NOTCH1 receptor binding agents and methods of use thereof
A receptor, antibody technology, used in the characterization, diagnosis and treatment of cancer and other diseases, the field of treatment of cancer, can solve problems such as loss of heterozygosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
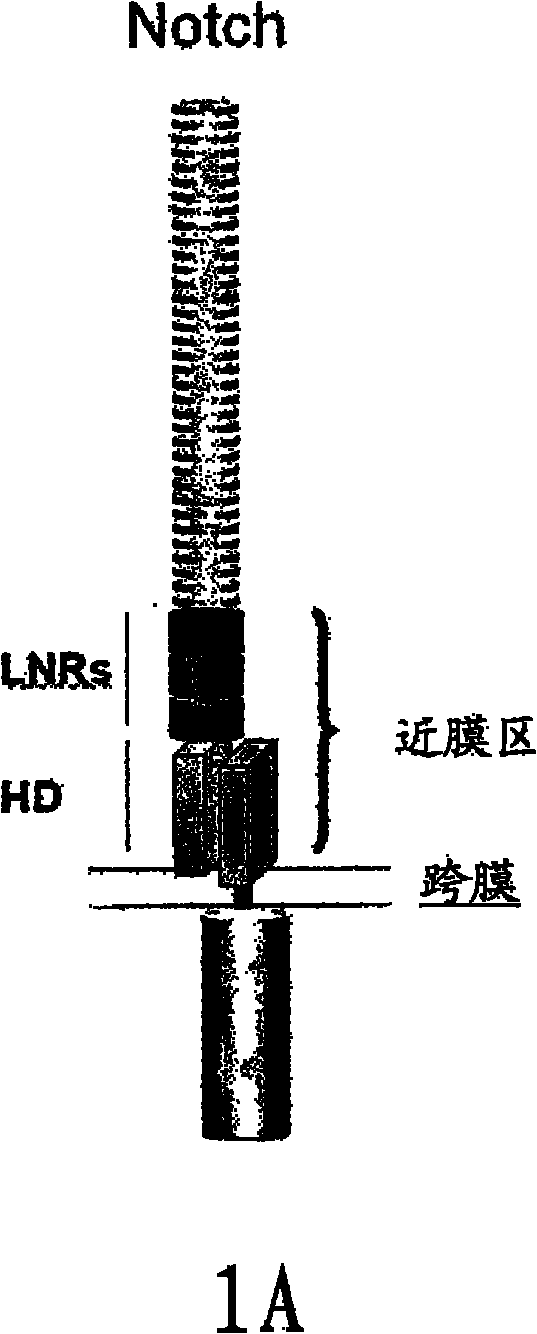
[0102] The present invention provides compositions and methods for the study, diagnosis, characterization and treatment of cancer. In particular, in certain embodiments, the present invention provides agents (including antagonists) that bind Notch receptors and methods of using the agents or antagonists to inhibit tumor growth and treat cancer and other diseases in human patients. In a specific embodiment, the antagonist is an antibody that specifically binds to the non-ligand binding region of the extracellular domain of the human Notch receptor.
[0103] In one aspect, the invention provides antibodies that specifically bind to the non-ligand-binding membrane-proximal region of the extracellular domain of the human Notchl receptor. In certain embodiments, the antibody binds a region of human Notch1 comprising about amino acid 1427 to about amino acid 1732. In certain embodiments, the antibody binds to a region comprising SEQ ID NO:2. In specific embodiments, the antibody s...
Embodiment 1
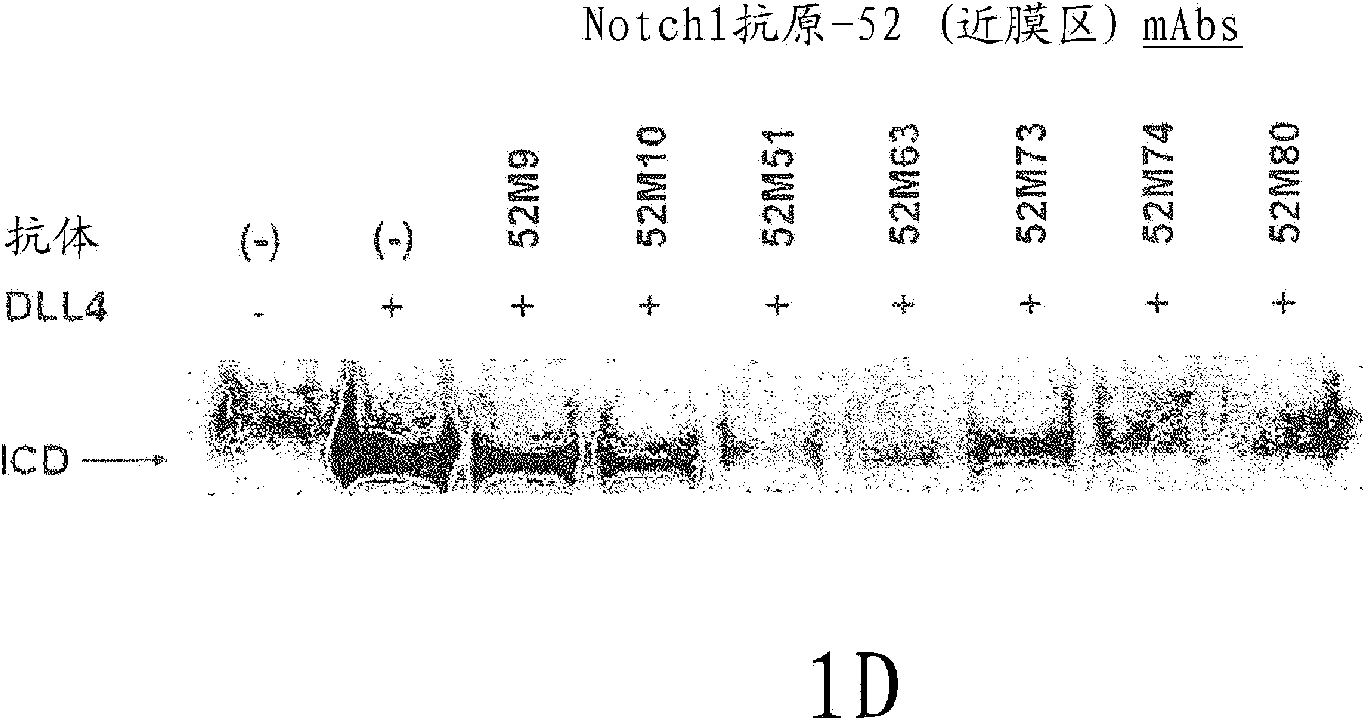
[0228] Antibodies were raised against the non-ligand-binding region of Notch1, particularly against the non-ligand-binding membrane-proximal region of the ectodomain. In a specific embodiment, recombinant polypeptide fragments of the extracellular domain of human Notchl are produced as antigens for antibody production. The polynucleotide (SEQ ID NO. 1) encoding the membrane-proximal region of the extracellular domain of human Notchl amino acid sequence 1427-1732 was isolated using standard recombinant DNA techniques. These polynucleotides were individually linked in N-terminal frame to human Fc and histidine tags and cloned into transfer plasmid vectors for baculovirus-mediated expression in insect cells. Standard transfection, infection, and cell culture protocols were used to generate recombinant insect cells expressing the corresponding Notch1 polypeptide (SEQ ID NO: 2) corresponding to the membrane-proximal region comprising amino acids 1427-1732 (O'Reilly et al., 1994, Ba...
Embodiment 2
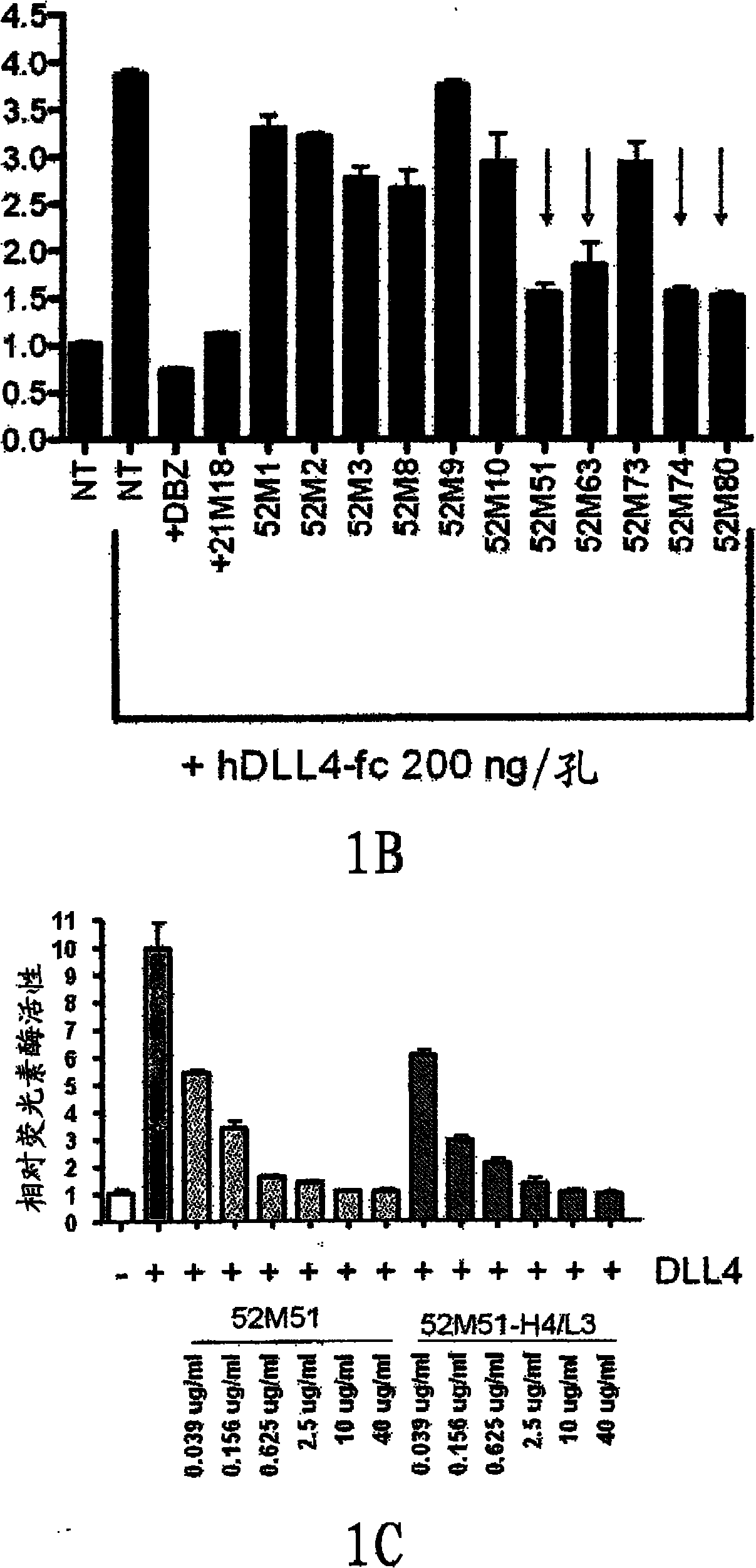
[0243] Humanized antibodies were raised against the membrane-proximal region of the extracellular domain of human Notchl. Degenerate PCR was used to hybridize The variable domains of the murine monoclonal antibody 52M51 were isolated from tumor lines and sequenced. Human heavy and light chain variable framework regions, which may be structurally similar to the parental 52M51 antibody amino acid sequence, were then considered reference human framework regions to help guide the design of novel synthetic frameworks. To identify human framework regions similar to the 52M51 murine framework, the predicted protein sequences encoded by the VH and VL murine variable domains of 52M51 were compared with those encoded by the expressed human cDNA using BLAST searches of human sequences deposited in Genbank. Comparison of human antibody sequences. Using this approach, expressed human cDNA sequences (eg genbank DA975021, DB242412) and germline Vh domains (eg IGHV1-24) were selected for fu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com