Obtaining method of optimal generation polynomial in type-II hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) system and repeat system adopting method
A technology for generating polynomials and acquisition methods, which is applied in the field of digital communication and can solve problems such as poor anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
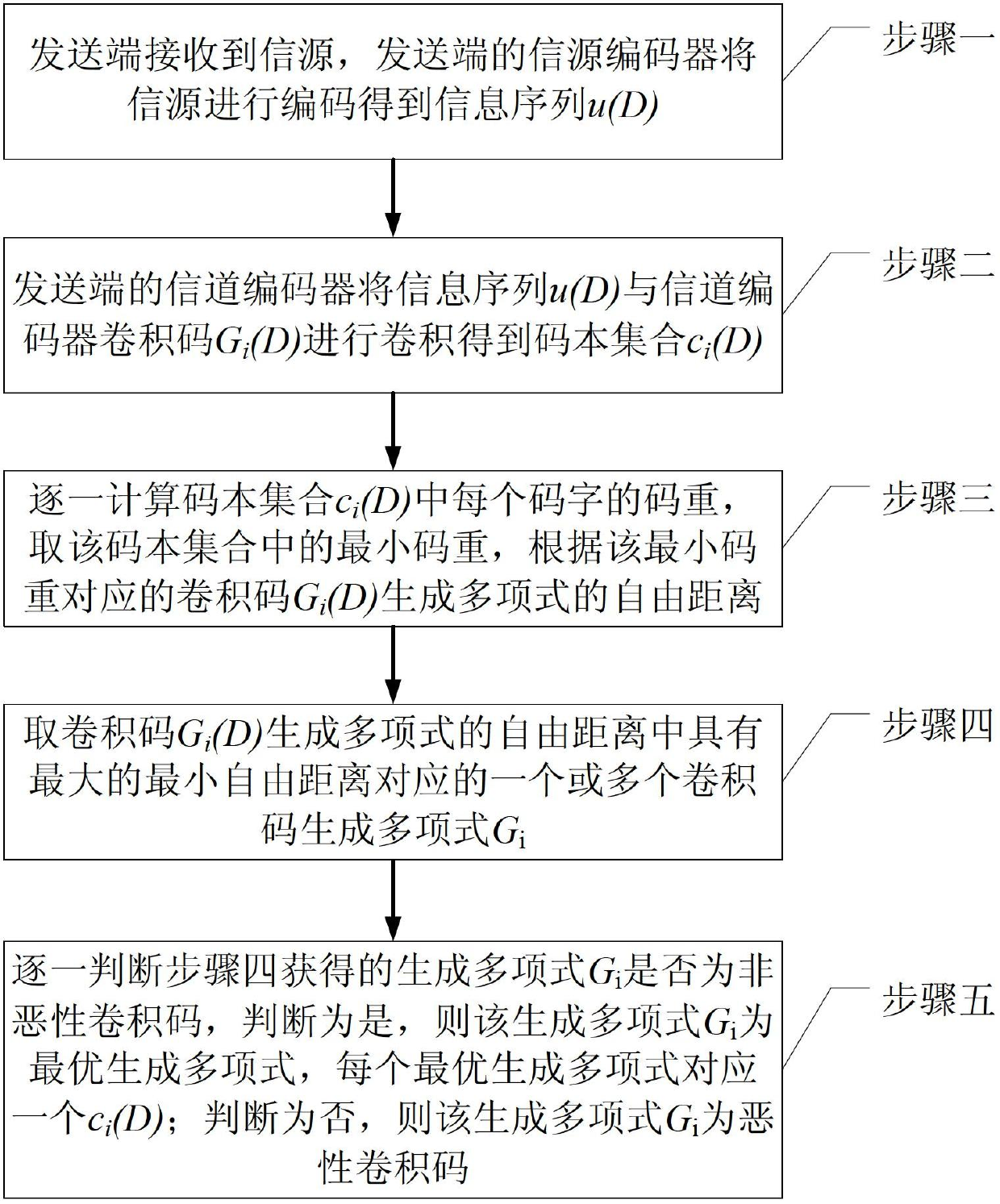
[0017] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 This embodiment is specifically described. The method for obtaining the optimal generator polynomial in the Type-II HARQ retransmission system described in this embodiment is:
[0018] Step 1. The sending end receives the information source, and the information source encoder at the sending end encodes the information source to obtain the information sequence u(D);
[0019] Step 2. The channel encoder at the sending end combines the information sequence u(D) with the convolutional code G of the channel encoder i (D) Perform convolution to obtain the codebook set c i (D),
[0020] Step 3: Calculate the codebook set c one by one i For the code weight of each codeword in (D), take the minimum code weight in the codebook set, and according to the convolutional code G corresponding to the minimum code weight i (D) the free distance of the generating polynomial;
[0021] Step 4: Take the convolutional code G i (D) One...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the method for obtaining the optimal generator polynomial in the Type-II HARQ retransmission system described in Embodiment 1 is that the channel encoder at the sending end in step 2 converts the information sequence u( D) Convolutional code G with channel encoder i (D) The specific steps for convolution are:
[0025] The maximum length of the information sequence u(D) is l max , the polynomial generated by the convolutional code (n, k, m) of the channel encoder has a total of 2 n(m+1) If the first bit of the sequence is specified as 1, then the sequence is from [1 0 ... 0] to [1 1 ... 1], a total of 2 lmax-1 , for each channel encoder structure composed of generator polynomials, the 2 lmax-1 Different information sequences u(D) are sequentially input into the channel encoder to obtain 2 lmax-1 output sequences, that is, the codebook set c i (D).
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0026] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the method for obtaining the optimal generator polynomial in the Type-II HARQ retransmission system described in Embodiment 2 is that the generator polynomial G obtained in step 4 is judged one by one in step 5. i The specific steps of whether it is a non-vicious convolutional code are: judge the generator polynomial G i Whether the non-zero sequence code in the state diagram of the state diagram has a loop in the diagram, and the coded output is all zero, if yes, the corresponding convolutional code is a vicious convolutional code, if not, the corresponding convolutional code is Non-vicious convolutional codes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com