Micro-electrolysis reaction technique of iron carbon filler three-phase circulating fluidized bed and reactor
A technology of micro-electrolysis reactor and circulating fluidized bed, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. Carbon fillers are prone to passivation and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
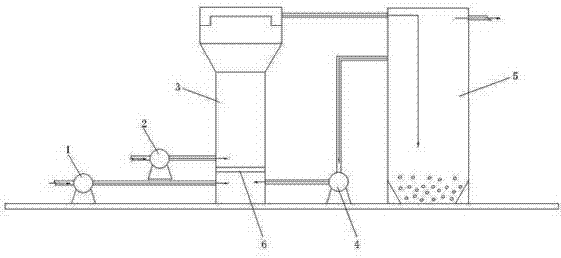
[0052] (a) Waste water enters below the distribution orifice of the fluidized bed, and the iron-carbon filler layer is arranged above the distribution orifice of the fluidized bed;
[0053] (b) Compressed air enters the iron-carbon filler layer at the same time;
[0054] (c) Gradually increase the flow of wastewater, the iron-carbon filler layer forms a fluidized suspension layer, the iron-carbon fillers collide and rub against each other, and the pollutant components in the wastewater undergo micro-electrolysis reactions on the surface of the iron-carbon filler;
[0055] (d) The product of the micro-electrolysis reaction is taken out of the fluidized bed by the wastewater, and then enters the circulation tank for deposition;
[0056] (e) After the waste water deposits and separates the products of the micro-electrolysis reaction in the circulating tank, part of it flows out as produced water, and part of it returns to the fluidized bed as circulating waste water.
[0057] Ex...
Embodiment 2
[0059] (a) The external waste water enters under the distribution orifice of the fluidized bed through the inlet pump and the circulating waste through the circulation pump, and the iron-carbon filler layer is arranged above the distribution orifice of the fluidized bed;
[0060] (b) Compressed air enters the iron-carbon packing layer through the air pump at the same time;
[0061] (c) Gradually increase the flow rate of circulating wastewater. The iron-carbon filler layer forms a fluidized suspension layer. The iron-carbon fillers collide and rub against each other in the fluidized suspension layer. The pollutant components in the wastewater of the fluidized bed are separated from the iron-carbon filler. A micro-electrolysis reaction occurs on the surface;
[0062] (d) The product of the micro-electrolysis reaction is taken out of the fluidized bed by the wastewater, and then enters the circulation tank for deposition;
[0063] (e) After the waste water deposits and separate...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The product of the micro-electrolysis reaction is deposited at the bottom of the circulation tank 5 described in this embodiment and discharged regularly, and the product water flows out from the upper part of the circulation tank 5 .
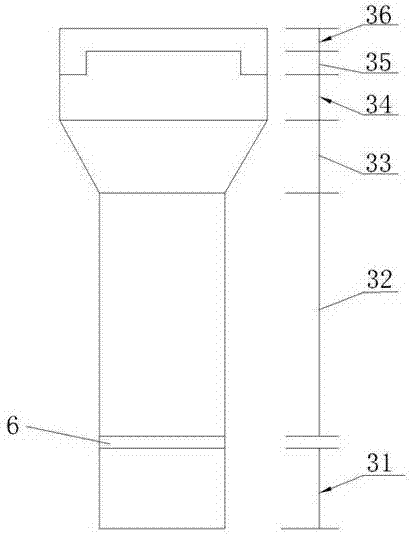
[0072] like figure 2 As shown, the fluidized bed 3 in this embodiment includes a water inlet section 31 , a distribution orifice plate 6 , a packing section 32 , an expanding section 33 , a separation section 34 , a water collection section 35 and a superelevation section 36 from bottom to top. The diameter of the water inlet section 31 and the filler section 32 is D; the height H1=0.5D of the water inlet section 31; the height H2=2D of the filler section 32; the height H3=D of the expansion section 33, The diameter is 1.5D; the height H4 of the separation section 34 = 0.5D; the height H5 of the water collection section 35 = 0.25D; the height H6 of the superelevation section 36 = 0.25D.
[0073] The water inlet section 31 plays the rol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com