An information encryption method and device
A technology of information encryption and equipment, which is applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as user information leakage, online information only using passwords to protect security risks, server server administrators' moral defects, etc., to ensure security, easy to promote, and avoid bilateral conflicts problem effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
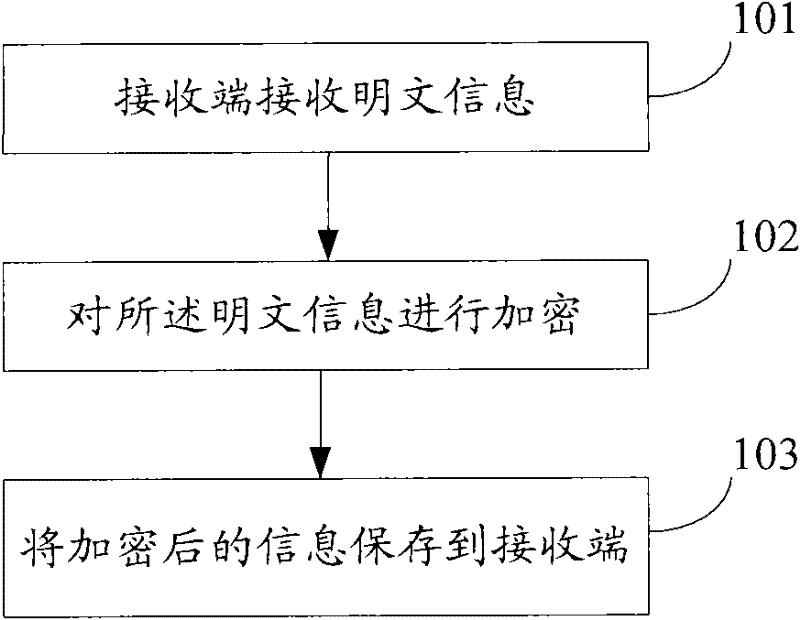
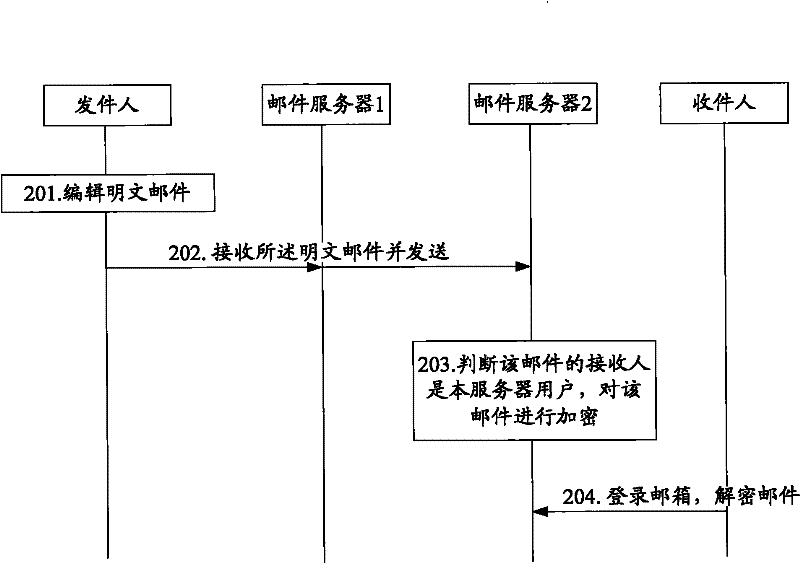
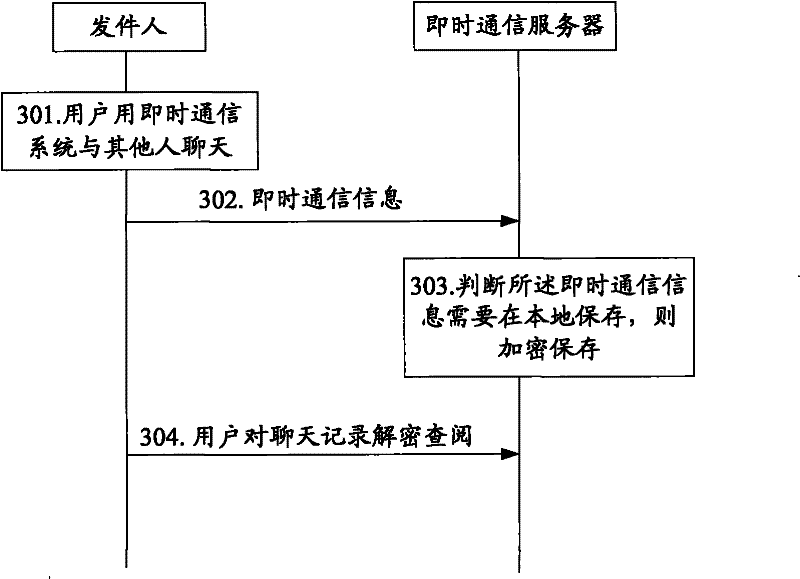
[0054]The information encryption method and equipment in the embodiment of the present invention aim at the security risks in the prior art that the information is transmitted in plain text and stored in plain text on the receiving server. Although the cryptographic system encrypts the information source, although it can guarantee the security of information in theory, the actual situation is that most netizens on the Internet do not use this method to encrypt information. The problem lies in the two-way nature of encryption promotion, such as If A wants to transmit encrypted information to B, B must have the encryption and decryption conditions such as asymmetric key pair and software supporting the key system. Moreover, B must transmit the response information to A, and A must also have the above encryption and decryption conditions. For the convenience of description, this problem is referred to as "encrypted mutuality problem" in the following. It is precisely because of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com