A multi-root peer-to-peer IoT identification analysis method
An IoT identification and analysis method technology, which is applied in user identity/authority verification, data exchange through path configuration, electrical components, etc. It can solve the problem of equal interoperability and information sharing without basic IoT resources, services, and the inability to ensure the independence of item analysis. rights, packet forwarding rule dependence, etc., to achieve the effect of ensuring legality and security, improving single-point failure, and ensuring good development.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be described in detail below through specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
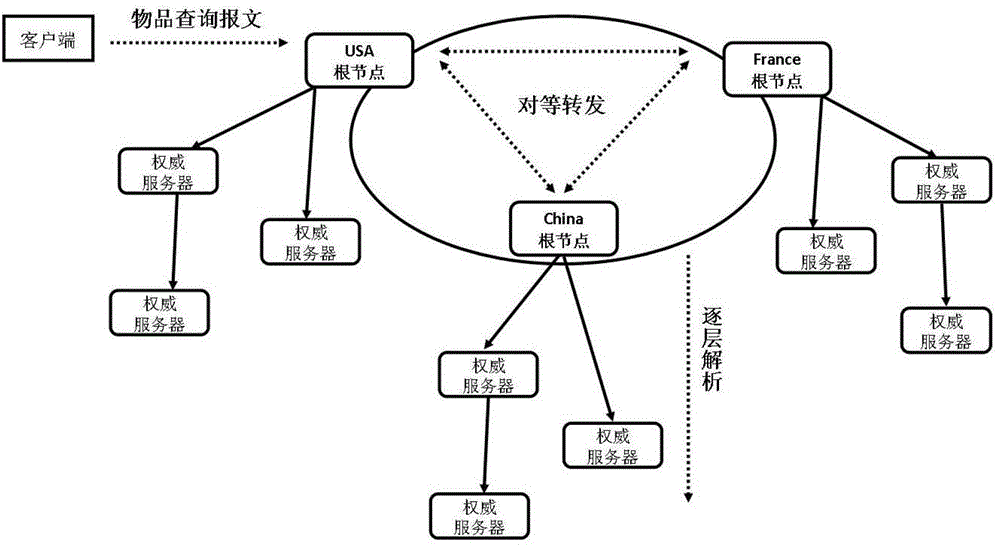
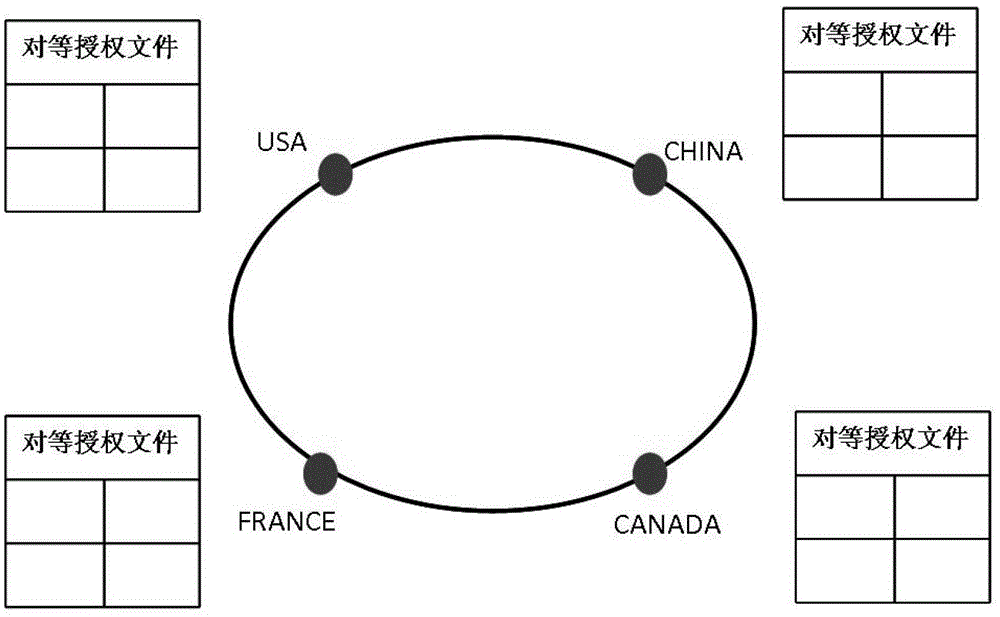
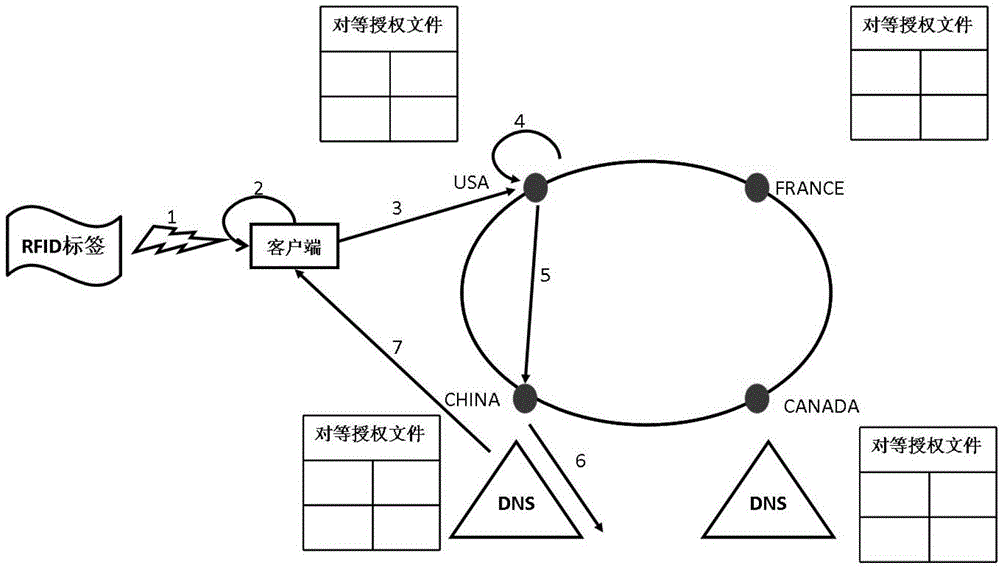
[0036] The internet of things identification peer-to-peer analysis framework proposed by the present invention converts a single root node into multiple peer root nodes with equal status, consistent functions and mutual cooperation at the top layer of the analysis system. These root nodes are respectively managed and controlled by corresponding countries or organizations, and on the basis of ensuring that each root node has resolution autonomy, they jointly process item object identification query requests. The specific implementation content will be described below.
[0037] 1. System architecture
[0038] 1) As attached figure 1 As shown in , the client that initiates the IoT ID resolution request is the resolver, which is responsible for receiving object identifiers such as RFID codes and converting them into FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com