Through-time non-cartesian GRAPPA calibration
A whole-process, calibration data technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, measuring magnetic variables, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unrealistic, limited radiation GRAPPA maximum undersampling, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
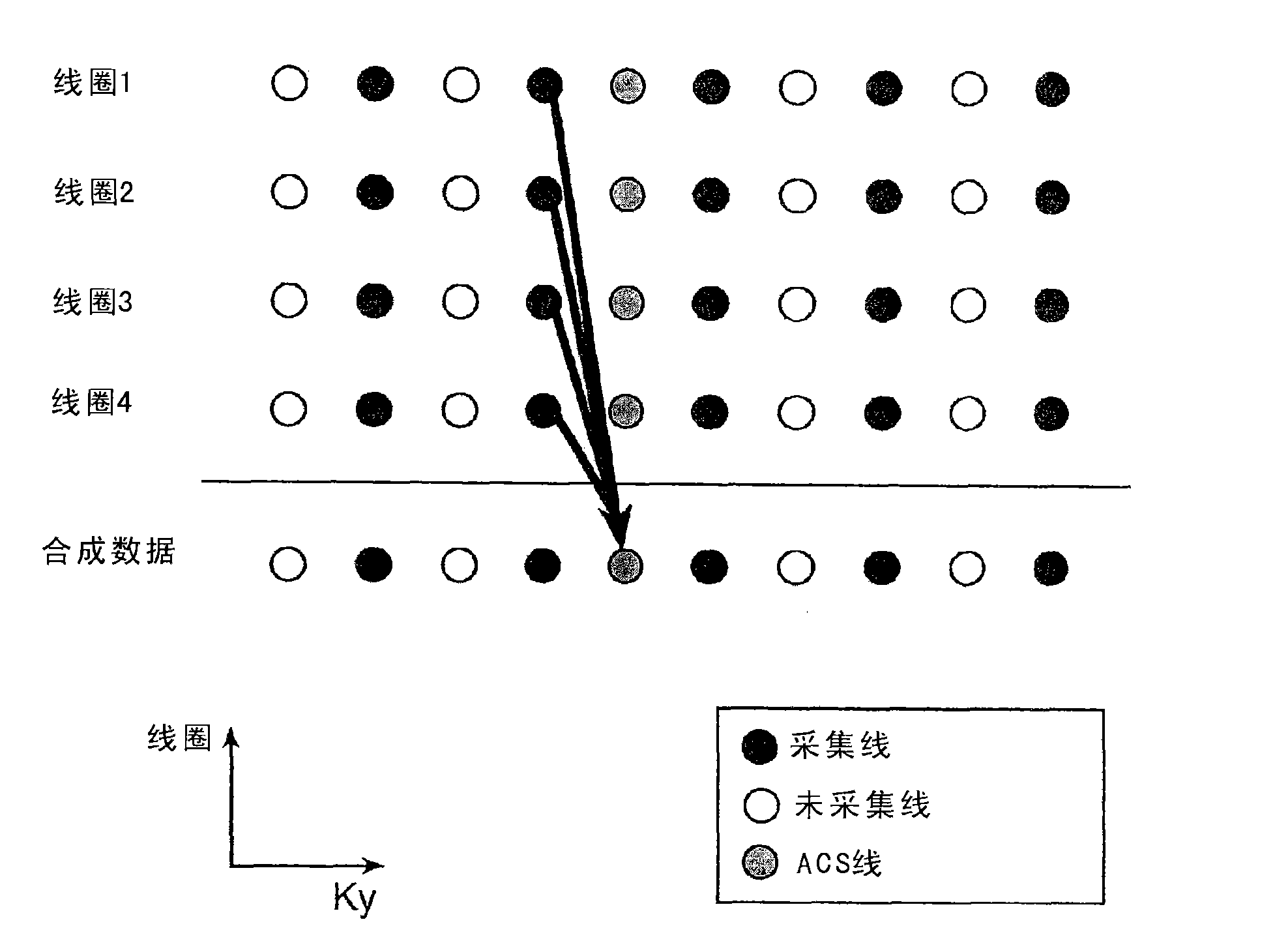
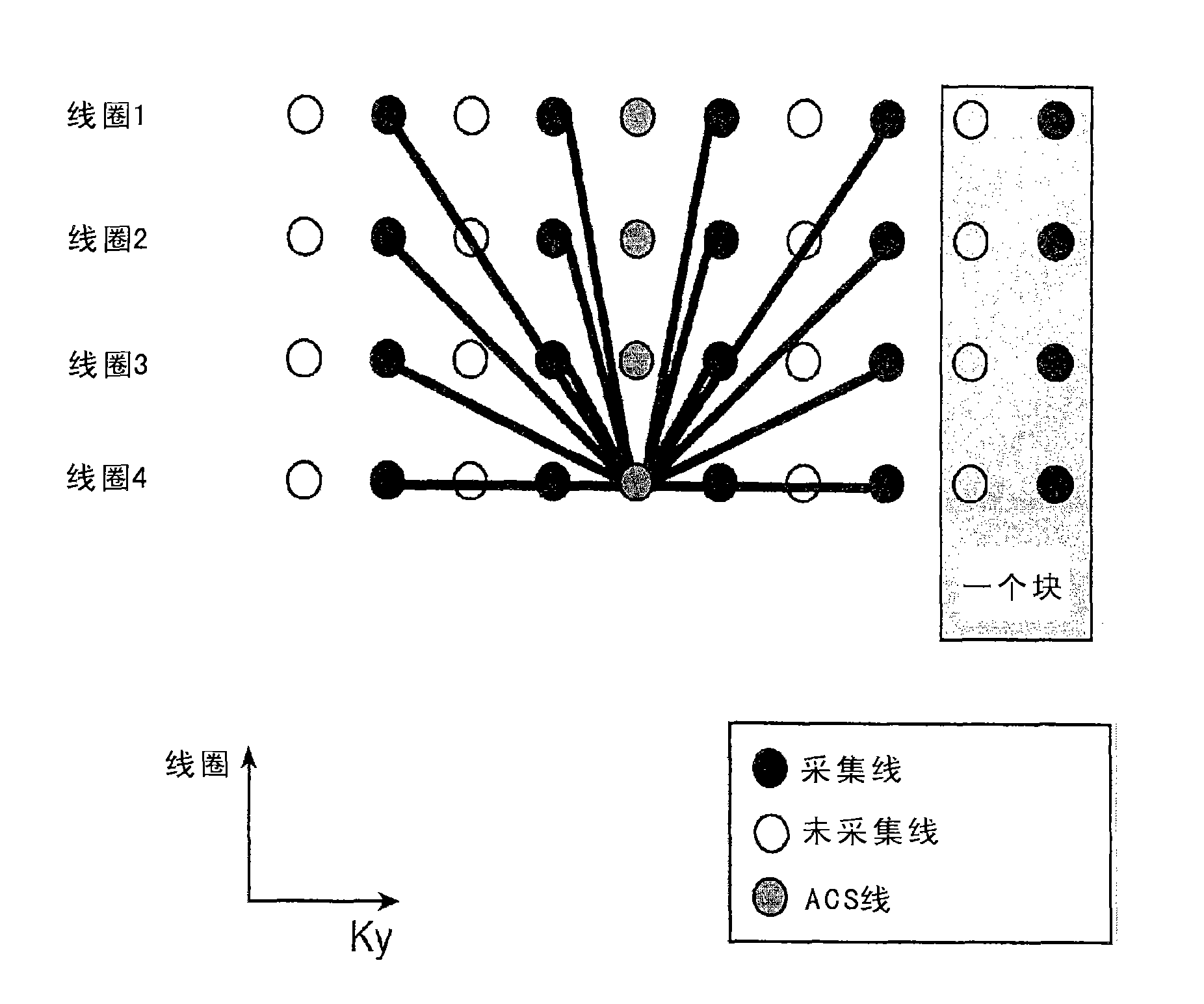
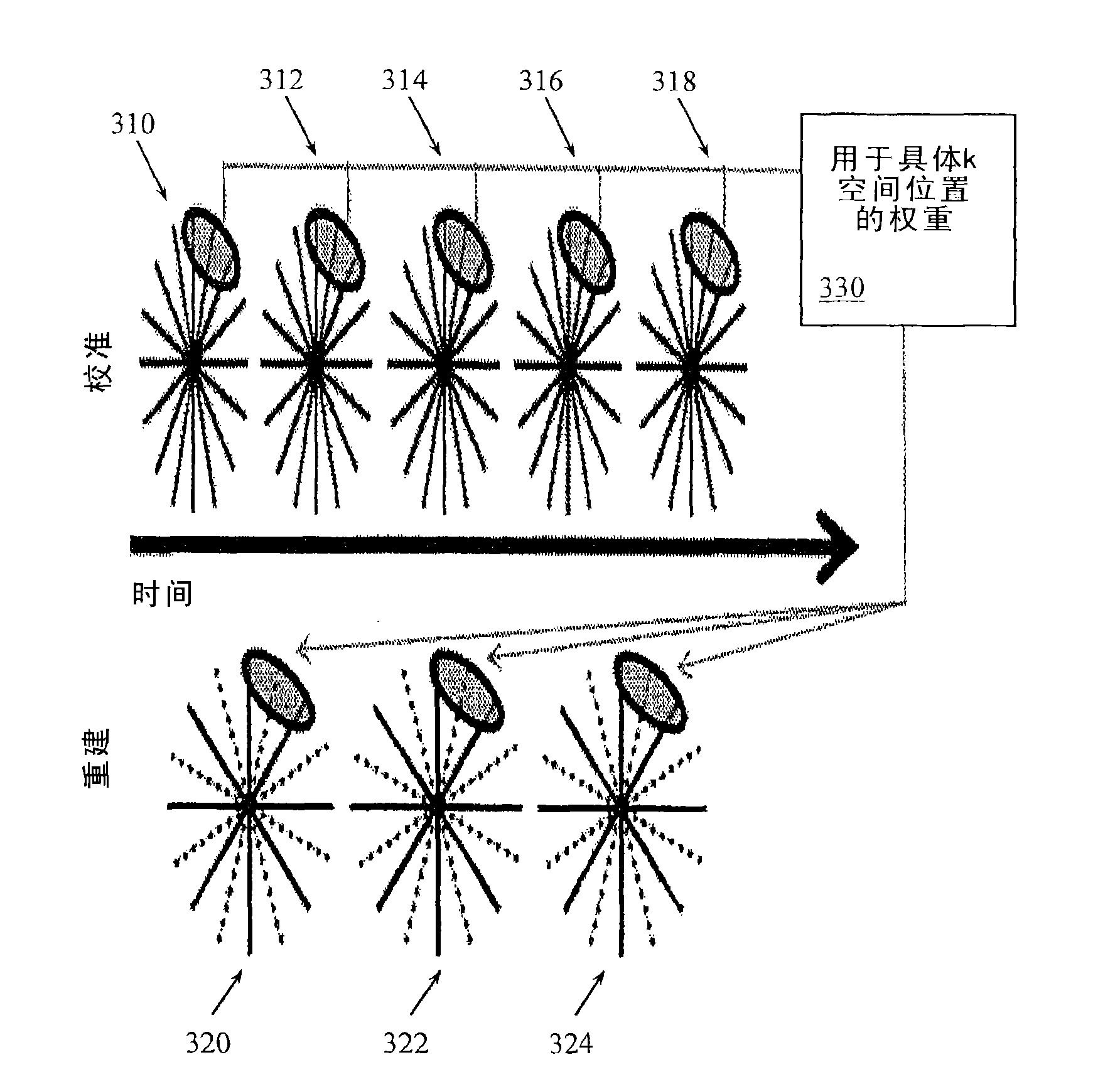
[0023] Example systems and methods acquire data at different time points and perform global calibration for radiological GRAPPA. The calibration data can be a fully sampled calibration set, but can also be less than a fully sampled calibration data set. By collecting calibration data throughout, multiple copies of each point can be collected. Using these multiple copies, reconstruction kernels can be derived separately for each desired reconstruction point in the original data. Since the exact kernel configuration can be computed for each point, the resulting reconstruction kernel will support a higher speedup factor for undersampling than previously thought possible for radial GRAPPA. The radiometric calibration data is acquired according to a plan to acquire radiographic rays of the same configuration as the rays to be used in the reconstruction. Since the data is collected in the whole process, the reconstruction and verification of rays collected multiple times in the wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com