Language translation quality auditing method
A language translation and quality technology, applied in the field of language translation quality audit, can solve the problems of difficulty in guaranteeing translation and audit quality and consuming human resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
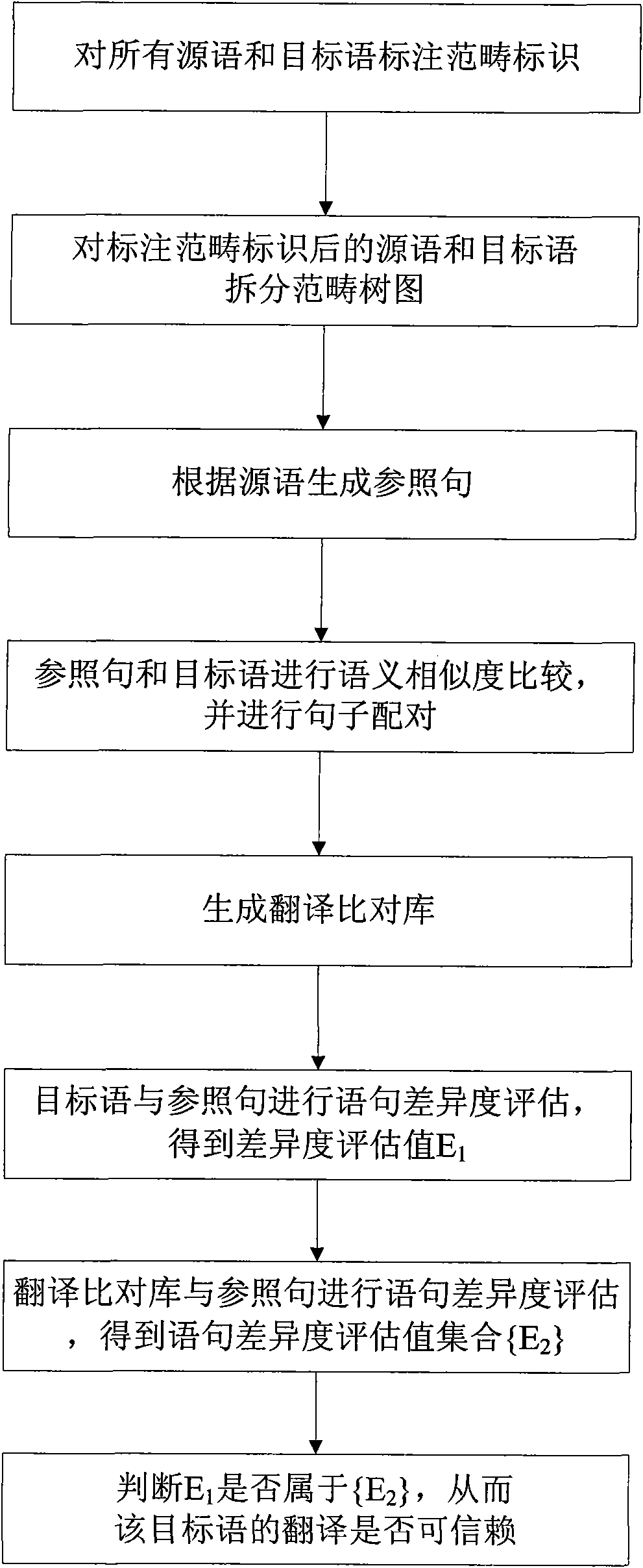
[0066] Based on the above design ideas, refer to figure 1 The flow chart of the auditing method of the present invention shown, the concrete steps of the language translation quality auditing method designed by the present invention are as follows:
[0067] (1) Mark category marks for all source and target languages;
[0068] Here, the so-called source language refers to the original article to be translated, and the so-called target language refers to the translated article to be reviewed.
[0069] As mentioned above, the semantic difference degree comparison between sentences in the present invention is based on the category identification in the category grammar as the structural basis. The so-called categorical grammar is a syntactic type calculus proposed by the mathematician J. Lambek in "The Mathematics of Sentence Structure" in 1958. It is a calculus theory that uses different symbols to represent each component in a sentence, and then uses the symbol string to ident...
Embodiment 2
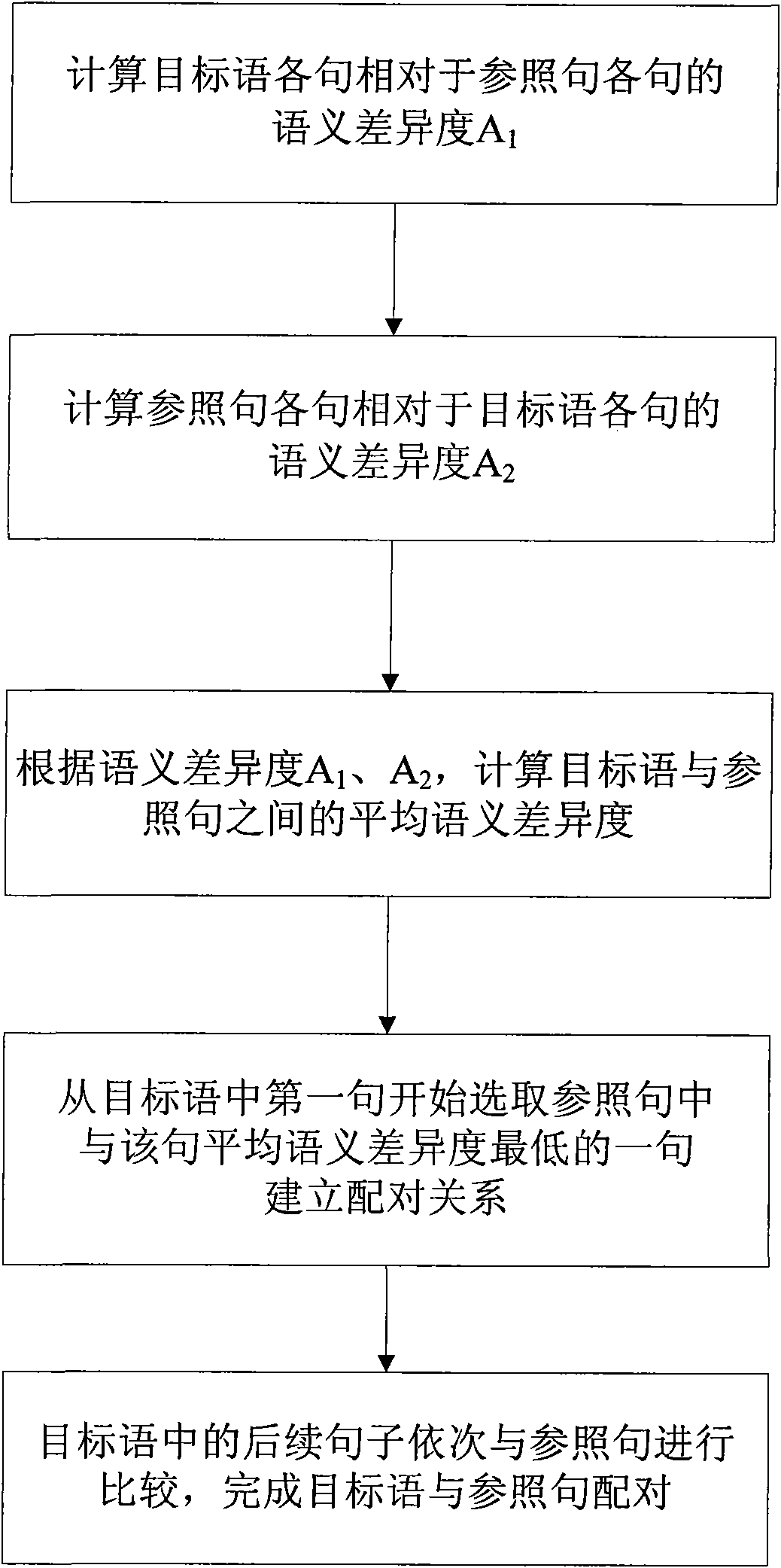
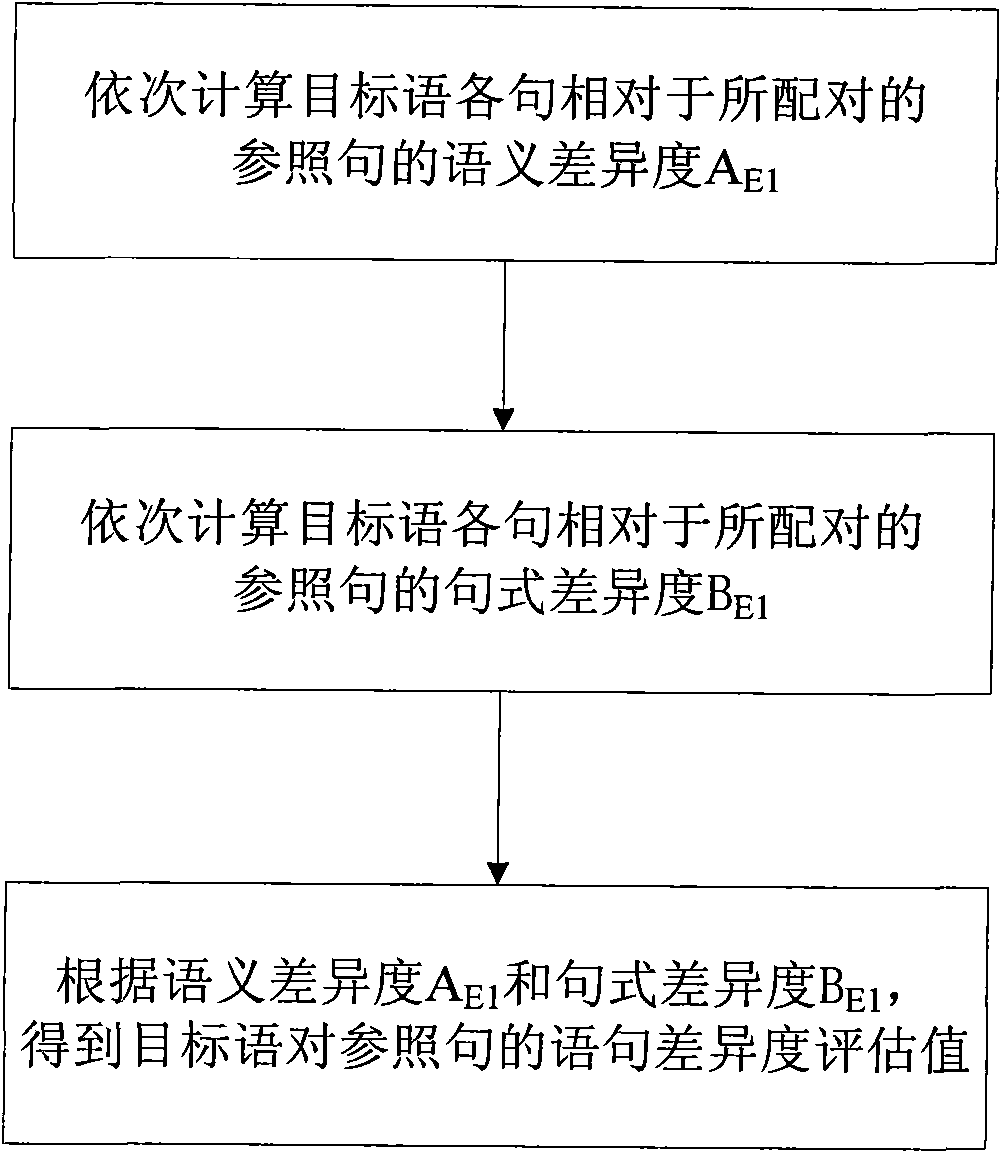
[0089] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1, the sentence pairing method in the step (4) is further limited. Such as figure 2 As shown, the step (4) includes the following specific steps:
[0090] (41) Calculate the semantic difference A of each sentence of the target language relative to each sentence of the reference sentence in turn according to the calculation formula of the degree of semantic difference 1 ; The formula for calculating the degree of semantic difference is A 1 (Sn, S'm) = ΣC XSn *δ XSn *DD X (Sn, S'm);
[0091] Among them, A 1 (Sn, S'm) indicates the degree of semantic difference between the Snth sentence in the target language and the S'mth sentence in the reference sentence, DD X (Sn, S'm) represents the range of lexical semantic change between the Snth sentence in the target language and the Xth pair of category labels in the S'mth sentence in the reference sentence, δ XSn Indicates the importance weight value of the category identif...
Embodiment 3
[0104] This embodiment further limits the generation process of the reference sentence in the step (3) on the basis of the first embodiment. The reference sentence generation process of described step (3) is specifically as follows:
[0105] (3) The source language is directly replaced with vocabulary based on the dictionary based on the category identification marked in step (1), thereby generating a reference sentence.
[0106] Here, the source language performs direct replacement of words or phrases with the minimum set of category labels. If a synonym or near-synonym is encountered, a group of synonyms or near-synonym are directly replaced for the category identifier at the same time. As mentioned above, the reference sentence generated here is only used as a reference basis for comparing the target language and each translation sentence in the translation comparison library, so it is not necessary to refer to any language grammar rules during the generation process, as l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com