Multicomponent alloy sealing-in material
A technology of sealing materials and multi-element alloys, which is applied in the field of silver and copper, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory effects, unsatisfactory air tightness, insufficient anti-oxidation and anti-corrosion performance, etc., so as to reduce volatilization and proportioning components Precise, melting point depressing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] (1) Put Cu, Co, and Ni in a vacuum melting furnace, evacuate the furnace to 1Pa, heat to 1350°C, and then cool to room temperature to make a copper-cobalt-nickel master alloy;
[0018] (2) Put the copper-cobalt-nickel master alloy together with Ag, Ge, Nd, and Yb components into a vacuum melting furnace, evacuate to 0.4Pa, and heat to 1300°C; after it forms a melt, cool down to 1000°C, Pour the molten liquid into the shaping mold, and after the temperature drops to room temperature, take the shaping mold out of the vacuum furnace to obtain the ingot required for processing the sealing material;
[0019] (3) When the ingot is rolled to a thickness of 1~2mm by a rough rolling mill, it is coiled and placed in a heat treatment furnace, and the temperature is raised to 700°C for 2 hours, then lowered to room temperature, and then rolled to a thickness of 0.03~0.2mm by a finishing mill , trimmed and stamped to the desired shape.
Embodiment 2
[0021] (1) Put Cu, Co, and Ni in a vacuum melting furnace, evacuate the furnace to 0.5Pa, heat to 1200°C, and then cool to room temperature to make a copper-cobalt-nickel master alloy;
[0022] (2) Put the copper-cobalt-nickel master alloy together with Ag, Ge, Nd, and Yb components into a vacuum melting furnace, evacuate to 0.2Pa, and heat to 1100°C; after it forms a molten liquid, cool down to 900°C, Pour the molten liquid into the shaping mold, and after the temperature drops to room temperature, take the shaping mold out of the vacuum furnace to obtain the ingot required for processing the sealing material;
[0023] (3) When the ingot is rolled to a thickness of 1~2mm by a rough rolling mill, it is coiled and placed in a heat treatment furnace, and the temperature is raised to 600°C for 5 hours, then lowered to room temperature, and then rolled to a thickness of 0.03~0.2mm by a finishing mill , trimmed and stamped to the desired shape.
Embodiment 3
[0025] (1) Put Cu, Co, and Ni in a vacuum melting furnace, evacuate the furnace to 0.1Pa, heat to 1280°C, and then cool to room temperature to make a copper-cobalt-nickel master alloy;
[0026] (2) Put the copper-cobalt-nickel master alloy together with Ag, Ge, Nd, and Yb components into a vacuum melting furnace, evacuate to 0.04Pa, and heat to 1200°C; after it forms a molten liquid, cool down to 950°C, Pour the molten liquid into the shaping mold, and after the temperature drops to room temperature, take the shaping mold out of the vacuum furnace to obtain the ingot required for processing the sealing material;
[0027] (3) When the ingot is rolled to a thickness of 1~2mm by a rough rolling mill, it is coiled and placed in a heat treatment furnace, and the temperature is raised to 650°C for 4 hours, then lowered to room temperature, and then rolled to a thickness of 0.03~0.2mm by a finishing mill , trimmed and stamped to the desired shape.
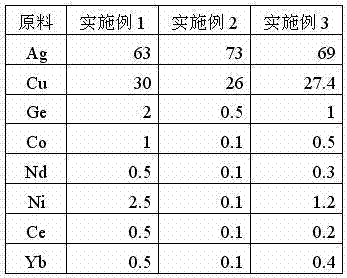
[0028] The quality of each raw ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com