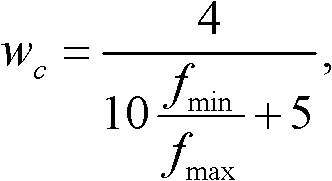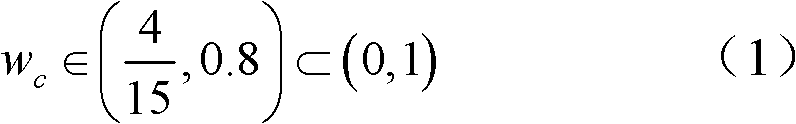Method for carrying out adaptive computing on importance weights of low-level features of image
A technology of self-adaptive computing and underlying features, applied in the field of computer vision, it can solve problems such as not being able to adapt well, inaccurate extraction of important areas, and inapplicability of various types of images.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
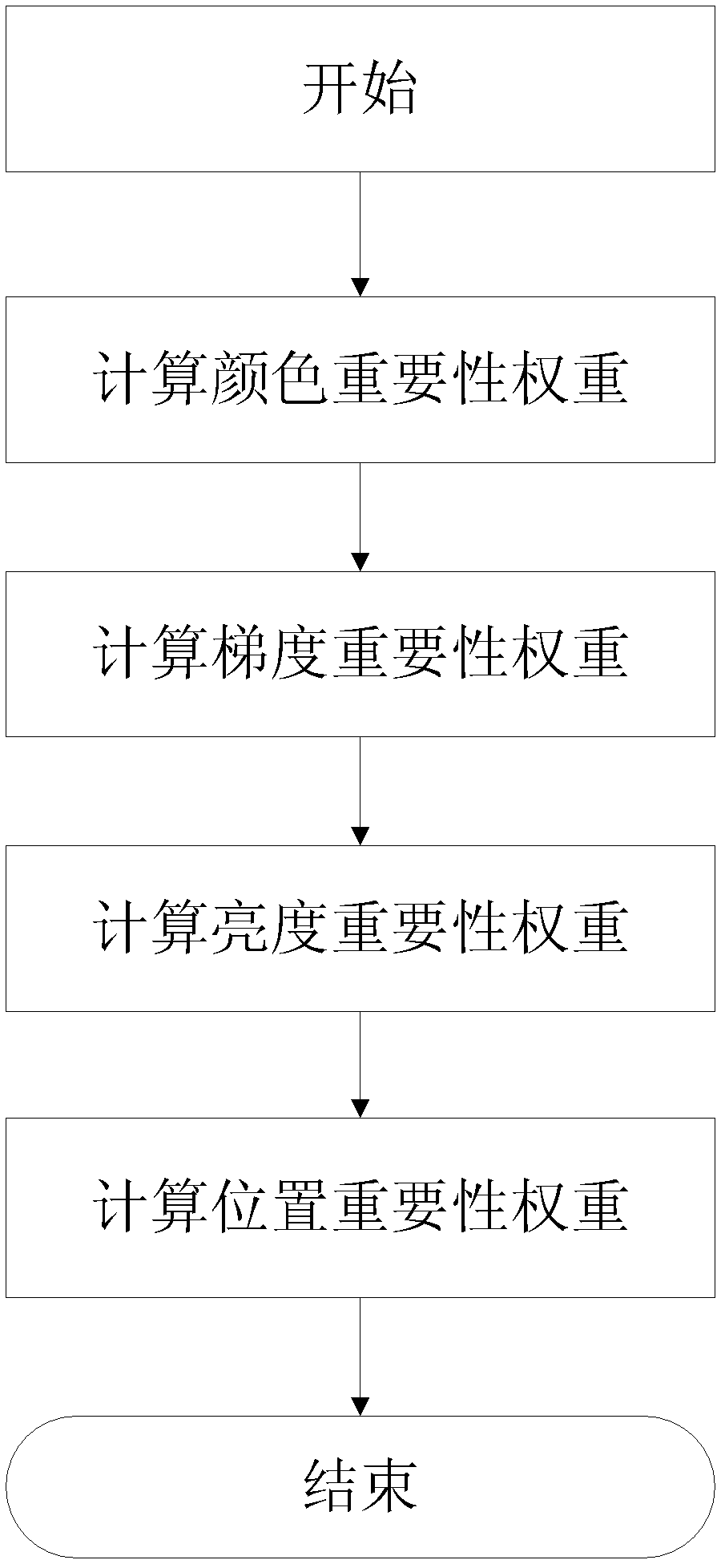
[0033] It should be noted that the following is only an example of an embodiment of the present invention: Step 1: Calculating image color importance weights
[0034] Although the three primary colors of RGB are directly expressed, the values of R, G, and B are not directly related to the three attributes of the color, and the relationship between colors cannot be revealed. The HSV color model evolved from the CIE three-dimensional color space, and it adopts the user-intuitive It is closer to the HVC spherical color stereo of the Munsell color rendering system, so it is more convenient to use the HSV space when studying the importance of colors.
[0035] In the present invention, the H channel of the HSV space is used to make statistics on the line histogram of the image, so that the frequency of color appearance can be seen intuitively, and a larger weight is assigned to the color with less distribution.
[0036] An exemplary implementation of step 1 is as follows:
[0037...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com