Demodulating device and method for optical fiber Young interference optical path difference based on low coherent interference
A low-coherence interference and demodulation device technology, which is applied in the field of optical path difference demodulation method and device, can solve problems such as small measurement range, and achieve the effects of high working stability, high-precision demodulation, and convenient system adjustment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: Optical path difference demodulation device based on low-coherence interference of optical fiber Young's interference
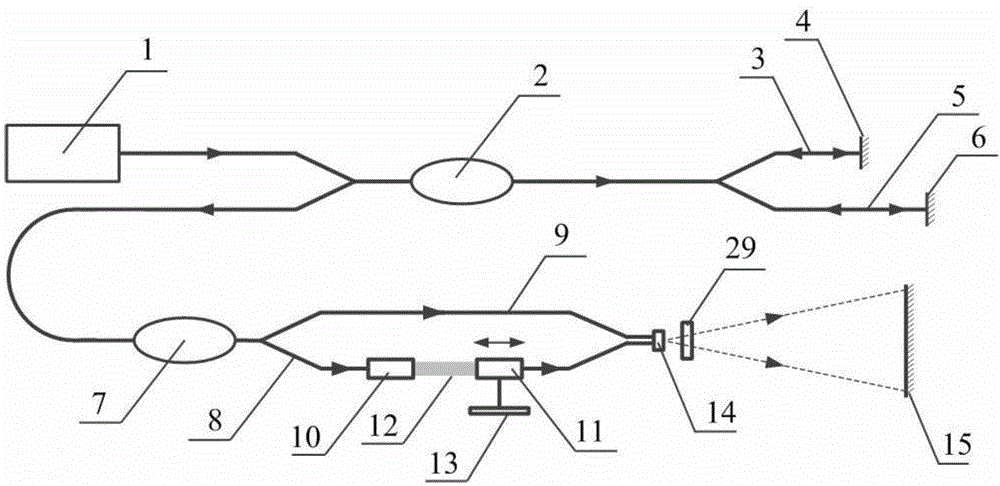
[0036] The system components include broadband light source, 3dB coupler, sensing interferometer, demodulation interferometer, correction interferometer and line array camera. Multimode optical fiber is used for optical signal transmission between the components.
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the light emitted by the broadband light source 1 is divided into two paths of light through the 2×2 3dB coupler 2, and the two paths of light pass through the No. 1 arm 3 and the No. After the reflective end face 4 of the No. arm and the reflective end face 6 of the No. 2 arm are reflected back, a beam of light is synthesized through the 2×2 3dB coupler 2 again, and transmitted to the 2×1 3dB coupler 7; the 2×1 3dB coupler 7 again The light is divided into two paths, passing through the No. 1 arm 8 and the No. 2 arm 9 of the Mach-Zehnder inte...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Fiber Young's interference optical path difference sensing method based on low coherence interference
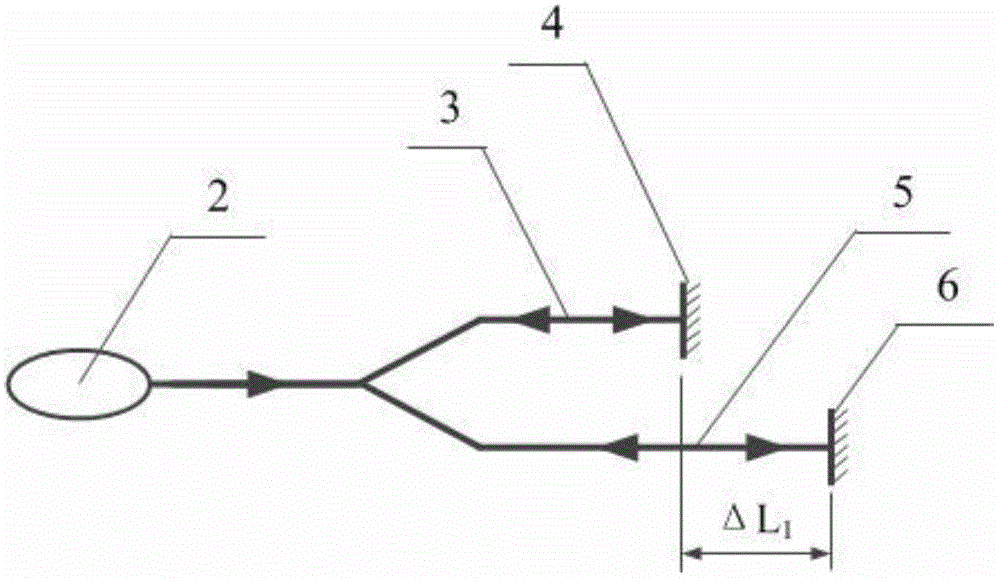
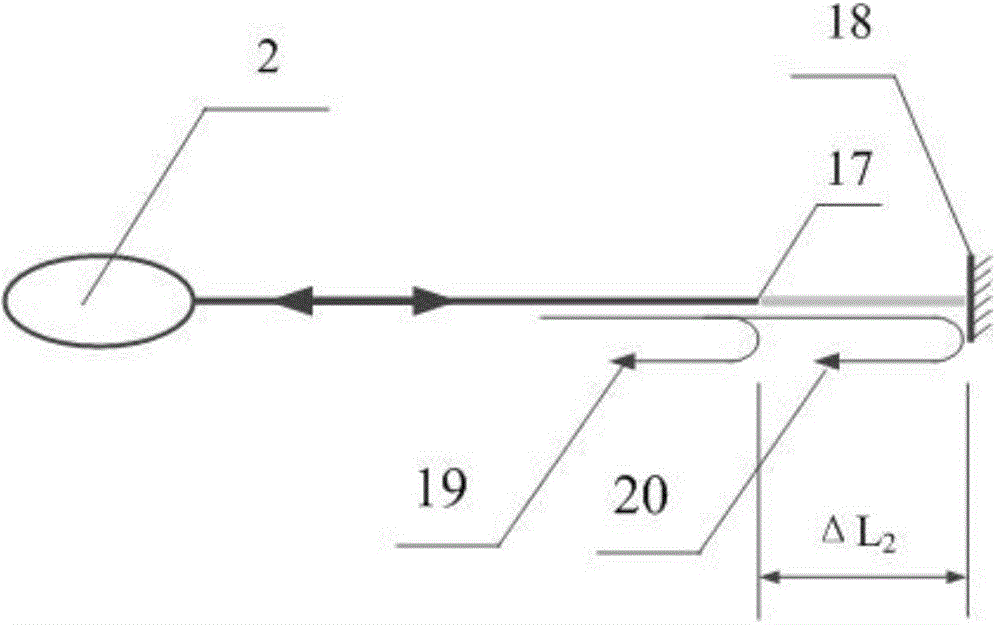
[0046] Optical path difference sensing method based on fiber optic Michelson interferometer such as figure 2 As shown, the 2×2 3dB coupler 2 divides the light into two paths, which are respectively input to the first arm 3 and the second arm 5 of the Michelson interferometer, and after being reflected on the end faces of the two arms, they are recombined into one beam of light. , due to the difference in the length of the two arms, the optical signal contains 2ΔL 1 The optical path difference information, changing the length of one of the arms, that is, changing the optical path difference sensing amount. In addition to the fiber-optic Michelson interferometer, the fiber-Perkin interferometer is also applicable, such as image 3 As shown: the light transmitted along the optical fiber is partially reflected at the end face 17 of the optical fiber to form ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: Fiber Young's interference optical path difference demodulation method based on low coherence interference
[0048] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the distance between the ends of the two optical fibers of the optical fiber Young's interferometer is d, the distance between the end face of the optical fiber and the line array camera is D, and the two beams of light are output to the light overlapping area 16 of the line array camera 15 to produce the final interference fringes, and are determined by the line Array camera 15 receives. Under the condition that d is much smaller than D, the optical path difference is linearly distributed in the light overlapping area 16, satisfying the formula: Δ=xd / D, where x represents the position. Then the normalized light intensity of the demodulated low-coherence interference fringes can be expressed as:
[0049] I ( λ , x ) =...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com