Method for preparing solid sulfonic acid from reproducible vegetable material
A solid and sulfonic acid technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as limited production and application, and achieve improved resource utilization, less energy consumption, and slow down energy consumption. The effect of the crisis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1: Get 4.0kg of sawn bamboo chips, dry, add 12.64kg of 95% sulfuric acid solution, stir, 60 ℃ of constant temperature reaction 3h, wash with deionized water after cooling until the filtrate is neutral, dry, obtain bamboo charcoal 1.39kg. Bamboo charcoal 1.0kg, add 10kg of 50% (mass percentage) chlorosulfonic acid, sulfonate at a constant temperature of 100°C for 2h, add deionized water to terminate the reaction, wash until the filtrate is neutral, wash with BaCl 2 There was no precipitation in the solution detection, and bamboo charcoal sulfonic acid was obtained by drying at 100°C, and the acid content was 2.0mmolg by titration -1 .
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2: Get 4.0kg of sawdust, add 42.7kg of 75% (mass percent) sulfuric acid, control the carbonization temperature at 80°C, stir and react at a constant temperature for 3h, add deionized water to wash until the filtrate is neutral after cooling, and dry to obtain sawdust. Charcoal 1.42kg. Take 1.0kg of sawn charcoal, add concentrated sulfuric acid at a mass ratio of 7:1, sulfonate at 120°C for 2 hours, add deionized water to terminate the reaction, wash until the filtrate is neutral, and wash with BaCl 2 The solution detected no precipitation, and dried at 100° C. to obtain 1.33 kg of saw charcoal sulfonic acid. The amount of sulfonic acid obtained by titration is 1.82mmol g -1 .
Embodiment 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: Take 4.0 kg of absorbent cotton, add 40.0 kg of 80% (mass percentage) sulfuric acid, control the carbonization temperature at 100 ° C, stir and react at a constant temperature for 1 hour, wash with deionized water after cooling until the filtrate is neutral, and dry to obtain cotton charcoal 1.58kg. Take 1.0kg of cotton charcoal, add 50% (mass percent) oleum at a mass ratio of 5:1, sulfonate at 80°C for 2 hours, add deionized water to terminate the reaction, wash until the filtrate is neutral, wash with BaCl 2 The solution detected no precipitation. Dry at 100° C. to obtain 1.10 kg of cotton-based sulfonic acid. The amount of cotton carbonyl sulfonic acid obtained by titration is 2.28mmol g -1 .
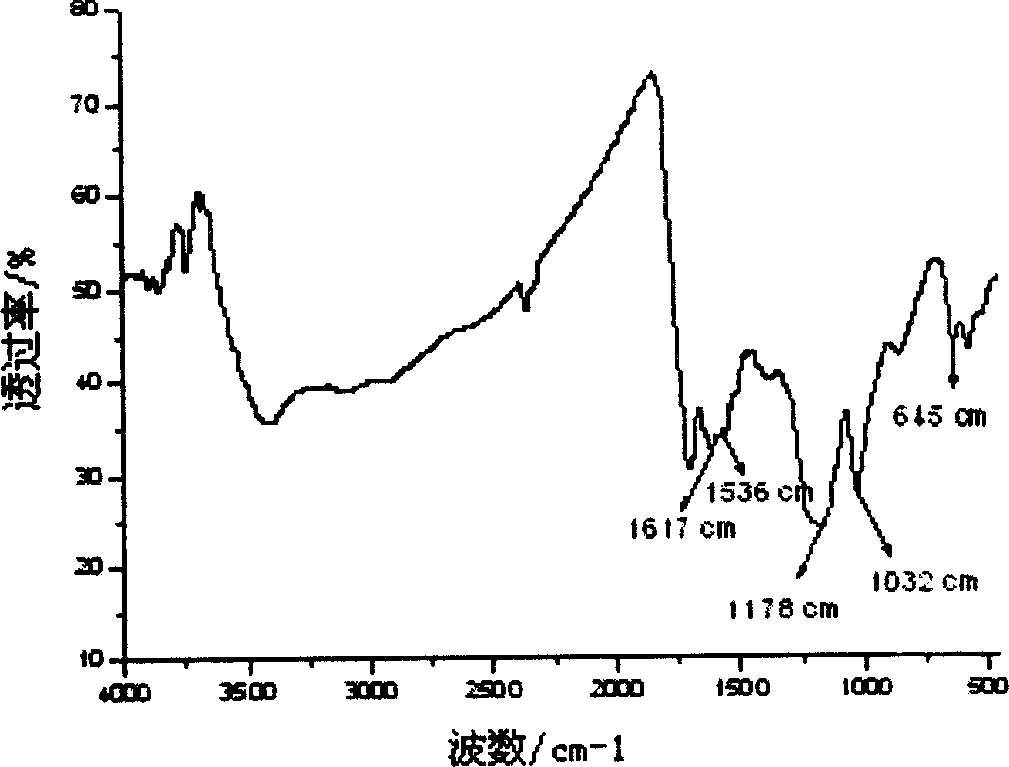
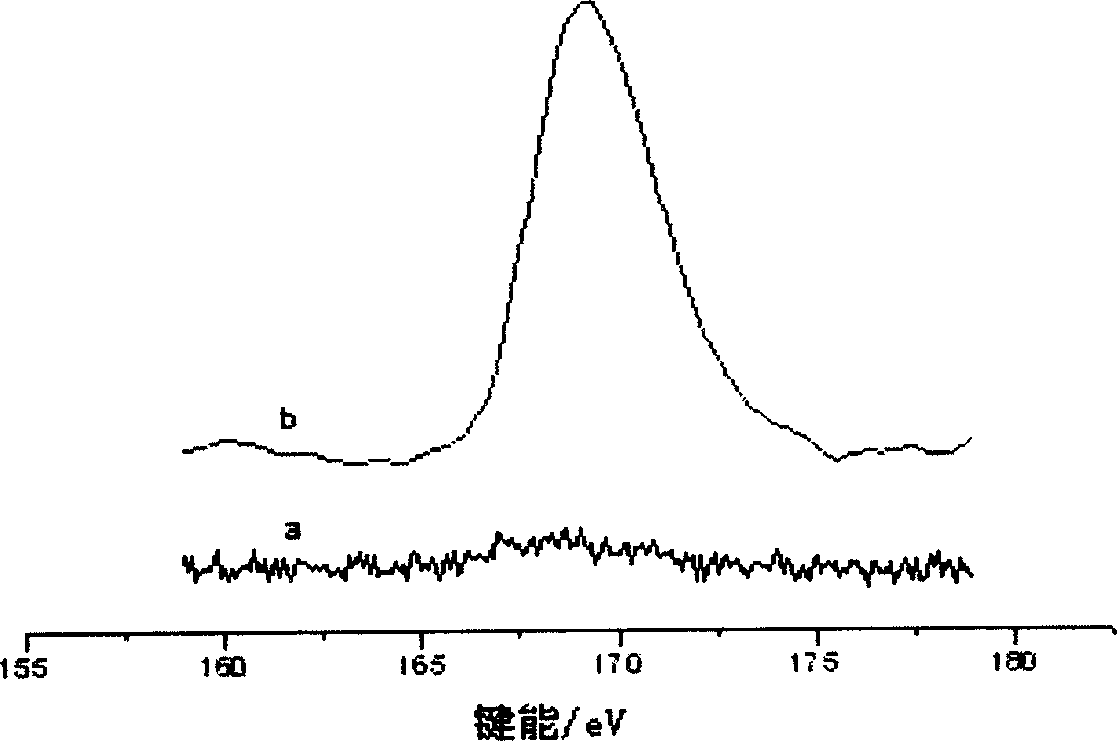
[0020] The obtained product cotton charcoal sulfonic acid is identified by FT-IR and XPS as a solid sulfonic acid containing sulfonic acid groups.
[0021] From the gained Cottonyl Sulfonic Acid FT-IR collection of spectra, it can be seen that ( figure 1 ): ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com