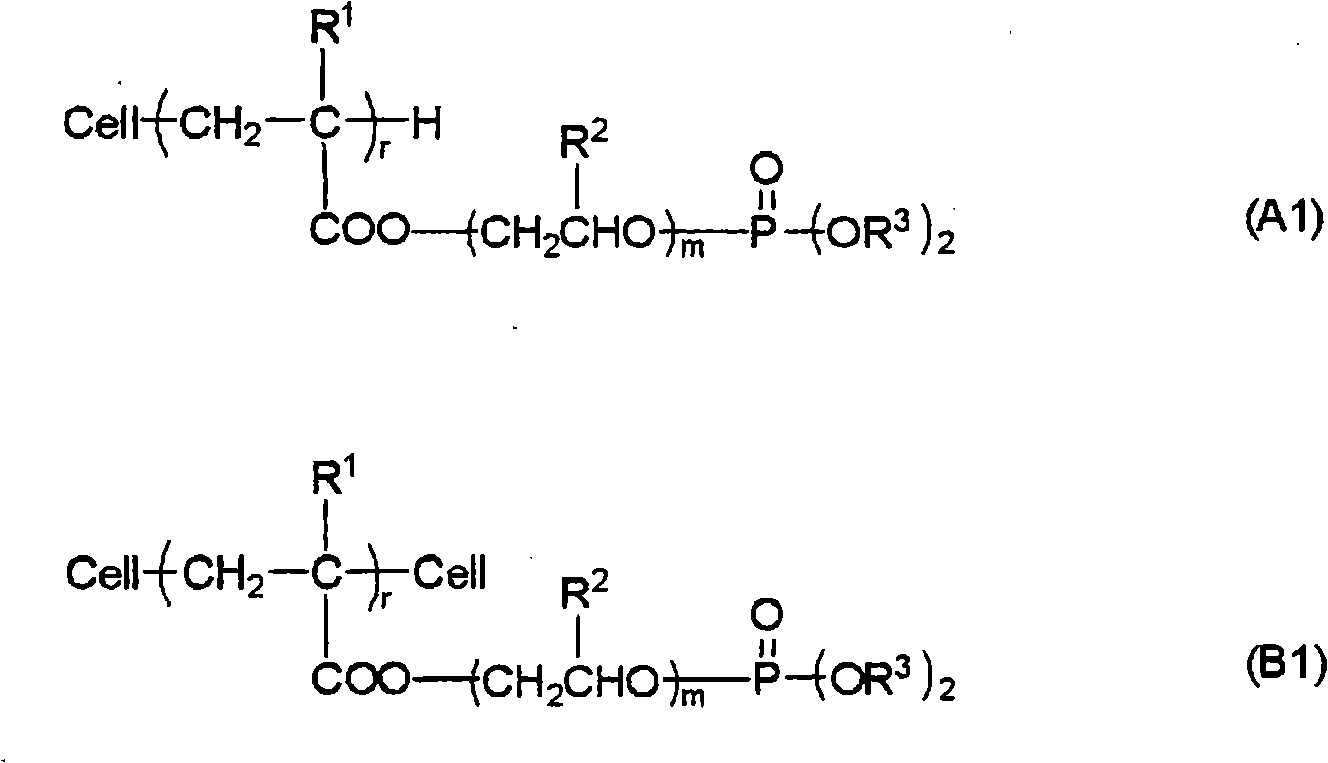Flame retardant processing method, and cellulosic fiber material imparted with flame retardancy
A processing method, cellulose technology, applied in the direction of flame-retardant fiber, fiber treatment, plant fiber, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to fully impart flame retardancy, not being able to speculate, not being able to be used for cellulosic fiber processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
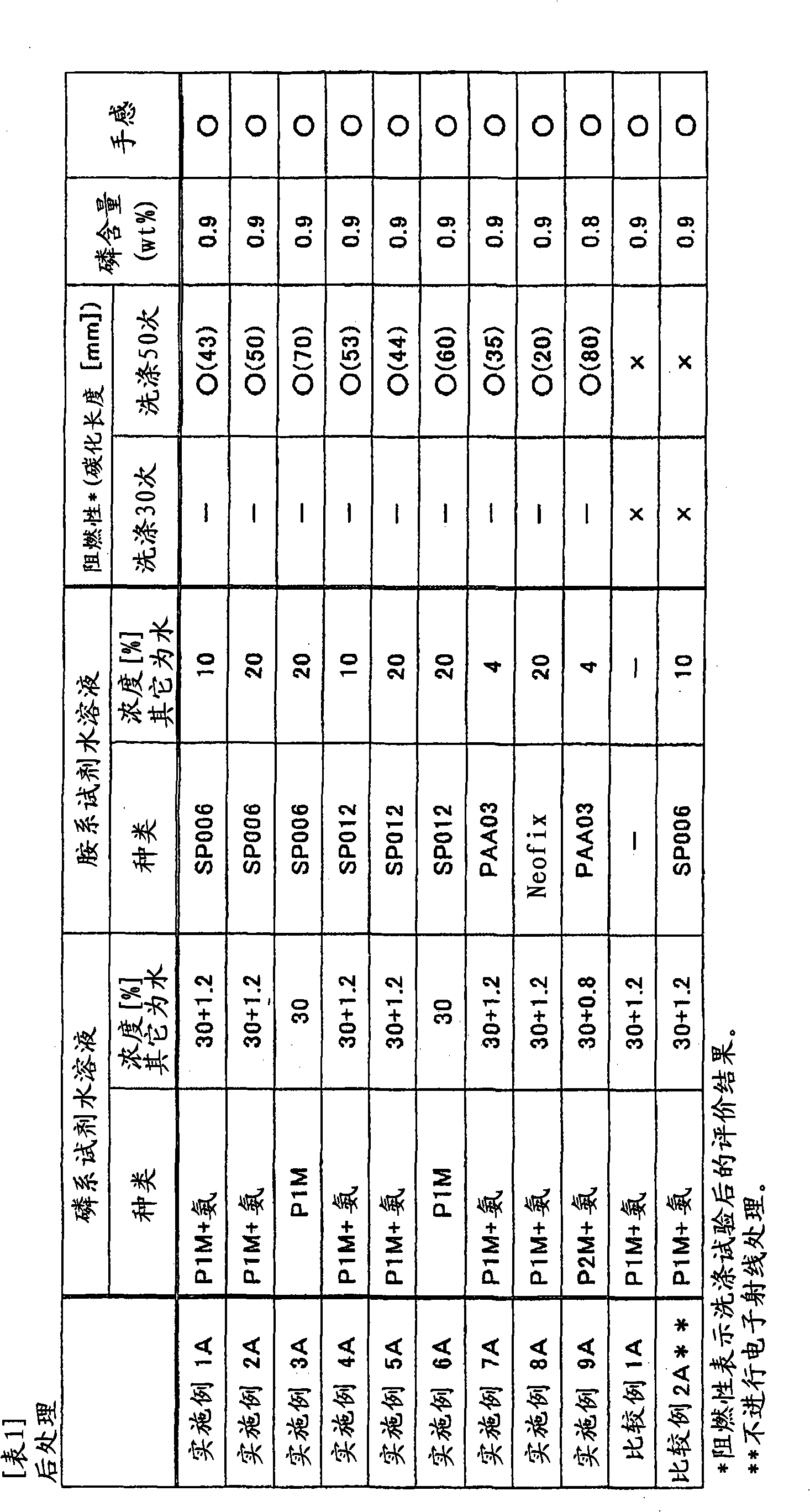
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0040] In the first embodiment of the present invention, the above-described procedure (1) is employed.
[0041] (ray processing step)
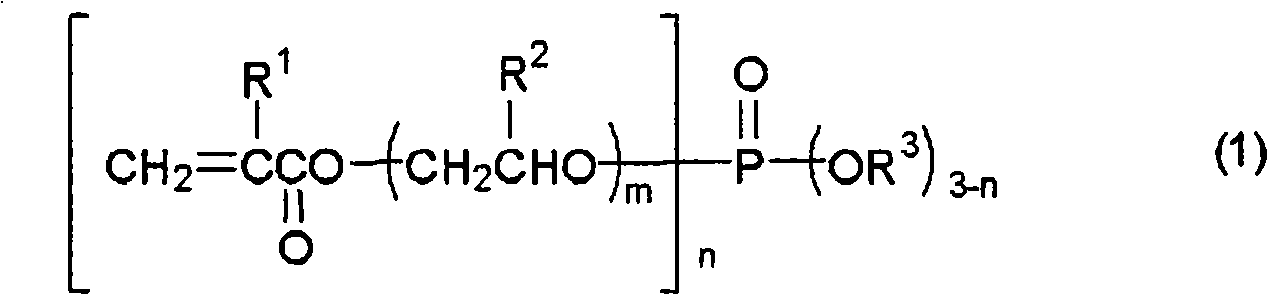
[0042] In this embodiment, first, the fiber raw material is irradiated with radiation. Thus, in the phosphorus treatment step described later, the radically polymerizable phosphorus-containing compound can be chemically bonded to the fiber raw material through an addition reaction using the radically polymerizable group. That is, radicals are generated in the cellulose fibers by radiation treatment, and the radical polymerizable groups of the phosphorus-containing compound are chemically bonded to the cellulose fibers in the phosphorus treatment step by utilizing the generated radicals. It is speculated that free radicals generated in cellulose-based fibers are likely to be generated at the 5-position carbon in the structural unit of the cellulose molecule, followed by the 4-position or 1-position carbon, and then at the 2-, 3-, and 6-positi...
no. 2 approach
[0099] In the second embodiment of the present invention, the above-mentioned procedure (2) is adopted. Hereinafter, each step of the second embodiment will be described, and unless otherwise specified, each step is the same as that of the first embodiment except that the execution order of each step is different.
[0100] (Amine treatment step)
[0101] In this embodiment, first, an amine compound is provided to the fiber raw material. The amine compound imparted in this step can rapidly react with the phosphorus-containing compound moiety bonded to the cellulose fiber by pre-existing on the surface of the cellulose fiber in the subsequent radiation treatment step and phosphorus treatment step.
[0102] In this step, after the amine treatment, aging treatment is preferably performed by the same method as the aging treatment in the phosphorus treatment step of the first embodiment, but the water washing treatment is preferably not performed. This is because the amine compoun...
no. 3 approach
[0110] In the third embodiment of the present invention, the above-mentioned procedure (3) is adopted. Hereinafter, each step of the third embodiment will be described, but unless otherwise specified, each step is the same as that of the first embodiment except that the order of implementation of each step is different.
[0111] (ray processing step)
[0112] In this embodiment, first, the fiber raw material is irradiated with radiation. Thereby, free radicals can be generated in the cellulose-based fibers, and the phosphorus-containing compound can be chemically bonded to the cellulose-based fibers through an addition reaction by radical polymerizable groups in the same-bath treatment step described later.
[0113] (same bath treatment step)
[0114] Next, the phosphorus-containing compound and the amine compound are simultaneously provided to the cellulose-based fiber raw material. That is, the phosphorus treatment of bonding the phosphorus-containing compound to the cell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com