Laser device for ophthalmology
An ophthalmic laser and laser device technology, applied in laser surgery, ophthalmic surgery, ophthalmic treatment, etc., can solve problems such as impossible to obtain, and achieve the effect of simple integration and high design flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
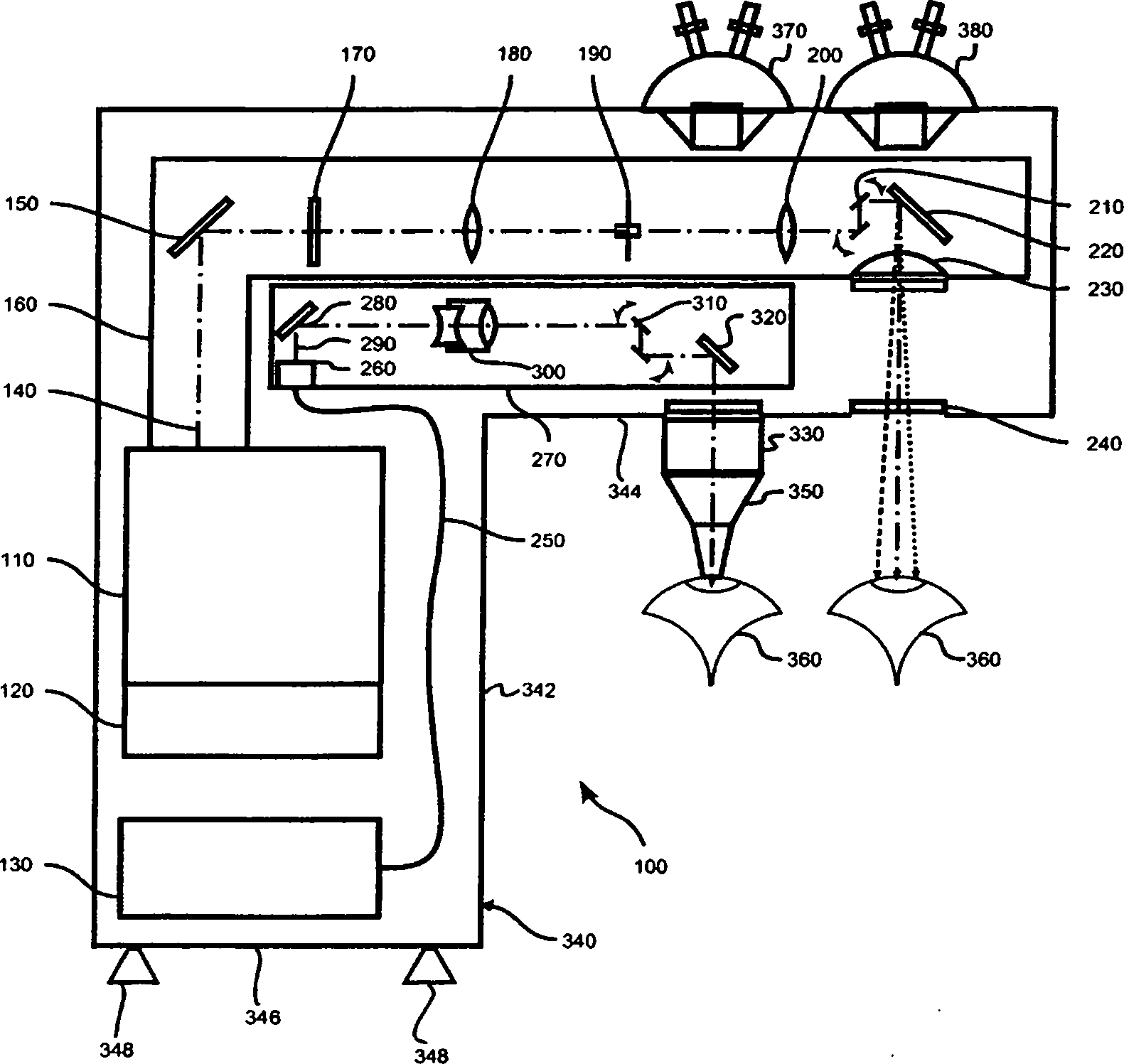
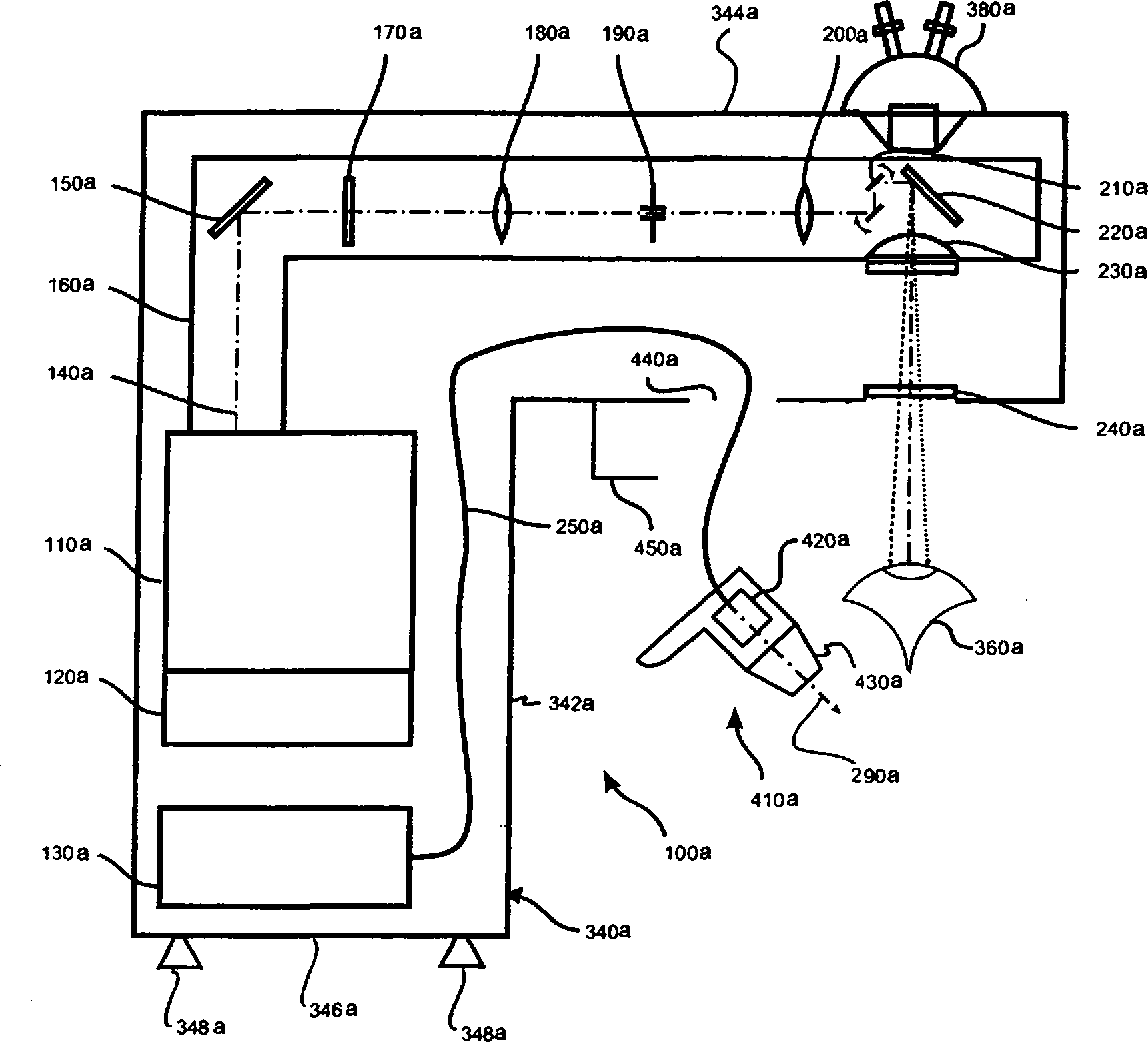
[0034] Such as figure 1 The illustrated exemplary embodiment of the laser device takes the form of a monolithic ophthalmic laser diagnostic system 100 particularly adapted for eye refraction treatment to eliminate visual defects in the eye 360 to be treated. The laser diagnostic system 100 includes an excimer laser 110 constituting a first laser source, the excimer laser 110 generating a pulsed laser beam 140 having a UV wavelength. For example, an excimer laser is an ArF reference laser emitting at 193 nm. The excimer laser 110 is assigned control electronics 120 with appropriate control software and operating software.
[0035] The laser diagnostic system 100 comprises, via a further laser source, an fs laser 130 which preferably takes the form of a fiber laser and which generates pulsed laser radiation with a pulse width in the femtosecond range. For example, the pulse width of the laser pulses generated by the fs laser 130 is between 100 fs and 800 fs; the laser radiat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com