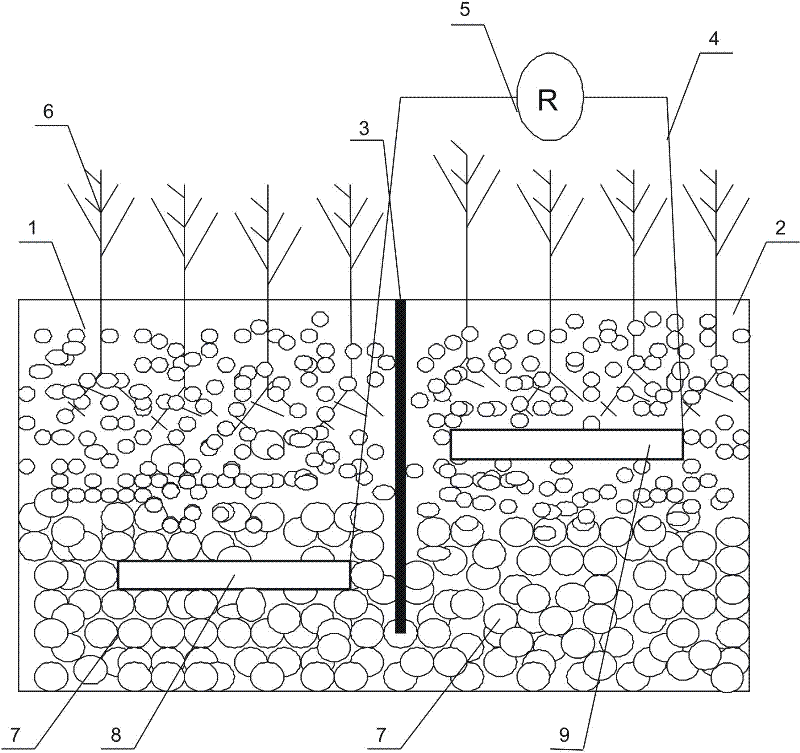
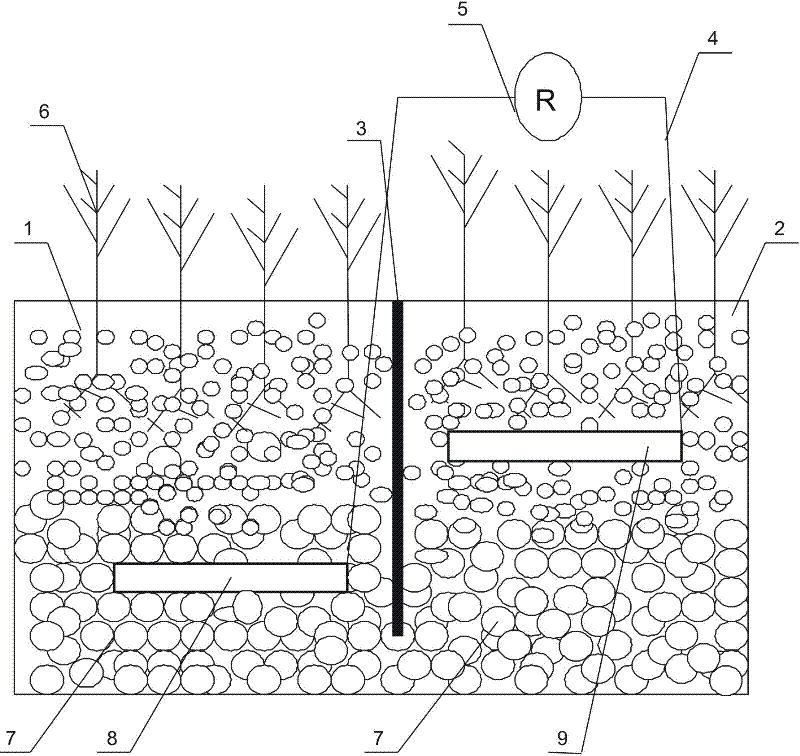
A microbial fuel cell device with aquatic plant electrodes in constructed wetlands
A technology of aquatic plants and artificial wetlands, applied in biochemical fuel cells, battery electrodes, sustainable biological treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, achieve high power generation, low planting cost, and good degradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029]Embodiment 1 (a microbial fuel cell device of a constructed wetland aquatic plant electrode of the present invention):
[0030] The heights of the cathode tank 1 and the anode tank 2 are both 1.5 meters. The separator 3 is made of PVC material and has 50 rows of through holes at the bottom, each row of 100 through holes with a diameter of 100 mm. Calamus is planted in cathode tank 1, and canna is planted in anode tank 2. Cathode tank 1 and anode tank 2 are provided with the same filler 7, large-grained zeolite is set 30mm upward from the bottom of the device, the middle is filled with small-grained stones, and the upper part is filled with quartz sand. The dosage ratio (weight) is about 3:2:1. Both the cathode electrode 8 and the anode electrode 9 are made of carbon felt.
[0031] After testing, the energy consumption per unit of water treated by the above-mentioned microbial fuel cell device is 0.36kW·h / m 3 , the removal efficiency of organic matter is over 90%, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2 (the microbial fuel cell device of the second constructed wetland aquatic plant electrode of the present invention)
[0037] The height of the cathode tank 1 and the anode tank 2 is 1 meter. The separator 3 is made of PE material, and there are 10 rows of through holes at the bottom, each row of 100 through holes, and the aperture is 100mm. Reeds are planted in the cathode tank 1, and reeds are planted in the anode tank 2. Cathode tank 1 and anode tank 2 are equipped with the same filler 7, large particles of charcoal are placed 30mm up from the bottom of the device, the middle is filled with small particle stones, and the upper part is filled with quartz sand. The dosage ratio (weight) is about 3:2:1. Both the cathode electrode 8 and the anode electrode 9 are made of carbon paper.
[0038] After testing, the energy consumption per unit of water treated by the above-mentioned microbial fuel cell device is 0.2kW·h / m 3 , the removal efficiency of organic ma...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3 (the microbial fuel cell device of the third constructed wetland aquatic plant electrode of the present invention)
[0044] The height of the cathode tank 1 and the anode tank 2 are both 1.8 meters. The separator 3 is made of PP material and has 30 rows of through holes at the bottom, each row of 100 through holes with a diameter of 60mm. Elephant grass is planted in the cathode tank 1, and wild ancient grass is planted in the anode tank 2. Cathode tank 1 and anode tank 2 are equipped with the same filler 7, and large-grained gravel is set 30mm upward from the bottom of the device, the middle part is filled with granular activated carbon, and the upper part is filled with quartz sand. The dosage ratio is about 1:3:1. The cathode electrode 8 is made of nickel foam, and the anode electrode 9 is made of carbon nanotubes.
[0045] After testing, the energy consumption per unit of sludge treated by the above-mentioned microbial fuel cell device is 0.2kW·h / m 3 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com