Method and device for selecting gateway in mobile communication network as well as system comprising device
A mobile communication network and gateway technology, applied in the field of mobile communication systems, can solve the problems of continuous change of the IMSI/MSISDN sequence, increase the time delay of the PDP activation procedure, etc., and achieve the effects of speeding up the establishment of EPS bearers, improving the success rate, and reducing the response time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
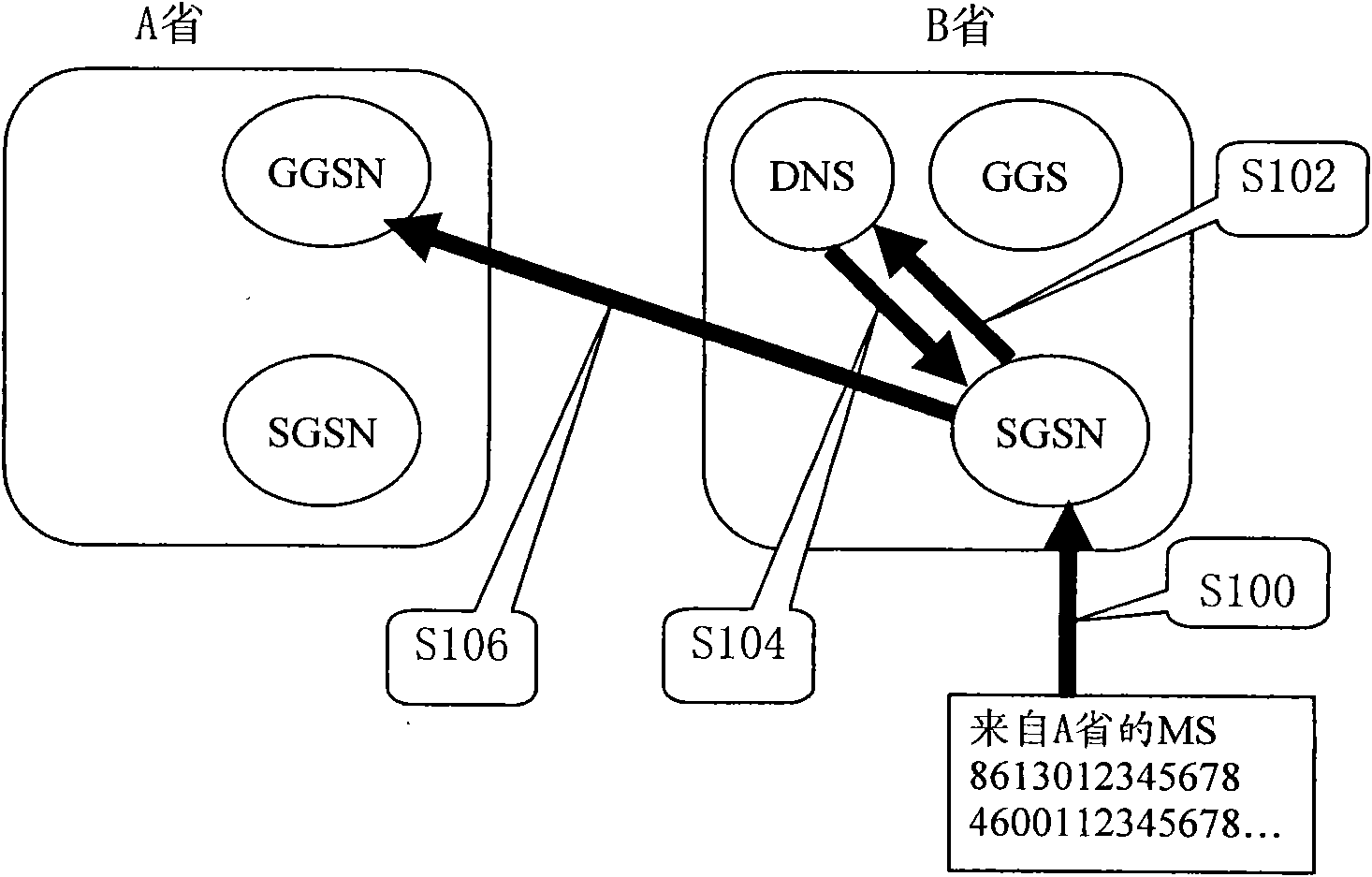
[0030] In this instance, APNs with a user login identifier is resolved as an extension. Preferably, the APN with a partial user login identifier is resolved as an extension.
[0031] As shown in Table 2, in the DNS server, the APN and some user login (such as home location registration HLR / home subscriber server HSS) identifiers are bound with the IP address of the dedicated gateway.
[0032] Table 2APN and some user login identifiers bundled in the DNS server
[0033] APN.SRI
Gateway IP address
cmwap.001
10.1.1.1
cmwap.002
10.1.1.2
...
...
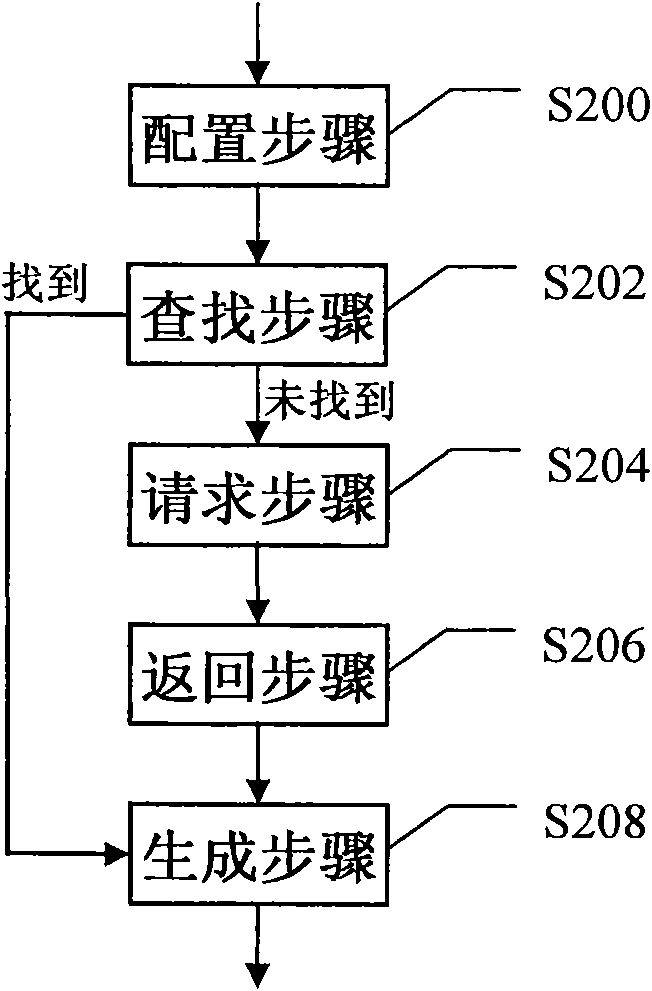
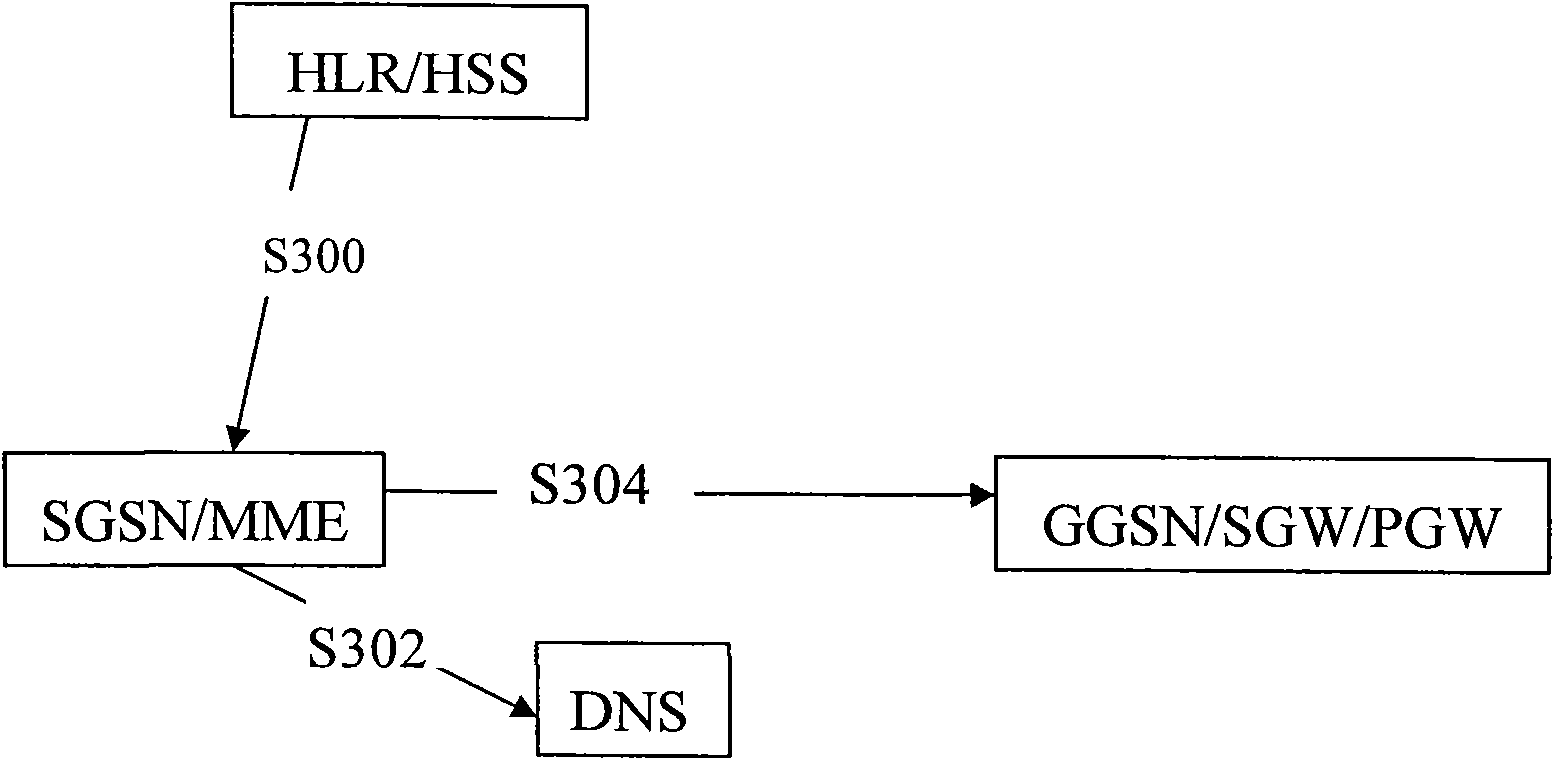
[0034] Such as image 3 As shown, when the MS / UE connects to the network, the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) or Mobility Management Engine (MME) will obtain the user login identifier (S300), and log in the user before sending a query to the DNS server (S302). The identifier (preferably a part of it) is added to the APN as an extension, and then the DNS server will return the de...
example 2
[0038] In this instance, the APNs resolution with the user-login predefined token is used as the extension.
[0039] In subscriber registration (HLR / HSS), a predefined tag indicating a specific home area is added to each subscribed APN.
[0040] As shown in Table 3, in the DNS server, the APN with a predefined tag is bound with the IP address of the dedicated gateway.
[0041] Table 3 APNs with predefined tags bundled in DNS server
[0042] APNs with predefined tags
Gateway IP address
cmwap.sh
10.1.1.1
cmwap.bj
10.1.1.2
...
...
[0043] In MS, APN itself (eg CMWAP or CMNET, without flags) is used to activate PDP context, which means no influence on MS side.
[0044] In the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) or Mobility Management Entity (MME), the APN from the MS is used as a prefix to find which subscribed APN should be used for the current PDP activation.
[0045]On the other hand, if the Serving GPRS Support Node (SG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com