Imaging lens assembly
A lens system and imaging technology, applied in optics, instruments, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing lens cost, long optical total length, difficult assembly, etc., and achieve the goals of reducing sensitivity, short optical total length, and shortening the back focal length Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
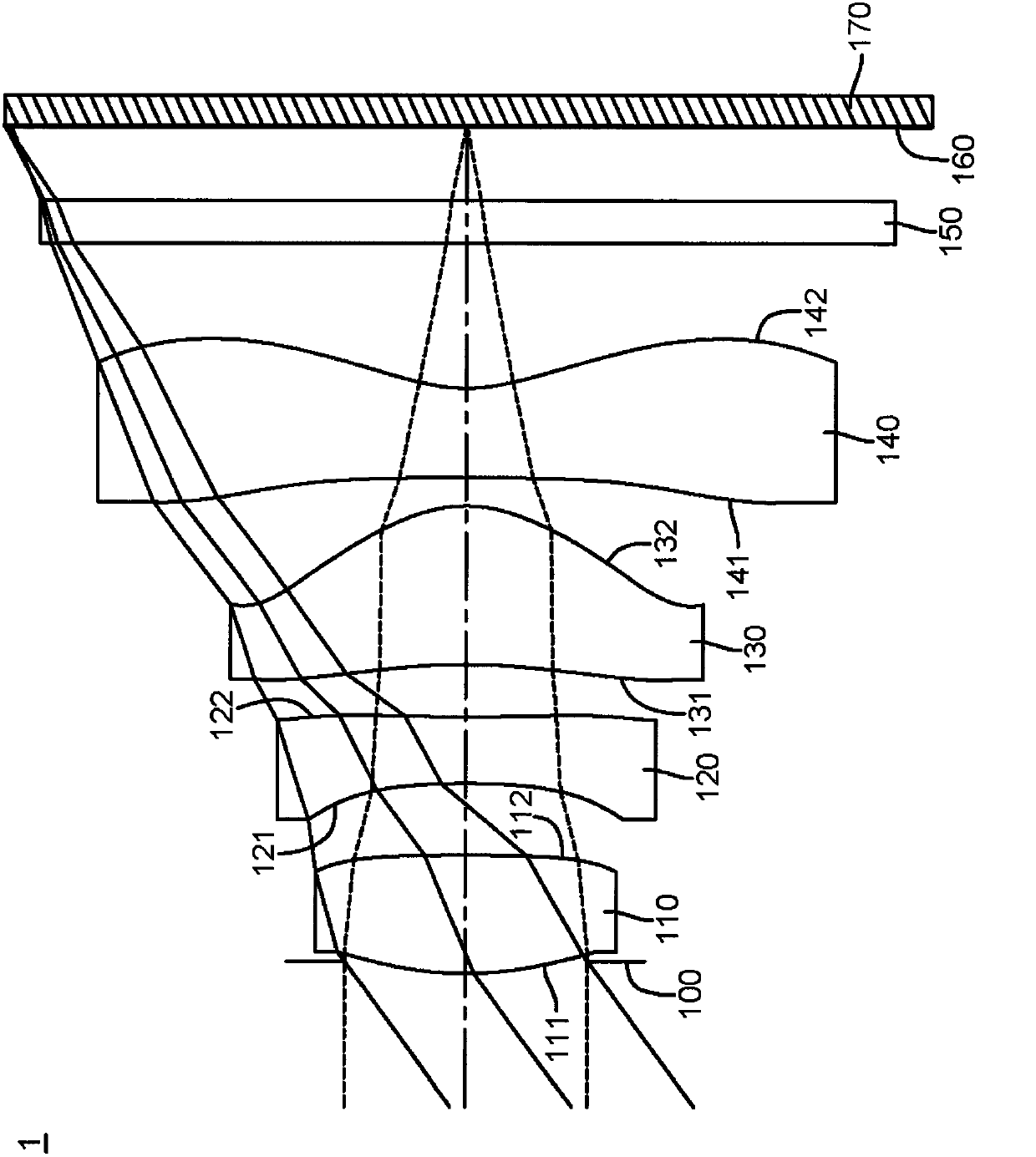
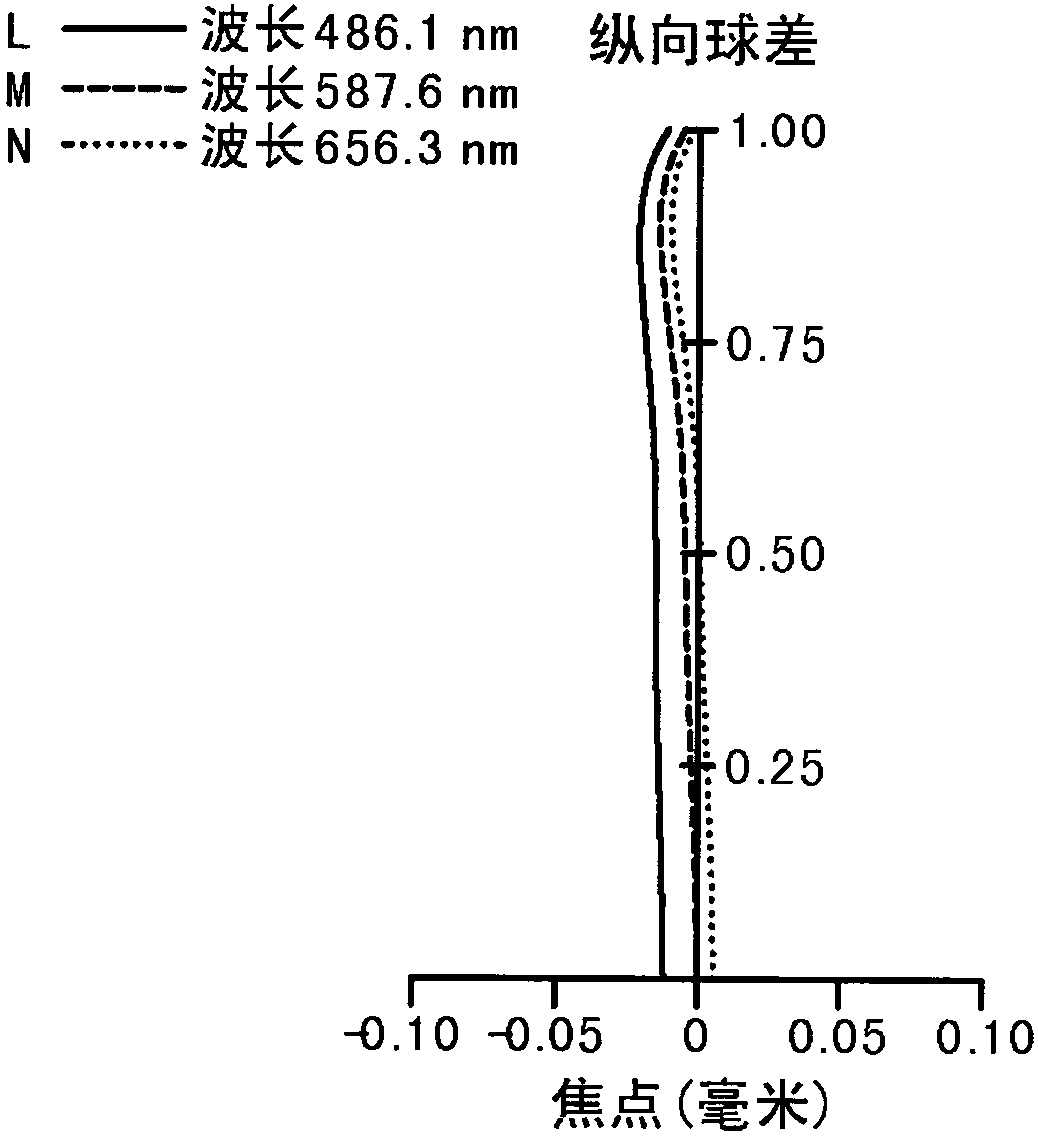
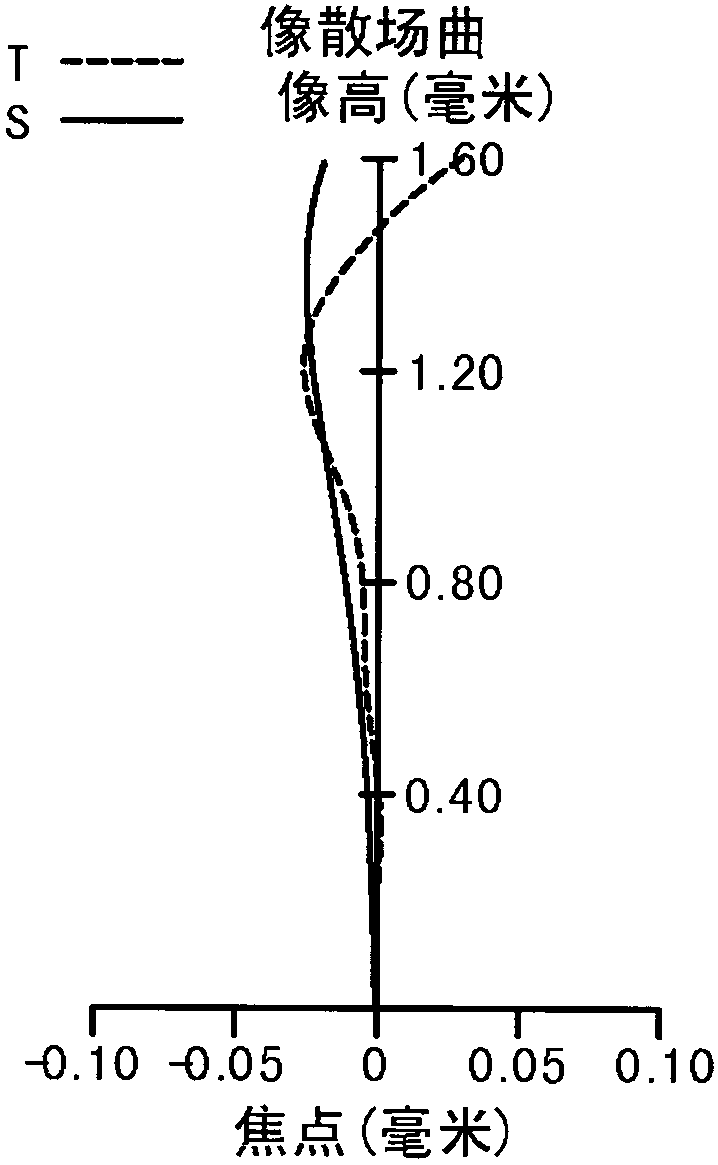
[0105] Please refer to Figure 1A Shown is a schematic structural diagram of the first embodiment of the imaging lens system. The imaging lens system 1 is from the object side to the image side (that is, along Figure 1A from the left side to the right side) sequentially includes an aperture 100, a first lens 110, a second lens 120, a third lens 130, a fourth lens 140, an infrared filter filter 150 and an image sensor The sensing element 170 is disposed on an imaging surface 160 .
[0106] In this embodiment, the wavelength of light received by the imaging lens system 1 is 587.6 nanometers (nm) as an example, however, the above wavelength can be adjusted according to actual needs, and is not limited to the above wavelength value.
[0107] In this embodiment, the first lens 110 has positive refractive power, the second lens 120 has negative refractive power, the third lens 130 has positive refractive power, and the fourth lens 140 has negative refractive power. Wherein, both t...
no. 2 example
[0125] Please refer to Figure 2A As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of the second embodiment of the imaging lens system disclosed in the present invention. Its specific implementation is substantially the same as the aforementioned first embodiment, which means that it has the same function or structure. To simplify the description, only the differences will be described below, and the rest of the similarities will not be repeated.
[0126] In this embodiment, the first lens 210 has positive refractive power, the second lens 220 has negative refractive power, the third lens 230 has positive refractive power, and the fourth lens 240 has negative refractive power. Wherein, the first lens object side surface 211 is an aspheric convex surface, and the first lens image side surface 212 is an aspheric concave surface. Both the second lens object side 221 and the second lens image side 222 are aspherical concave surfaces. The third lens object side surface 231 is an as...
no. 3 example
[0139] Please refer to Figure 3A Shown is a schematic structural view of the third embodiment of the imaging lens system disclosed in the present invention. Its specific implementation is substantially the same as the aforementioned first embodiment, which means that it has the same function or structure. To simplify the description, only the differences will be described below, and the rest of the similarities will not be repeated.
[0140] In this embodiment, the first lens 310 has positive refractive power, the second lens 320 has negative refractive power, the third lens 330 has positive refractive power, and the fourth lens 340 has negative refractive power. Wherein, both the first lens object side surface 311 and the first lens image side surface 312 are aspherical convex surfaces. Both the second lens object side 321 and the second lens image side 322 are aspherical concave surfaces. The third lens object side surface 331 is an aspherical concave surface, and the thi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com