Method and system for performing anycast in internet protocol (IP) network capable of supporting node movement
An IP network and node-supporting technology, applied in the field of computer networks, can solve problems such as the inability to transmit anycast data packets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
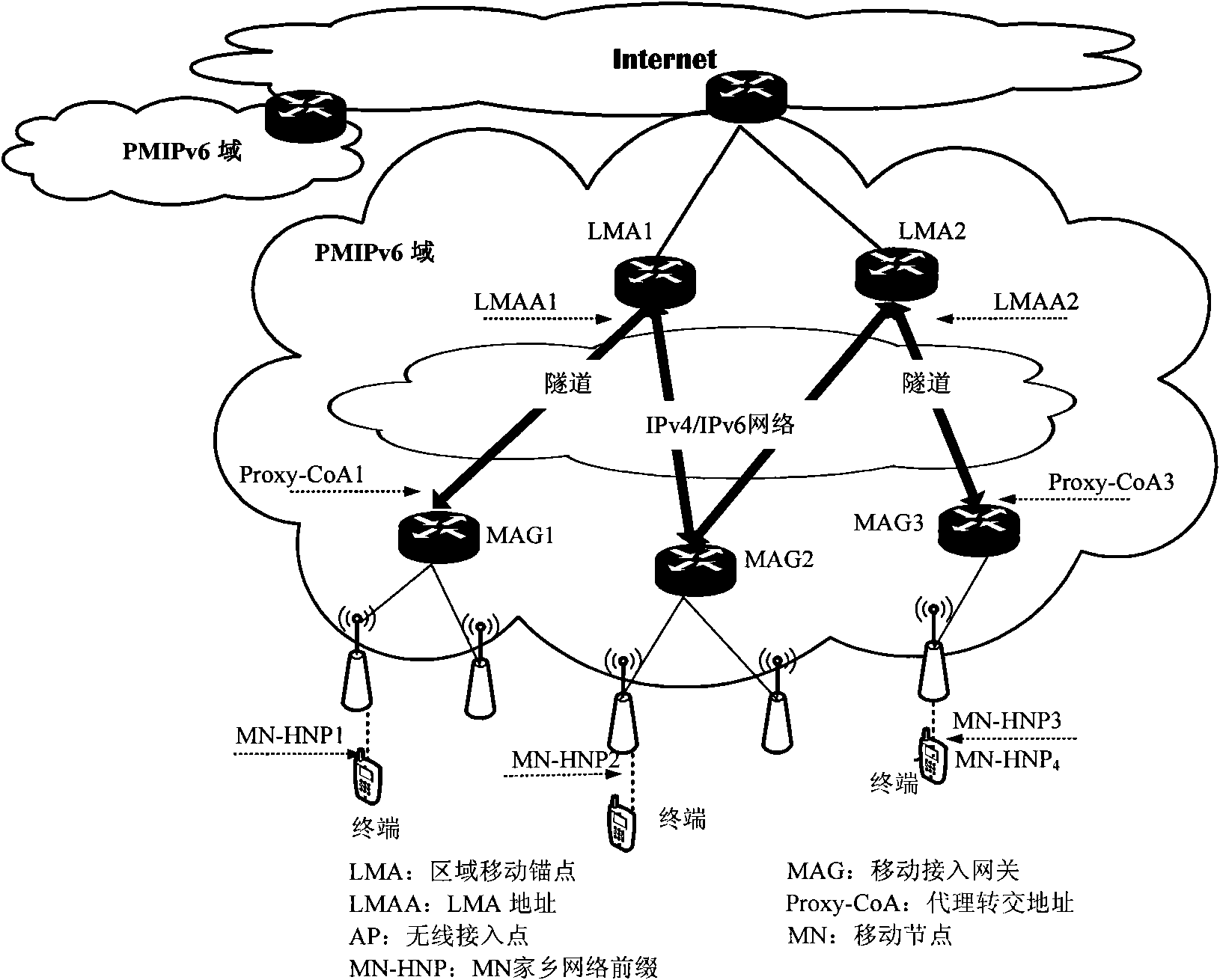
[0135] Described network is PMIPv6 network, and PMIPv6 network comprises LMA and MAG, and LMA is mobile management entity, and LMA has PMIPv6 domain egress router function;
[0136] The step S200 is further that the mobile node sends an anycast group joining request message to the corresponding MAG, and the request message needs to carry MN-ID, MN-HNP, and anycast address; the MAG sends the anycast group to the LMA instead of the mobile node Adding a request message, the request message carrying MN-ID, MN-HNP and anycast address;
[0137] The step S300 further detects the actual distance between the LMA and the MAG for the LMA;
[0138] The step S400 further records the anycast routing information of the mobile node for the LMA, and the LMA sends routing signaling to the neighbor router outside the domain to transfer the anycast routing information, and the signaling carries the LMA to the anycast group in the domain where the LMA is located The distance information of the ne...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0153] The network is a PMIPv6 network, and the PMIPv6 network includes an LMA, a MAG, and a PMIPv6 domain egress router. The LMA is a mobility management entity, and the LMA does not have the function of a PMIPv6 domain egress router.
[0154] The step S200 is further that the mobile node sends an anycast group joining request message to the corresponding MAG, and the request message needs to carry MN-ID, MN-HNP, and anycast address; the MAG sends the anycast group to the LMA instead of the mobile node A join request message, where the request message carries MN-ID, MN-HNP and anycast address.
[0155] The step S300 further detects the actual distance between the LMA and the MAG for the LMA.
[0156] The step S400 is further that the LMA sends routing signaling to the neighbor router outside the domain through the egress router of the PMIPv6 domain, and the signaling carries the distance information from the egress router of the PMIPv6 domain to the nearest mobile node in the...
specific Embodiment approach 3
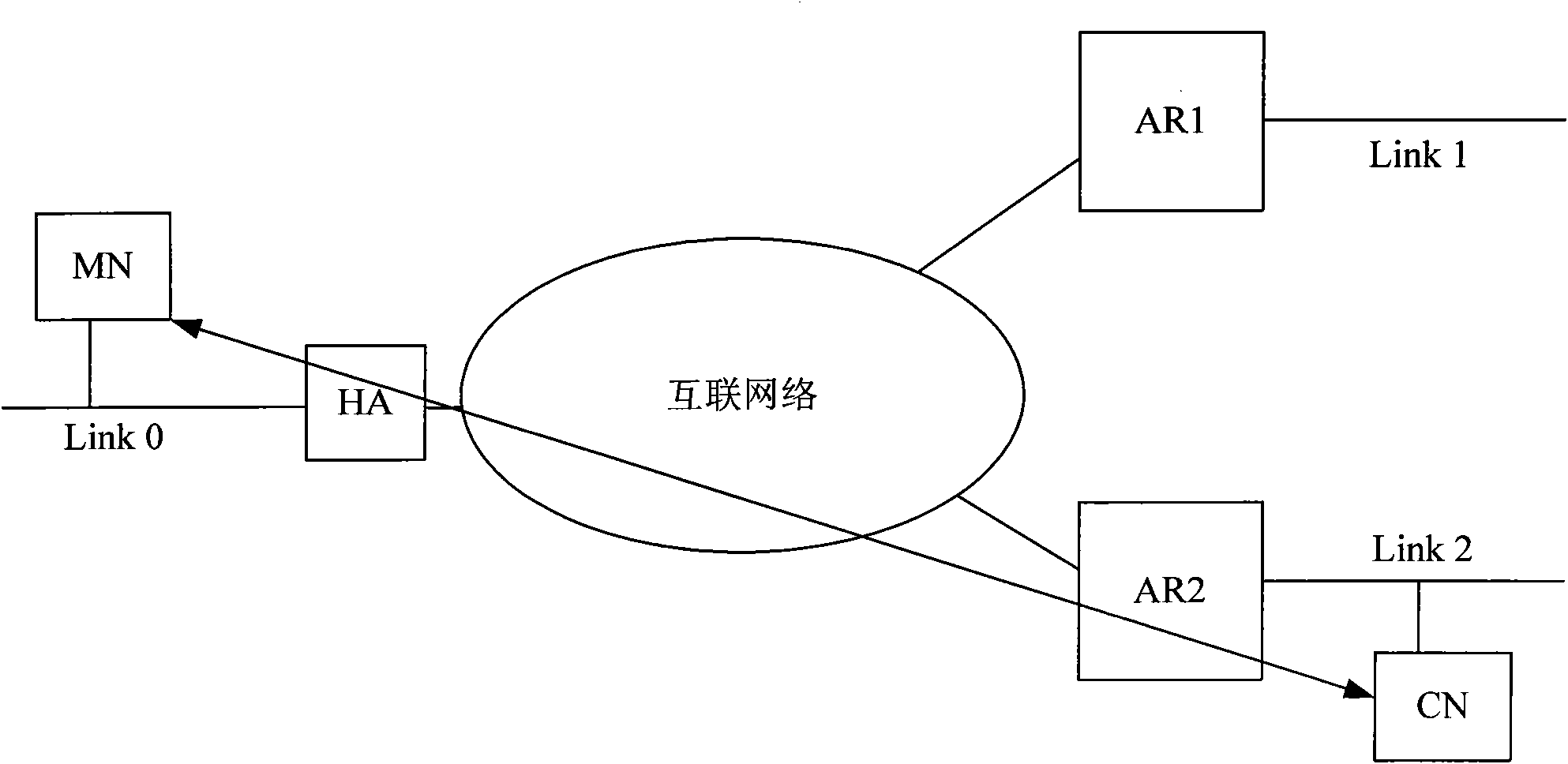
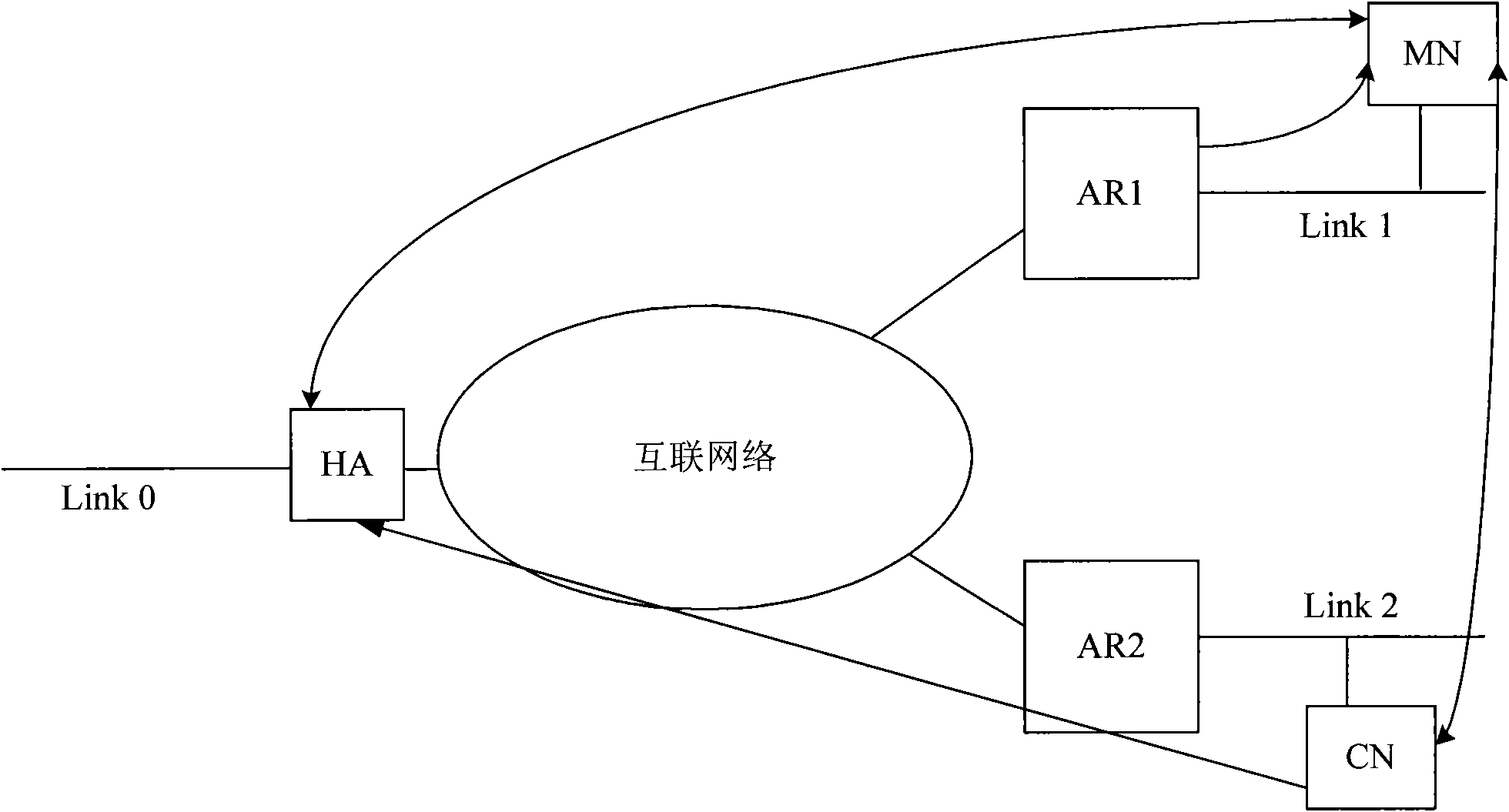
[0175] The network is an MIPv6 network, and the network includes an HA, which is a mobility management entity, and the HA has a router function.
[0176] The step S200 is further that the mobile node sends an anycast group joining request message to the HA, and the request message carries MN-ID, MN-HoA and anycast address.
[0177] The step S300 is further for the HA to judge whether the mobile node is in the home area or a foreign area, and if the mobile node is in the home area, stop the operation; otherwise, the HA detects the actual distance between the HA and the mobile node.
[0178] The step S400 is further that the HA sends routing signaling to neighbor routers in the domain to transfer anycast routing information; the signaling carries actual distance information from the HA to the mobile node.
[0179] Example Figure 12 shown.
[0180] HA and routers are deployed on the same entity in an MIPv6 network. In this case, HA can directly send anycast routing informatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com