Security processing method, device and system in conversion process
A switching process and security processing technology, applied in the field of network communication, can solve problems such as solutions that do not consider security processing, and achieve the effect of improving security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
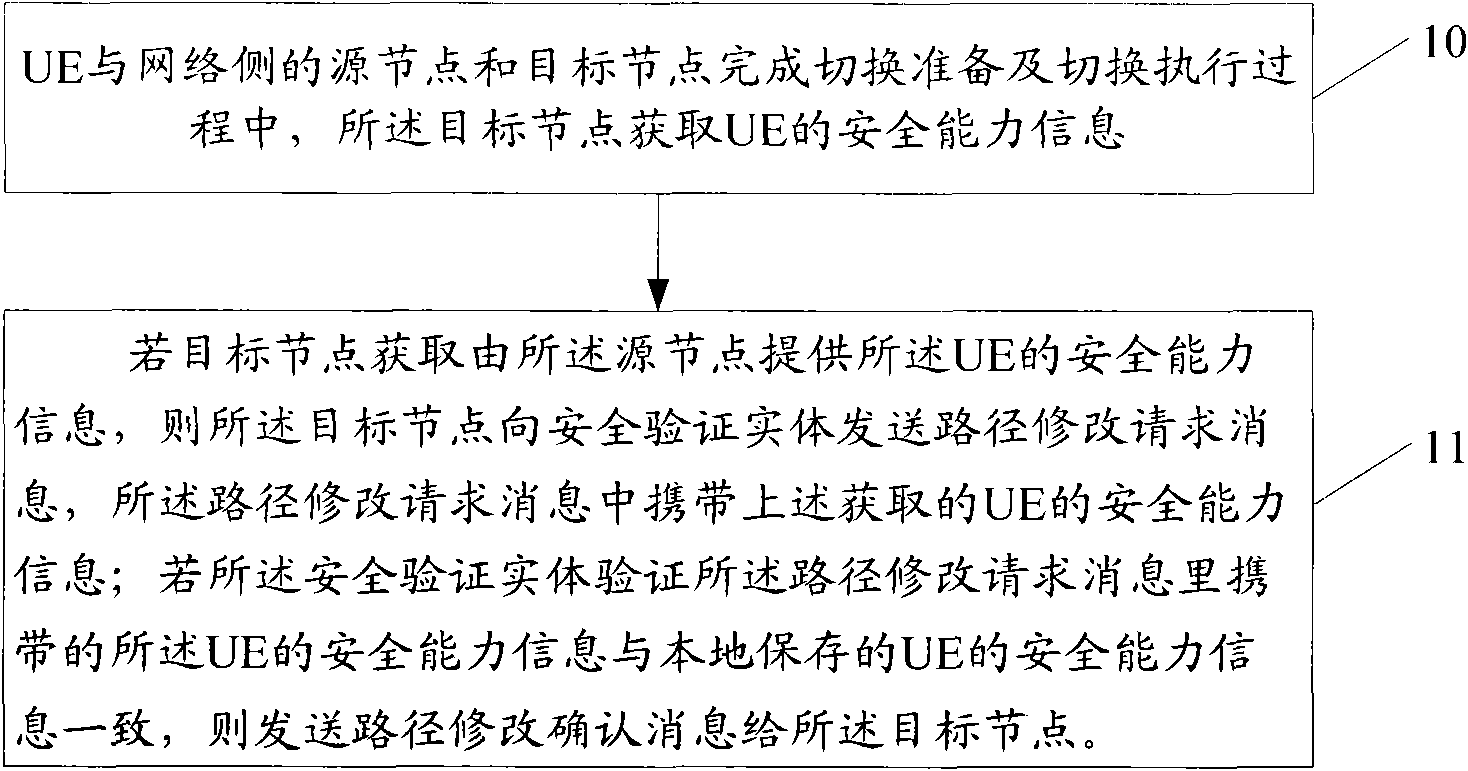
Image
Examples
example 1
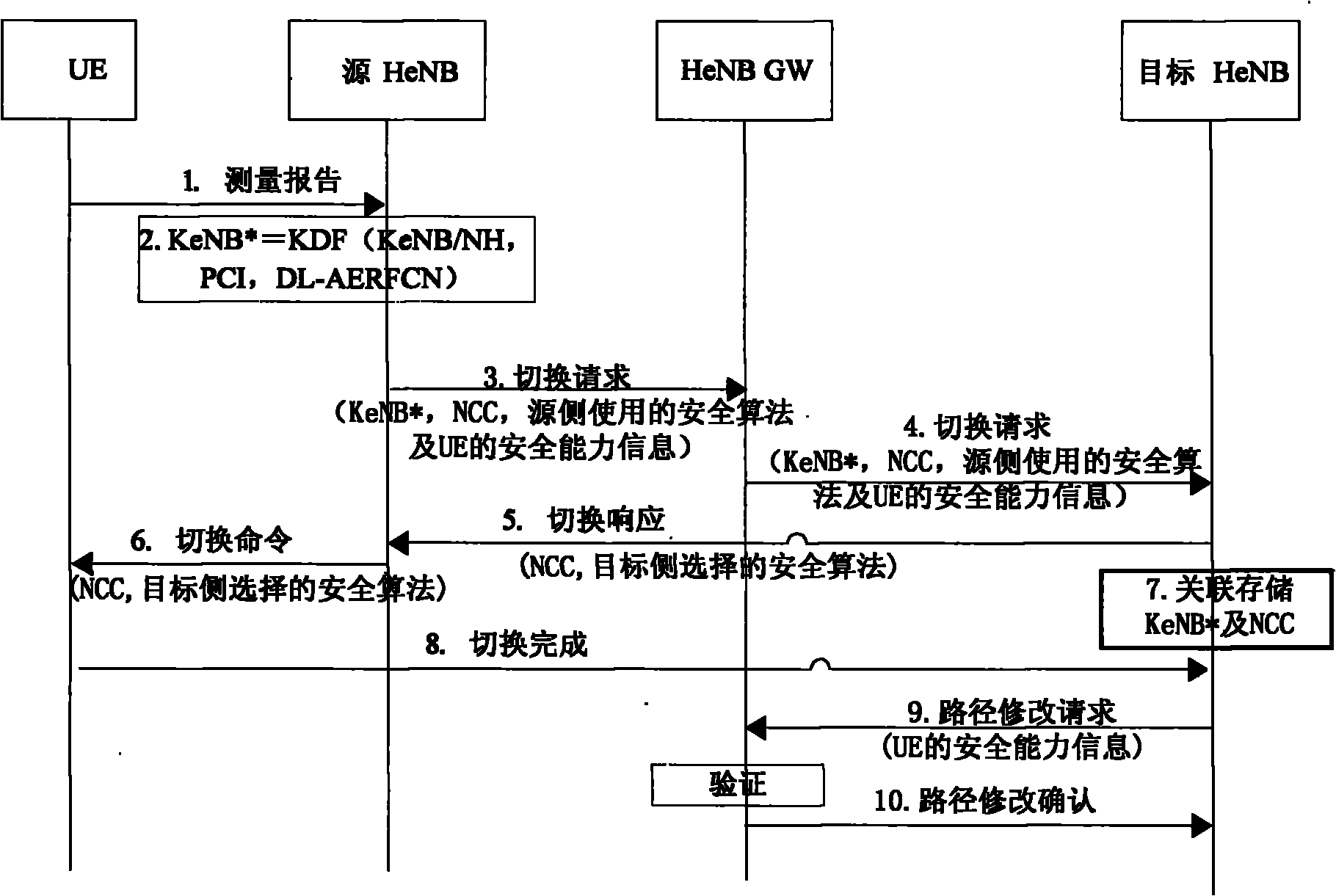
[0072] Example 1 scenario is: the security processing method in the UE handover process under the HeNB based on the X2 interface, the process of the method is as follows figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0073] Step 1. The UE sends a measurement report message to the source HeNB.
[0074] Step 2. The source HeNB checks whether there are fresh security parameters of the UE locally, such as fresh NCC and NH. If there are fresh security parameters of the UE, the source HeNB calculates a new access stratum root key KeNB according to the NH in the fresh security parameters. *; otherwise, the source HeNB calculates KeNB* according to the original access stratum root key KeNB.
[0075] The fresh safety parameters are unused safety parameters, including unused NCC, NH.
[0076] The process of calculating the new KeNB* by the source HeNB in step 2 can be described as:
[0077] KeNB*=KDF(KeNB / NH, PCI, DL-AERFCN); KDF(*) represents the key derivation function, KeNB / N...
example 2
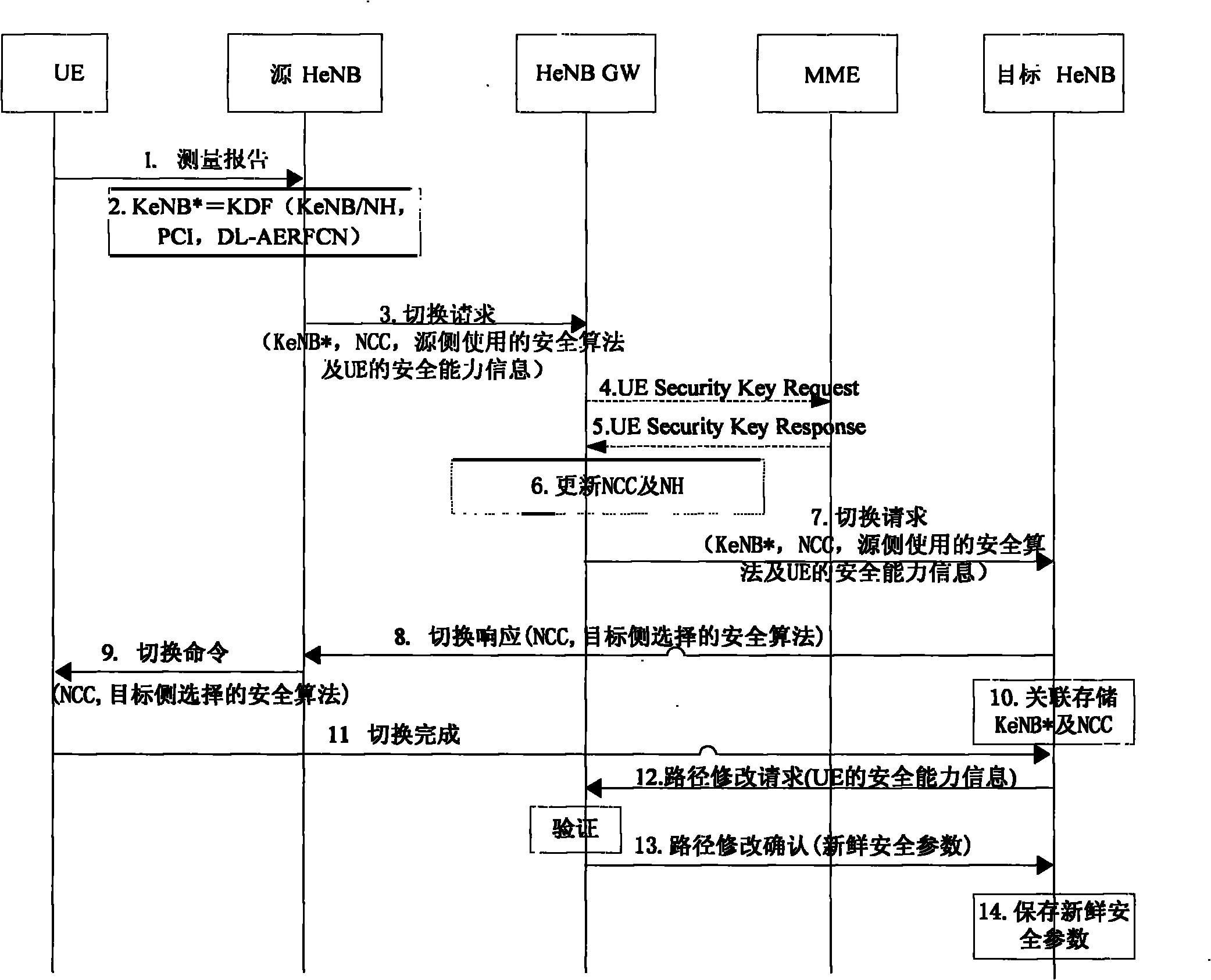
[0097] The scenario is: the security processing method in the UE handover process under the HeNB based on the X2 interface. In this example, there is no direct X2 interface between the source HeNB and the target HeNB. X2 message. The process of this method is attached image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0098] Wherein, steps 1 to 3 are the same as those in Example 1, and are not repeated here in this example.
[0099] Step 4. The HeNB GW judges that the optimized handover process needs to be performed according to the target cell information. If the HeNB GW has the fresh security parameters of the UE locally, it can go directly to step 7; if the HeNB GW does not have the fresh security parameters of the UE locally, then the HeNB GW Send a UE Security KeyRequest (UE Security Context Request) message to the MME, where the message includes the UE identity, to request to obtain the security parameters and key KASME of the UE.
[0100] In step 4, there are various m...
example 3
[0115] The scenario is the same as that of the second example, and the operation difference from the second example is that steps 4 to 6 are replaced by the following steps. This example only introduces different steps, and other steps will not be repeated.
[0116] Step 4. The HeNB GW determines that the optimized handover process needs to be performed according to the received handover request message. If the HeNB GW locally has the fresh security parameters of the UE, it can go directly to step 7;
[0117] If the HeNB GW locally stores the non-fresh NCC and NH, the HeNB GW sends a UE Security Key Request (UE Security Context Request) message to the MME, the message contains the UE identifier, to request to obtain the security parameters and key of the UE KASME.
[0118] The non-fresh NCC and NH stored locally by the HeNB GW are obtained by the security verification entity from the path modification confirmation message or the handover request message sent by the MME in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com