Vehicle dynamic weighing system
A vehicle and load cell technology, applied in the field of weighing, can solve the problems of vehicle weight error, weighing result deviation, weight deviation, etc., and achieve the effect of improving weighing deviation, reducing weighing deviation, and reducing deviation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
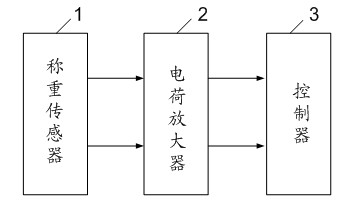
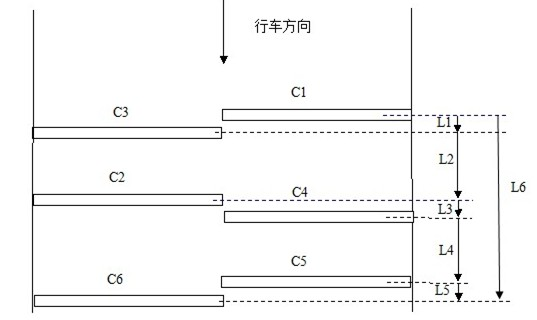
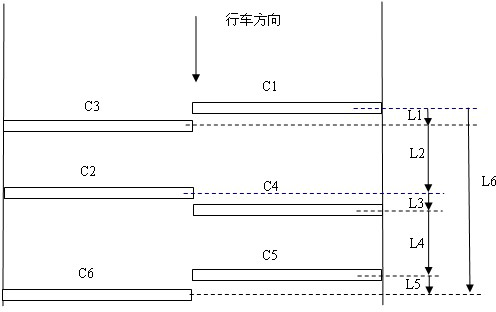
[0027] see figure 1 , is a schematic structural diagram of a vehicle dynamic weighing system in an embodiment of the present invention. The vehicle dynamic weighing system of the present invention includes a load cell 1, a charge amplifier 2 and a controller 3. The load cell 1 includes at least Three rows of quartz sensors, the waveform signal generated by the load cell 1 when the wheel is rolling, is amplified by the charge amplifier 2 and transmitted to the contr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com