Saving method of data and device thereof
A storage device and data technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as inability to save energy, high hard disk failure rate, data loss, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing consumption, increasing service life, and increasing security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
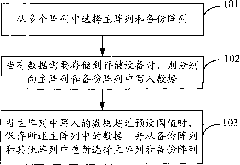
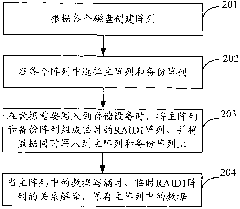
[0041] In the present invention, by selecting a main array and a backup array from multiple arrays, and writing data to the main array and the backup array, only when the data written in the main array exceeds a preset threshold (for example, the main array is full) data), the primary and backup arrays will be reselected.
[0042] In the process of selecting the primary array and the backup array, the selection can be made according to the data writing times of each array and the number of times that each array is used as a backup array, so that the number of times each array is used as a primary array and the number of times that each array is used as a backup array are not much different, thus Make full use of each disk in the storage device, reduce the wear and tear of the disk in the disk cabinet, and increase the service life of the storage device. Moreover, it can ensure that only a small number of hard disks are running on each disk cabinet, and the combination of disk ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com