Demodulator circuit for the UHF (Ultrahigh Frequency) radio frequency identification label chip
A technology of radio frequency identification tags and demodulation circuits, which is applied to record carriers used in machines, instruments, computer components, etc., can solve the problem of small dynamic range and achieve the effect of large input dynamic range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
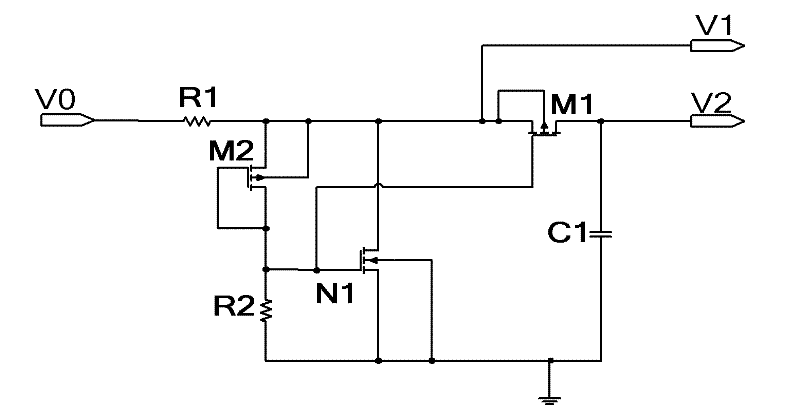
[0020] Embodiment one: if figure 1 As shown, the demodulation circuit for the UHF RFID tag chip includes an overvoltage protection circuit and an average generating circuit. The overvoltage protection circuit is composed of the first resistor R1, the second resistor R2, the second PMOS transistor M2 and the first NMOS transistor N1; the average generating circuit is composed of the first PMOS transistor M1 and the first capacitor C1, which is used to generate the envelope signal The source of the first PMOS transistor M1 is connected to the drain of the first NMOS transistor N1 in the overvoltage protection circuit; the gate of the first PMOS transistor M1 is connected to the first NMOS transistor N1 in the overvoltage protection circuit. The gates of the NMOS transistor N1 are connected; the drain of the first PMOS transistor M1 is connected to the ground through the first capacitor C1 as the output terminal of the average generating circuit.
[0021] In the overvoltage prot...
Embodiment 2
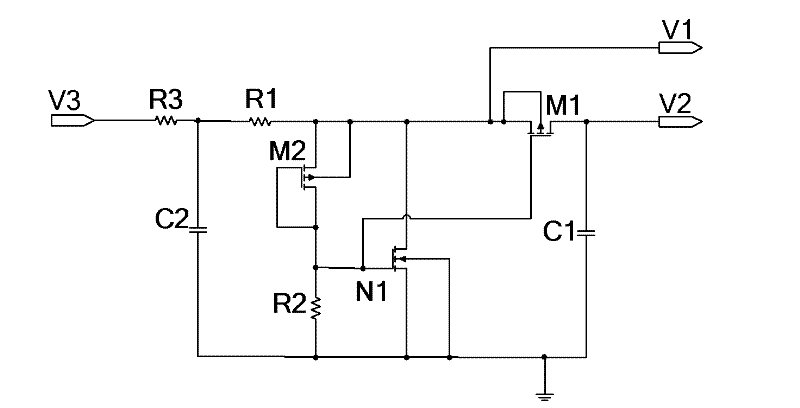
[0023] Embodiment two: if figure 2 As shown, on the basis of the first embodiment, the demodulation circuit for the UHF radio frequency identification tag chip also includes a low-pass filter circuit. The low-pass filter circuit is composed of a second capacitor C2 and a third resistor R3, one end of the third resistor R3 is grounded through the second capacitor C2, and is connected to the input end of the overvoltage protection circuit as the output end of the low-pass filter circuit, The other end of the third resistor R3 serves as the input end of the low-pass filter circuit to input the envelope signal.
[0024] The envelope signal V3 passes through a low-pass filter circuit and an overvoltage protection circuit to generate an envelope signal V1 after overvoltage protection, and then passes through an average value generating circuit to generate an envelope average value signal V2.
Embodiment 3
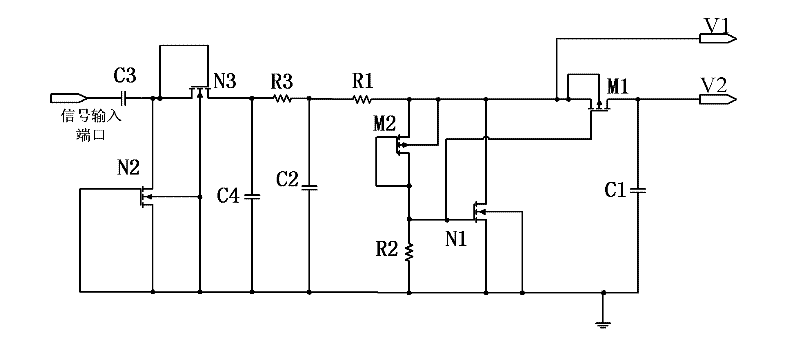
[0025] Embodiment three: as image 3 As shown, on the basis of the second embodiment, the demodulation circuit for the UHF radio frequency identification tag chip also includes an envelope detection circuit. The envelope detection circuit is composed of a third capacitor C3, a fourth capacitor C4, a second NMOS transistor N2 and a third NMOS transistor N3, the third capacitor C3 is connected to a signal input port; the second NMOS transistor N2 The source of the second NMOS transistor N2 is connected to the signal input port through the third capacitor C3; the gate and drain of the second NMOS transistor N2 are connected and connected to the ground; the gate and drain of the third NMOS transistor N3 are connected to the second The source of the NMOS transistor N2; the source of the third NMOS transistor N3 is connected to the input terminal of the low-pass filter circuit and connected to the ground through the fourth capacitor C4.
[0026] The signal received by the signal in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com