Method for culturing conjoined trees
A cultivation method and tree species technology, applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, horticulture, etc., can solve problems such as large limitations, no modeling type, inapplicability to ornamental seedling cultivation and garden landscaping, etc., to achieve economical improvement Benefits, the effect of saving nursery land
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Cultivation of Seedlings of Osmanthus osmanthus with branches and branches
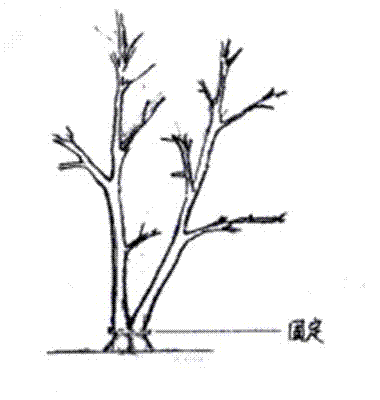
[0042] Step 1: Select 2 osmanthus saplings with a DBH of about 2-3cm and a height of about 2-2.5m;
[0043] The second step: close the bases of the selected two seedlings together, and make each of the two seedlings have a thicker branch that grows relatively. If the soil ball prevents the base of the seedlings from being close, the soil ball or soil of the hindering part can be cut off so that the base of the seedlings can be in close contact. At the same time, cut off the bark of the contact part to make it easy to heal and grow;
[0044] Step 3: Drill a 0.5-diameter hole through the base of the two seedlings, and fix them with bolts of the same diameter ( figure 1 ). Or tie it with cloth strips or hemp rope, such as nylon, metal and other non-perishable materials, which need to be removed in time after growth and healing, so as not to affect the rough growth of seedlings;
[0045] Step 4...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Cultivation of two-twisted and three-in-one connected-branch type ginkgo biloba seedlings:
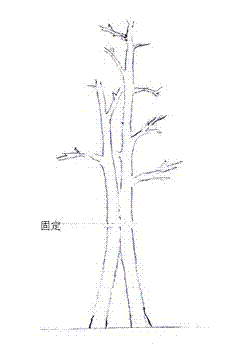
[0050] Step 1: Select 2 ginkgo seedlings with a diameter at breast height of about 3cm and a height of about 2.5-3m;
[0051] The second step: put the bases of the selected two seedlings close together and plant them with a slight inclination according to the conventional method;
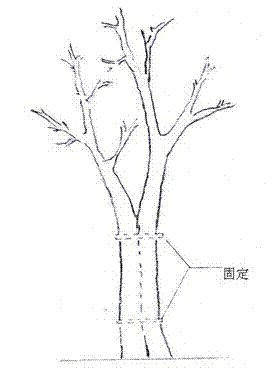
[0052] The third step: the trunks of the above-mentioned 2 seedlings planted obliquely are twisted together, and the bark of the mutual contact position is cut off during twisting, and the cambium is exposed, and fixed ( Figure 3a );
[0053] Step 4: Select a ginkgo sapling with a DBH of about 3-3.5cm and a height of about 3m;
[0054] Step 5: plant the ginkgo seedlings of a single plant closely with the bases of the twisted double plant seedlings and plant them obliquely, and reinforce one of them with bolts; and make the relatively stretched branches approach;
[0055] Step 6: Twist (graft) the ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Three Lianli camphor tree landscaping:
[0060] Step 1: Select 3 large camphor seedlings with a DBH of about 15cm. The trunks of the 3 seedlings have more than 2 main branches that grow well and are easy to connect at an angle of 2-3m. Among them, 2 are slightly larger and 1 is slightly smaller. Keep the above-mentioned main branches and leaves, and trim the branches and leaves according to the conventional method and raise the seedlings;
[0061] Step 2: Dig 3 planting holes according to the design in the planned area, 2 closer and 1 farther away. The two larger seedlings mentioned above are initially implanted in the planting hole with a relatively short distance. The distance between the planting hole is about 2-3m depending on the length of the main branch. The method (thick branches are not easy to twist, so the twisting method cannot be used, the same below) to fix. The other main branch points to the direction of the third seedling to be planted in the same direc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com