Human monoclonal antibodies to programmed death 1 (pd-1) and methods for treating cancer using anti-pd-1 antibodies alone or in combination with other immunotherapeutics
A monoclonal antibody, PD-1 technology, applied in the direction of using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, antibody medical components, antibodies, etc., can solve problems such as lack of MYPPPY motifs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0788] Example 1: Generation of human monoclonal antibodies against PD-1
[0789] antigen
[0790] The immunization protocol utilizes as antigens both (i) a recombinant fusion protein comprising the extracellular portion of PD-1, and (ii) membrane-bound full-length PD-1. Both antigens were produced in CHO cell lines by recombinant transfection methods.
[0791] Transgenic HuMab and KM mice TM
[0792] Fully human monoclonal antibodies against PD-1 were prepared using the HCo7 strain of HuMab transgenic mice and the KM strain of transgenic transchromosomal mice, both of which express human antibody genes. In each of these mouse strains, the endogenous mouse kappa light chain gene has been homozygously disrupted as described in Chen et al. (1993) EMBO J. 12:811-820, and as described in PCT Publication WO01 The homozygosity described in Example 1 of / 09187 disrupts the endogenous mouse heavy chain gene. Each of these mouse lines carried the human kappa light chain transg...
Embodiment 2
[0801] Example 2: Structural characterization of human monoclonal antibodies 17D8, 2D3, 4H1, 5C4, 4A11, 7D3 and 5F4
[0802] DNA encoding the heavy and light chain variable regions of the 17D8, 2D3, 4H1, 5C4, 4A11, 7D3, and 5F4 monoclonal antibodies were obtained from 17D8, 2D3, 4H1, 5C4, 4A11, 7D3, and 5F4 hybridomas, respectively, using standard PCR techniques. cDNA sequences and were sequenced using standard DNA sequencing techniques.
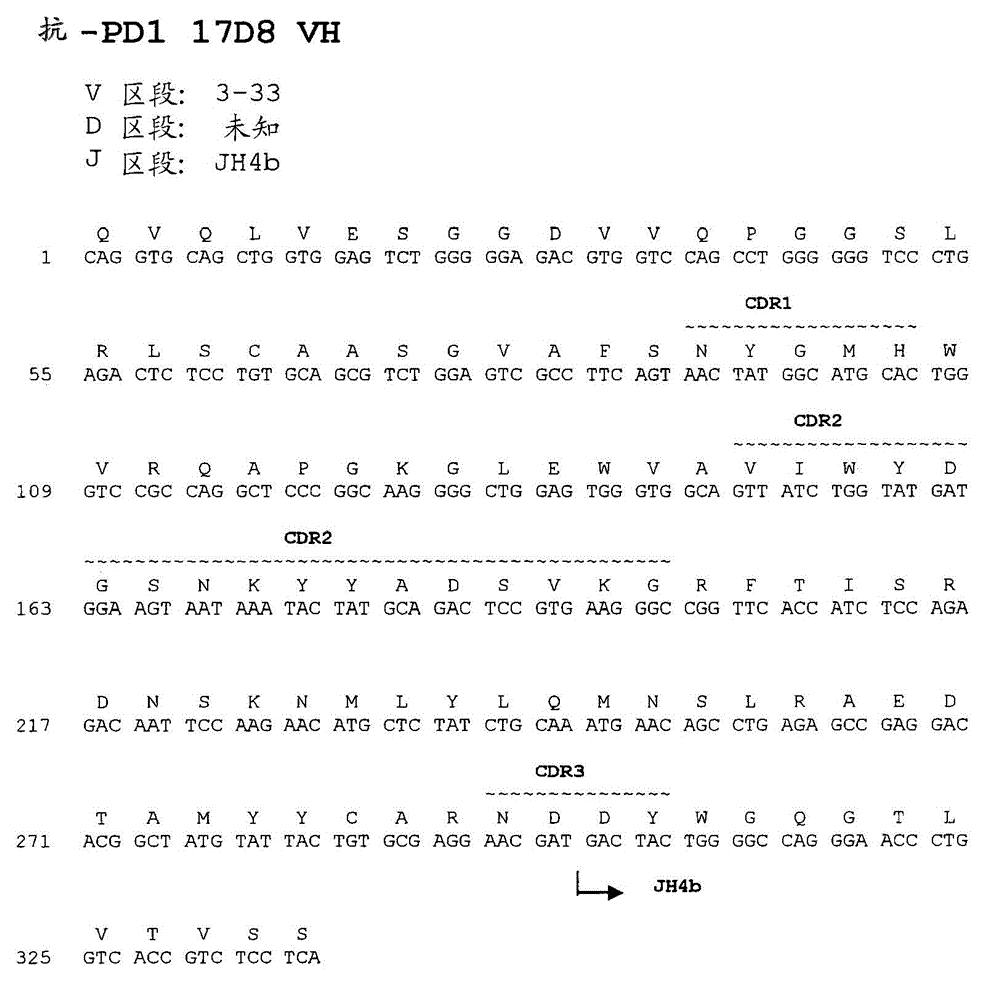
[0803] The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the heavy chain variable region of 17D8 are shown in Figure 1A and SEQ ID NO:57 and 1.
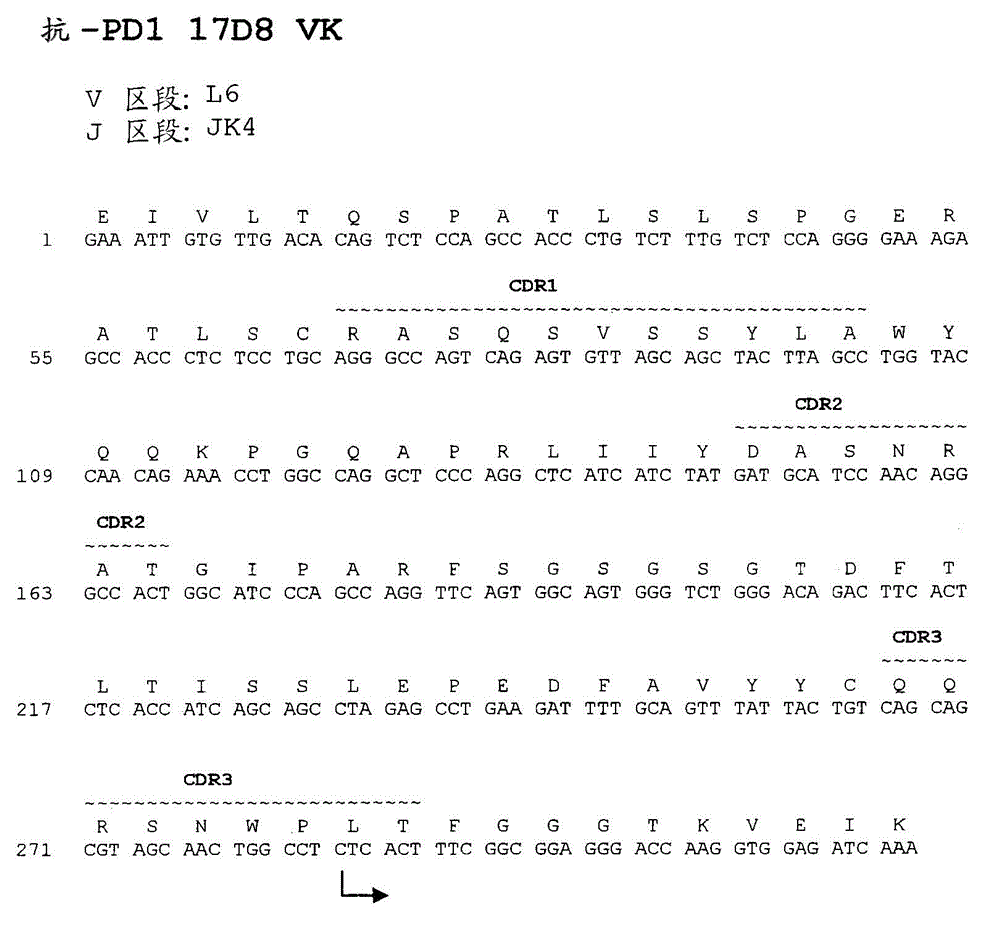
[0804] The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the light chain variable region of 17D8 are shown in Figure 1B and SEQ ID NO:64 and 8.
[0805] Comparison of the 17D8 heavy chain immunoglobulin sequence with known human germline immunoglobulin heavy chain sequences indicates that the 17D8 heavy chain utilizes a VH segment from human germline VH3-33, an undetermined D segment, and a human germline JH...
Embodiment 3
[0831] Example 3: Characterization of Binding Specificity and Binding Kinetics of Anti-PD-1 Human Monoclonal Antibodies
[0832] In this example, the binding affinity and binding kinetics of anti-PD-1 antibodies were examined by Biacore analysis. Binding specificity and cross-competition were examined by flow cytometry.
[0833] Binding affinity and kinetics
[0834] Anti-PD-1 antibodies were characterized for affinity and binding kinetics by Biacore analysis (Biacore AB, Uppsala, Sweden). Purified recombinant human PD-1 fusion protein was covalently attached to a CM5 chip (carboxymethyl dextran-coated chip) via a primary amine using standard amine coupling chemistry and kits provided by Biacore. Binding was measured by flowing the antibody in HBS EP buffer (provided by Biacore AB) at a concentration of 267 nM at a flow rate of 50 μl / min. Antigen-antibody binding kinetics were followed for 3 minutes and dissociation kinetics were followed for 7 minutes. Association and d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com