Method for eliminating interference during signal sampling
A technology for eliminating signals and sampling values, applied in measurement devices, instruments, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as large system resource consumption, the possibility of obtaining real values, and the sampling signal not being able to truly reflect the state of the monitored signal.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
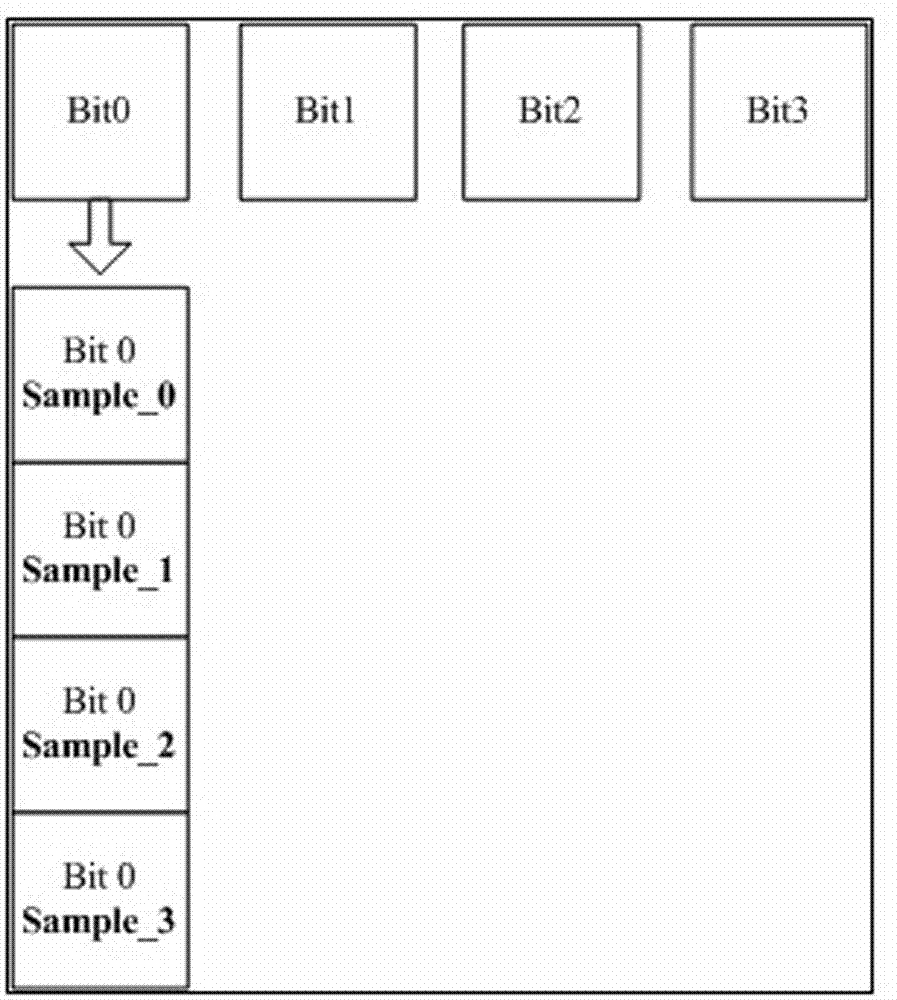
[0015] Refer to the attached figure 1 , the sampled signal Bit0~Bit3, that is, 4 groups of signals are sampled in one sampling period, the sampling register Sample0~3, a group of 4.
[0016] Description of the sampling process:
[0017] 1. Use four consecutive clock cycles, that is, use four consecutive working cycles to complete four samplings of Bit0, and write to Sample0 to Sample3 in sequence.
[0018] 2. Compare the values stored in the four registers Sample0, Sample1, Sample2, and Sample3. If they are the same, determine the value as the sampling value of Bit0. If they are different, the sampling value is invalid and discarded.
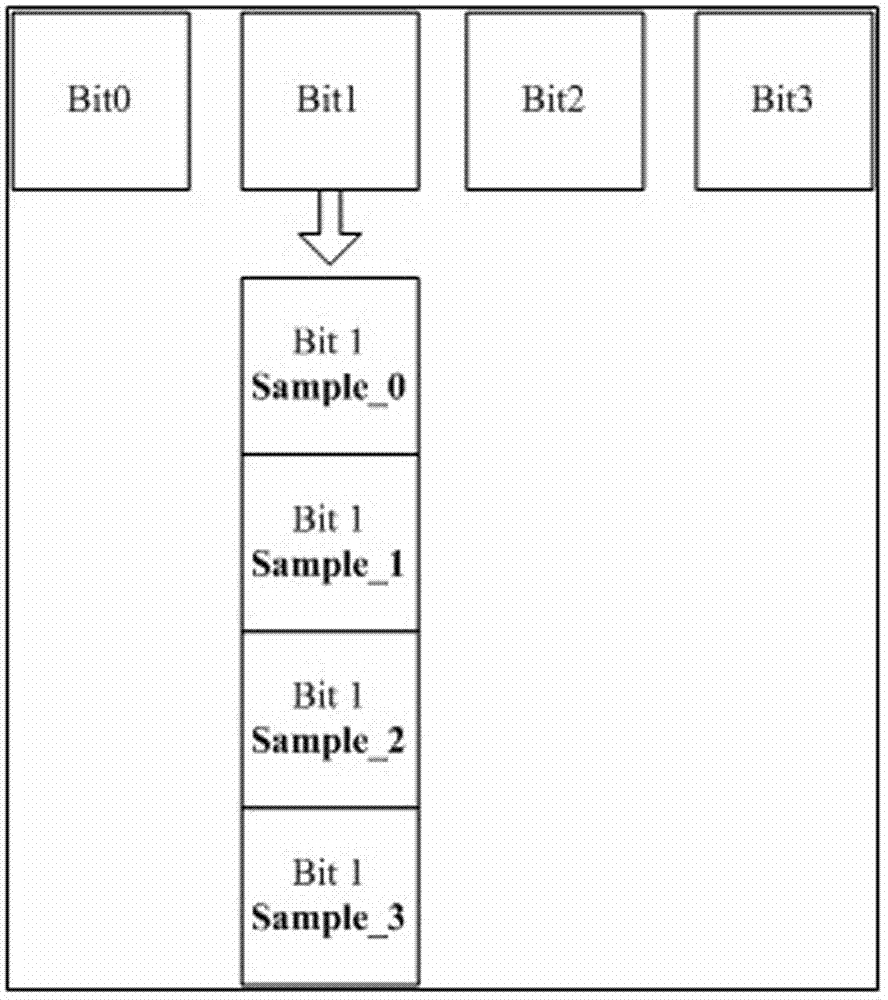
[0019] 3. Sample Bit1 in the next four clocks, and write to Sample0, Sample1, Sample2, and Sample3 in sequence.
[0020] 4. Compare the values stored in the four registers Sample0, Sample1, Sample2, and Sample3. If they are the same, determine the value as the sampling value of Bit1. If they are different, the sampling value is invalid and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com