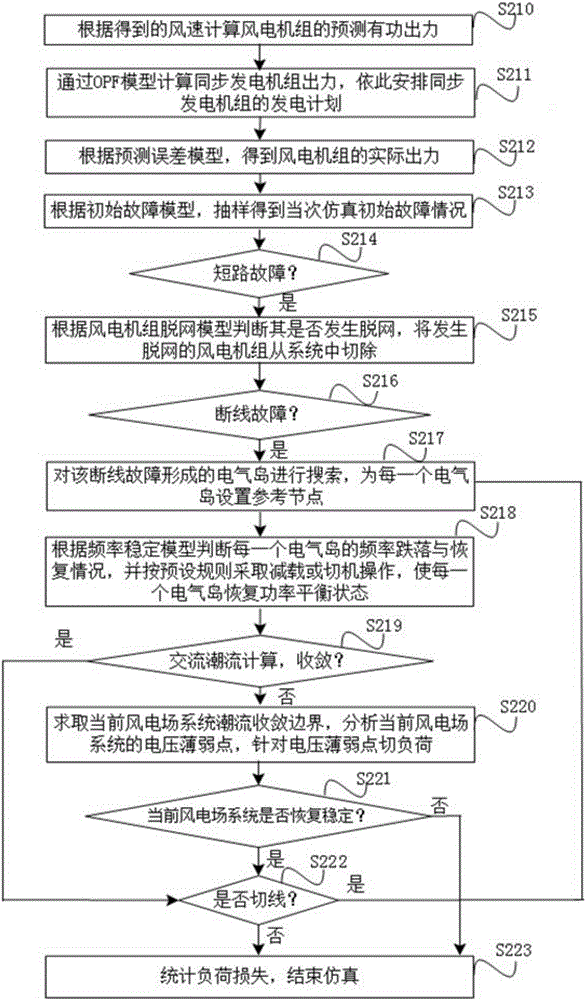
ActiveCN106230024AReduce load sheddingEasy to compare horizontallySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationFrequency stabilizationCascading failure
The invention discloses a power failure risk computing method for an electric power system containing double-fed wind power plant. The power failure risk computing method comprises the steps of pre-establishing multiple models, wherein a simulation process comprises the steps of determining the initial working condition of a system, and setting an initial fault; determining whether a short circuit fault or line broken fault occurs or not, if the short circuit fault occurs, processing according to an off-network model of a wind turbine generator, and then performing island-division searching; determining a frequency fall-off and recovery condition of an electrical island according to a frequency stabilization model, and enabling the electrical island to restore to a power balancing state; carrying out alternating current power flow calculation on the system and determining whether the system is converged or not, if not, solving a power flow convergence boundary, and analyzing voltage weak points; switching loads for the voltage weak points; next, determining whether the system is restored to be stable or not, if not, determining that the current wind power plant system is subjected to global voltage collapse, cutting all loads; and if the system is restored to be stable, determining whether a tangent line exists or not, if so, returning to perform the island-division searching step, and or otherwise, finishing the simulation process. By adoption of the power failure risk computing method, the load reducing amount required by the system for system recovery can be reduced to the minimum, and cascading failure analysis error is lowered.
Owner:STATE GRID ECONOMIC TECH RES INST CO +3
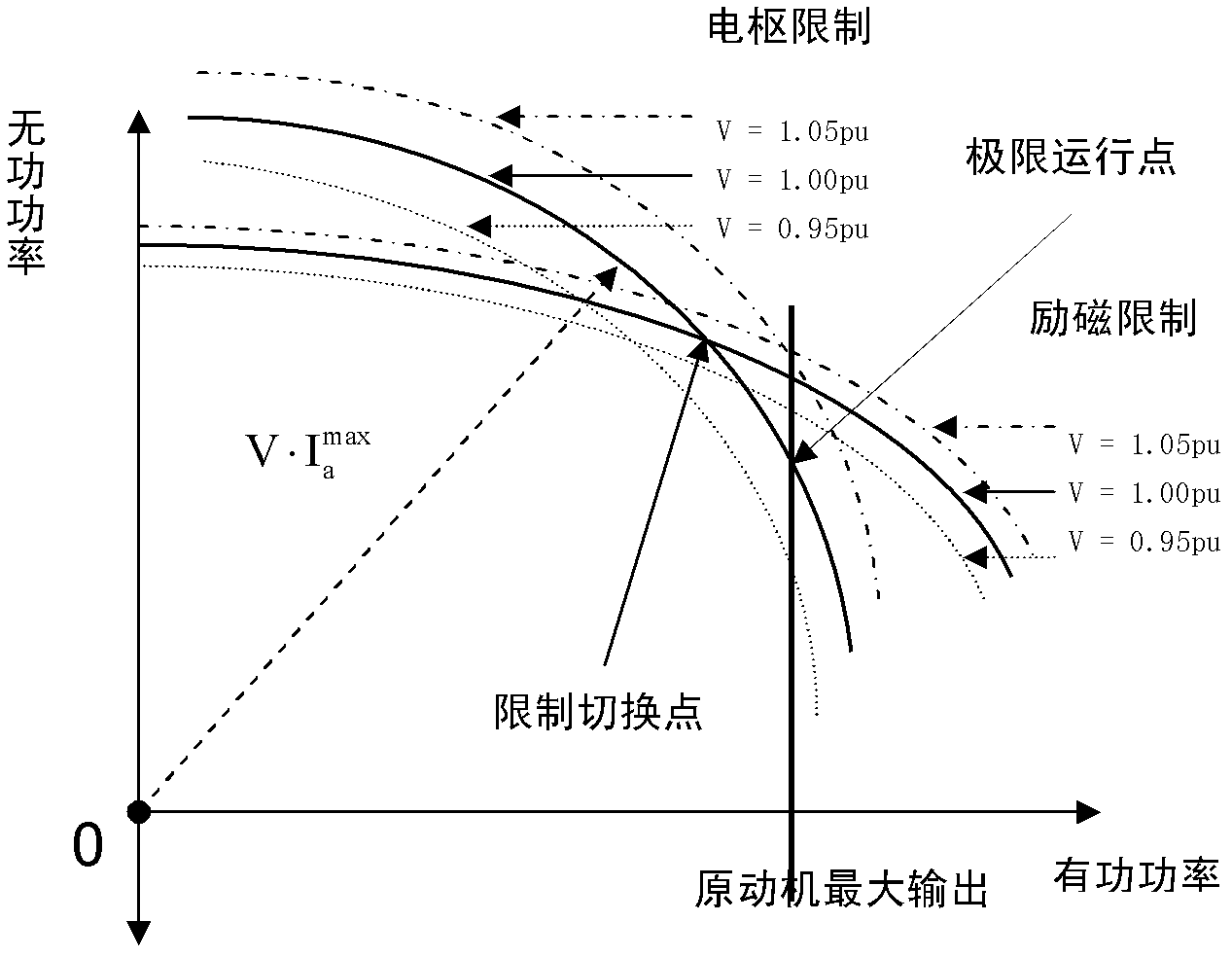
Continuation power flow algorithm considering field current constraint and armature current constraint of power generator
ActiveCN102593820ASolve continuous power flow calculation problemsPerfect reactive modelSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsContinuationPower flow
The invention discloses a continuation power flow algorithm considering field current constraint and armature current constraint of a power generator, which belongs to the technical field of electric power system stable analysis and control. Considering the influence of the field current constraint and the armature current constraint of the power generator on a reactive power output of the power generator, reactive output models under the maximal field current constrain and the maximal armature current constraint are respectively established, a Jacobian matrix is corrected in the continuation power flow calculation, power flow solution can be obtained through iteration, a pressure-volume (PV) curve is drawn, and more precise voltage stability margins can be obtained. In addition, the invention also provides a method for identifying a type of a static bifurcation point and key constraint conditions, so the type of the static bifurcation point and the key constraint condition causing the voltage failure can be identified, and the system prevention control validity can be improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Switching control system to reduce coil output voltage when commencing coil charging
ActiveUS7675346B2Eliminate errorsMinimize dwell timing error and current conduction overlapElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorIgnition coilCapacitor voltage
A switching control system and method is provided that optimizes switching efficiencies for power switching applications including automotive ignition systems, solenoid drivers, motor drivers and power regulation systems. In an ignition system, a coil current switching magnitude is controlled at the start of ignition coil charging, thereby avoiding an untimely spark event. When the transistor threshold voltage is reached, the collapse rate of the ignition system transistor collector voltage is reduced by reducing the gate charging current. The reduced collector voltage slew rate results in a reduced primary and secondary coil output voltage. After the collector voltage collapses, a continued rapid charge is provided to place the transistor in a hard saturation bias condition. In an aspect, the present invention dynamically determines the threshold voltage of a power transistor. A mirror capacitor substantially matches a transistor gate voltage and a signal is generated when the mirror capacitor voltage proportionally exceeds the transistor gate voltage as a consequence of the transistor reaching a threshold voltage.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Continuous power flow method of alternating current and direct current power system considering wind power randomness
ActiveCN106877336AVerify validityVerify availabilityAc networks with different sources same frequencyAlternating currentLoad following power plant
The invention discloses a continuous power flow method of an alternating current and direct current power system considering wind power randomness. Specific to the problem existing in stability calculation of a static voltage of a wind power plant-containing alternating current and direct current hybrid power transmission system, a Monte carlo method is adopted creatively to obtain a function relation between wind power output and voltage collapse point load margin through fitting; a calculation formula of voltage collapse point load margin expectation is deduced according to an air speed weibull distribution function, a relation between wind power output and power and a fitted function; the effectiveness of the method is verified on an improved IEEE9 node system; compared with the conventional Monte carlo method, the continuous power flow method disclosed by the invention is higher in accuracy and higher in speed; influence to the voltage collapse point load margin expectation from a direct current variable control value and air speed probability distribution parameters k, c values is further analyzed; and the method also can perform analysis on load margin of different load output directions conveniently, so that a direct current control value can be reasonably set by an operator according to the current air speed distribution condition so as to regulate an operating way favorably.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
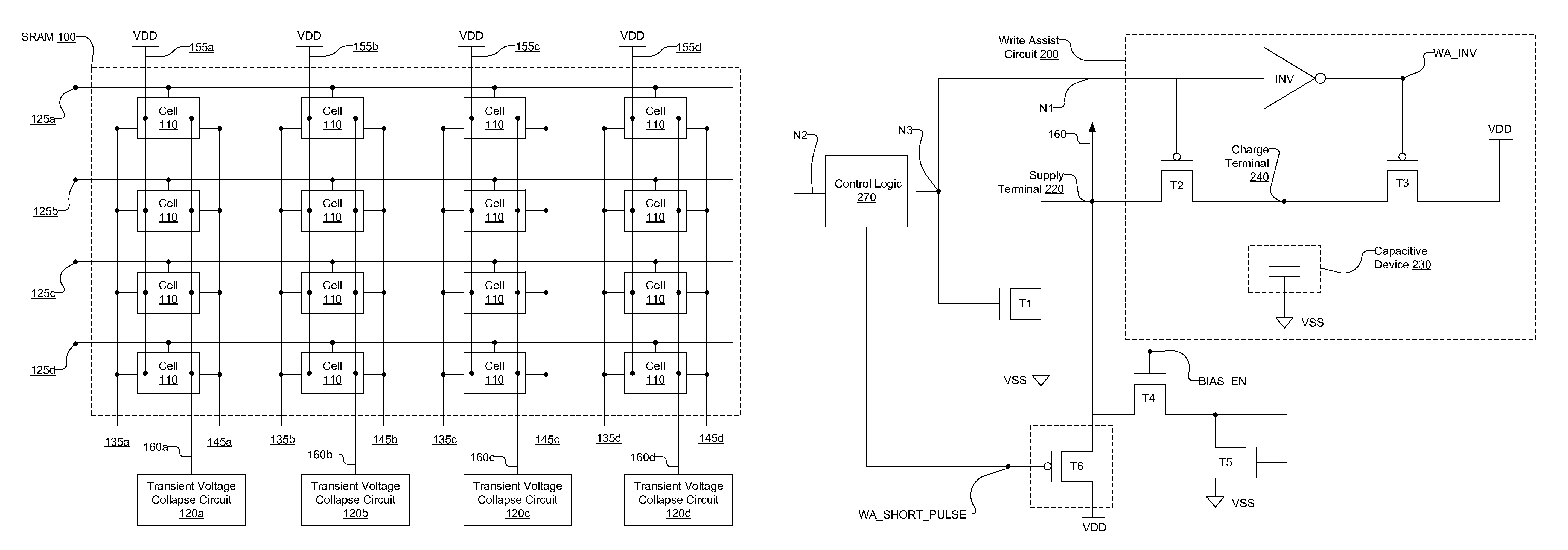
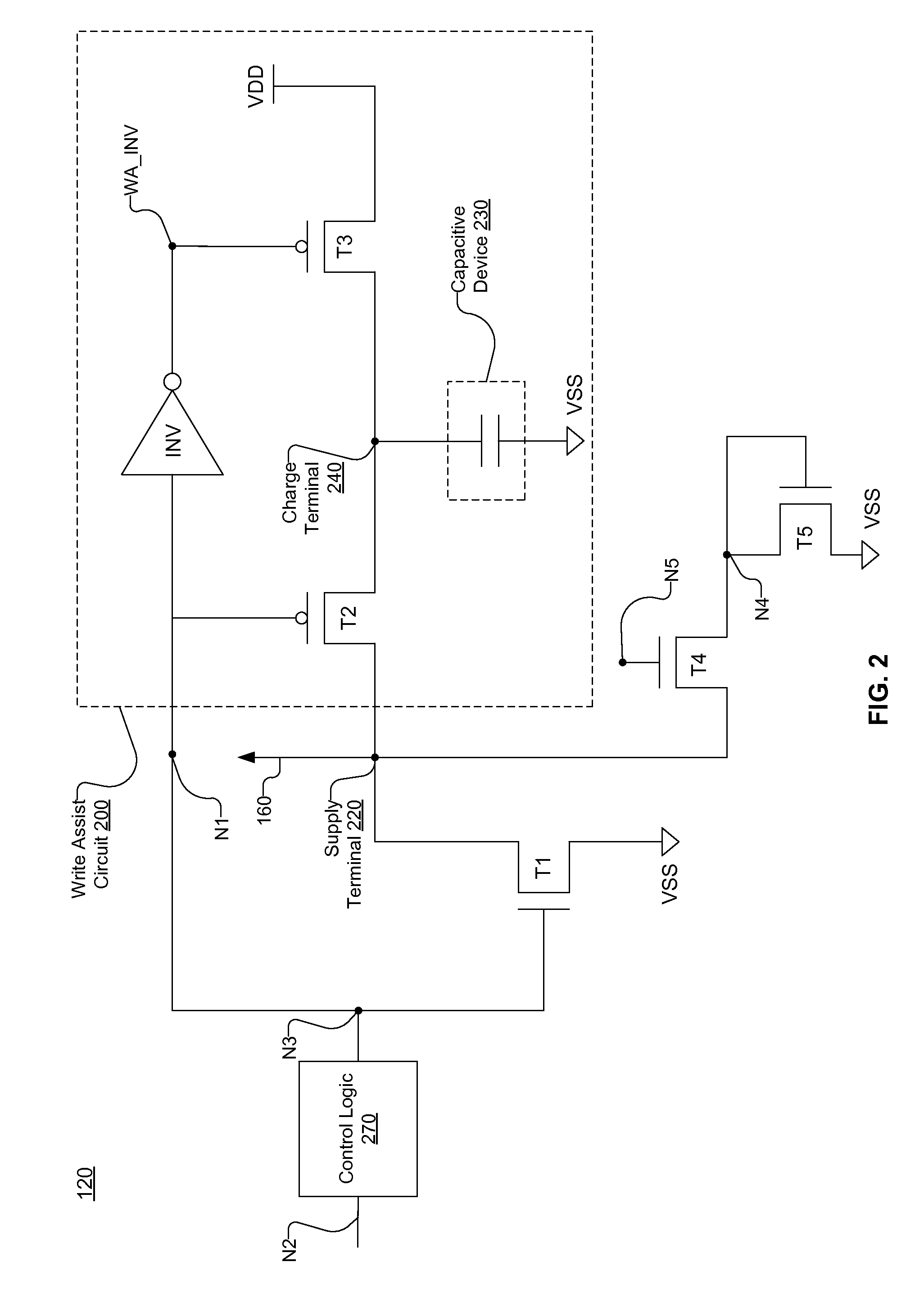
Write assist circuit integrated with leakage reduction circuit of a static random access memory for increasing the low voltage supply during write operations
ActiveUS9542998B1Reduce leakageSave extra spaceDigital storageStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
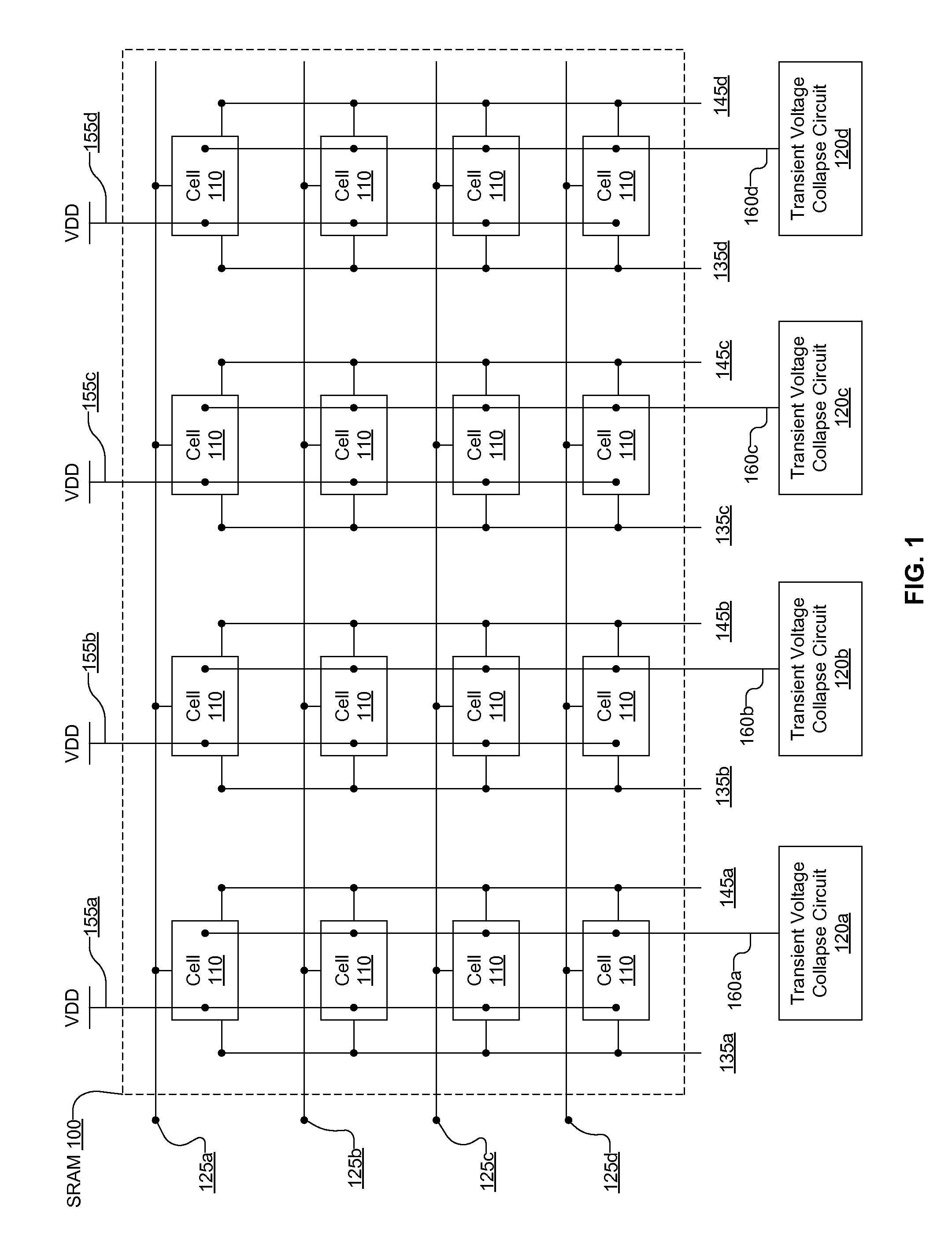
A transient voltage collapse circuit provides a reference voltage for an SRAM (static random access memory). The SRAM receives a first reference voltage and a second reference voltage higher than the first reference voltage. The transient voltage collapse circuit provides the first reference voltage to the SRAM via a voltage supply line. The transient voltage collapse circuit maintains the voltage supply line at a first voltage level during a power save mode of the SRAM. The transient voltage collapse circuit increases the voltage of the voltage supply line during a write operation of the SRAM. The increase in the voltage of the supply line reduces the gap between first reference voltage and the second reference voltage, thereby assisting with the write operation of the SRAM.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method for identifying cascading failure of power system
ActiveCN103311923AAccurate identificationMeet needsData processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsCascading failurePower grid
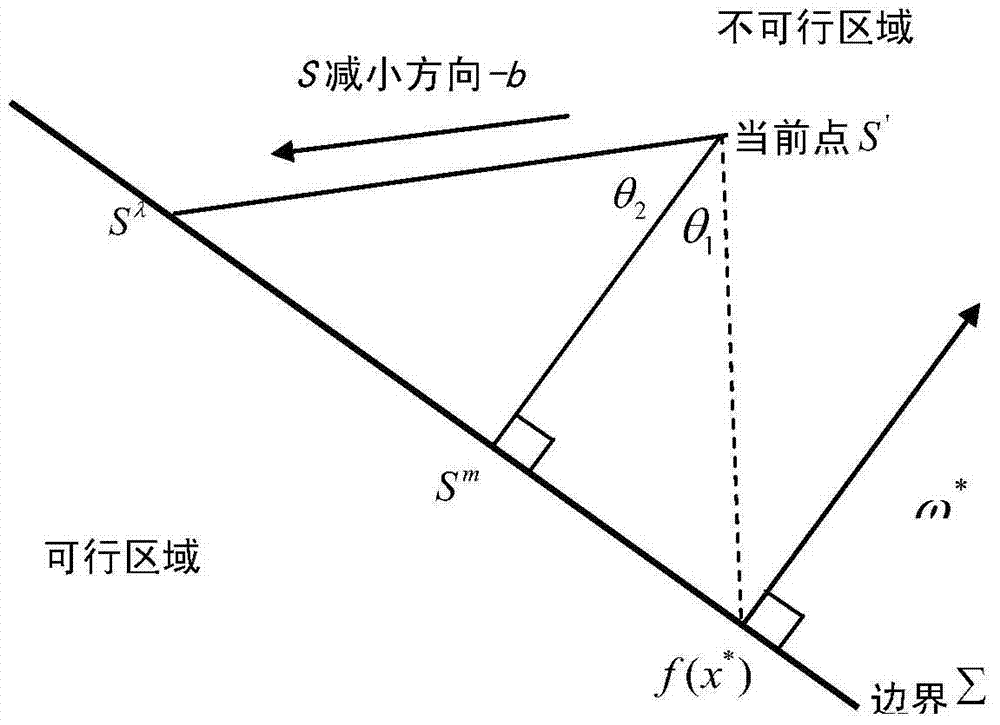
The invention discloses a method for identifying the cascading failure of a power system. Considering the speed governing and load response of a power generator, a more practical power system load flow calculation model is established, and the method overcomes the impact that a traditional load flow calculation model cannot reflect the regulation action and load response of the power generator in the load flow calculation model. From the perspective of the operation status of the system, the method analyzes the relationship between stable voltage and the failure in the cascading failure; and deducts the stable indicator of the system voltage and the critical value of the indicator by analyzing the change of a Jacobi matrix element value in order to quantitatively analyze the relationship between the critical value of the voltage and the operation status of the system. As the load is increased, the system has higher risk of the cascading failure. During the process, the stable indicator of the system voltage is gradually reduced, and the critical value is always maintained at 0.5 (+ / -0.03). In an actual system, the critical value of the voltage which is calculated remains unchanged in the cascading failure, 0.6 is selected as the critical value of voltage collapse in a power grid in the actual system, so as to identify whether the power grid faces the risk of large-scale power-off or not. In such a manner, the method has better actual guiding significance.
Owner:湖南世优电力科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com