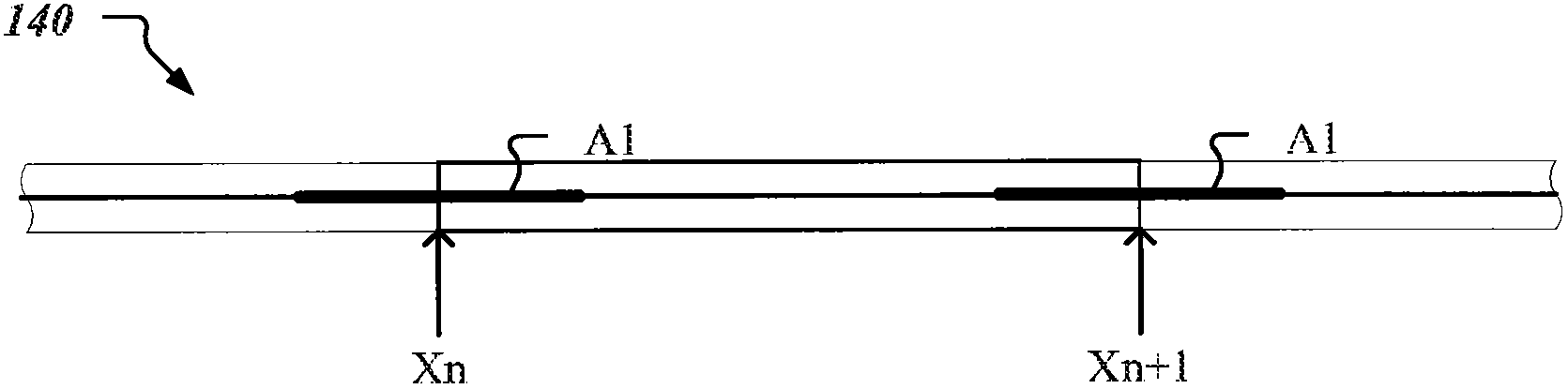Caching based on spatial distribution of accesses to data storage devices
A high-speed cache and space distribution technology, applied in the field of high-speed cache, can solve the problems of limited size of cache memory and limited amount of data, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
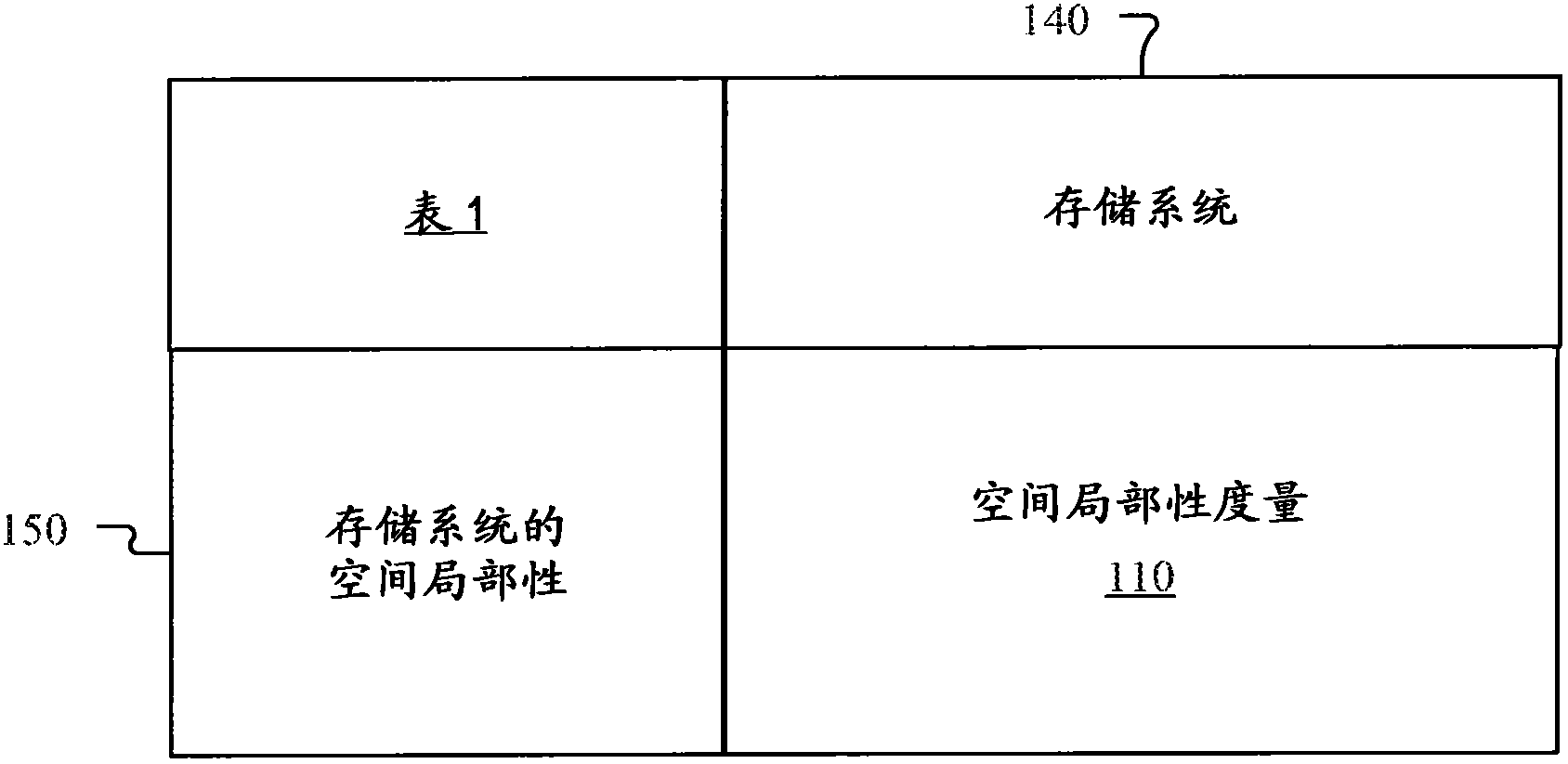
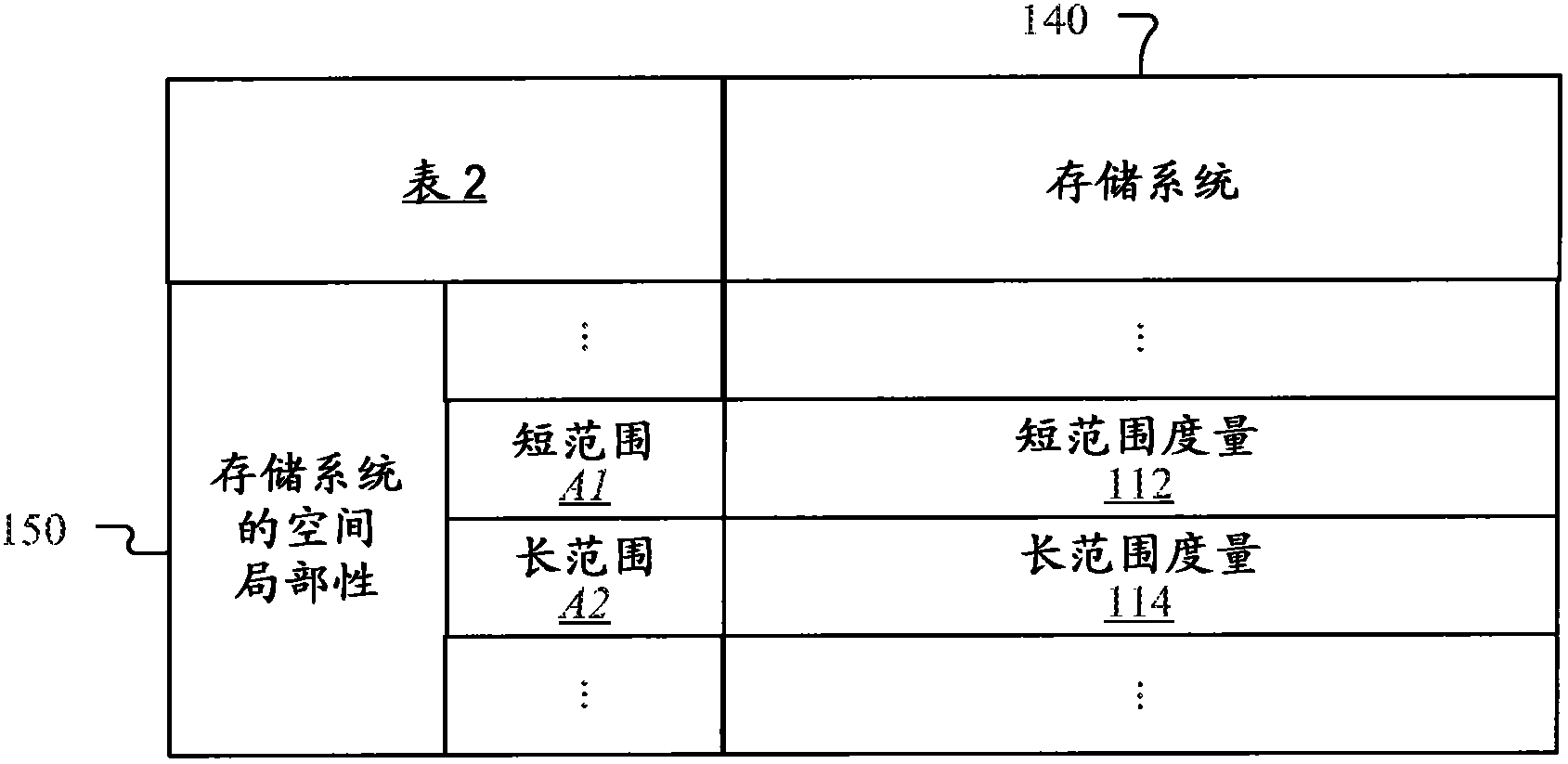
[0027]Caching for storage systems (eg, individual storage devices such as hard drives or combinations of storage devices) by utilizing small, but fast random-access or solid-state (eg, flash) memory has become particularly popular. Most caching systems cache blocks of data when a cache miss occurs when the host references the block for access, but cannot find the referenced block in cache memory. However, the host may not need to use the cached block again. Thus, caching blocks based solely on cache miss occurrences may result in filling cache memory with blocks that the host may not reuse, thus reducing the amount of cache memory available for caching other data that the host may reuse. However, depending on the applications running on the host (eg, Microsoft Exchange, SQL Server, Oracle, etc.), virtual volumes may experience temporal and / or spatial access patterns that may be unique to the respective application. In this way, caches can benefit when there is a reasonably hi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com