Wireless sensor implemented by using radio frequency identification (RFID) tag
A technology of RFID tags and wireless sensors, which is applied in the direction of recording carriers used in machines, instruments, and collaborative work devices, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and restrictions on wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments.
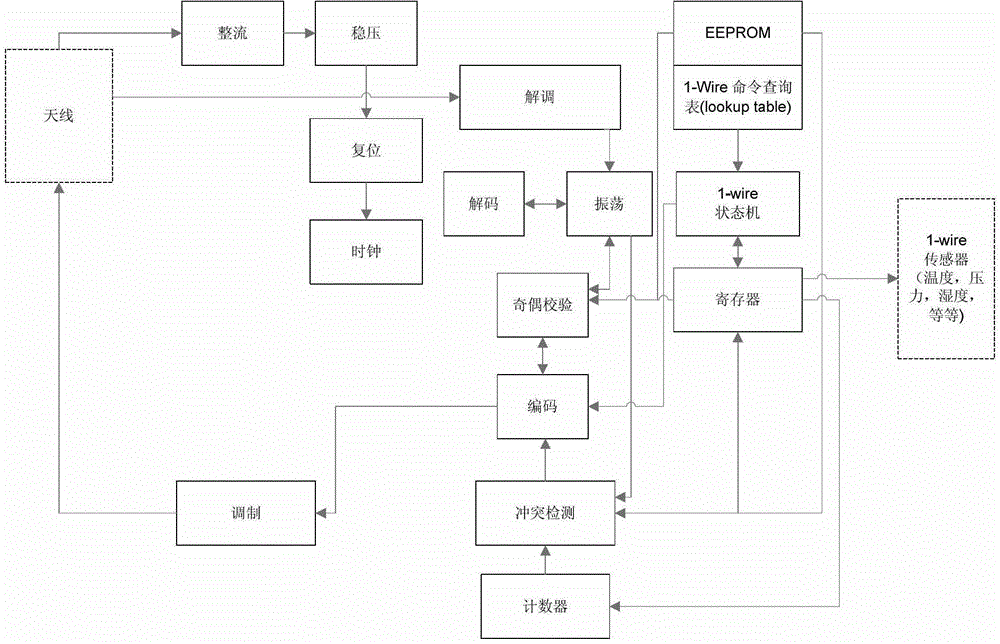
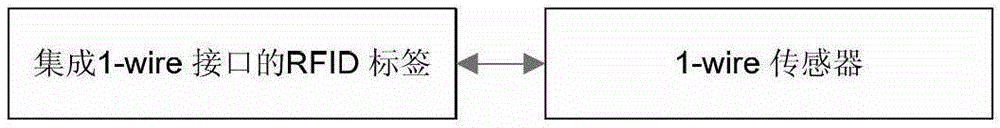
[0024] The present invention adopts far field (far field) very high frequency or RFID technology in microwave frequency band, and the passive tag adopts back scattering to modulate information. Based on the standard RFID tag circuit, make some changes to realize the interface with the 1-wire sensor.
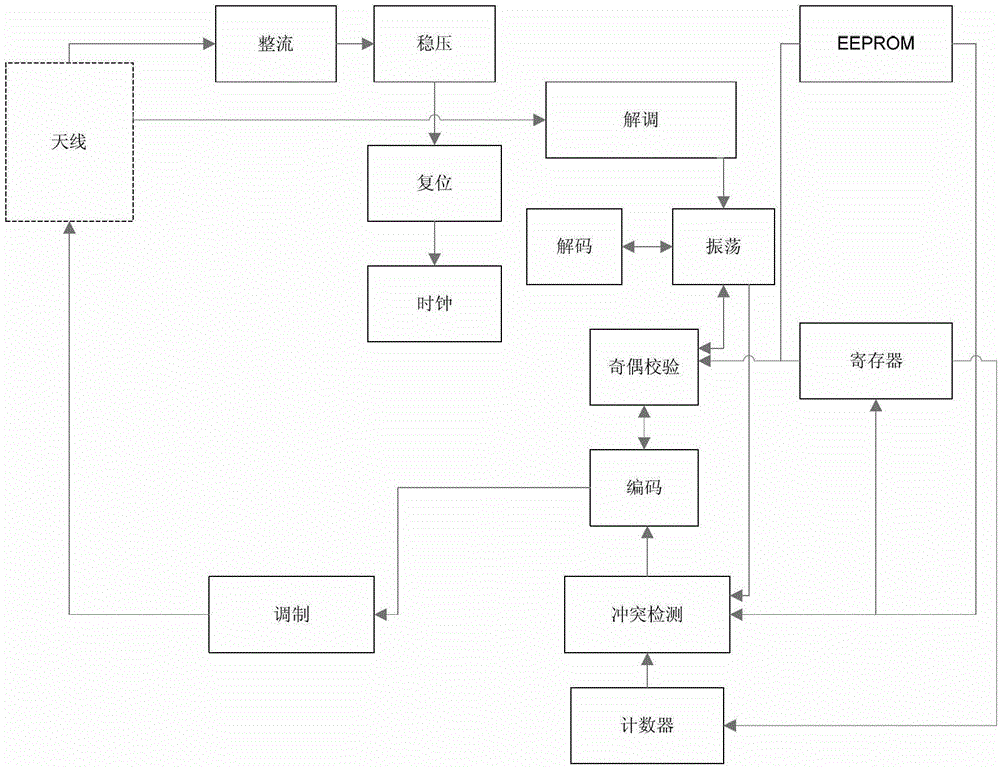
[0025] The RFID tag consists of an antenna, a radio frequency front-end circuit, a signal processing circuit, a conflict detection logic circuit, and an EEPROM. figure 1 It is a block diagram of a typical RFID tag structure.
[0026] The passive tag has no power supply, and its front-end circuit obtains power from the RF signal of the RFID reader, which is composed of rectification, voltage stabilization, reset (generate POR, power-on reset signal) and other circuits. Typically, RFID tag digital circuits consist of thousands of gate circuits, and more advanced RFID tags ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com