Imaging device, imaging module, electronic still camera, and electronic movie camera
A camera device and pixel technology, applied to static cameras, signal generators with a single pick-up device, TV, etc., can solve problems such as lower resolution, larger camera system, and image quality deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
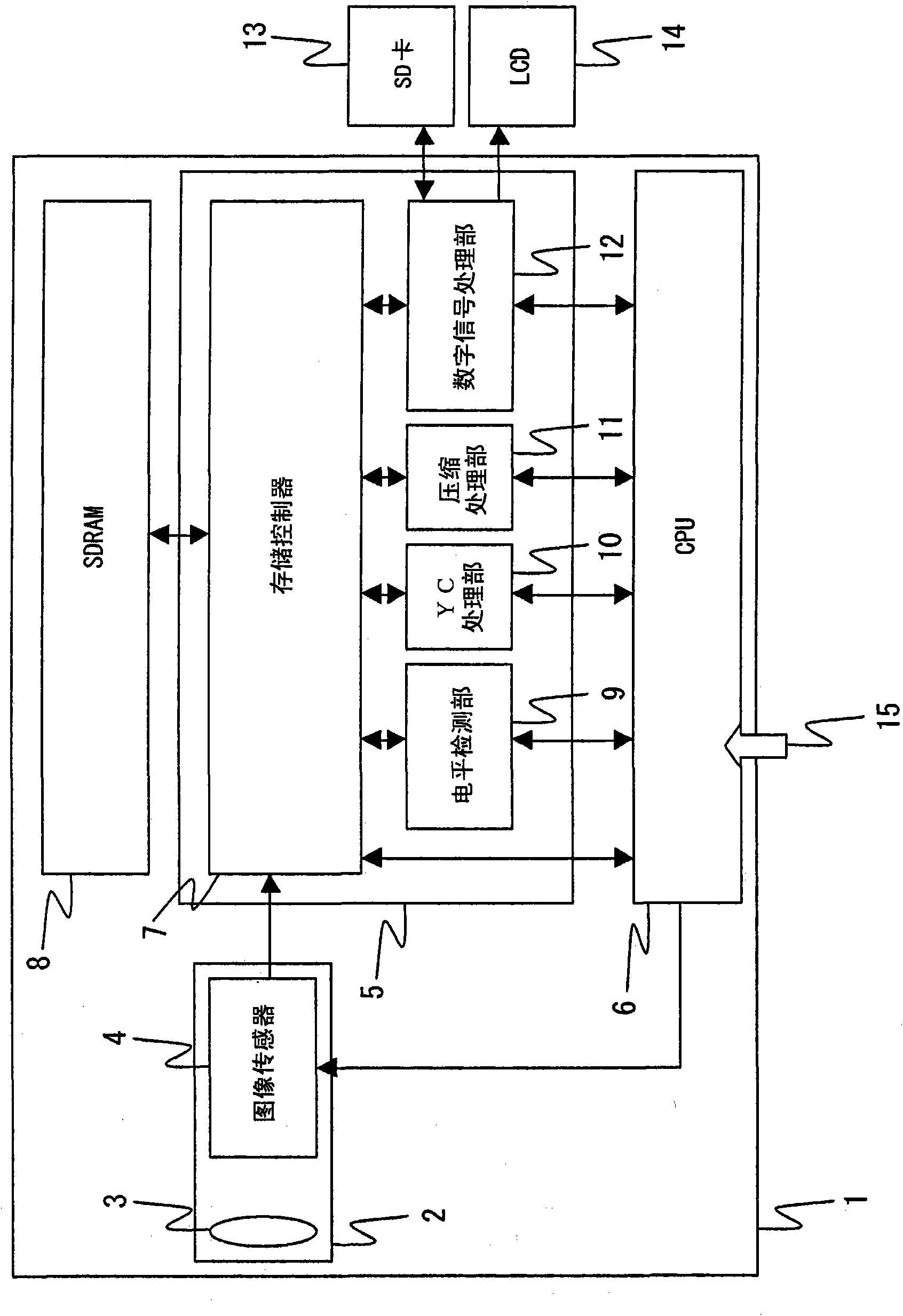
[0104] Hereinafter, the imaging system in Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described. figure 1 It is a block diagram which shows the functional structure of the imaging system in this embodiment. The imaging system in this embodiment is constituted by a digital video camera 1 (electronic dynamic camera), which includes an imaging module 2 , a DSP 5 , a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 6 , and an SDRAM 8 .
[0105] (Configuration of camera module 2)
[0106] The camera module 2 has a lens 3 and an image sensor 4 . In addition, although not shown, the camera module 2 further includes a TG (timing generator) for generating a control signal necessary for driving the image sensor 4 .
[0107] (DSP and SDRAM)
[0108] The DSP 5 includes a memory controller 7 , a level detection unit 9 , a YC processing unit 10 , a compression processing unit 11 , and a digital signal processing unit 12 . The DSP 5 processes the output from the image sensor 4 .
[0109] The memory cont...
Embodiment approach 2
[0197] Here, the imaging system in Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. The imaging system in Embodiment 2 of the present invention is a part of the configuration of Embodiment 1 of the present invention that has been changed, and the following description will start from the difference.
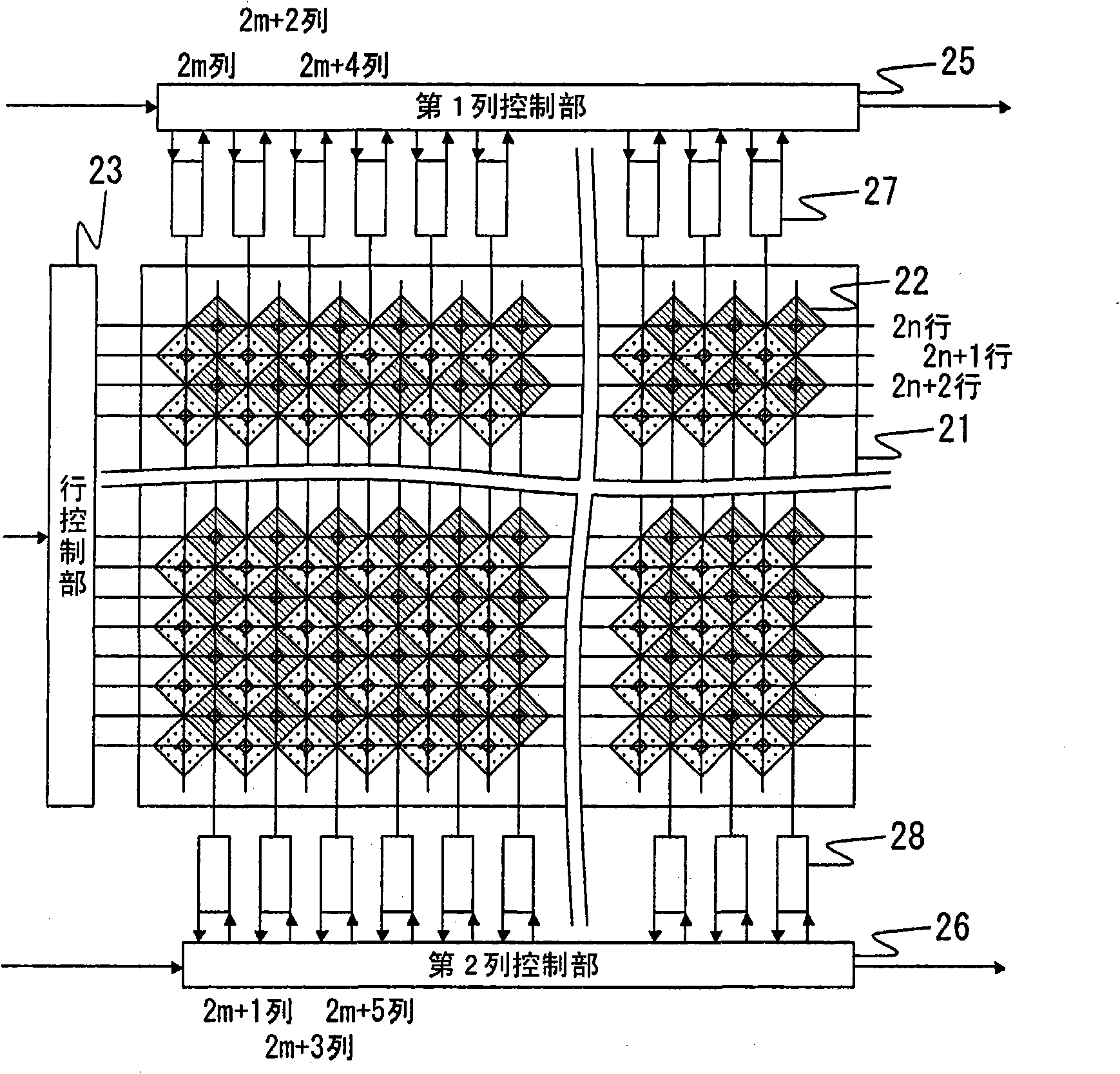
[0198] (Image sensor driver and column control section)
[0199] A method of driving the image sensor 4 will be described.
[0200] This embodiment is equivalent to Embodiment 1, and the difference only relates to the case where pixel signals are mixed and read in the column direction, and only this part will be described here.
[0201] After the exposure of the pixels 22 for a predetermined exposure time is completed, the row control unit 23 outputs a row selection signal for executing the reading of the imaging signal for the pixels 22 in the 2nth row. Based on the row selection signal, it is determined to read the imaging signal stored in the pixel 22 of the 2nth row...
Embodiment approach 3
[0216] Here, the imaging system in Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. The imaging system in Embodiment 3 of the present invention is a part of the configuration of Embodiment 1 of the present invention that has been changed, and the following description will start from the difference.
[0217] -Image sensor driver and column control section-
[0218] Hereinafter, a method of driving the image sensor 4 will be described.
[0219] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 only relates to the case where pixel signals are mixed and read in the column direction, and only this part will be described here.
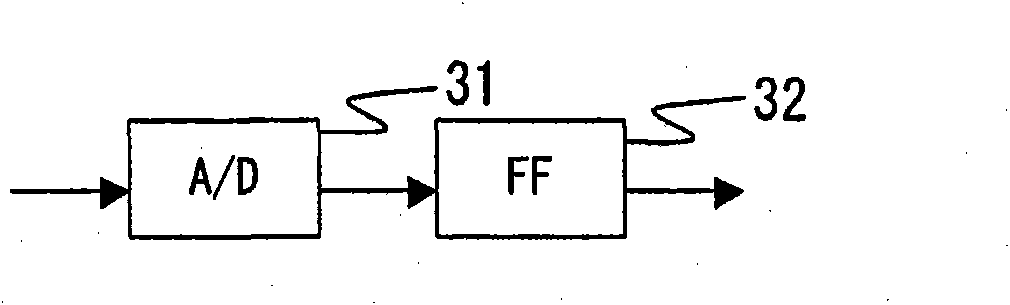
[0220] In the present embodiment, the configuration and operation method of the first column control unit 25 are different. The first column control unit 25 of the present embodiment has the following Figure 14 composition shown. The first column control unit includes a selector 1441, an adder 1442, a selector 1443, and a flip-flop 1444 (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com