Integrated work-low for accurate input function estimation
A data and scan data technology, applied in the field of arterial input function estimation, can solve the problems of reducing the apparent peak amplitude of the input function, incorrect dynamic model estimation, inaccurate pixels depicting arterial blood, etc., and minimize the invasiveness. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
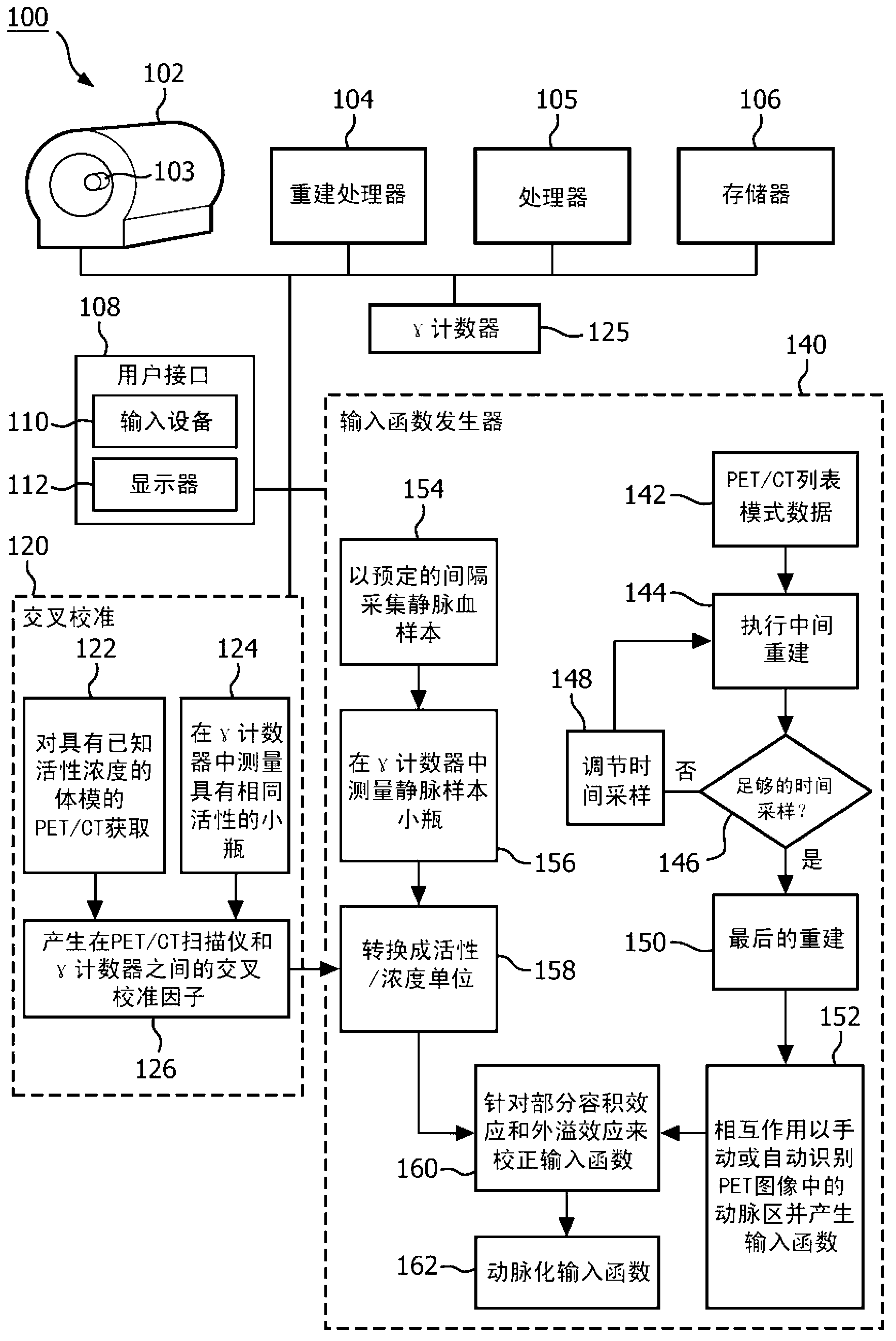
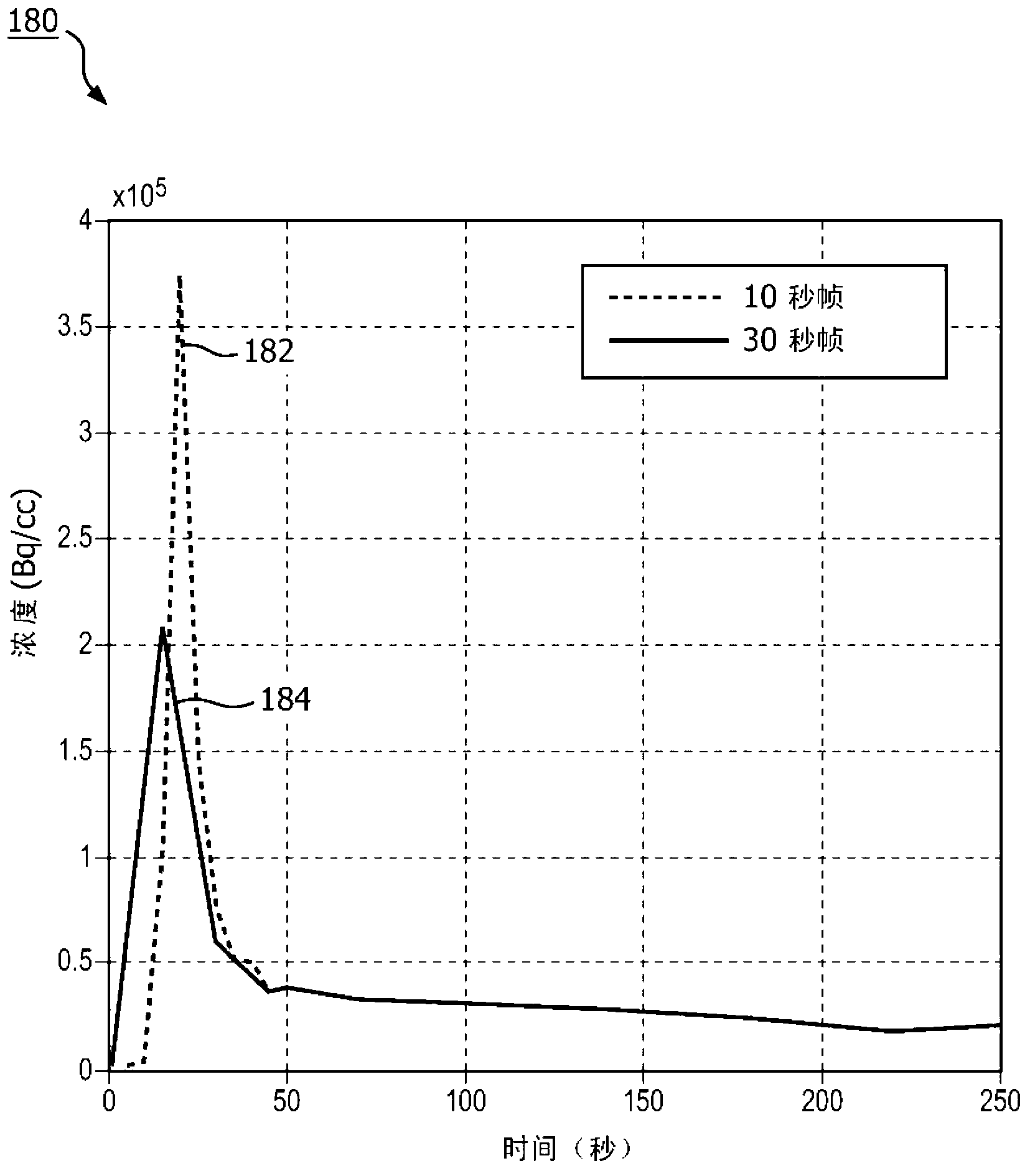
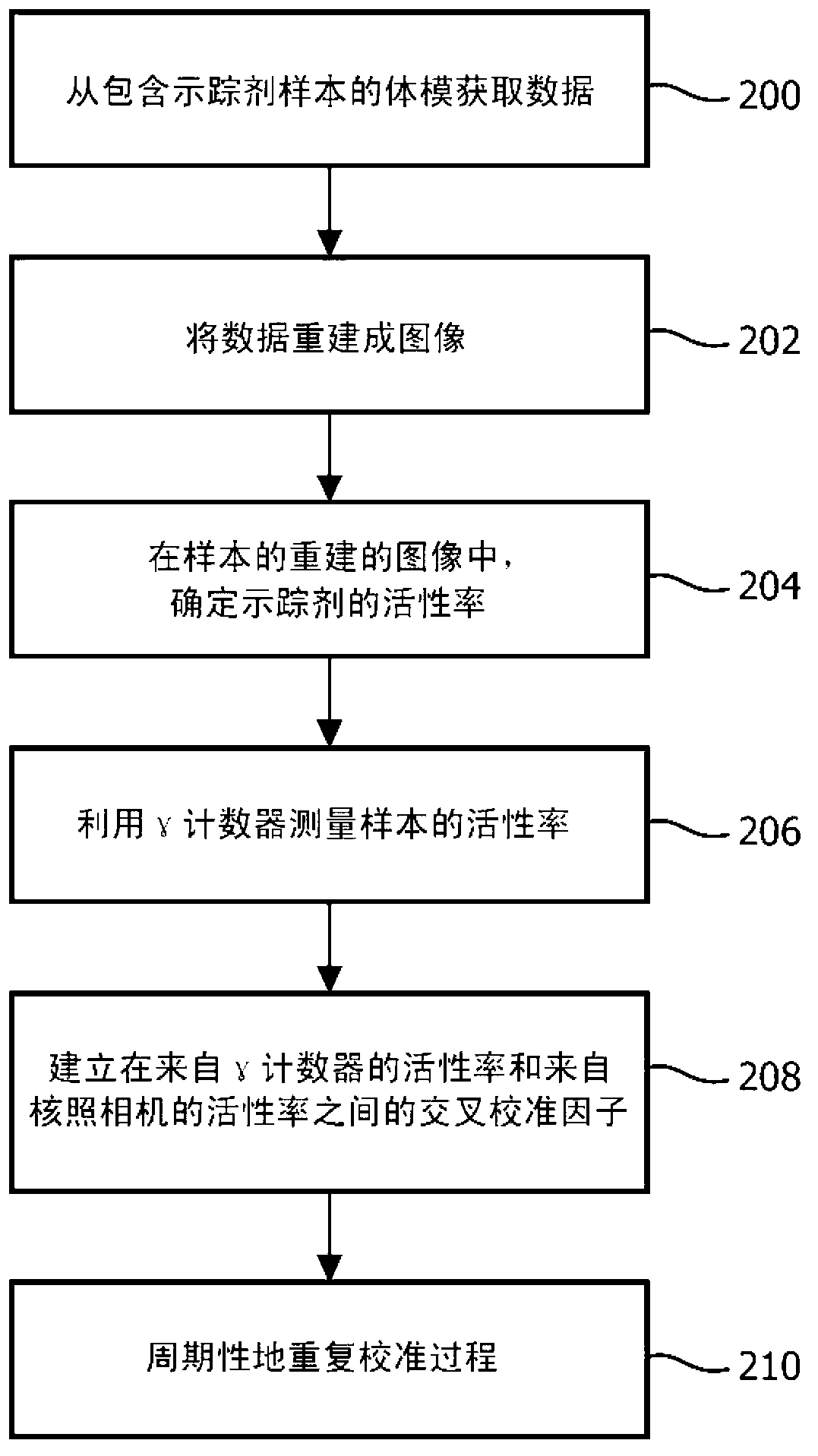
[0020] The subject innovation overcomes the aforementioned problems in the art by acquiring scan data in list mode and binning the data retrospectively to generate images including arterial regions. When acquiring data in list mode, the raw data is stored in the list, and each entry carries a timestamp indicating the time of acquisition. This makes the raw data available for later analysis or reuse (eg, re-construction), even after the diagnostic image has been reconstructed. Because the data is collected and stored in tabular mode, the size of the time bins can be retrospectively adjusted, and the process repeated for bins of different sizes and time offsets, until the true peak is determined. During the imaging procedure, a blood sample is drawn and the concentration of tracer in the sample is empirically measured. Because these samples are taken relatively late in the imaging process, the concentrations of radiopharmaceuticals in arteries and vessels become substantially e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com