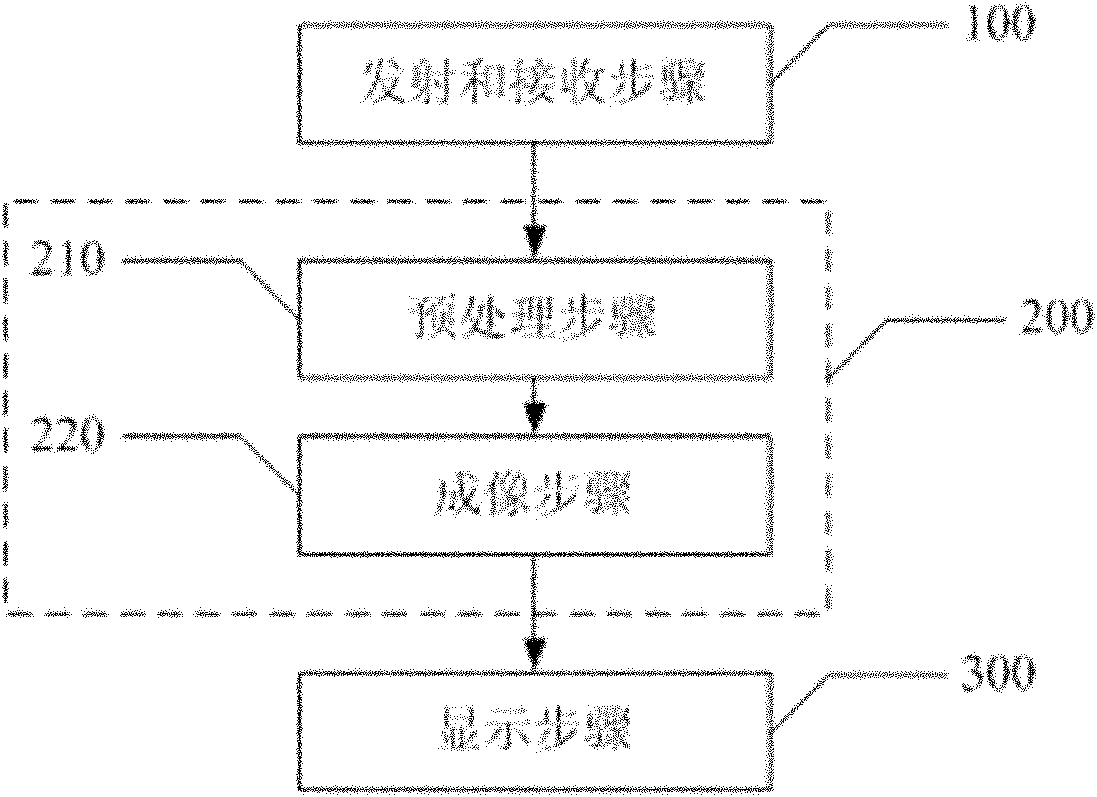
Ultrasonic imaging method and device
An ultrasonic imaging method and imaging technology, applied in blood flow measurement devices, ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosis, sound wave diagnosis, etc., can solve the problems of scanning time compression, poor time resolution, image mismatch, etc., and achieve quality assurance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
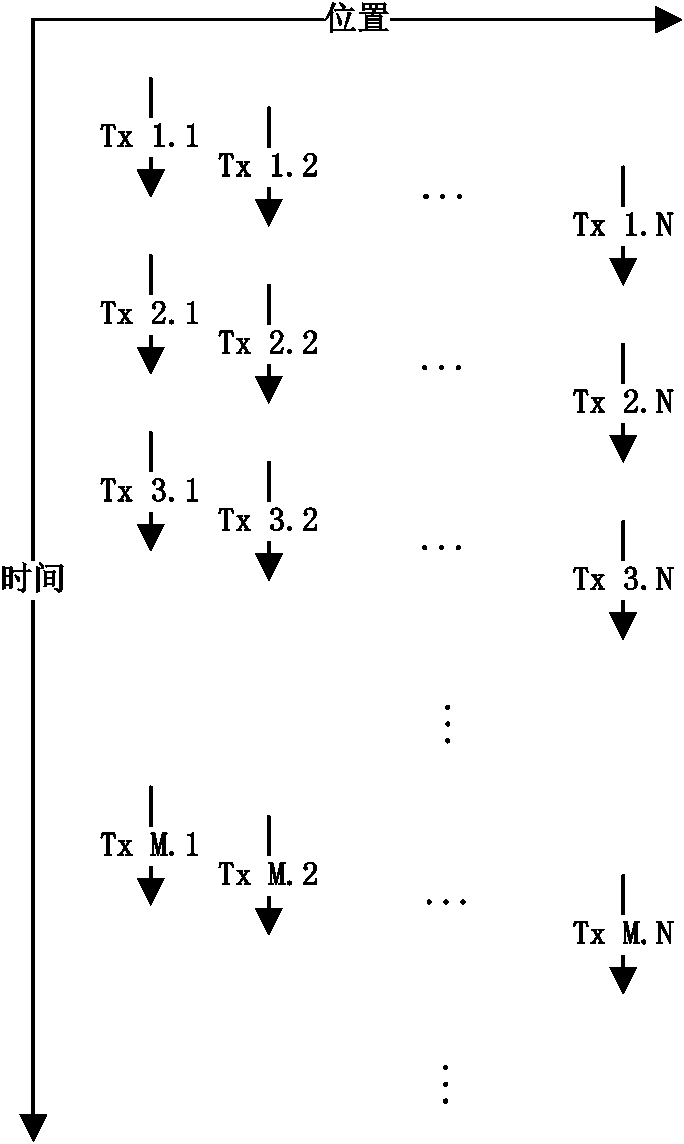
[0038] In this embodiment, only Doppler pulses are emitted, and Doppler pulses can be used to generate two-dimensional images, blood flow images and spectrum images, and the transducer emits Doppler pulses for Doppler scanning; the transducer The received echo signal is a Doppler pulse echo signal. Such as figure 2 As shown, Tx1.1 to Tx1.N constitute a complete Doppler pulse scanning frame; Tx1.1 to TxM.1 constitute a spectrum calculation package; the frequency of Tx1.1 to Tx2.1 is the pulse repetition frequency ( PRF, Pulse Repetition Frequency), which determines the maximum measurable velocity, from which the Doppler information of a scan line can be calculated. In the imaging step 200, the two-dimensional image processing step, the blood flow image processing step and the spectral image processing step are performed in parallel, that is, all scan lines (ie, from 1 to N) are combined to reconstruct the The two-dimensional image of each scan line (such as Tx1. 2 to TxM.2)...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the transmitted pulses are Doppler pulses and B pulses, and the pulse transmission sequence is: B pulses are transmitted between two adjacent frames of Doppler scans. Doppler pulses can be used to generate two-dimensional images, blood flow images, and spectrum images, while B pulses can be used to generate two-dimensional images; the transducer uses Doppler pulses for Doppler scanning, and B pulses for B-line Scanning; the echo signals received by the transducer are Doppler pulse echo signals and B pulse echo signals.
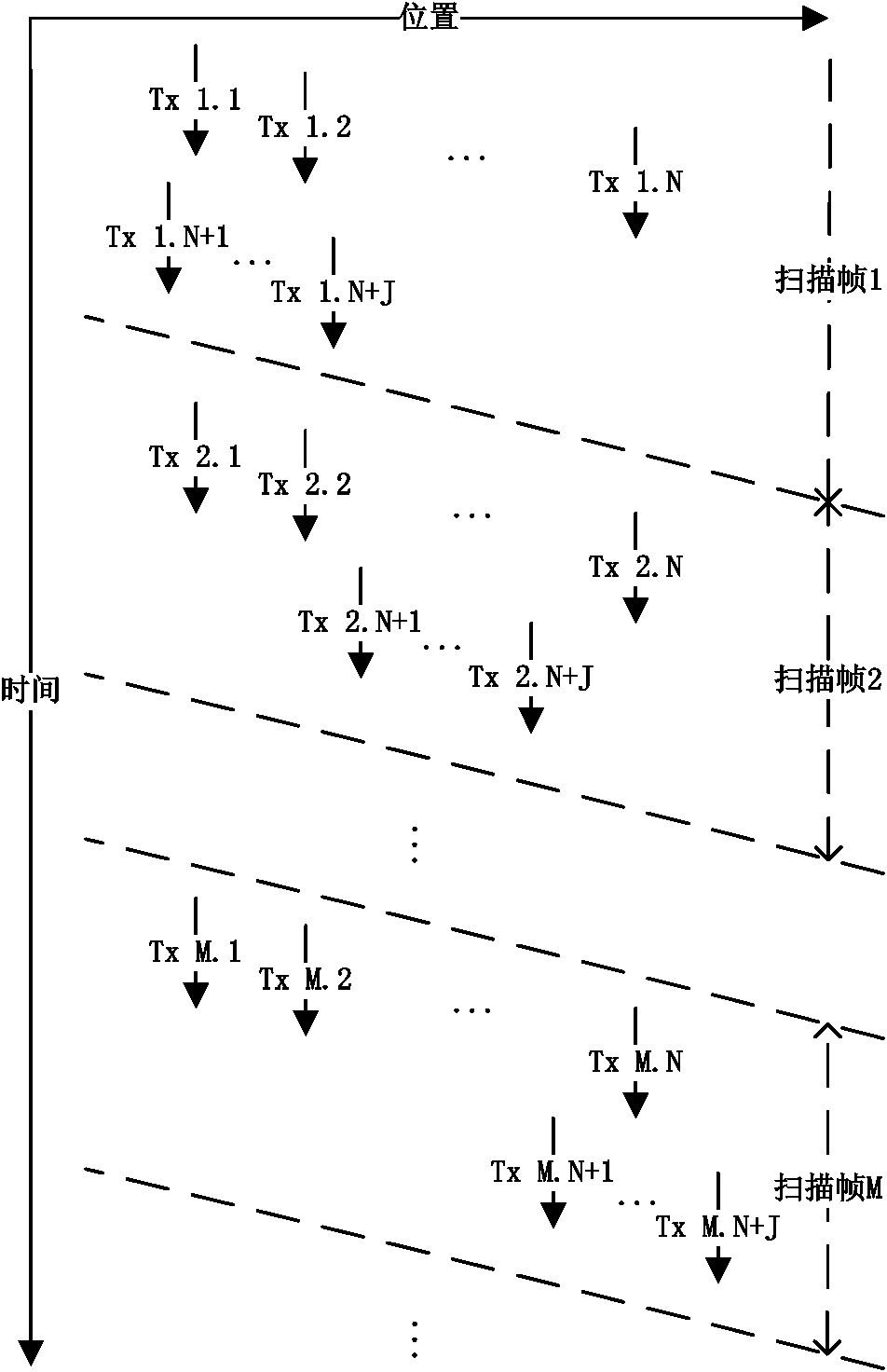
[0041] Such as image 3 As shown, the Doppler pulse scan is from Tx1.1 to TxM.N, which is the same as the case of only Doppler pulse scan described in Embodiment 1, and J times are added in the scanning gap from Tx1.N to Tx2.1 The B-line scan is Tx1.N+1 to Tx1.N+J, and the scan position can be the same as that of the Doppler pulse scan, or it can be different. That is to say, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that although the transmitted pulses are Doppler pulses and B pulses, the pulse transmission sequence is: B pulses are transmitted between two adjacent Doppler scan data packets, One of the Doppler scan packets contains several frames of Doppler scans. Doppler pulses can be used to generate two-dimensional images, blood flow images, and spectrum images, while B pulses can be used to generate two-dimensional images; the transducer uses Doppler pulses for Doppler scanning, and B pulses for B-line Scanning; the echo signals received by the transducer are Doppler pulse echo signals and B pulse echo signals.
[0045] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is that the scanning gap between two adjacent frames from Tx1. A B-line scan frame is inserted between two adjacent Doppler pulse scan data packets, each frame contains J transmissions, and its scan position ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com