Methods for sending, receiving and transmitting downlink control information and related devices
A technology for controlling information and sending methods, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of low overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
application example 1
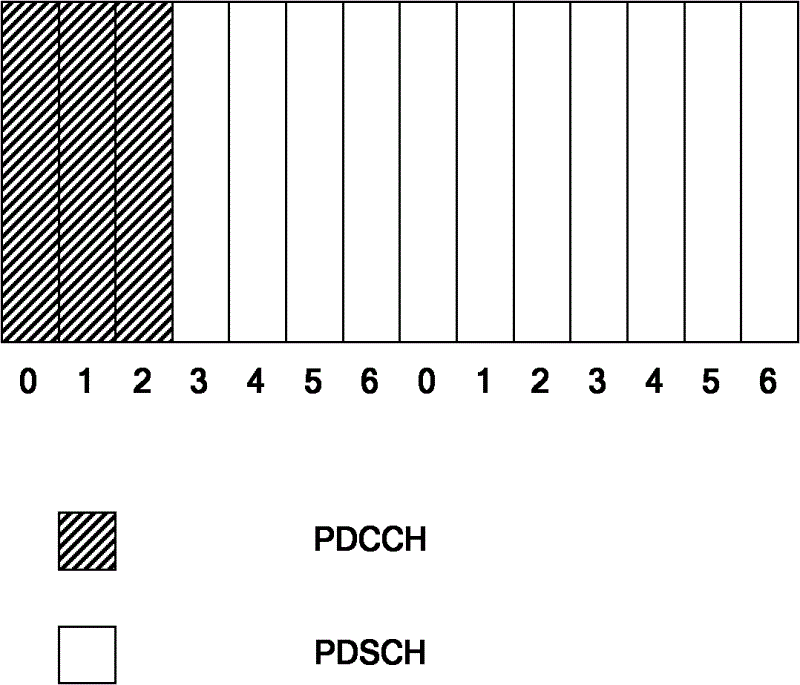
[0134] In the LTE or LTE-Advance indoor hotspot coverage scenario, which can also be called the LTE-LAN scenario, a subframe that transmits a PDCCH, how to schedule PDSCH or PUSCH resources on other subframes or other serving cells (serving cells) (The serving cell may also be referred to as a component carrier), which has the following configuration:
[0135] Configuration one:
[0136] The PDCCH on the subframe can continuously schedule PDSCH or PUSCH resources on n subframes including itself.
[0137] The n is a positive integer greater than 1.
[0138] Configuration two:
[0139] The PDCCH on the subframe may schedule PDSCH or PUSCH resources of other n serving cells including its own serving cell on this subframe.
[0140] The n is a positive integer greater than 1, which is notified by high-layer signaling.
[0141] Configuration three:
[0142] The PDCCH on the subframe can schedule the PDSCH or PUSCH resources of other m serving cells including its own serving c...
application example 2
[0145] A transmission mode is newly defined, which is used for the user terminal UE in the LTE-LAN network to perform corresponding PDCCH monitoring, receive PDSCH data and send PUSCH data.
[0146] When the user terminal UE accesses the LTE-LAN network, the UE is semi-statically set to the transmission mode X through high-layer signaling, and the preferred value of X is 10. The transmission mode corresponds to DCI format Y, and the preferred value of Y is 5, which is used to represent the transmission of up to 8 layers.
[0147] For DCI format Y, the information transmitted in the corresponding DCI can be:
[0148] method one:
[0149] DCI includes resource block allocation information and modulation and coding scheme information, which are used to indicate one or more serving cells and / or PDSCH resources or PUSCH resources scheduled on one or more subframes, that is, each serving cell and / or each The same resource block allocation information and modulation and coding ...
application example 3
[0160] Two transmission modes are newly defined, which are used for the LTE-LAN network user terminal UE to perform corresponding PDCCH monitoring, receive PDSCH data and send PUSCH data.
[0161] When the user terminal UE accesses the LTE-LAN network, the UE is semi-statically set to transmission modes X1 and X2 through high-layer signaling, and the preferred values of X1 and X2 are 10 and 11. The transmission mode corresponds to DCI format Y1 and DCI format Y2, and the preferred values of Y1 and Y2 are 5 and 6, which are used to represent the transmission of up to 8 layers.
[0162] When the UE is semi-statically set to the transmission mode X1 through high-level signaling, its corresponding DCI format Y1 is only used to schedule its own subframe and PDSCH resources on the serving cell.
[0163] When the UE is semi-statically set to the transmission mode X2 through high-layer signaling, its corresponding DCI format Y2 method for scheduling PDSCH resources is as in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com