Patents
Literature
190 results about "Lens thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
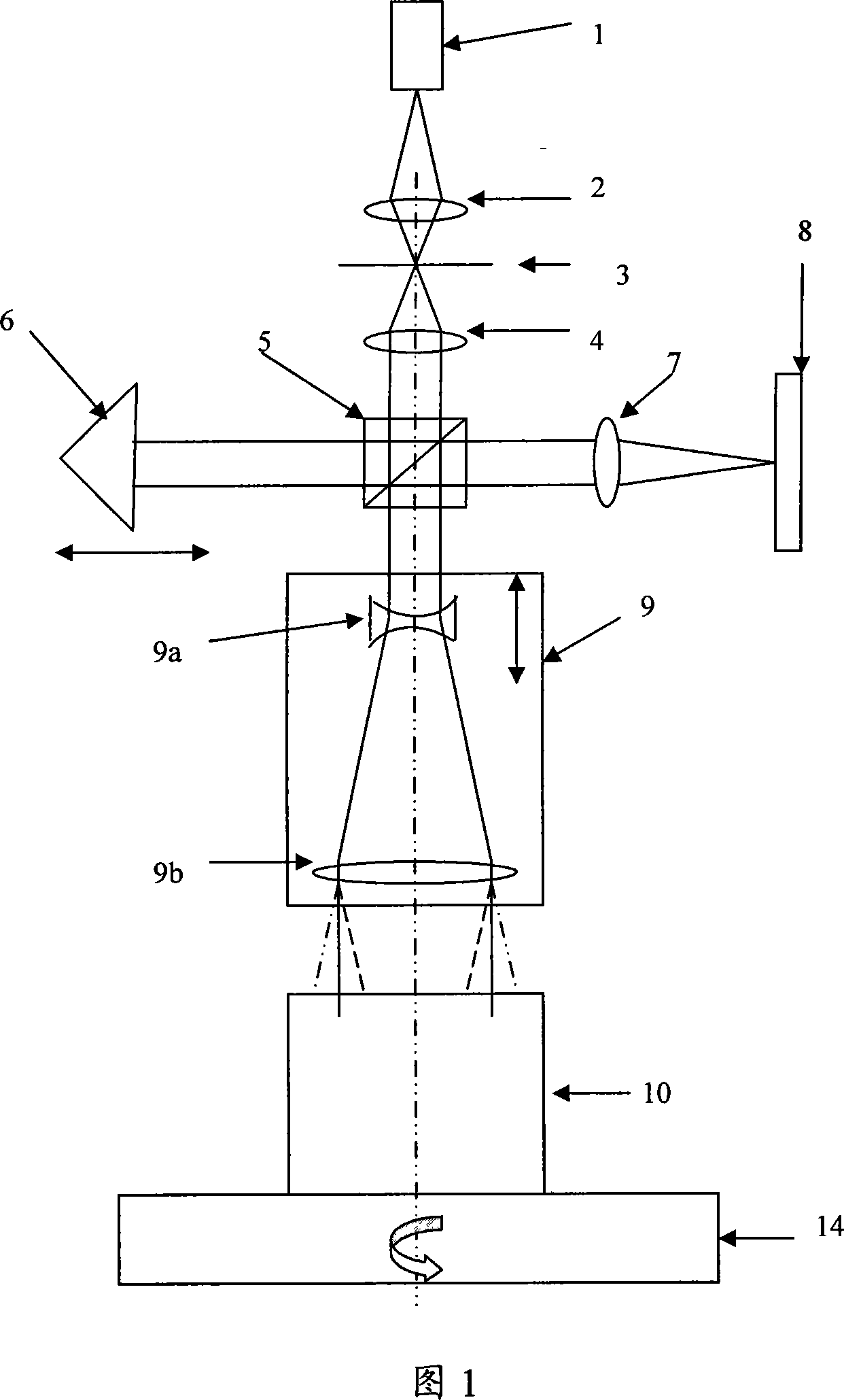
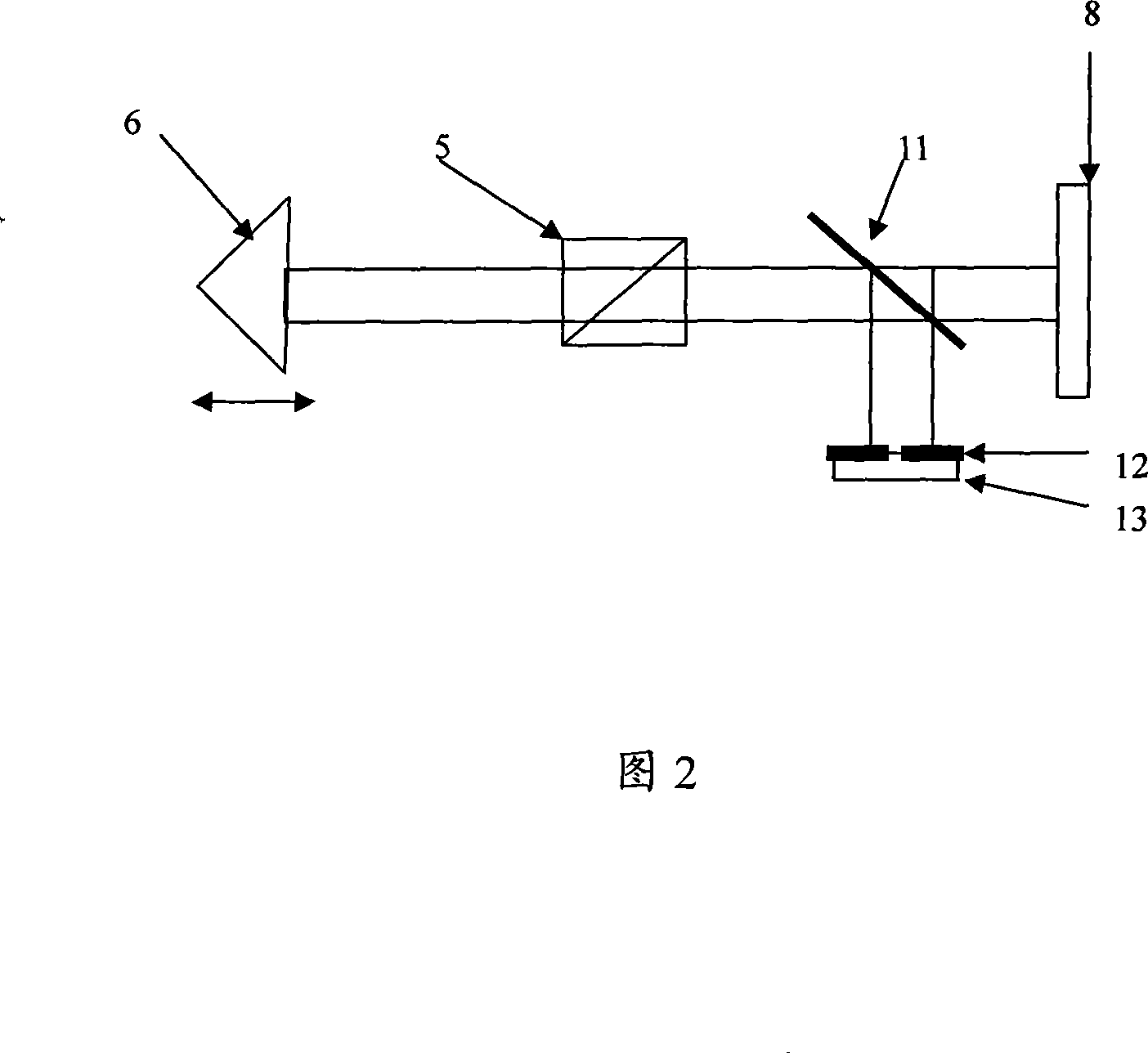
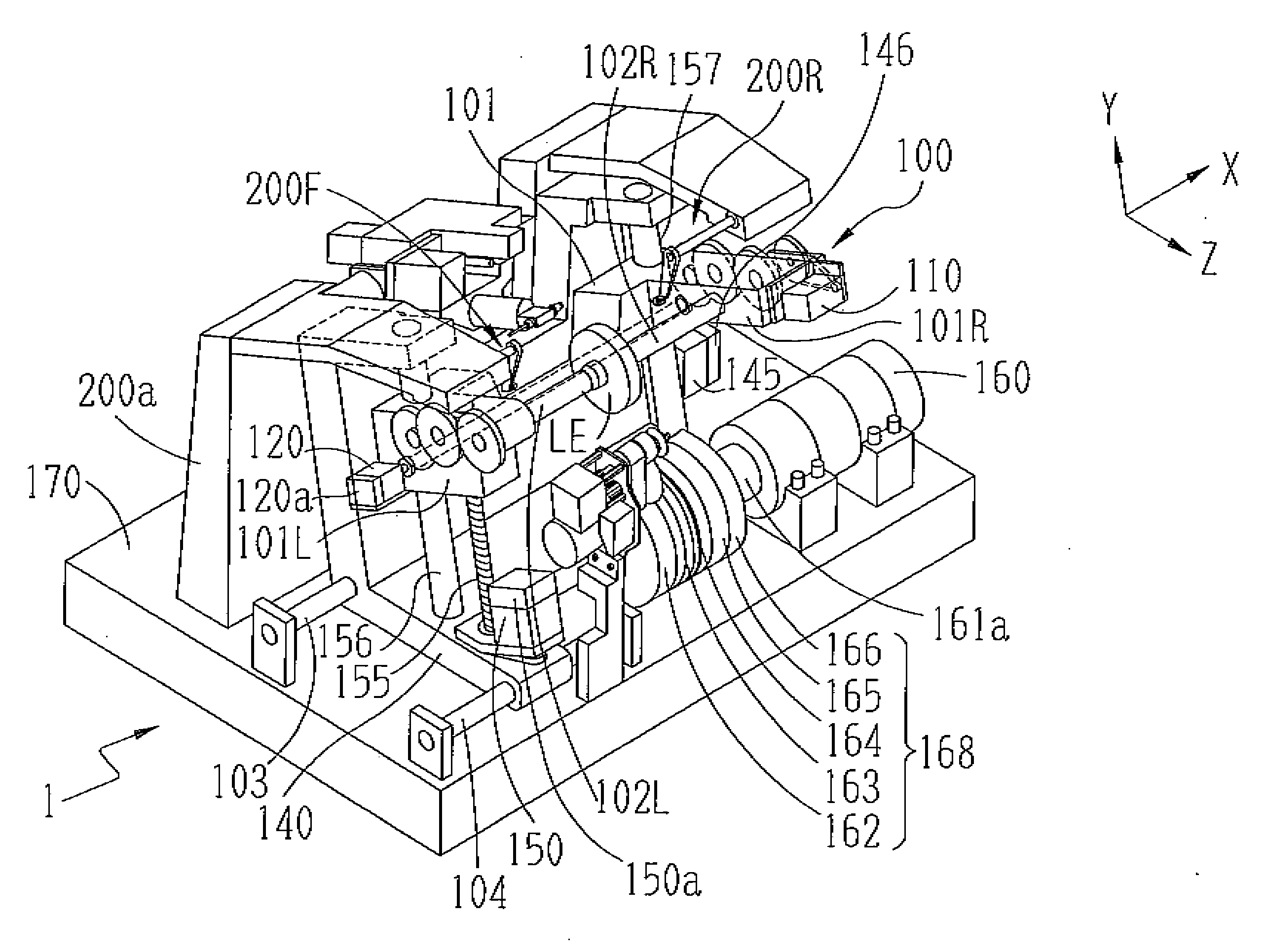
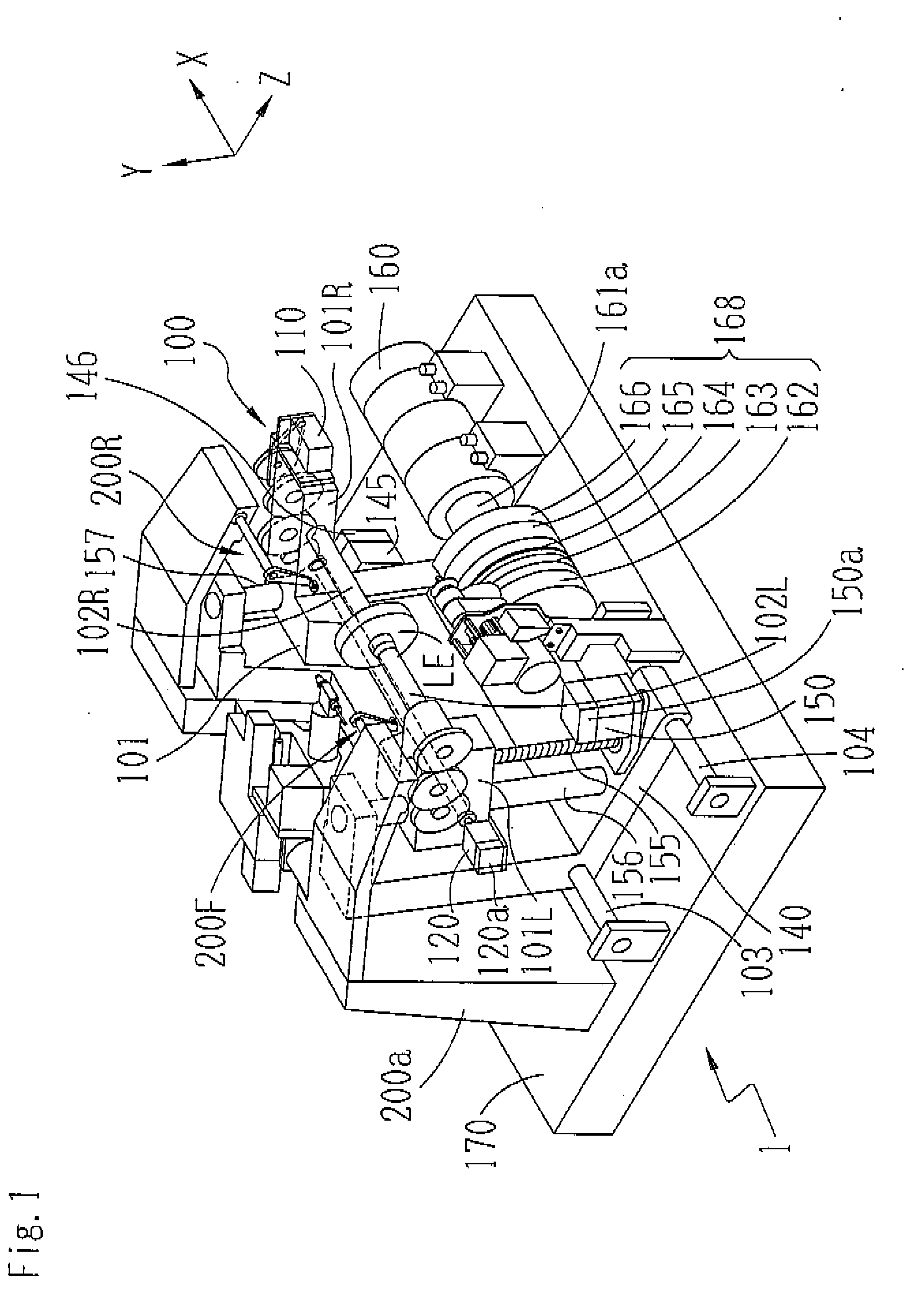
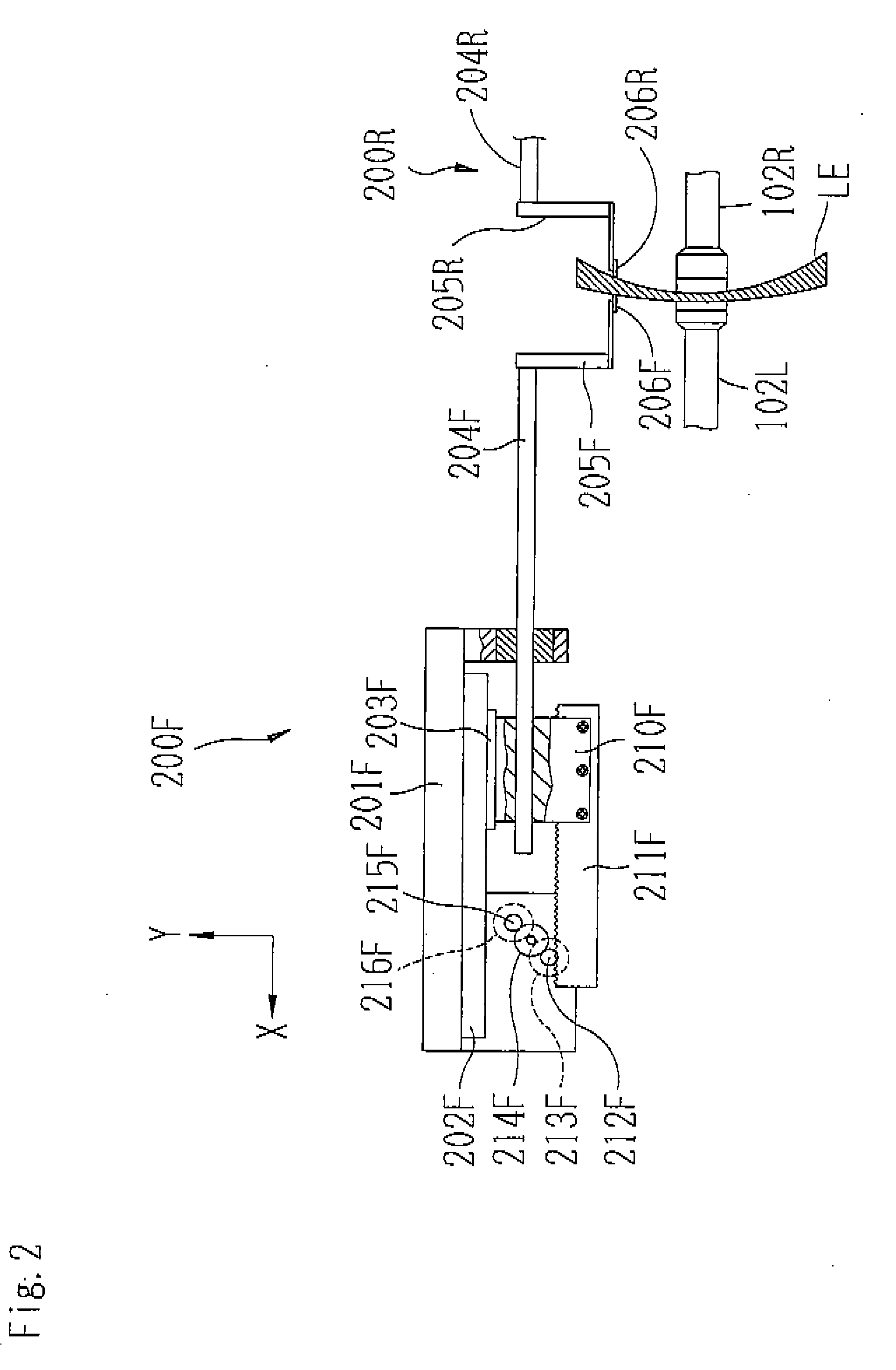
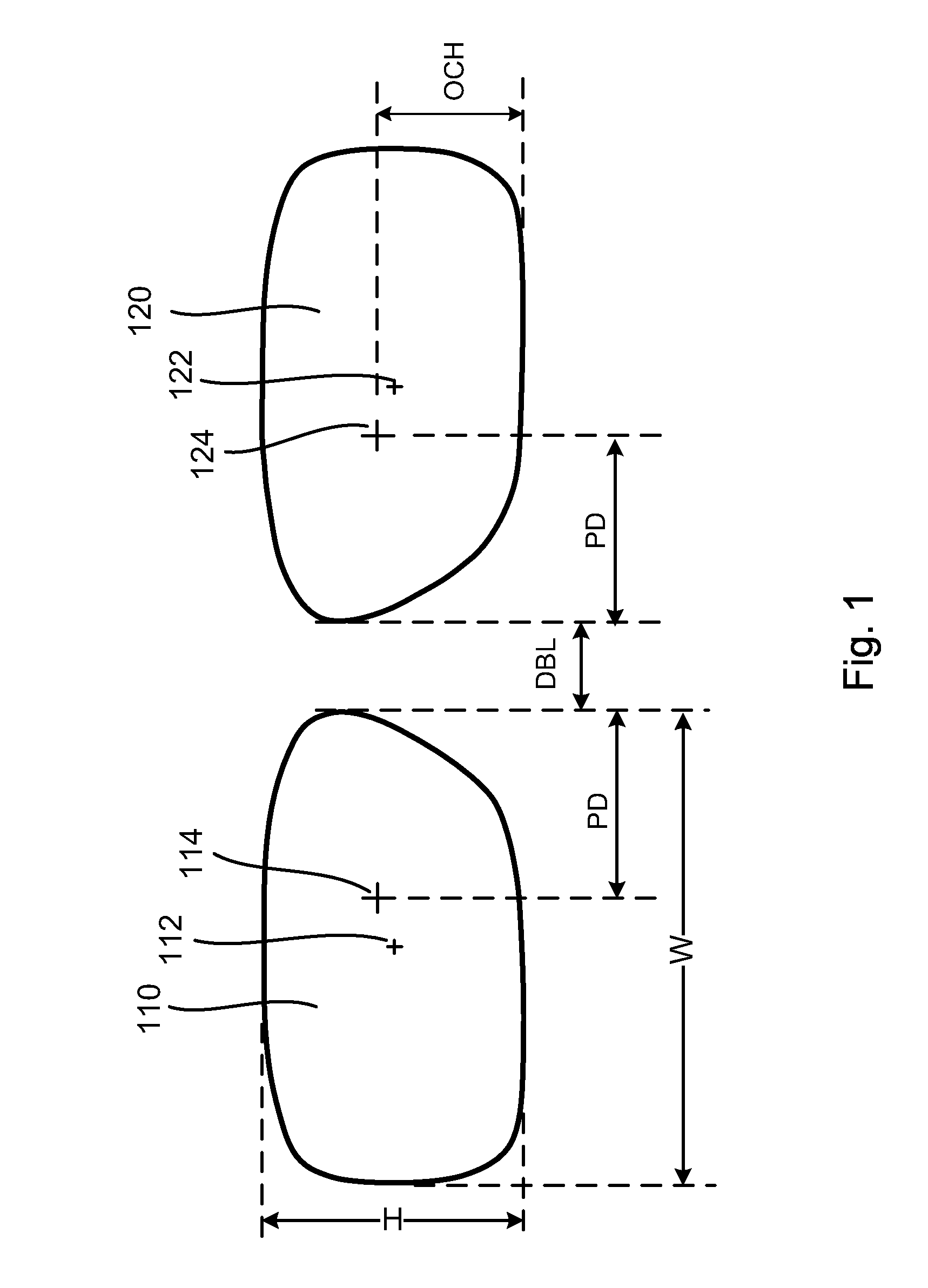
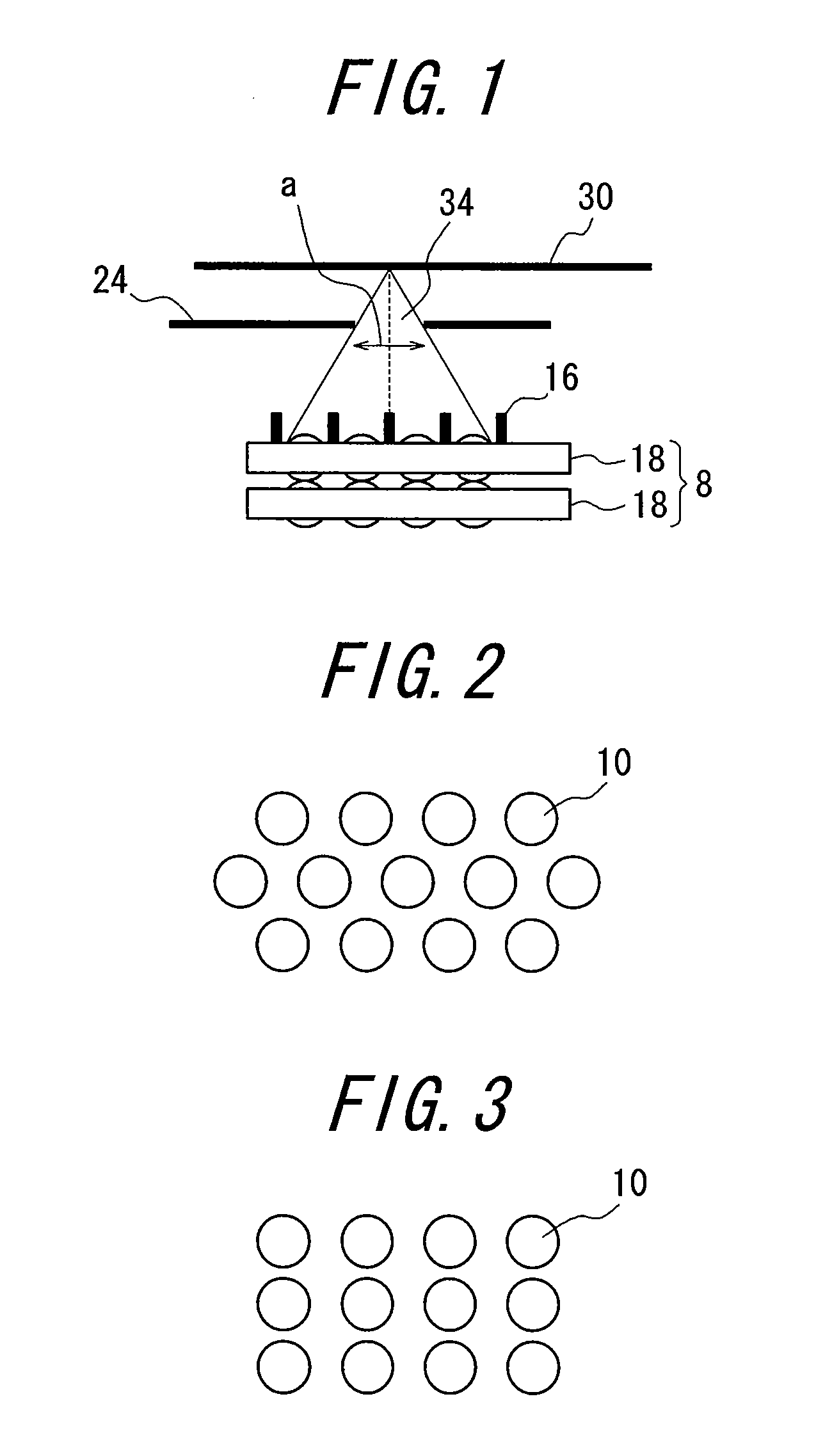
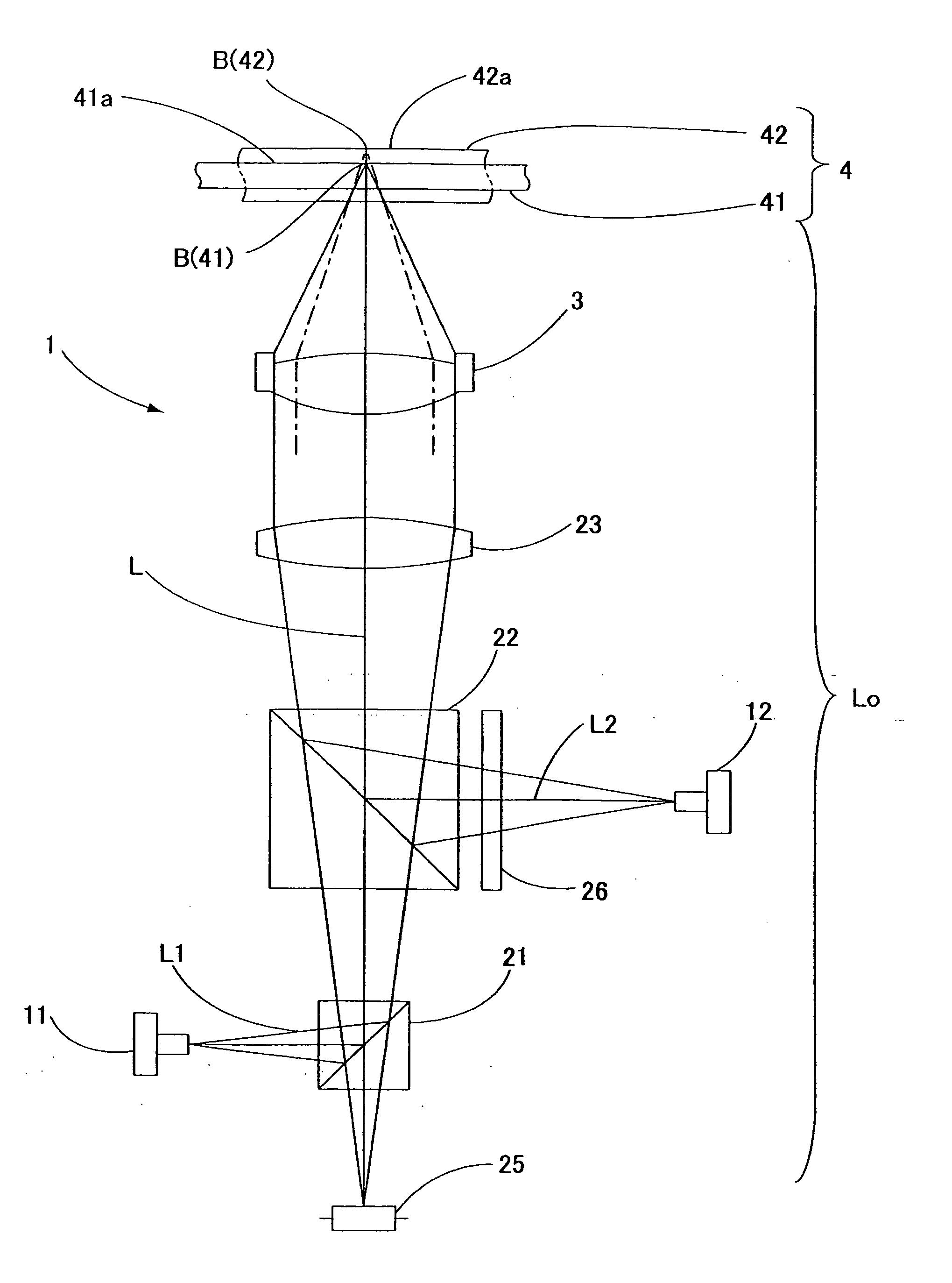
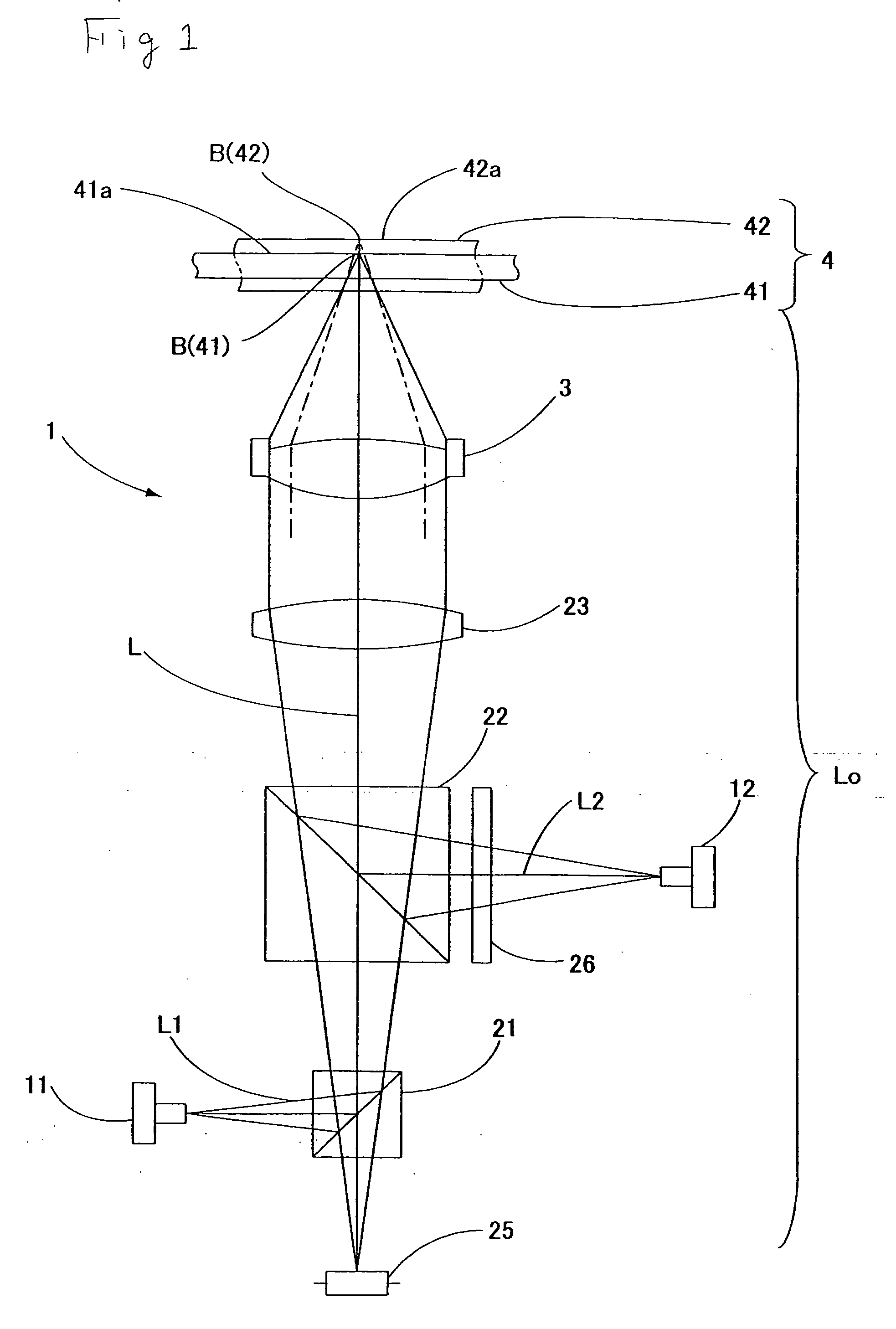
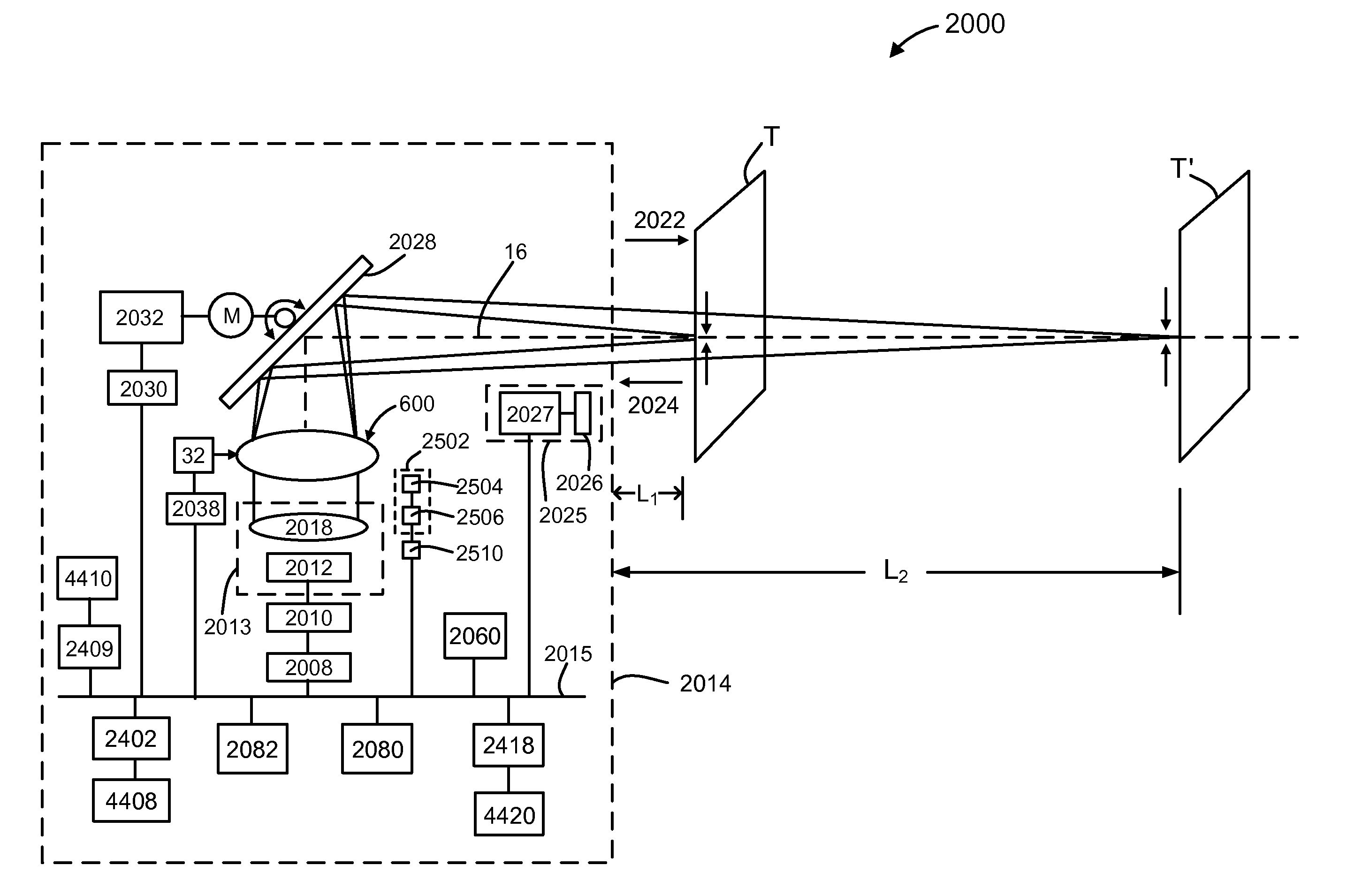
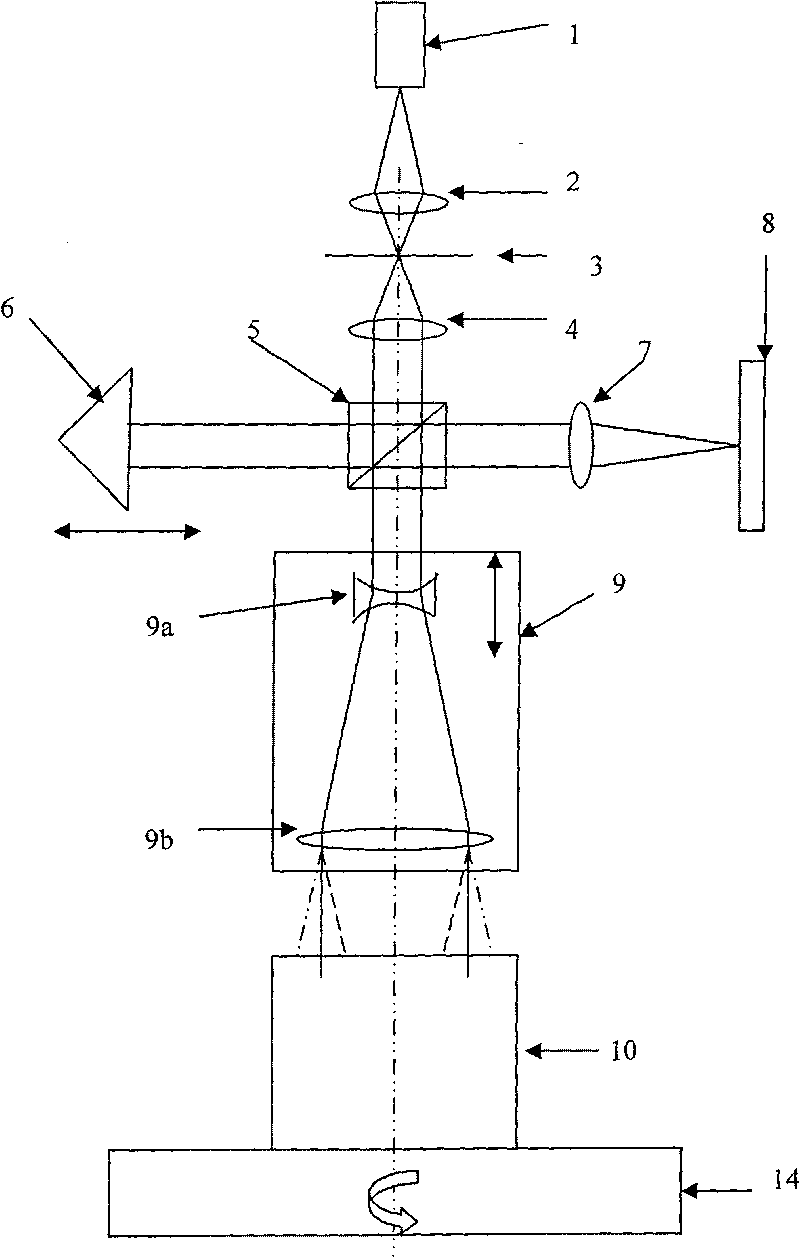
Apparatus and method for measuring optical system parameter
ActiveCN101226344AImprove the accuracy of eccentricity detectionAchieve final measurementUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMeasurement deviceMobile station
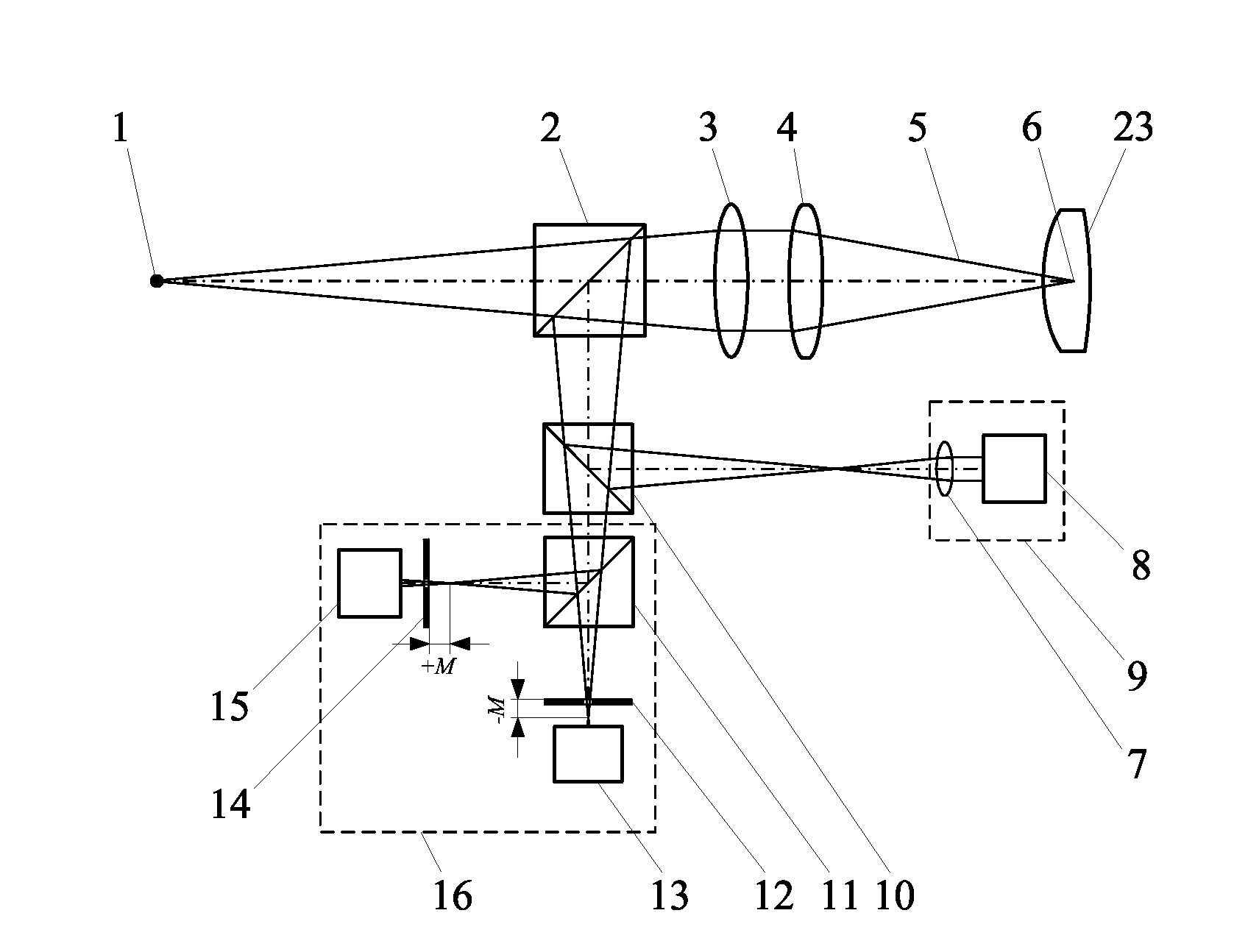
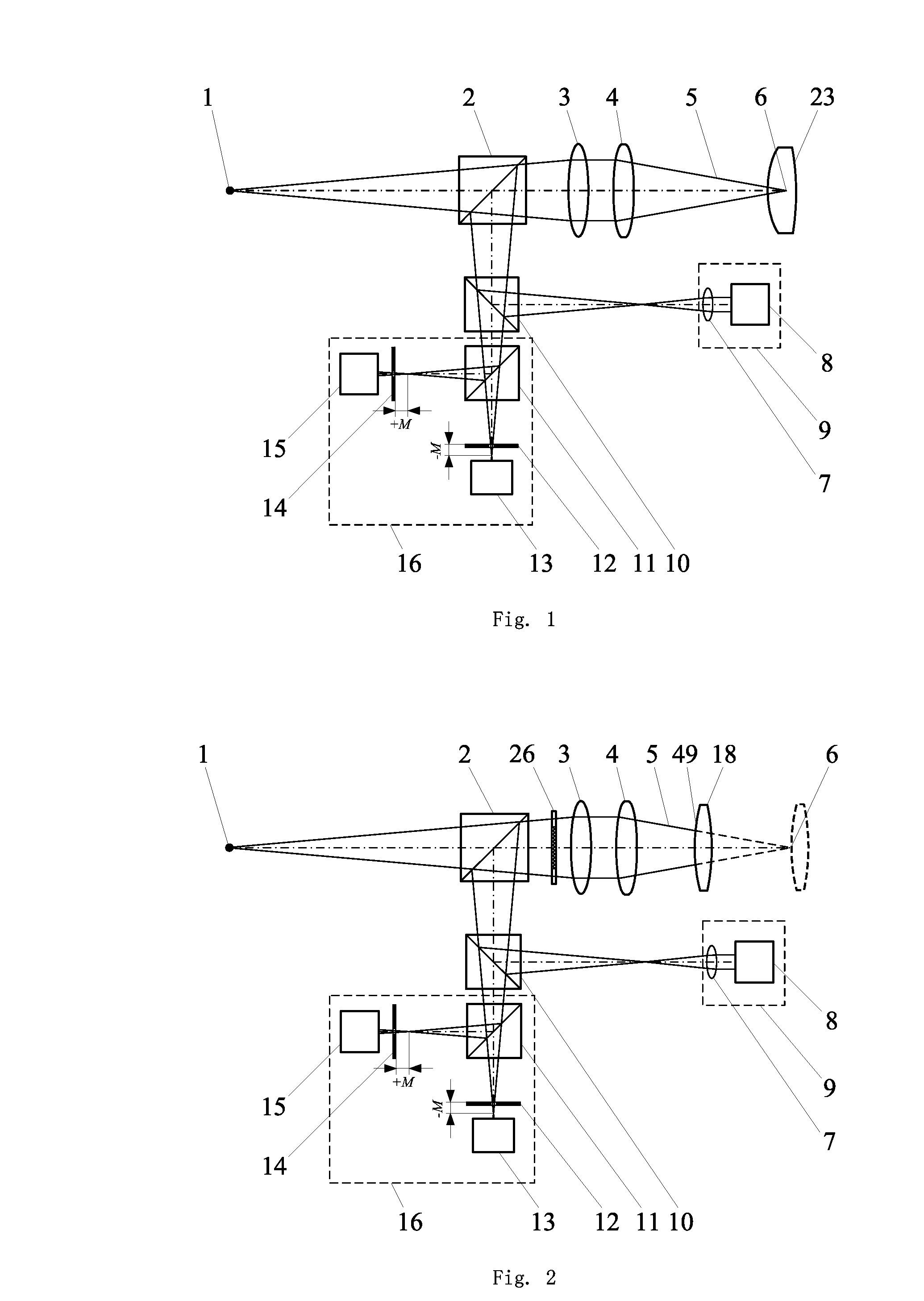
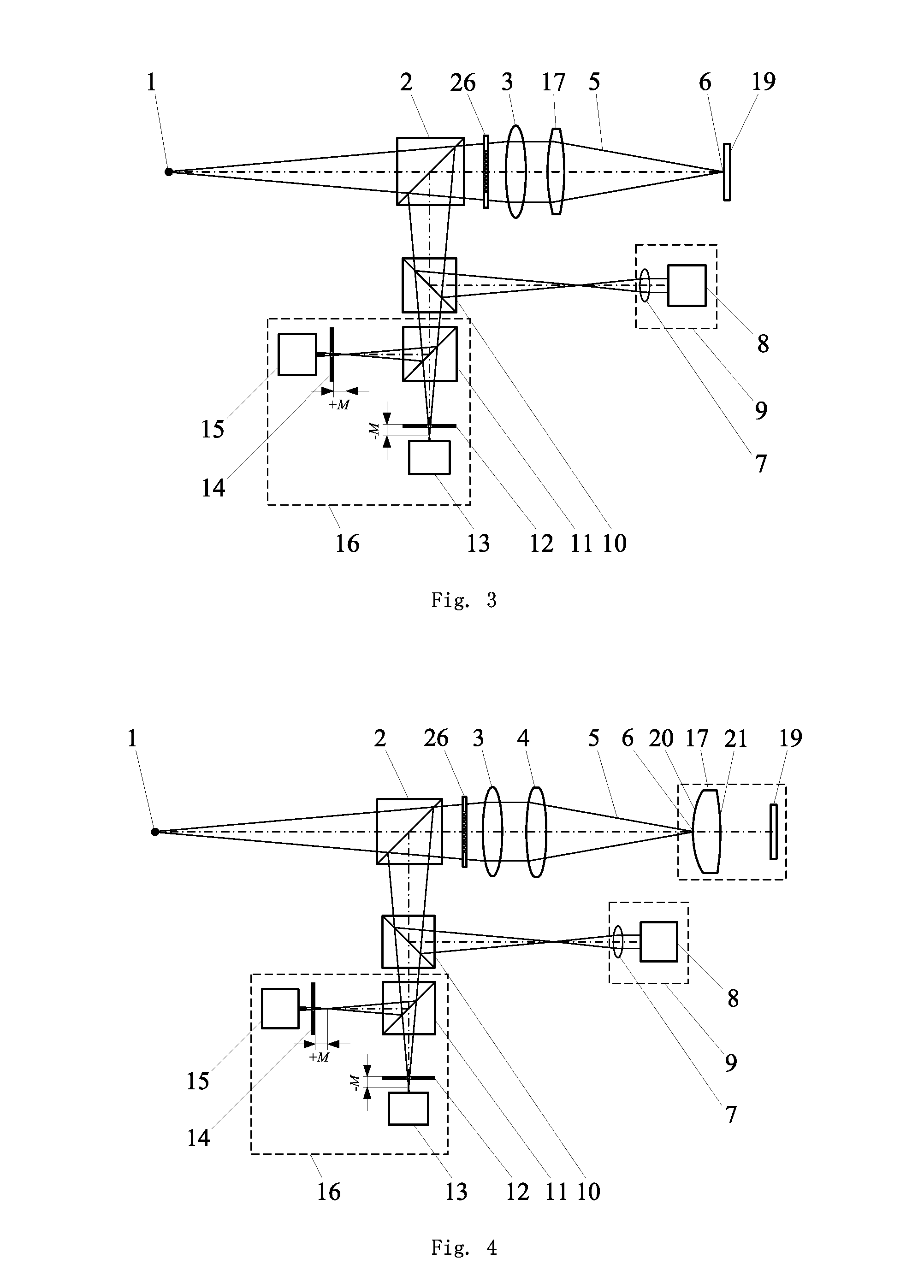
A parameter measurement device of optical system comprises a short coherent light module, a focusing lens, a collimation lens, a filtering pinhole, a splitter, a corner reflector, an one-dimension accurate mobile station, an adjustable focus telescope, a micro swivel, a focusing lens and an imaging CCD. And a relative measurement method uses optical interferometry to accurately measure the eccentricity, inclination, lens thickness and lens distances of an object optical system. The invention can improve the eccentricity measurement accuracy of lens to match higher eccentricity demand, realize the final measurement of internal distances in optical system and realize the distance of assembled optical system.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
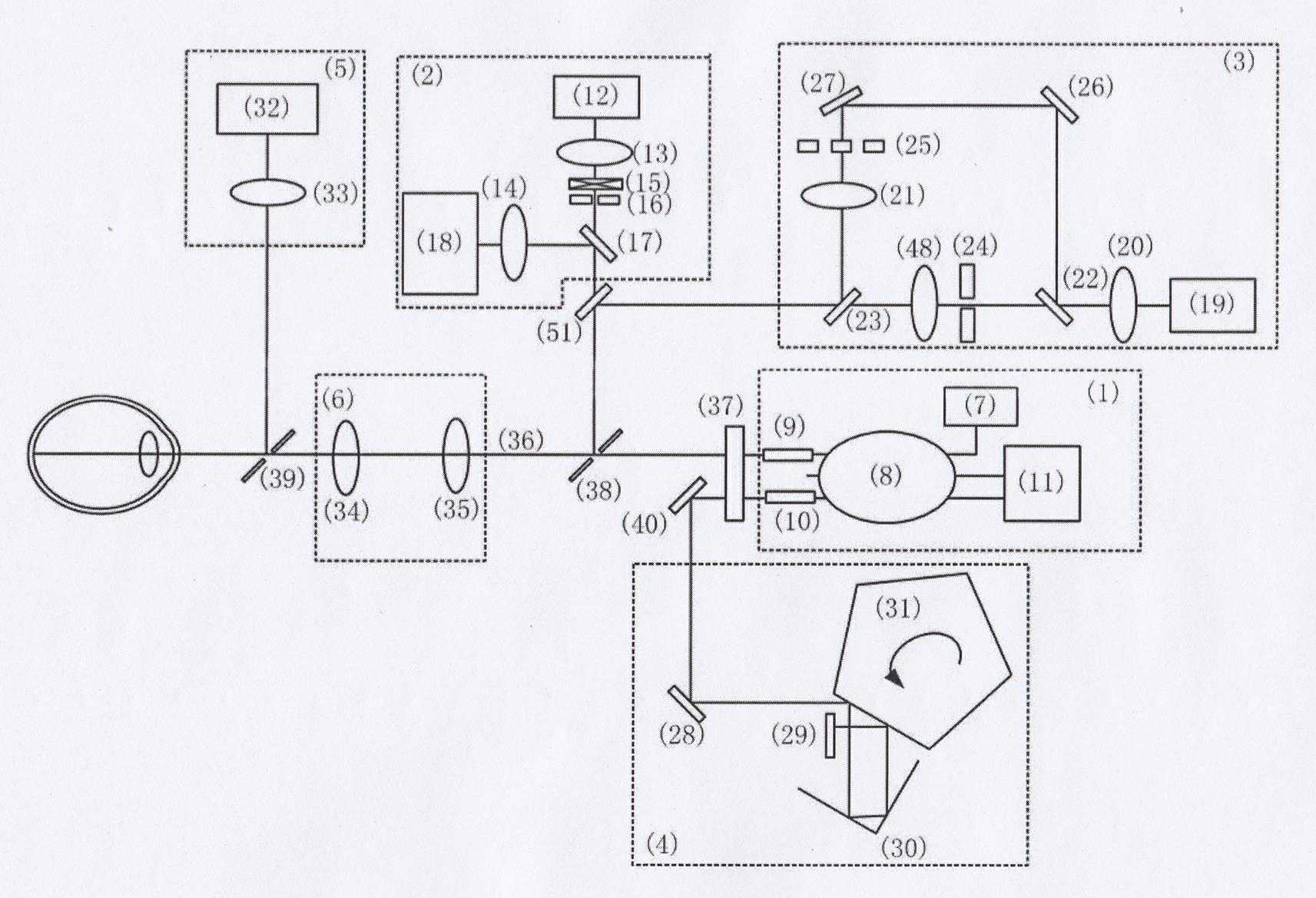
Optical coherence biological measurer and method for biologically measuring eyes
Disclosed is an optical coherence biological measurer. Parameters including corneal thicknesses, anterior chamber depths, lens thicknesses and visual axis lengths of eyes are obtained in once measurement by the aid of optical coherence measurement technology. The optical coherence biological measurer comprises a short coherence interferometry system detecting by the aid of balance, a retina splitimage focusing system, a visual axis aligning system with double fixation lamps, an optical length variable system, an eye positioning system and an auxiliary focusing system. The eye positioning system images the surface of a cornea and positions an eye, a system optical axis matches with an visual axis of the eye by the aid of the visual axis aligning system with the double fixation lamps, detecting light is respectively focused on a retina, a vitreous body and the cornea by an optical length and focus linkage device, simultaneously, optical length compensation of reference light is realized, the optical length variable system is used for realizing scanning measurement for return light signals of the retina, the vitreous body and the cornea, and the visual axis length, the vitreous bodythickness, the anterior chamber depth and the corneal thickness are calculated by the aid of output signals of a balance photoelectric detector.
Owner:王毅 +2
Bilateral dislocation differential confocal element parameter measuring method
ActiveCN104568389AIncrease the radius of curvatureHigh measurement accuracyTesting optical propertiesAxial displacementRefractive index
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical imaging and detecting and relates to a bilateral dislocation differential confocal element parameter measuring method. The method includes the steps that dislocation differential subtracting processing is conducted on the two sides of a confocal axial characteristic data set measured by the starting points and the ending points of all various size parameters including the curvature radius, the lens thickness, the refractive rate, the focal distance and the interval, and therefore the positioning precision of the starting points and the ending points of the size parameters is improved, and the measuring precision of optical elements of the curvature radius, the lens thickness, the refractive rate, the focal distance, the interval and the like is improved. According to the bilateral dislocation differential confocal element parameter measuring method, due to the fact that two sections of data, close to the position of the full width at half maximum and very sensitive to axial displacement, of a confocal characteristic curve are used for conducting the dislocation differential subtracting processing, the position, calculated by the data sections, of the extreme point of the confocal characteristic curve is more sensitive and more accurate than the position, calculated through an existing confocal characteristic curve top fitting method, of the extreme point of the confocal characteristic curve, according to the result of the bilateral dislocation differential confocal element parameter measuring method, under the condition that the confocal element parameter system structure is not changed, the axial focusing capability, the signal-to-noise ratio and the like of the system can be obviously improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and device of differential confocal and interference measurement for multiple parameters of an element
InactiveUS20130010286A1Improve measurement efficiencyRealize measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansRefractive indexTest element
The present invention relates to the field of optical precision measurement technologies, and in particular, to a method and a device of differential confocal (confocal) and interference measurement for multiple parameters of an element. The core concept of the invention lies in that: the concurrent high-precision measurement of multiple parameters of an element may be realized by measuring the surface curvature radius of an element with spherical surface, the back focal length of a lens, the refractive index of a lens, the thickness of a lens and the axial spaces of an assembled lenses by using a differential confocal (confocal) measuring system and measuring the surface profile of the element by using a figure interference measuring system. In the invention, a differential confocal (confocal) detection system and a figure interference measuring system are combined for the first time, the method covers more measured parameters, and during the measurement of multiple parameters of an element, it is not essential to readjust the optical path or disassemble the test element, thus no damage will be caused on the test element, and the measurement speed will be fast.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
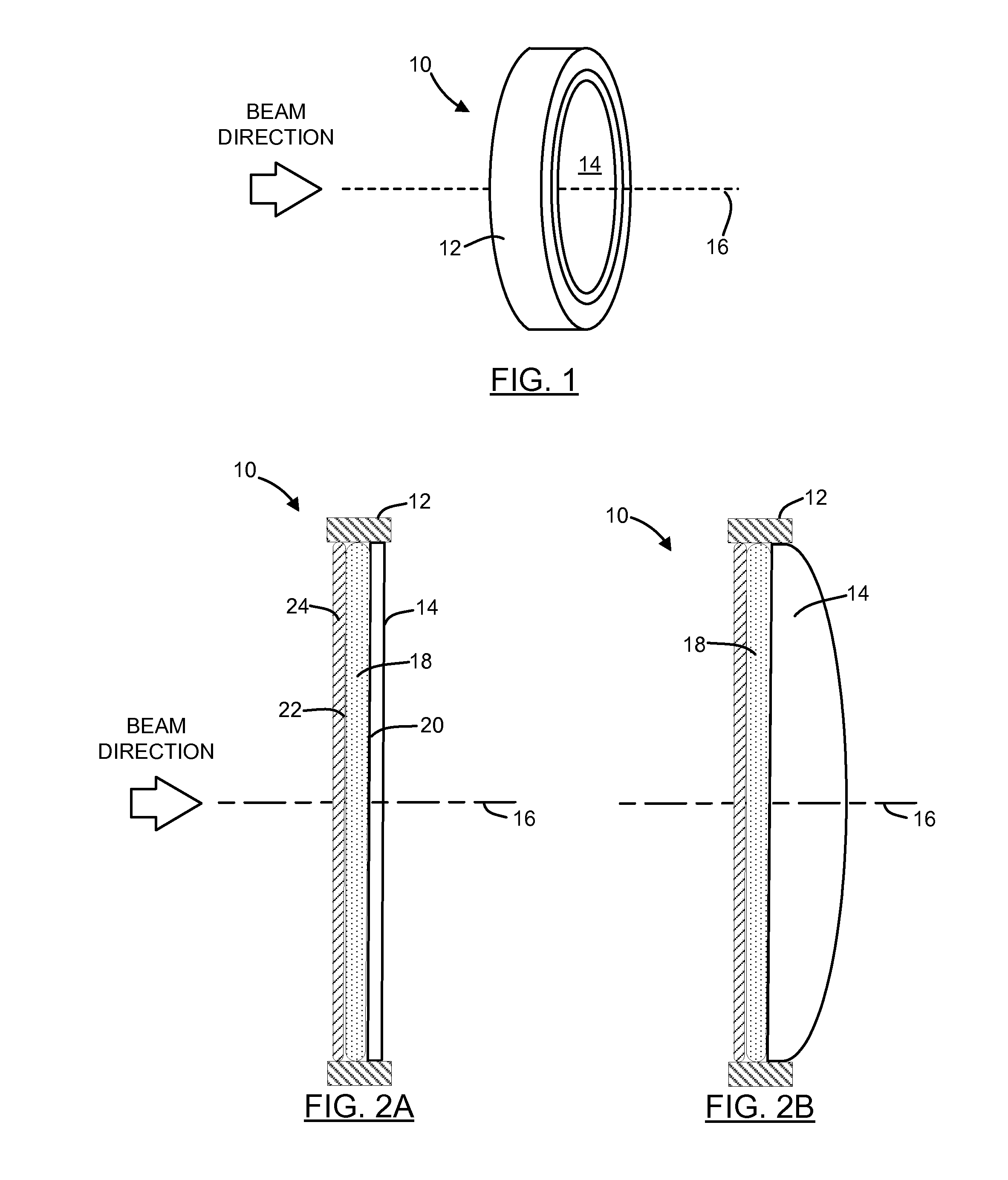
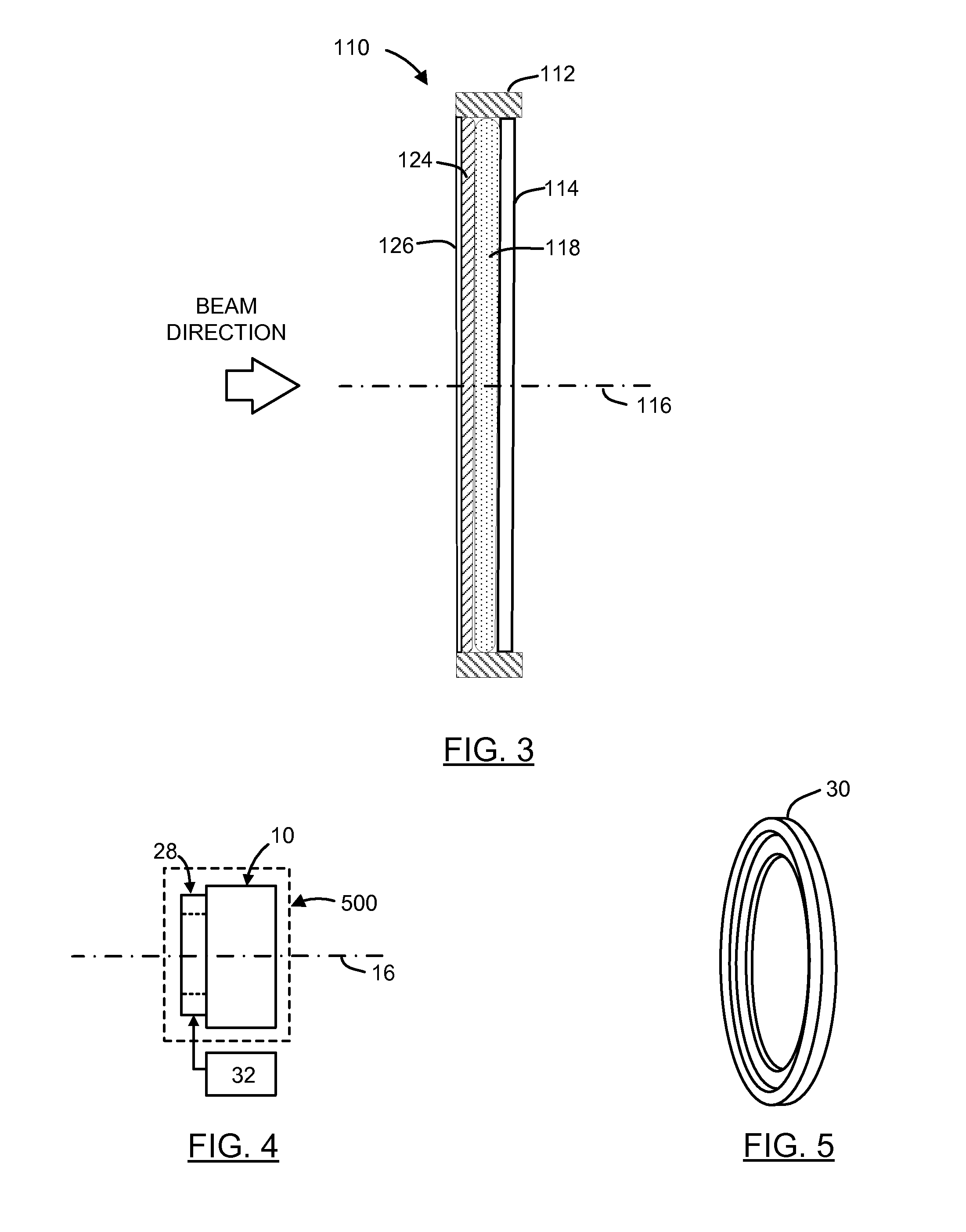
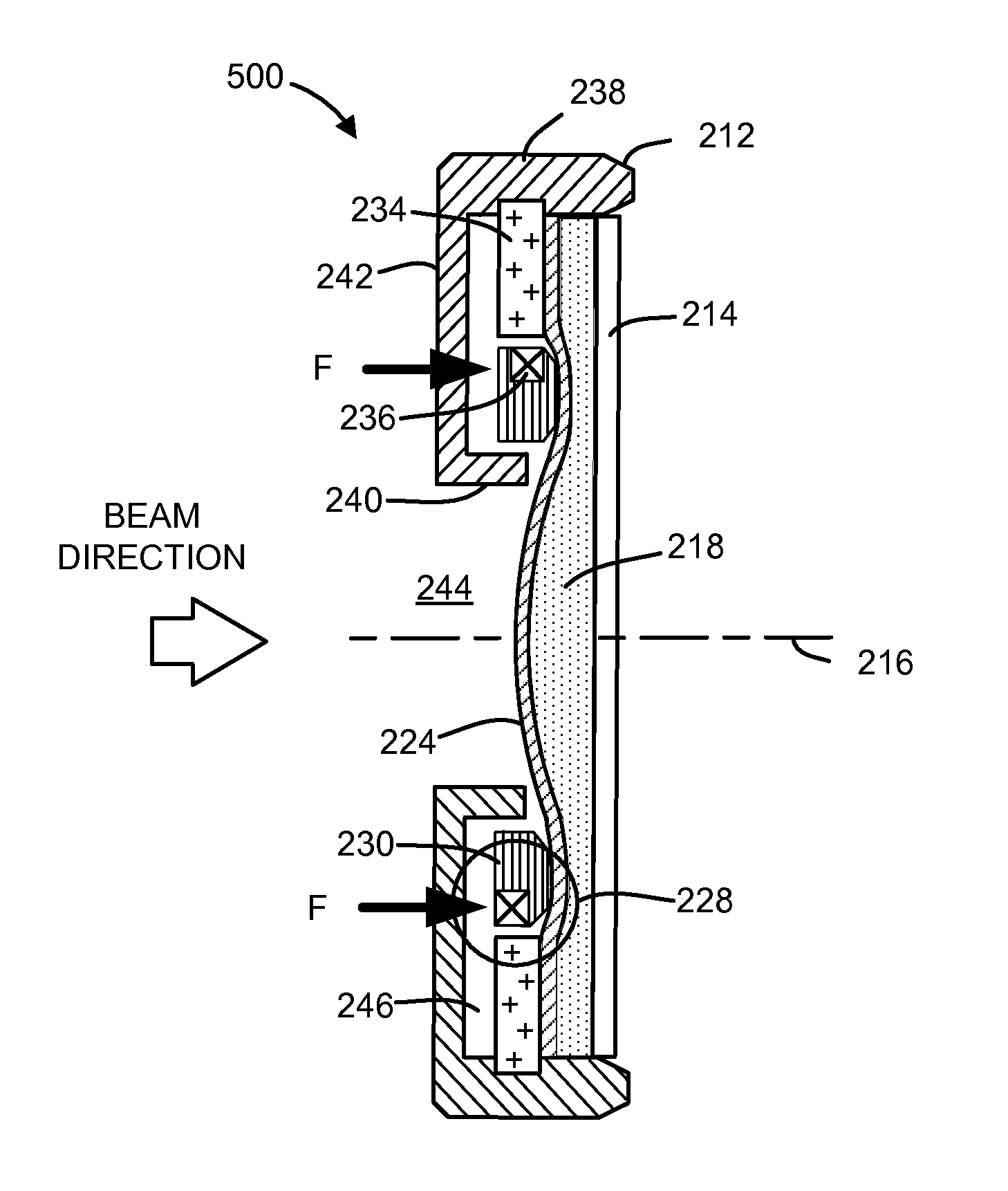
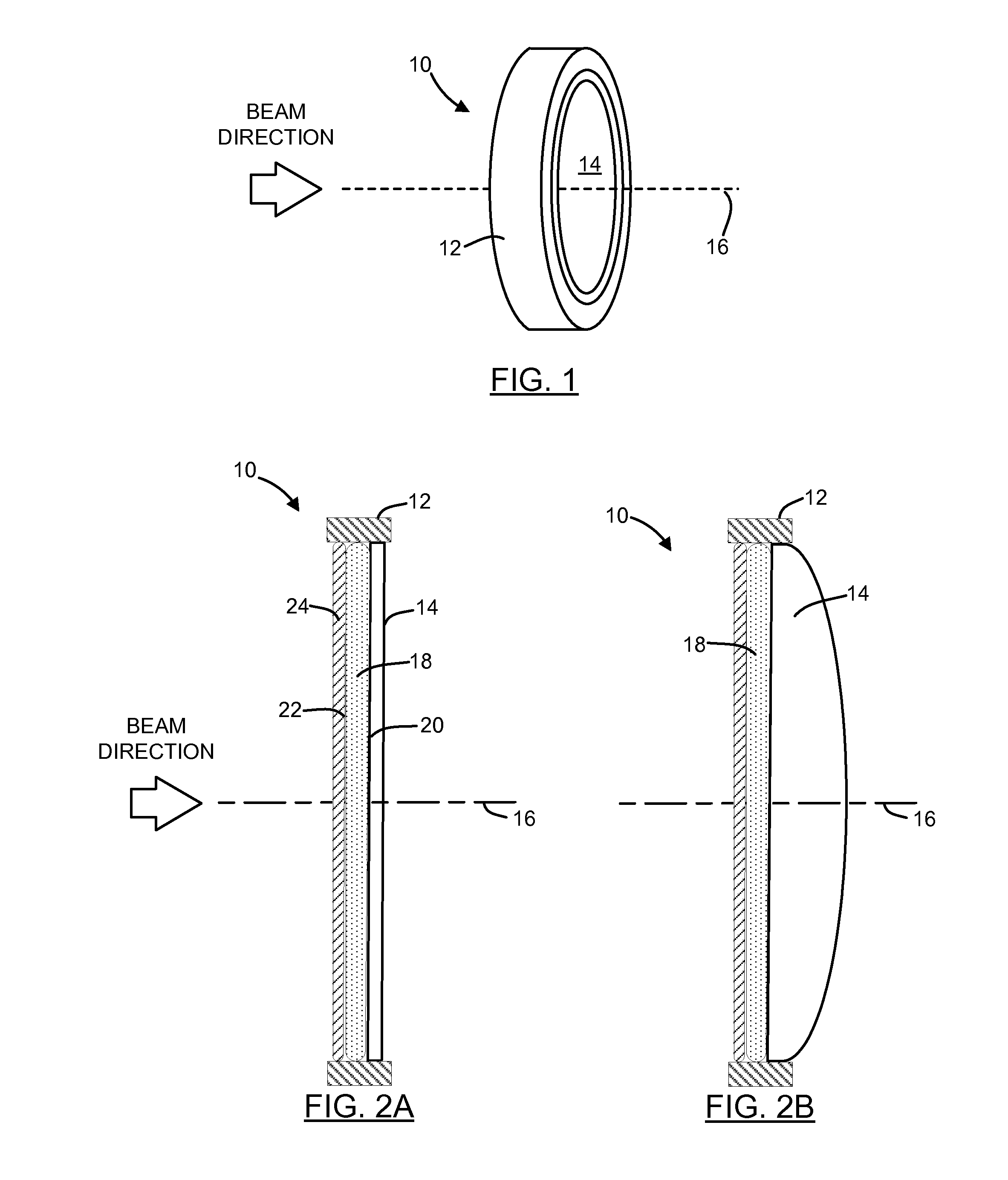
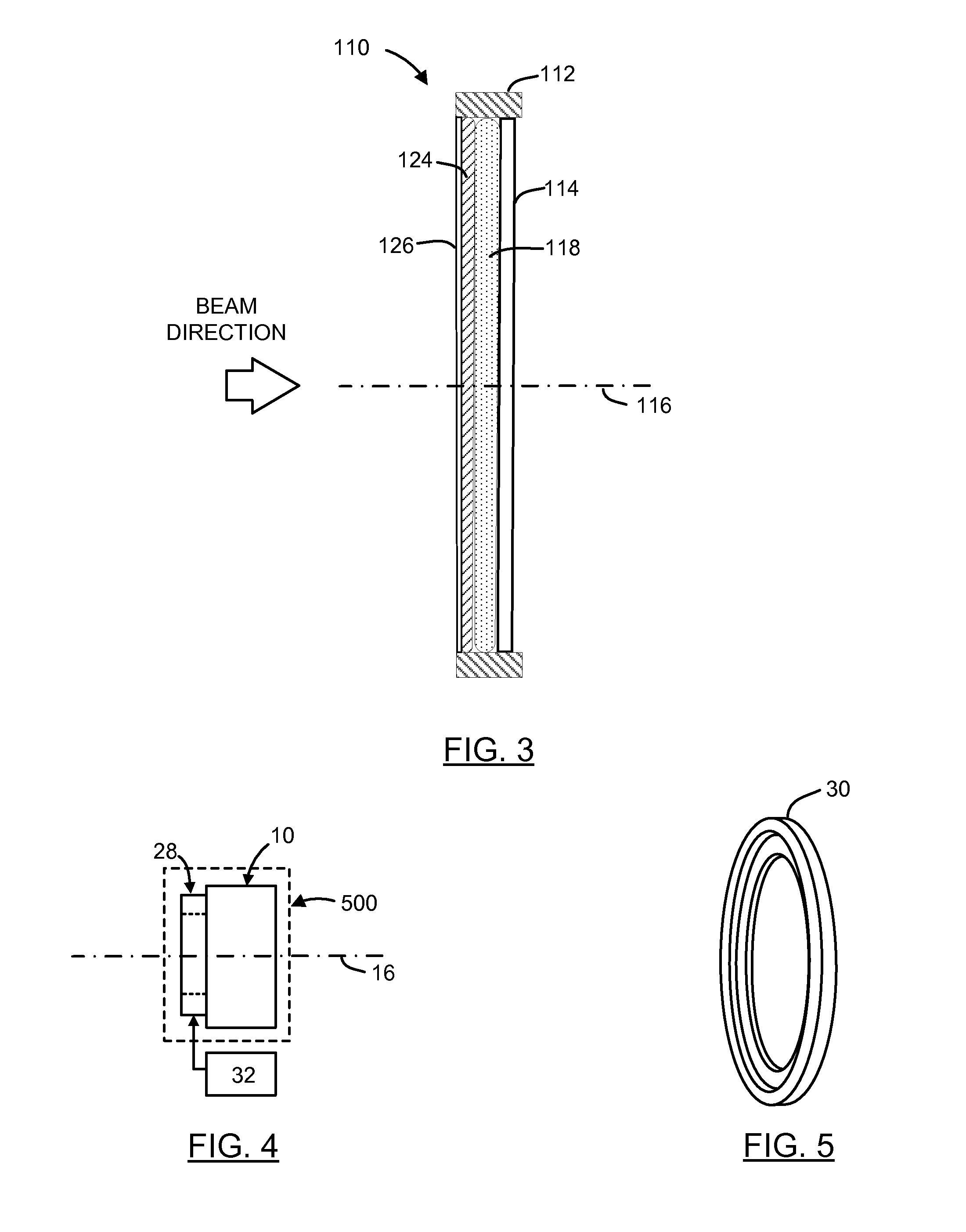
Apparatus and method for detecting lens thickness
Owner:ALCON INC
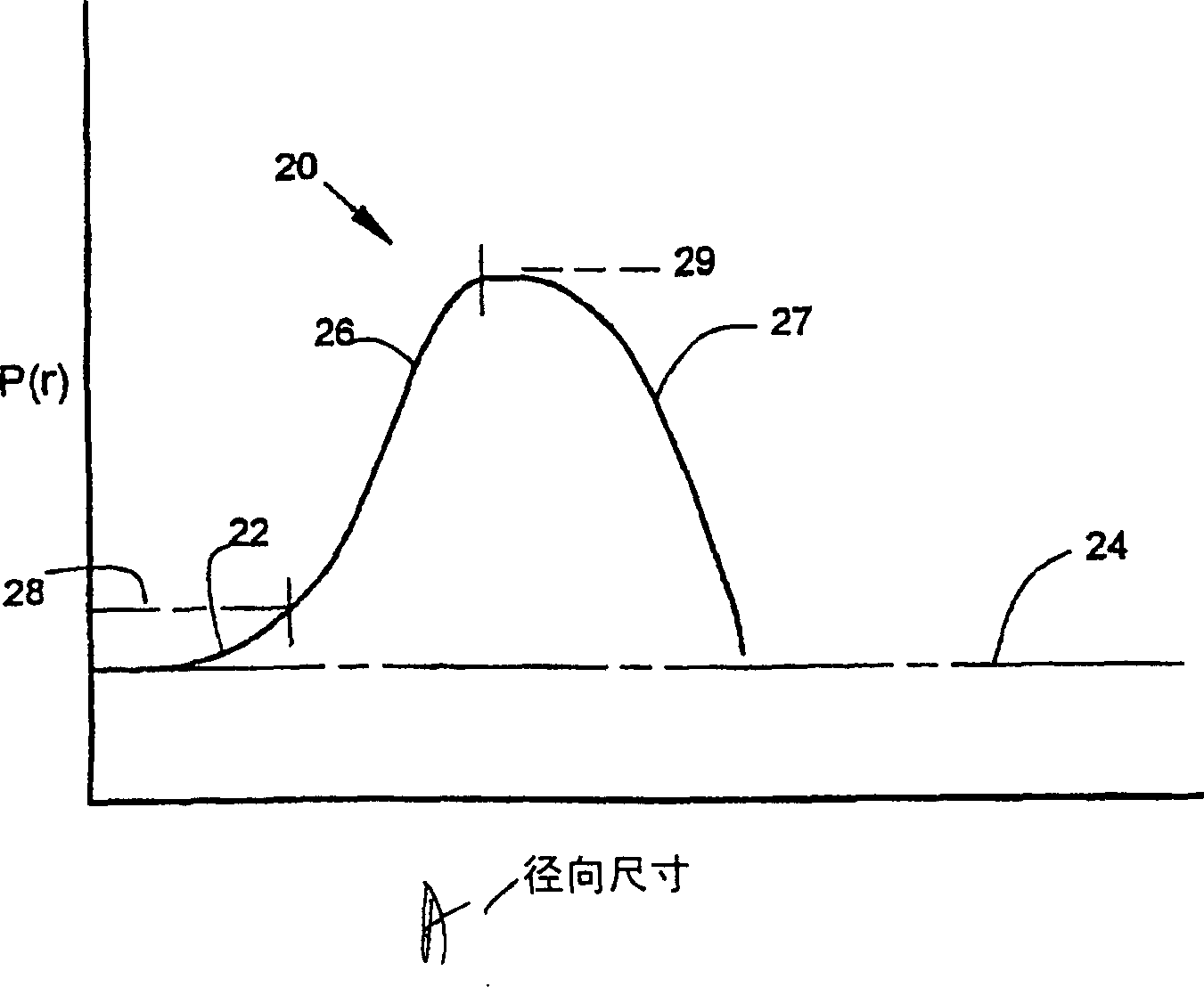
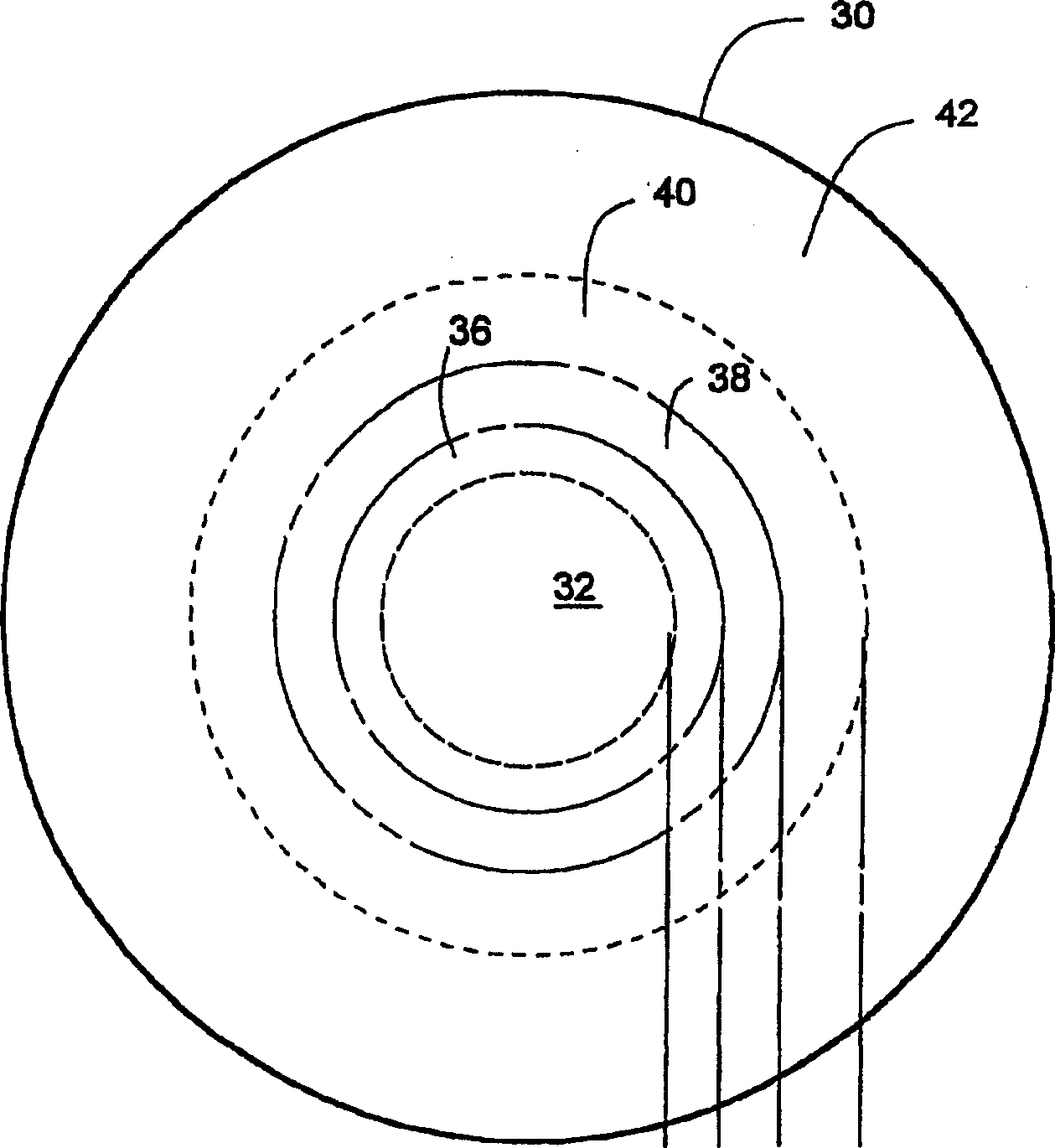
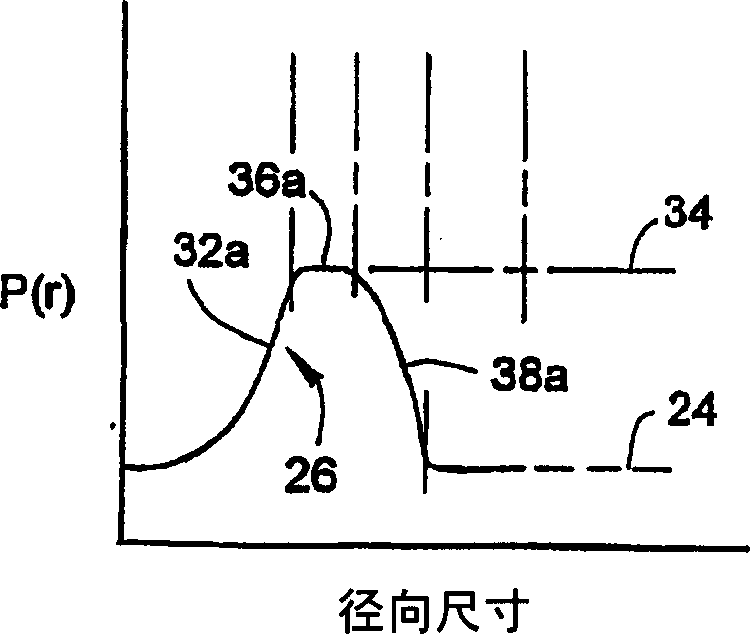
Inspection of ophthalmic lenses using absorption
A method and system for inspecting ophthalmic lenses using absorption where an ophthalmic lens is illuminated with light comprising wavelengths that are substantially absorptive to said lens, the image subsequently detected being created using only light at said absorptive wavelengths. Variations in transmitted light intensity translate into thickness changes in the lens caused by cosmetic flaws. The invention is also directed to imaging lens assemblies employing highly positive-powered field flattening lens elements to image a curved object, such as an ophthalmic lens, onto a flat image plane.
Owner:ROSS DENWOOD F III +7
Method of making prescription lens
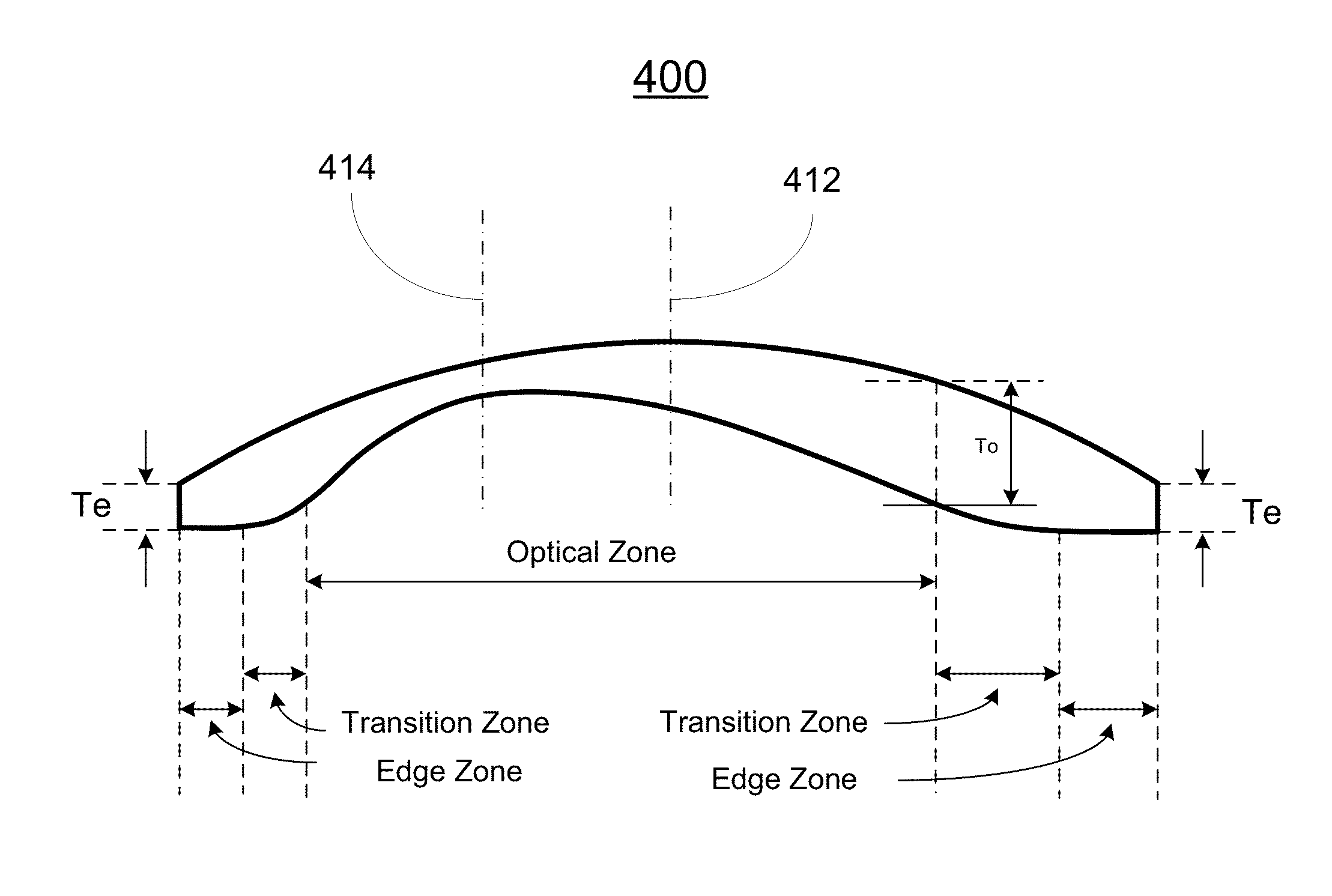
In one aspect of the present invention, a method for manufacturing a prescription lens includes obtaining information of a prescription lens and a frame to accommodate the prescription lens, the information of the prescription lens comprising a lens power, an optical zone and a spherical front base curve, and the information of the frame comprises a frame curve; calculating the maximum lens thickness of the prescription lens at the optical zone according to the information of the prescription lens; selecting a lens according to the calculated maximum lens thickness at the optical zone, the information of the prescription lens and the frame; and processing the selected lens so as to obtain the prescription lens having an intermediate zone surrounding the optical zone and an edge zone surrounding the intermediate zone such that the thickness of the edge zone is substantially thinner than the maximum lens thickness of the optical zone.
Owner:POLYLITE TAIWAN
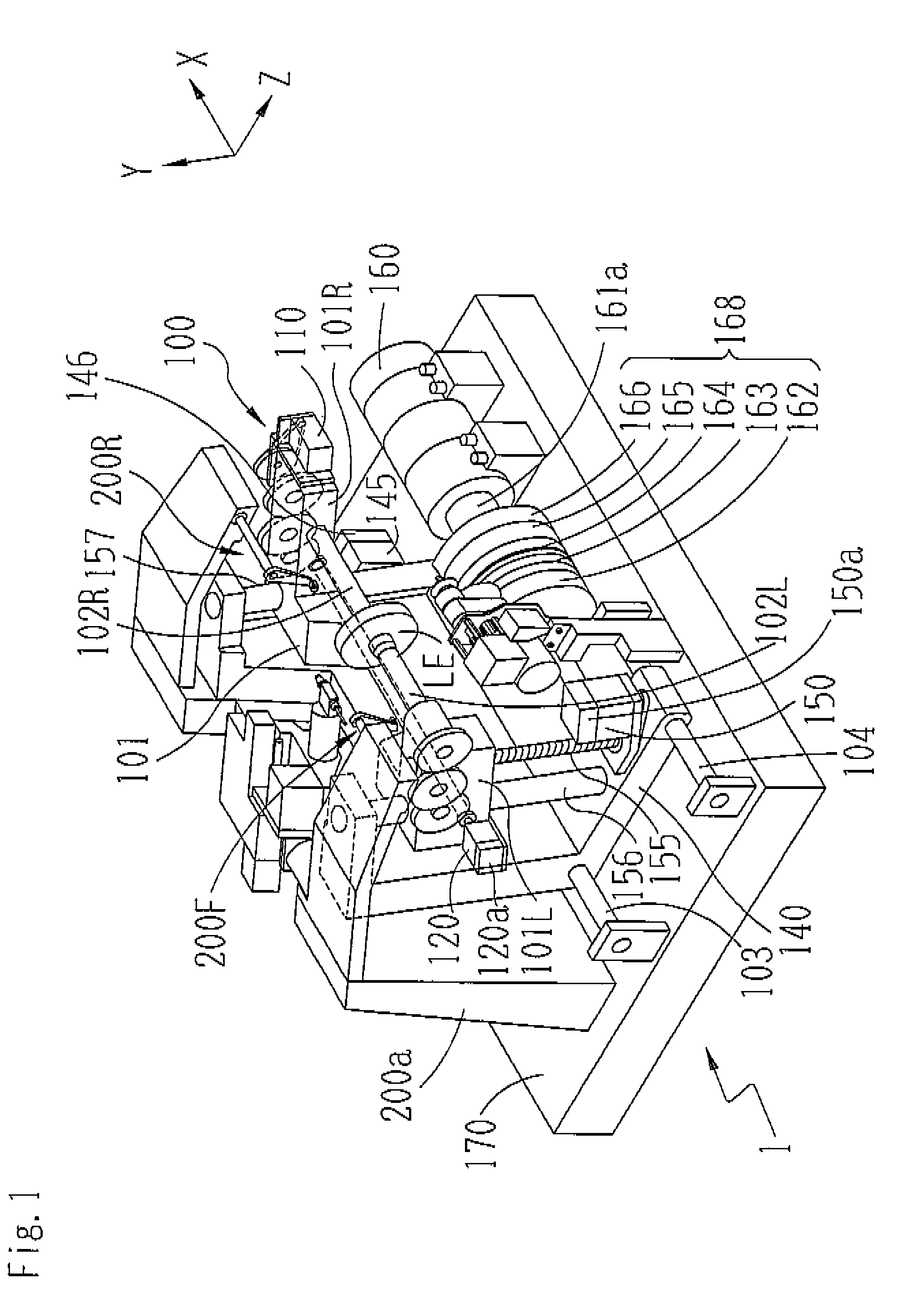
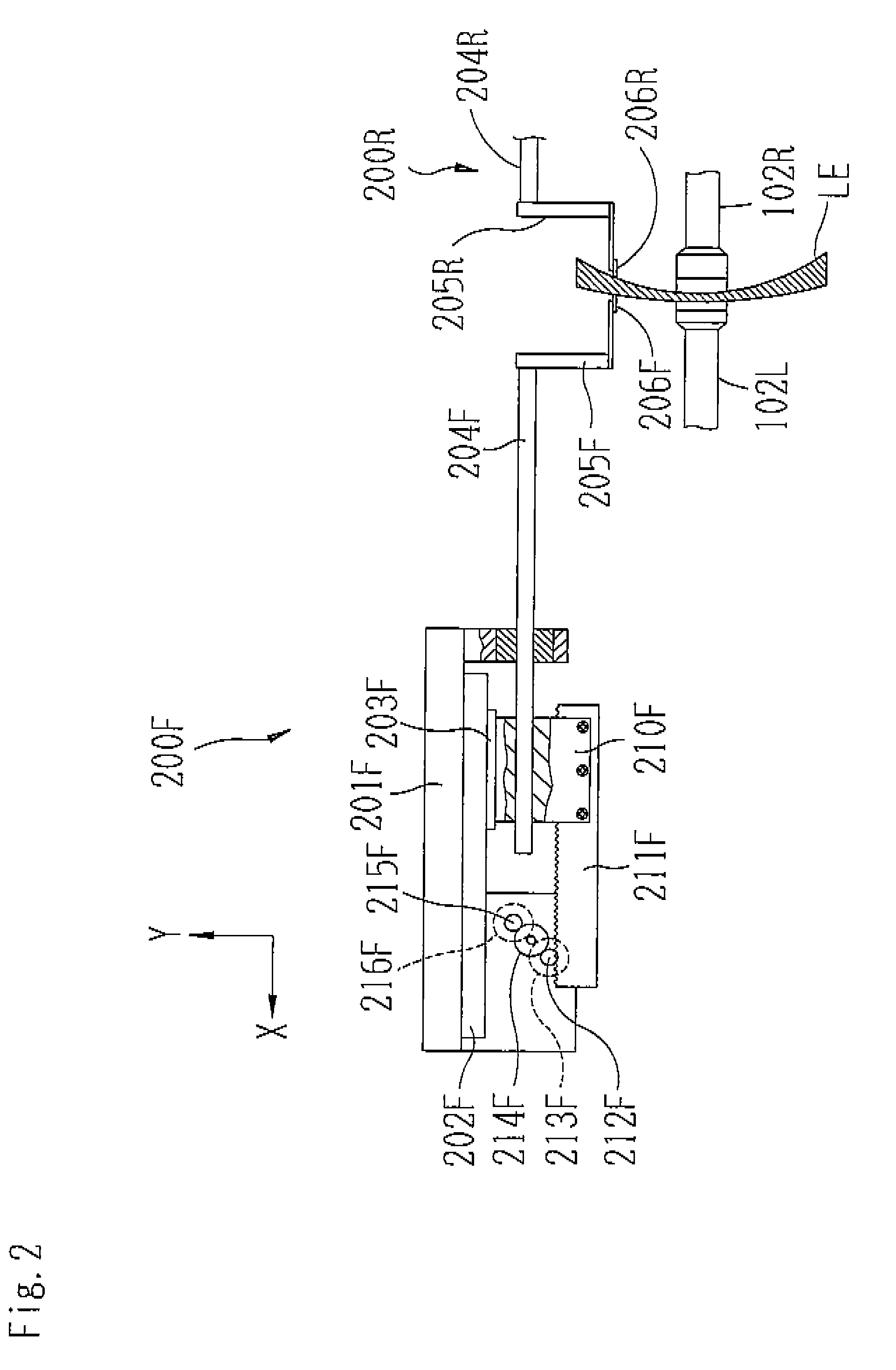
Device and method for measuring and machining spectacle lens, spectacle lens manufacturing method, and spectacles manufacturing method
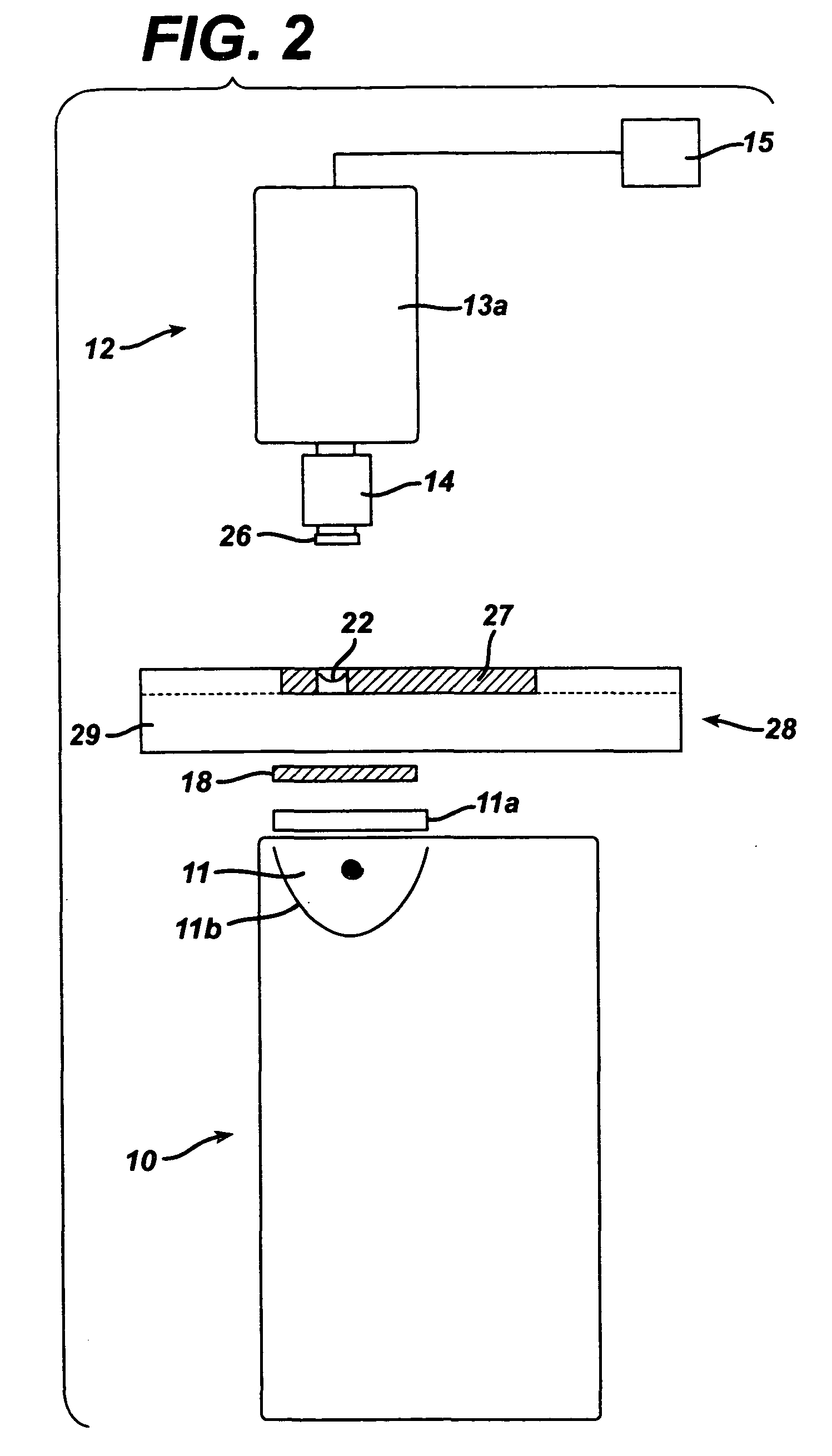
A mounting part for mounting spectacle frame components such as lugs can be machined after confirming that a lens thickness at a mounting part-machined portion where the mounting part is machined is equal to or larger than the specified value, and can be installed the spectacle lens components on the spectacle lens with a requested strength. The device, the method for the above, a spectacle lens manufacturing method, and a spectacles manufacturing method are given. The spectacle lens (1) is fed to a lens thickness measuring device (70) by a lens feeder. The fed amount of the spectacle lens in this feeding is based on the measured results of a distance between a frame center forming a block center by a lens holder in an edging for manufacturing the spectacle lens (1) from a raw material lens and the edge face of the spectacle lens (1) where the mounting part is to be machined. The thickness of the lens at the mounting part-machined portion can be accurately measured by the measuring device (70) even if an error produced in the edging is included in the distance.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Zoom liquid crystal lens
InactiveCN101672990AGood optical performanceImprove qualityNon-linear opticsCamera lensOptical property
The invention provides a zoom liquid crystal lens, which comprises a single-layer or multi-layer liquid crystal lens unit. The liquid crystal lens unit utilizes at least two pieces of glass substratesin a scheduled thickness; an aluminium film, a silver film or other translucent metal films are arranged on one side or double sides of each glass substrate respectively in an etching mode to form asurface alignment electrode which can be controlled independently; and then the glass substrates are arranged in parallel at intervals, so that a layer of accommodating space in a predetermined thickness is arranged between two adjacent glass substrates to seal liquid crystals so as to form a layer of liquid crystal lens unit. The arrangement direction and the optical properties such as the refractive index and the like of liquid crystal molecules in each liquid crystal lens unit are independently controlled by voltage so as to improve the imaging quality, accelerate zoom switching, improve the convenience of assembling the zoom liquid crystal lens and reduce the overall lens thickness and the manufacturing cost.
Owner:E PIN OPTICAL IND
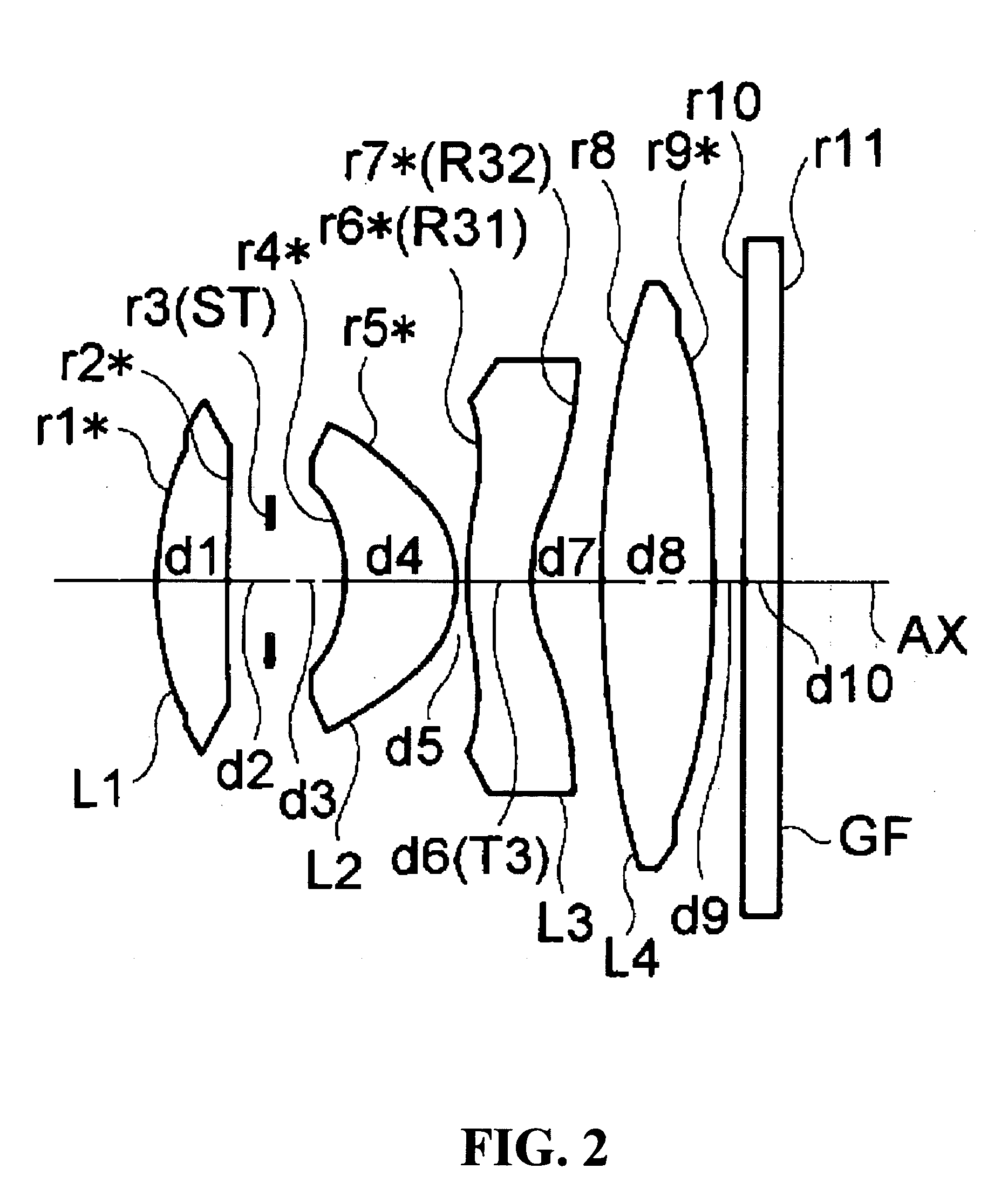
Image pickup lens system
ActiveUS20050117047A1Good optical performanceSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsExit pupilOphthalmology
An image pickup lens system has a four-lens configuration which forms an image on a solid-state image pickup device. The image pickup lens system includes, from an object side, a positive first lens, an aperture stop, a positive second lens, a negative third lens whose concave surface is faced toward an image surface side, and a positive fourth lens in the order from an object side. A ratio of an axial lens thickness of the third lens to a focal length of the whole system is optimally set. Therefore, an exit pupil position can be kept far away from the image surface while the image pickup lens system has good optical performance and a compact size.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Eyeglass lens processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100197198A1Effective preventionExtended processing timeEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesCamera lensEyewear
An eyeglass lens processing apparatus includes: a lens rotation unit rotating a lens; a processing tool rotation unit processing the lens; an axis-to-axis distance changing unit for changing an axis-to-axis distance between the chuck shaft and the processing tool rotation shaft; a lens surface configuration acquiring unit which acquires a front surface curve configuration and a rear surface curve configuration of the lens; a lens outer diameter acquiring unit which acquires an outer diameter of a lens; a calculation unit which calculates a thickness of the lens and calculates a cutting depth of the lens, so that torque applied onto the chuck shaft in rough processing becomes substantially constant, based on the calculated lens thickness and a processing distance from the rotation center of the lens; and a control unit which controls the axis-to-axis distance changing unit in accordance with the calculated cutting depth and for rough processing the lens.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Multifocal ophthalmic lens with induced aperture
Multifocal lenses are defined by nonconical aspheric optical surfaces. Various alternative surface shapes provide a central distance vision region surrounded by an optical step. The optical step has repidly increasing power in the radial direction which creates an induced aperture through which the cortical elements of the vision system are induced to concentrate. The induced aperture results in increased clarity in distance vision. Nonconical aspheric optical surfaces are defined to produce the desired optical power distributions. These surface functions are also provided in form of polynomial series for simplicity of use in computer driven lathes for shaping contact lenses. To allow increased manipulation of the defining functions additional elements such as conic terms are added. To improve near vision correction in some configurations, an annular near vision region extends radially outward from the optical step. To improve low light distance vision, power is reduced in the lens region outside the mesopic pupillary dimension. In alternative embodiments, the distance vision region and optical step are formed by cyclic functions. These have benefits in ease of manipulation to fit various specific user geometry requirements. In some configurations, an extended near vision region is used outside the optical step to improve near vision correction. The invention includes contact lenses, scleral lenses, intraocular lenses, and lenses impressed or surgically shaped within the corneal tissue as well as methods of designing and fitting these lenses. Although nominally positive power lenses are also within the present invention, negative lenses gain particular benefit due to decreased lens thickness at the lens perimeter and consequent reduced spherical aberration.
Owner:FLORIDA OPTICAL ENG
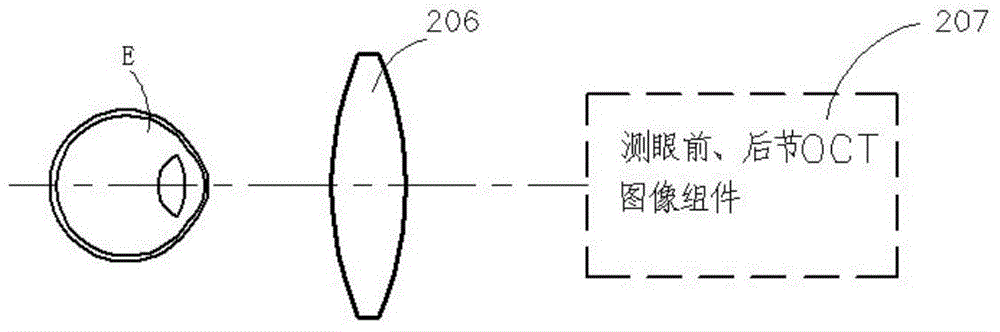
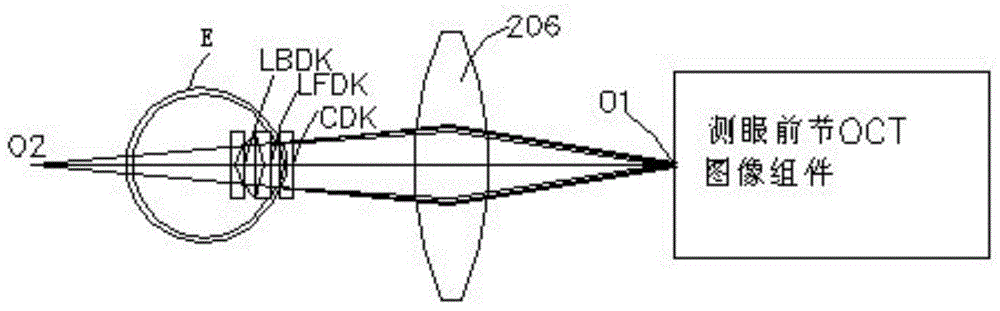
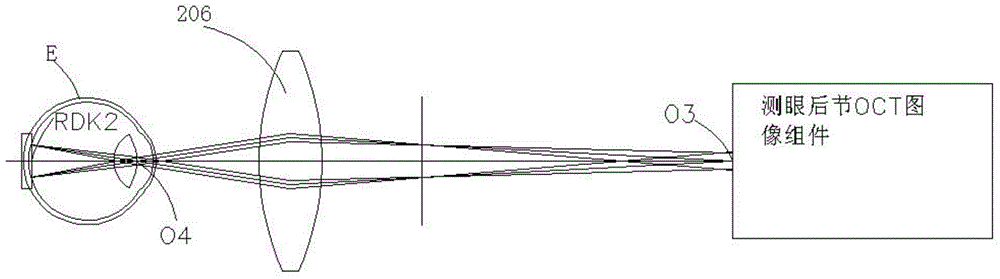
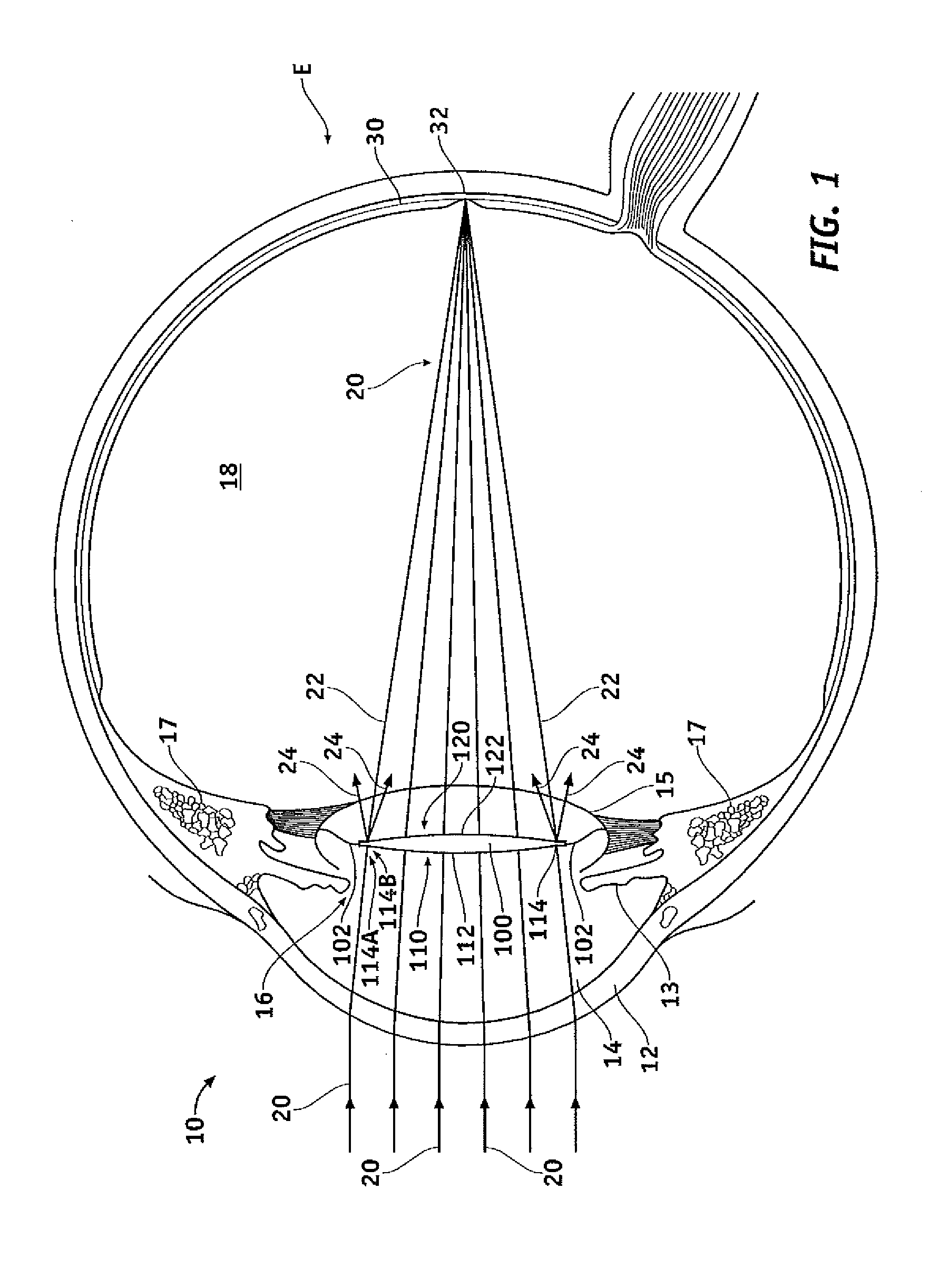
Eye ground retina OCT image correction method
The invention discloses an eye ground retina OCT image correction method. The method comprises the steps that scanning beams scan an anterior segment and a posterior segment, and meanwhile a human anterior segment OCT image and an eye ground retina OCT image are obtained, wherein the human anterior segment OCT image contains a corneal OCT image, a crystalline lens anterior surface OCT image and a crystalline lens posterior surface OCT image, and the human anterior segment OCT image and the eye ground retina OCT image are processed by a computer without correction; the OCT images are corrected and restored to images with a true form to obtain the corneal anterior surface curvature radius, the corneal posterior surface curvature radius, the crystalline lens anterior surface curvature radius, the crystalline lens posterior surface curvature radius, the corneal thickness, the anterior chamber depth and the crystalline lens thickness; a rendezvous point (O45) of center lines of the scanning beams which are refracted by the posterior surface of a crystalline lens is determined, and the circle center of the sector scanning region and the scanning angle (uO45) are calculated; the uncorrected eye ground retina OCT image is restored to an image with a true form, and finally a true sectional image of an eye ground retina is obtained through restoration and the curvature of the eye ground retina is measured according to a measured anterior segment OCT image and a measured posterior segment OCT image.
Owner:SHENZHEN CERTAINN TECH CO LTD
Wide-angle photographic lens system enabling correction of distortion
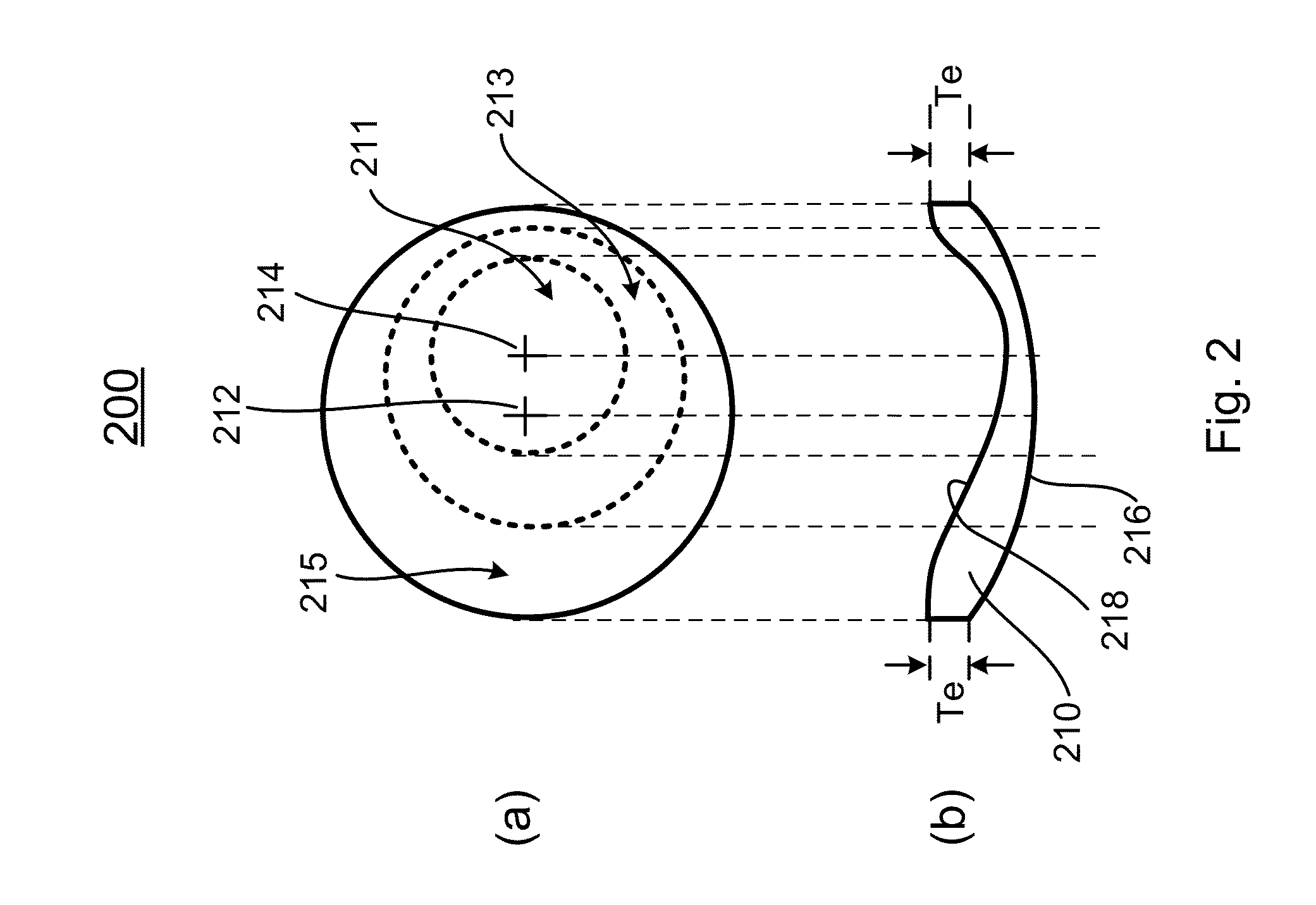
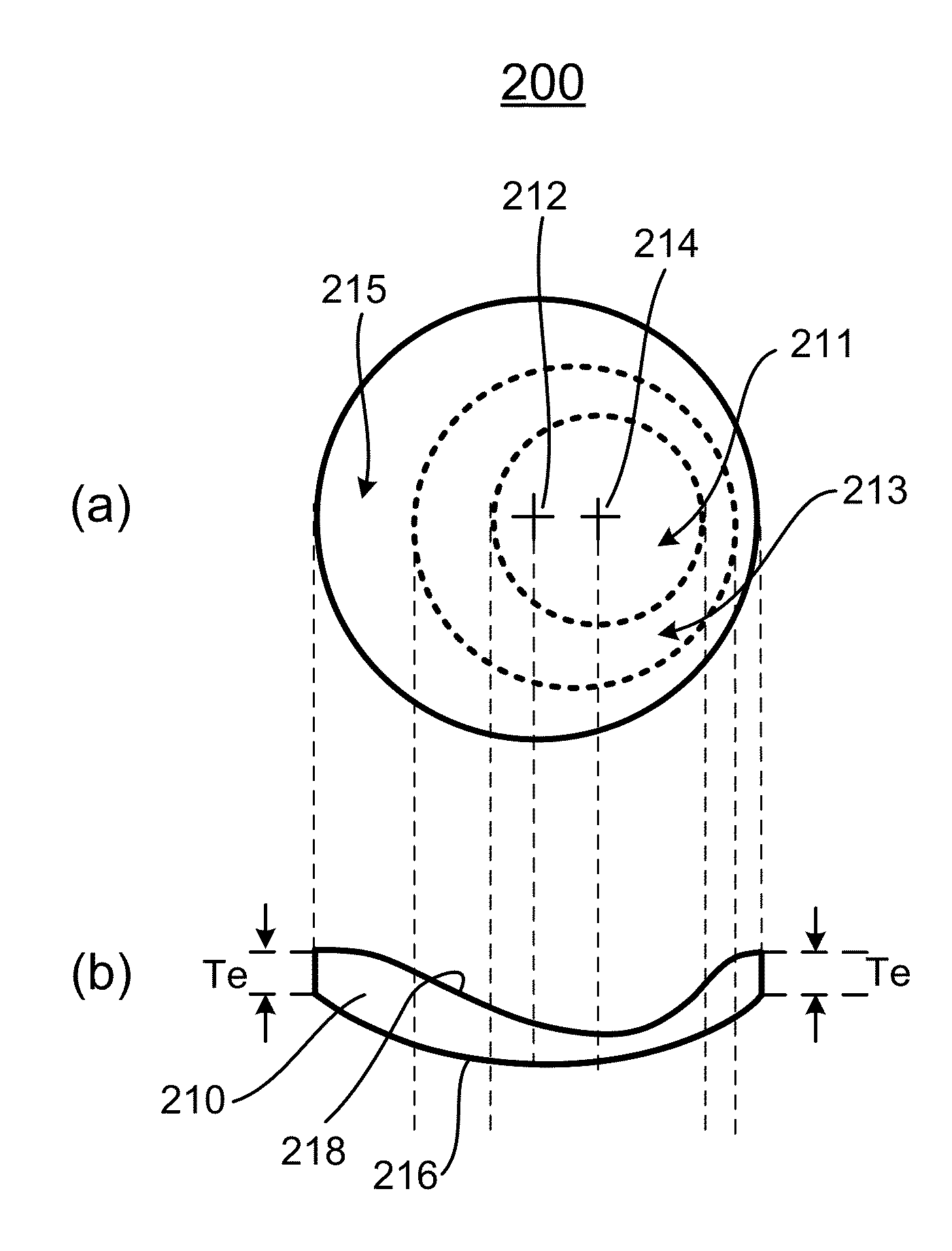
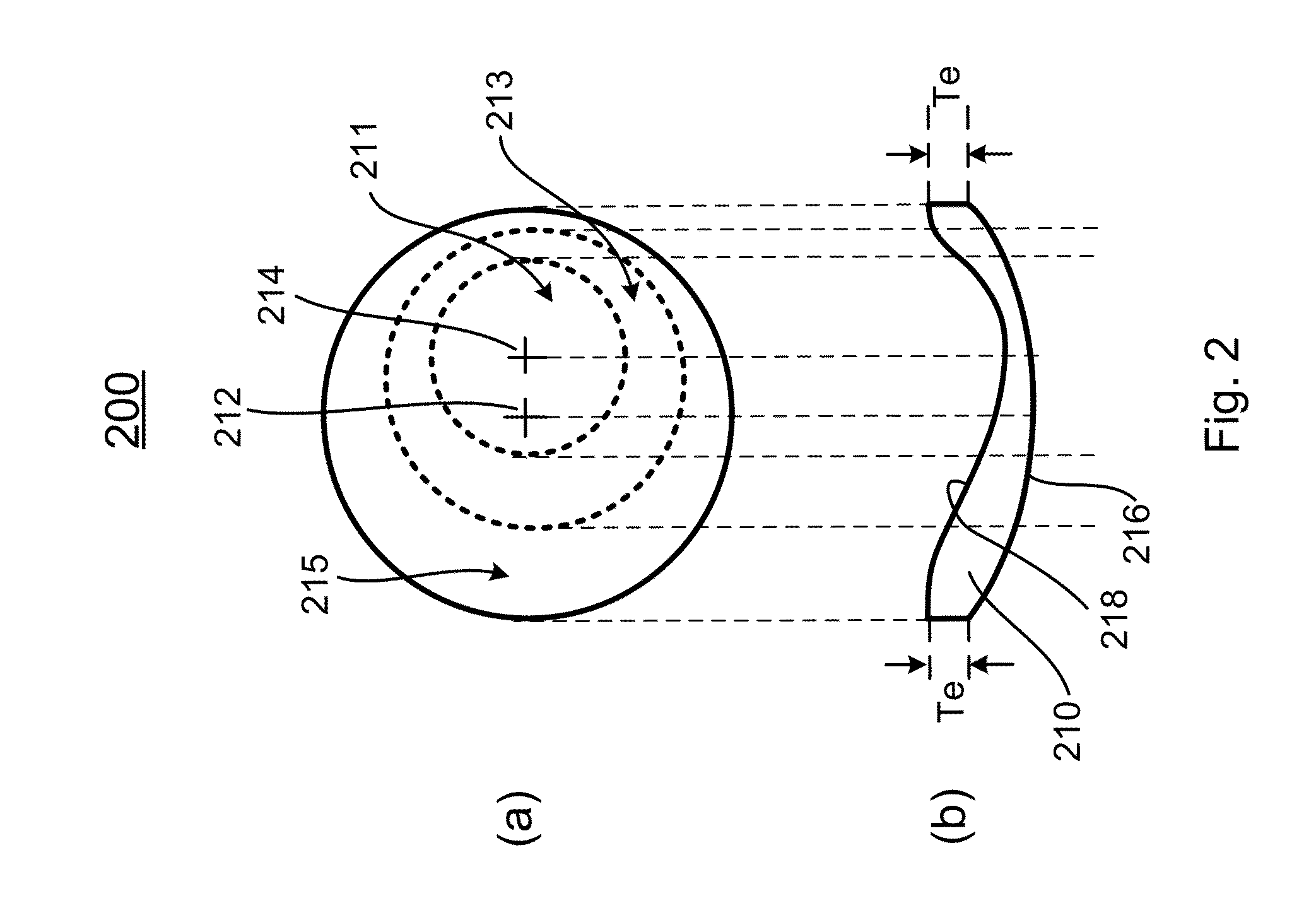
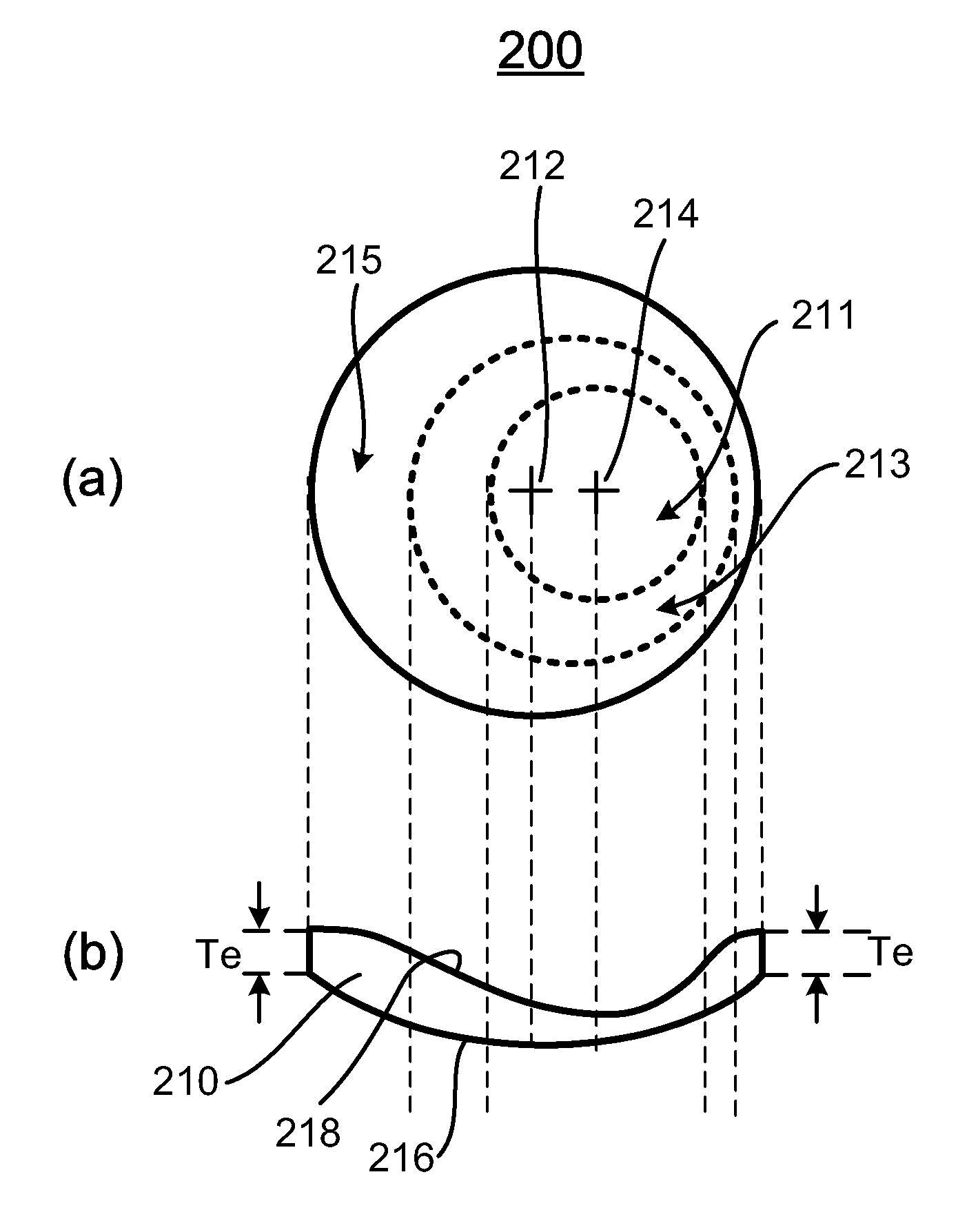
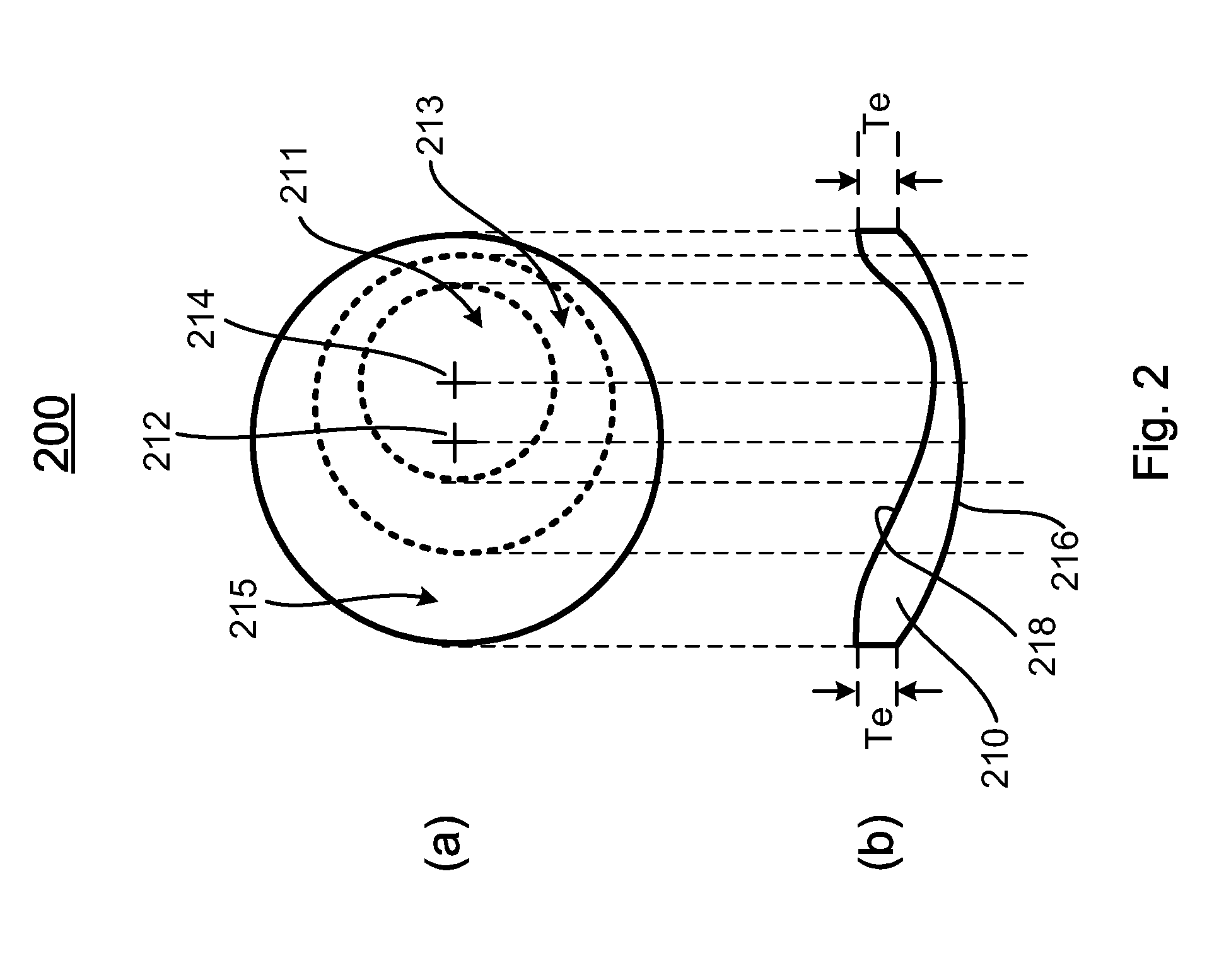
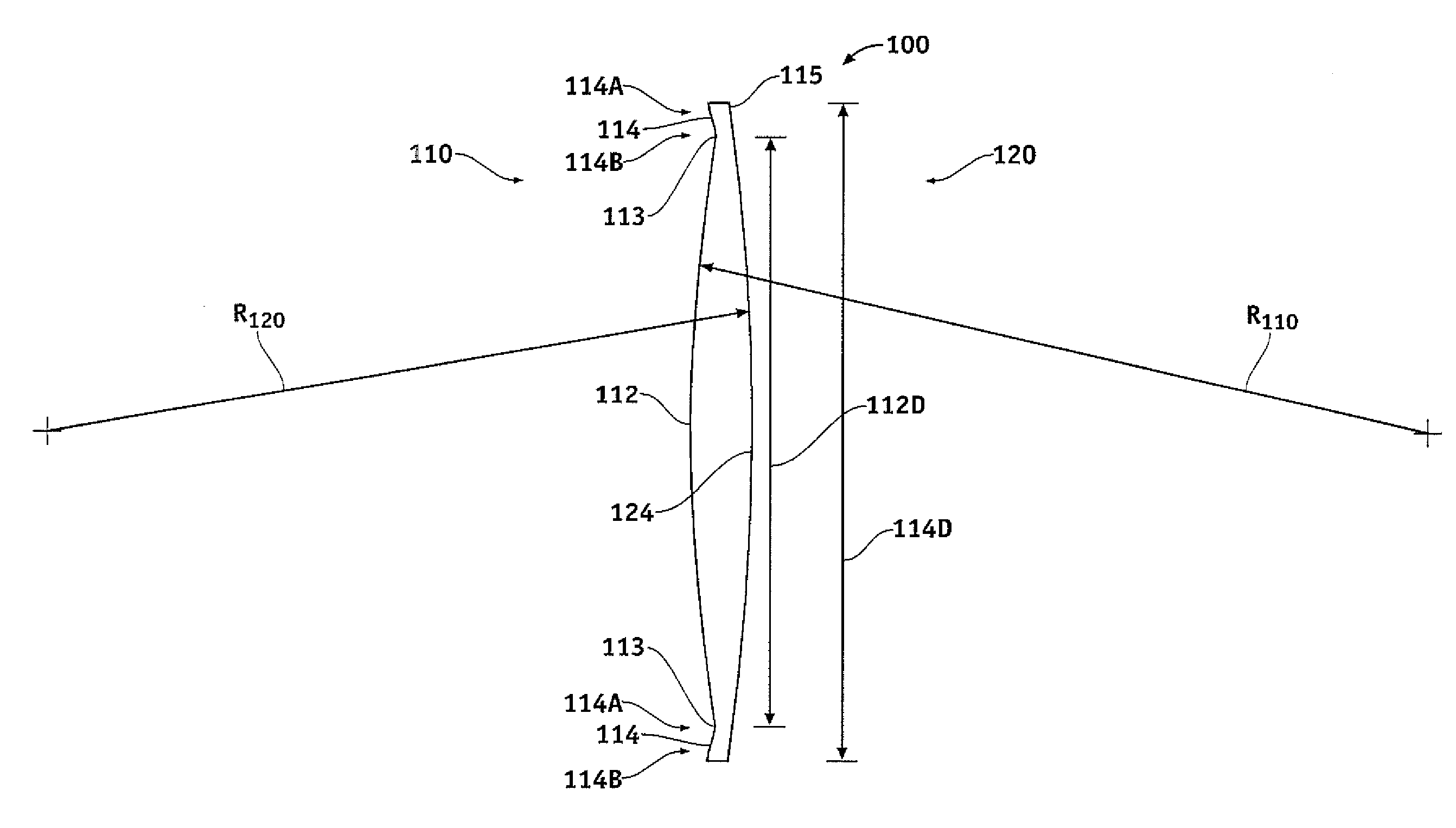
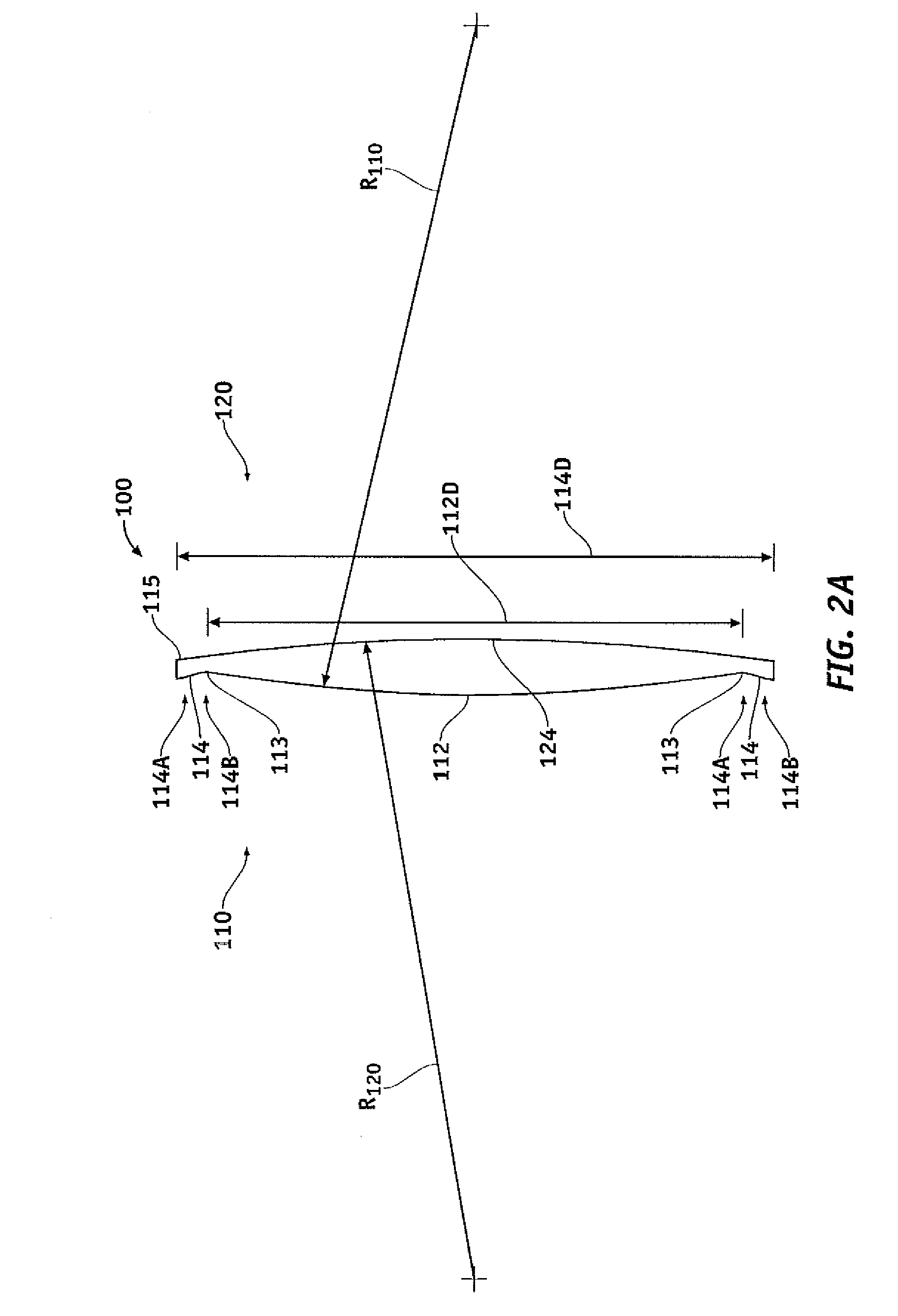
A wide-angle photographic lens system enabling correction of distortion composed of three lenses, in which a first lens, an iris, a second lens and a third lens sequentially arranged along an optical axis from an object, wherein the first lens has weak refractivity, the second lens has strong positive refractivity, and the third lens has negative refractivity, wherein the lens system satisfies relations, |f1 / f|>2.8, f2 / f<1, and te / tc<0.4, wherein f1 is a focal length of the first lens, f is a total focal length of all the lenses, f2 is a focal length of the second lens, te is a lens thickness on an effective diameter of a rear surface of the second lens, and tc is a center thickness of the second lens.
Owner:SEKONIX
Prescription lens and method of making same
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a prescription lens. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of obtaining information of a prescription lens and information of a frame to accommodate the prescription lens, wherein the information of the prescription lens comprises a lens power, an optical area and a spherical front base curve, and wherein the information of the frame comprises a frame curve; calculating the maximum lens thickness of the prescription lens at the optical area according to the information of the prescription lens; selecting a lens according to the calculated maximum lens thickness at the optical area, the information of the prescription lens and the information of the frame; and processing the selected lens so as to obtain the prescription lens that has a transition zone surrounding the optical area and an edge portion surrounding the transition zone such that the thickness of the edge portion is substantially thinner that the maximum lens thickness of the optical area.
Owner:POLYLITE TAIWAN
Method of making prescription lens
In one aspect of the present invention, a method for manufacturing a prescription lens includes obtaining information of a prescription lens and a frame to accommodate the prescription lens, the information of the prescription lens comprising a lens power, an optical zone and a spherical front base curve, and the information of the frame comprises a frame curve; calculating the maximum lens thickness of the prescription lens at the optical zone according to the information of the prescription lens; selecting a lens according to the calculated maximum lens thickness at the optical zone, the information of the prescription lens and the frame; and processing the selected lens so as to obtain the prescription lens having an intermediate zone surrounding the optical zone and an edge zone surrounding the intermediate zone such that the thickness of the edge zone is substantially thinner than the maximum lens thickness of the optical zone.
Owner:POLYLITE TAIWAN
Prescription lens and method of making same
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a prescription lens. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of obtaining information of a prescription lens and information of a frame to accommodate the prescription lens, wherein the information of the prescription lens comprises a lens power, an optical area and a spherical front base curve, and wherein the information of the frame comprises a frame curve; calculating the maximum lens thickness of the prescription lens at the optical area according to the information of the prescription lens; selecting a lens according to the calculated maximum lens thickness at the optical area, the information of the prescription lens and the information of the frame; and processing the selected lens so as to obtain the prescription lens that has an intermediate zone surrounding the optical area and an edge portion surrounding the intermediate zone such that the thickness of the edge portion is substantially thinner than the maximum lens thickness of the optical area.
Owner:POLYLITE TAIWAN
Apparatus and method for detecting lens thickness
Owner:ALCON INC
Microincision lens
ActiveUS20120059464A1Aberration correctionReduction in lens thicknessEye surgeryIntraocular lensOptical powerImage View
A foldable lens comprises an outer refractive surface portion comprising a first plurality of convexly curved refractive profile regions having positive optical power to converge light energy with refraction toward a focus on the retina. The convexly curved refractive profile regions of the outer region may correspond to at least about a quarter of the refractive power of the lens, such that the lens thickness is decreased substantially and the folded lens can fit through a small incision. The outer refractive surface portion focuses light with refraction, in focus images viewed through the outer portion of the lens can appear sharp to the patient. The outer refractive surface portion also comprises a second plurality of concavely curved refractive profile regions having negative optical power disposed between the first plurality, so as to diverge the light energy substantially away from the focus on the retina, such that visual artifacts are inhibited.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
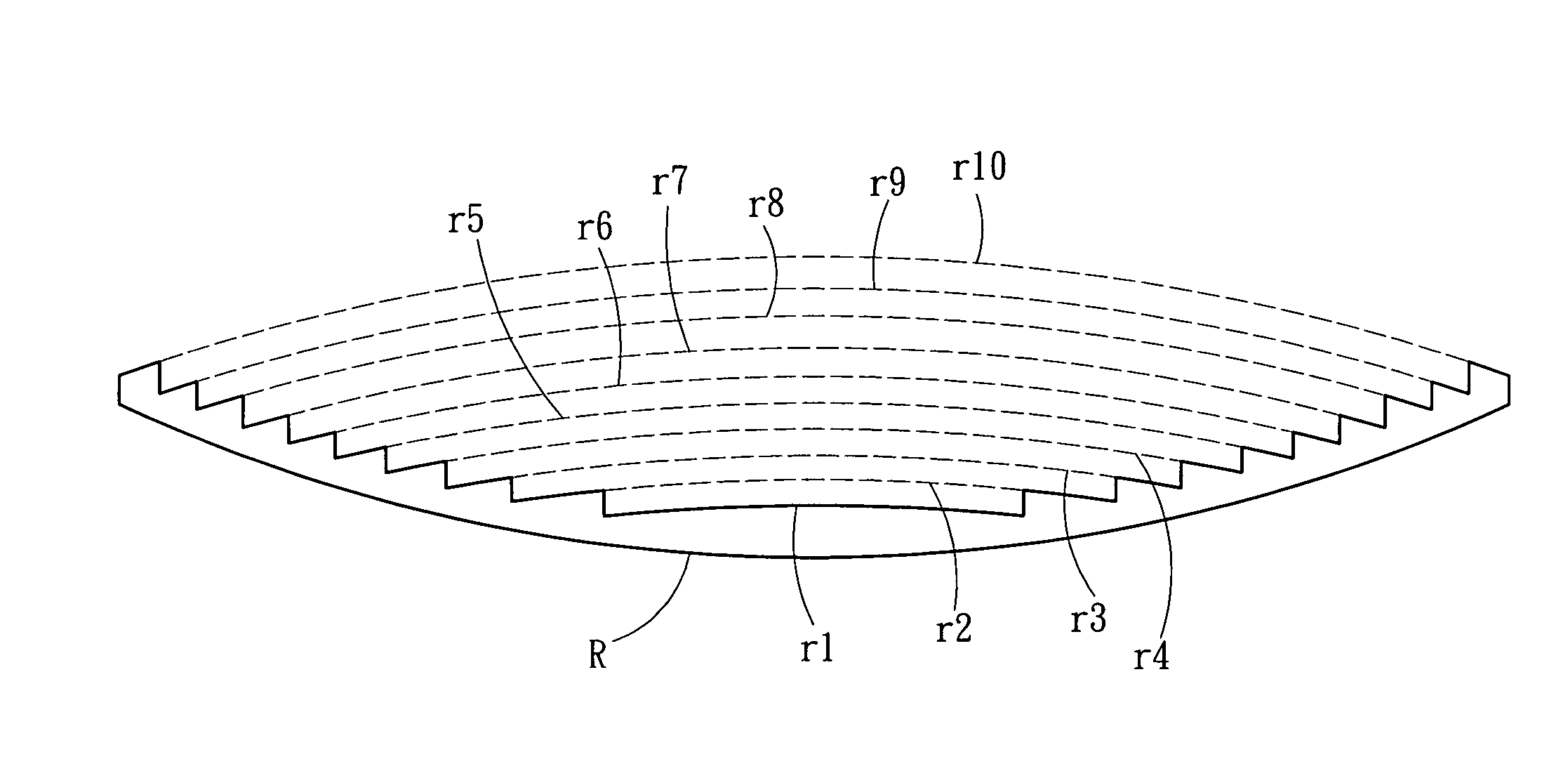
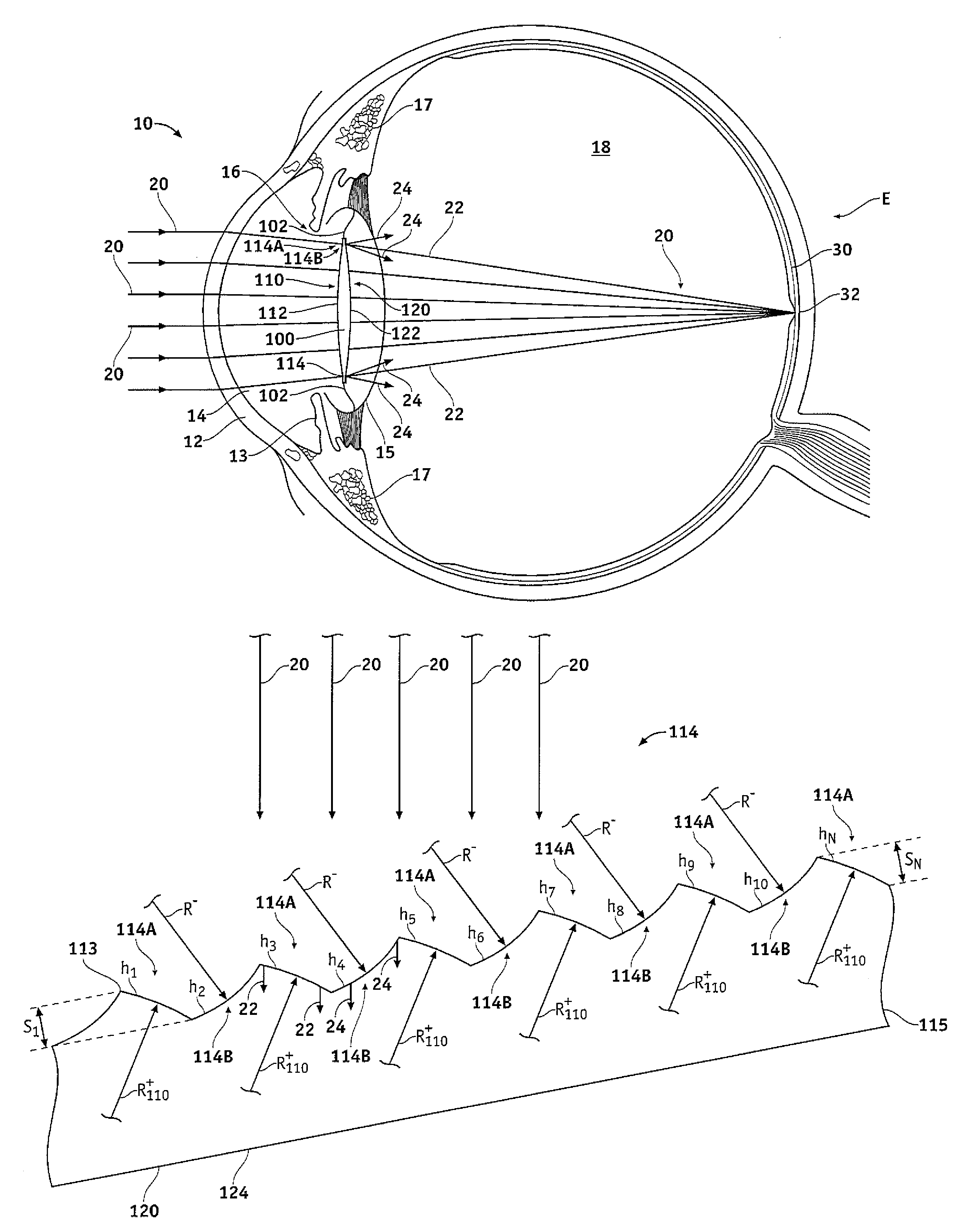
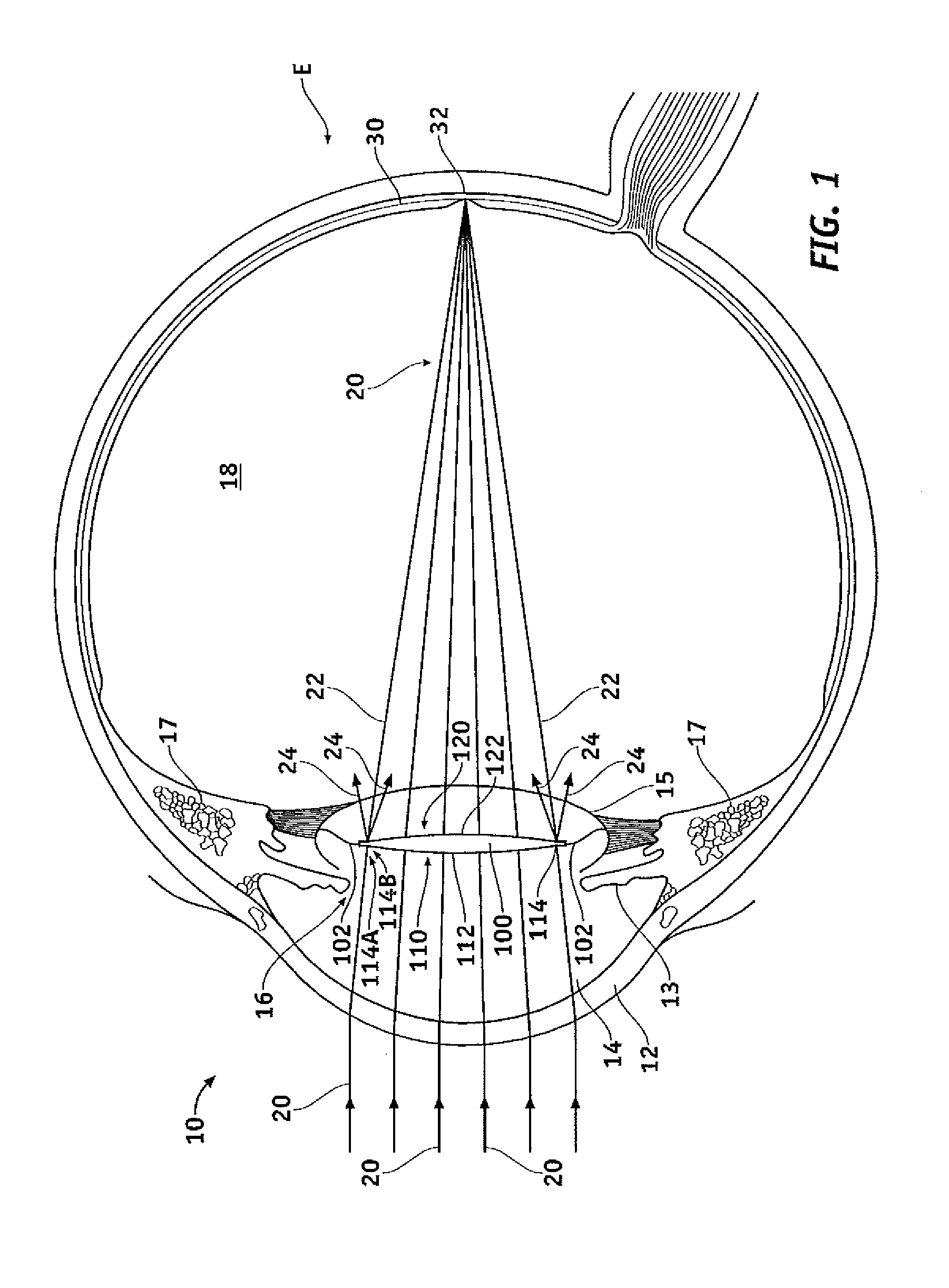
Thin-type spherical lens
ActiveUS20060256452A1Increasing the lens apertureIncreasing the thicknessBurglar alarmLensFresnel lensOptical axis
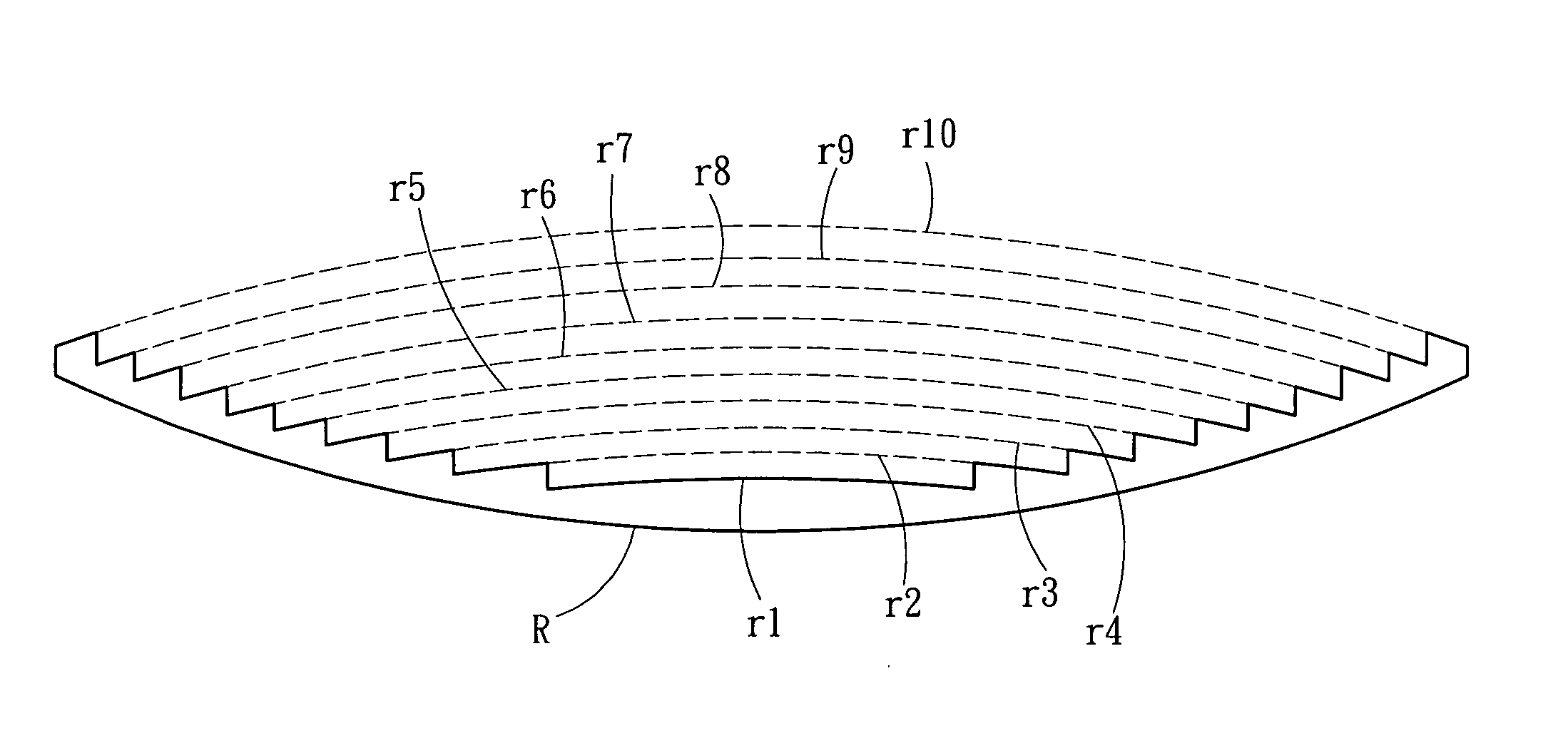
A thin-type spherical lens, fabricated according to the result of the virtual procedures of removing the portion of each of a plurality of lens bodies with different radii of curvature of light-exiting faces, which corresponds to a spherical surface with the optical axis of the thin-type spherical lens as its central axis, and assembling the preserved portions thereof to form a plurality of grooves as the light-exiting faces, which are equivalent to the grooves of the conventional Fresnel lens, wherein the depths or the widths of the plurality of grooves are different, and the curvature radii of the plurality of light-exiting faces are also designed to be different so that the lights emerging from the plurality of light-exiting faces are all focused on an identical point. The present invention can, as compare to the conventional approach, reduce the lens thickness when the radius of the apertures on the lens increased.
Owner:EVERSPRING IND
Imaging optical system, image reading apparatus and image reading apparatus using the imaging optical system
InactiveUS20100128353A1Simple manufacturing processReduce image sizeLensPictoral communicationCamera lensOcular straylight
An imaging optical system a high quality image may be implemented by determining the optimum design conditions for suppressing the generation of ghost while holding uniform and sufficient light using a simulation method. In the imaging optical system having a slit, the requirements for removing the stray light are the inclination of a lens arrangement direction, the slit width, the lens pitch, the view angle, and the height of the light-shielding wall. The slit location, the lens thickness, and the lens row width do not affect the stray light removal, but affect the brightness. In the imaging optical system having no slit, the essential requirements for removing the stray light are the height of the light-shielding wall and the lens pitch. The lens thickness and the lens row width do not affect the stray light removal, but affect the brightness.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Zone phase correcting lens and optical head device
InactiveUS20060002279A1Offset and reduce change in spherical aberrationWide operating temperature rangeRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansPhase correctionOptical axis
A zone phase correcting lens wherein a change in the third-order spherical aberration or the like is small in the case of a change in temperature and an optical head device having the zone phase correcting lens used as an objective lens. A minus sign is appended to the height measurement of a step formed so as to make the lens thickness in the optical axis thinner toward the outer region and a plus sign is appended to a step formed so as to make the lens thickness thicker toward the outer region. Supposing that D is an absolute value of the sum of the height measurements of the steps having the minus sign on the first surface and the second surface and E is an absolute value of the sum of the height measurements of the steps having the plus sign on the first surface and the second surface, a wavelength λ1 and a refractive index N1 of the lens for a first laser beam satisfy the following conditions: 10×λ1<{D×(N1−1)}<30×λ1 2×E<D.
Owner:NIDEC NISSIN CORP
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) imaging system and method for monitoring shaping effect of orthokeratology lens by using living body
ActiveCN104545790AMonitor applanation progressMonitor the shaping effectEye diagnosticsSpectral domainLiving body
The invention relates to an OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) imaging system and a measurement method for monitoring the shaping effect of an orthokeratology lens by using a living body, wherein the OCT imaging system comprises a control computer, a spectral-domain OCT imaging module, a human eye scanning module and an optotype aligning module; the spectral-domain OCT imaging module comprises a partial spectral-domain OCT imaging module and a full spectral-domain OCT imaging module; a movable 45-degree spectroscope is arranged between the partial spectral-domain OCT imaging module and the full spectral-domain OCT imaging module. The measurement method comprises the following steps of (1) obtaining a full orthokeratology image of a living body; (2) obtaining an actual lens thickness contour image; (3) analyzing the center positioning state of the whole orthokeratology lens; (4) obtaining a partial high-definition image of the orthokeratology lens, and obtaining the length, width and area of a transition region. According to the OCT imaging system and the measurement method for monitoring the shaping effect of the orthokeratology lens by using the living body, the orthokeratology image of the living body and the partial orthokeratology image in a feature region are analyzed, the transition region of the orthokeratology lens is directly imaged, and a purpose of dynamically monitoring the cornea flattening progress and the cornea shaping effect according to the dynamic variation of a tear film along with time is achieved.
Owner:维视艾康特(广东)医疗科技股份有限公司 +1
Solid elastic lens element and method of making same
A lens element is provided that includes a housing defining a center bore and an optical axis, and a light transmissive cover coupled to the housing. A first elastic solid lens is disposed within the housing adjacent the light transmissive cover, and is characterized by a first thickness and a first durometer hardness. A second elastic solid lens is disposed in the housing adjacent to and substantially conforming to the first elastic solid lens, and is characterized by a second thickness and a second durometer hardness. The second lens thickness is less than the first lens thickness, and the second durometer hardness is greater than the first durometer hardness. In one embodiment, the first durometer hardness is less than OO60 as measured by the Shore method, and the second durometer hardness is in the range of A20 to A60 as measured by the Shore method.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Solid elastic lens element and method of making same
A lens element is provided that includes a housing defining a center bore and an optical axis, and a light transmissive cover coupled to the housing. A first elastic solid lens is disposed within the housing adjacent the light transmissive cover, and is characterized by a first thickness and a first durometer hardness. A second elastic solid lens is disposed in the housing adjacent to and substantially conforming to the first elastic solid lens, and is characterized by a second thickness and a second durometer hardness. The second lens thickness is less than the first lens thickness, and the second durometer hardness is greater than the first durometer hardness. In one embodiment, the first durometer hardness is less than OO60 as measured by the Shore method, and the second durometer hardness is in the range of A20 to A60 as measured by the Shore method.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Apparatus and method for measuring optical system parameter
ActiveCN101226344BImprove eccentricity measurement accuracyEliminate errorsUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMeasurement deviceMobile station
A parameter measurement device of optical system comprises a short coherent light module, a focusing lens, a collimation lens, a filtering pinhole, a splitter, a corner reflector, an one-dimension accurate mobile station, an adjustable focus telescope, a micro swivel, a focusing lens and an imaging CCD. And a relative measurement method uses optical interferometry to accurately measure the eccentricity, inclination, lens thickness and lens distances of an object optical system. The invention can improve the eccentricity measurement accuracy of lens to match higher eccentricity demand, realizethe final measurement of internal distances in optical system and realize the distance of assembled optical system.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Wide-angle photographic lens system enabling correction of distortion
A wide-angle photographic lens system enabling correction of distortion composed of four lenses, in which a first lens, an iris, a second lens, a third lens and a fourth lens sequentially arranged along an optical axis from an object, wherein the first lens has weak refractivity, the second lens has positive refractivity, the third lens has strong positive refractivity, and the fourth lens has negative refractivity, wherein the lens system satisfies relations, |f1 / f|>4, f3 / f<1.5, and te / tc<0.5, wherein f1 is a focal length of the first lens, f is a total focal length of all the lenses, f3 is a focal length of the third lens, to is a lens thickness on an effective diameter of a rear surface of the third lens, and tc is a center thickness of the third lens.
Owner:SEKONIX
Thin-type spherical lens
ActiveUS7151639B2Increasing the lens apertureIncreasing the thicknessGrain huskingGrain polishingFresnel lensOptical axis
A thin-type spherical lens, fabricated according to the result of the virtual procedures of removing the portion of each of a plurality of lens bodies with different radii of curvature of light-exiting faces, which corresponds to a spherical surface with the optical axis of the thin-type spherical lens as its central axis, and assembling the preserved portions thereof to form a plurality of grooves as the light-exiting faces, which are equivalent to the grooves of the conventional Fresnel lens, wherein the depths or the widths of the plurality of grooves are different, and the curvature radii of the plurality of light-exiting faces are also designed to be different so that the lights emerging from the plurality of light-exiting faces are all focused on an identical point. The present invention can, as compare to the conventional approach, reduce the lens thickness when the radius of the apertures on the lens increased.
Owner:EVERSPRING IND
Eyeglass lens processing apparatus
ActiveUS8241091B2Effectively preventExtended processing timeEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesCamera lensEyewear
An eyeglass lens processing apparatus includes: a lens rotation unit rotating a lens; a processing tool rotation unit processing the lens; an axis-to-axis distance changing unit for changing an axis-to-axis distance between the chuck shaft and the processing tool rotation shaft; a lens surface configuration acquiring unit which acquires a front surface curve configuration and a rear surface curve configuration of the lens; a lens outer diameter acquiring unit which acquires an outer diameter of a lens; a calculation unit which calculates a thickness of the lens and calculates a cutting depth of the lens, so that torque applied onto the chuck shaft in rough processing becomes substantially constant, based on the calculated lens thickness and a processing distance from the rotation center of the lens; and a control unit which controls the axis-to-axis distance changing unit in accordance with the calculated cutting depth and for rough processing the lens.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Microincision lens
A foldable lens comprises an outer refractive surface portion comprising a first plurality of convexly curved refractive profile regions having positive optical power to converge light energy with refraction toward a focus on the retina. The convexly curved refractive profile regions of the outer region may correspond to at least about a quarter of the refractive power of the lens, such that the lens thickness is decreased substantially and the folded lens can fit through a small incision. The outer refractive surface portion focuses light with refraction, in focus images viewed through the outer portion of the lens can appear sharp to the patient. The outer refractive surface portion also comprises a second plurality of concavely curved refractive profile regions having negative optical power disposed between the first plurality, so as to diverge the light energy substantially away from the focus on the retina, such that visual artifacts are inhibited.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com