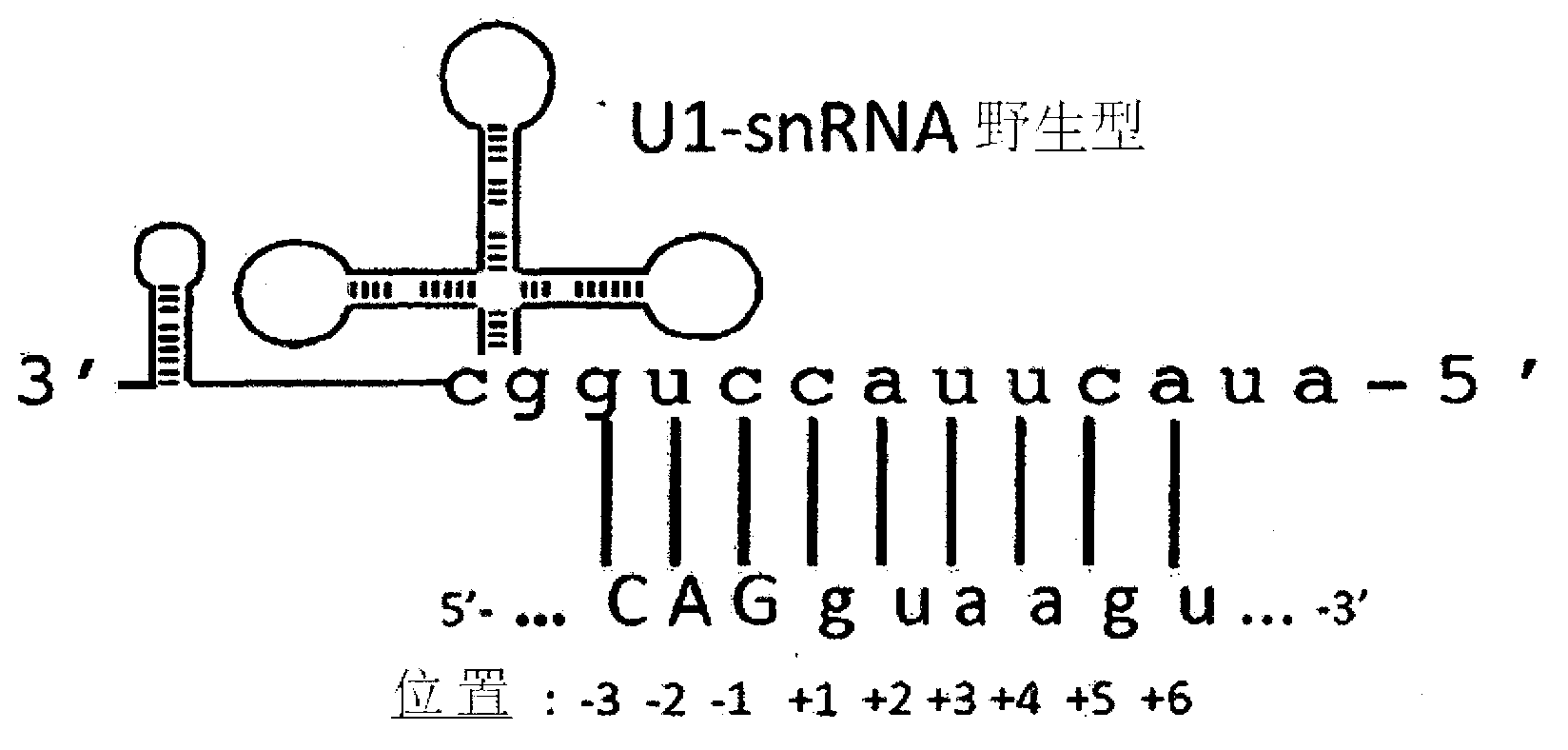A modified human U1snRNA molecule, a gene encoding for the modified human U1snRNA molecule, an expression vector including the gene, and the use thereof in gene therapy
An expression vector, human technology, applied in the field of modified human snRNA molecules to achieve highly selective effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Generation of modified U1snRNA
[0037] The modified U1snRNA was generated by the following procedure: the plasmid containing the wild-type U1-snRNA gene, that is, the unmodified U1-snRNA, was digested with BglII and BclI restriction enzymes. The sequence formed between the two restriction sites is replaced with a double-stranded oligonucleotide containing the binding sequence. The following Table 1 describes the forward sequence and reverse sequence of each oligonucleotide, and the resulting modified U1-snRNA is named after the oligonucleotide used.
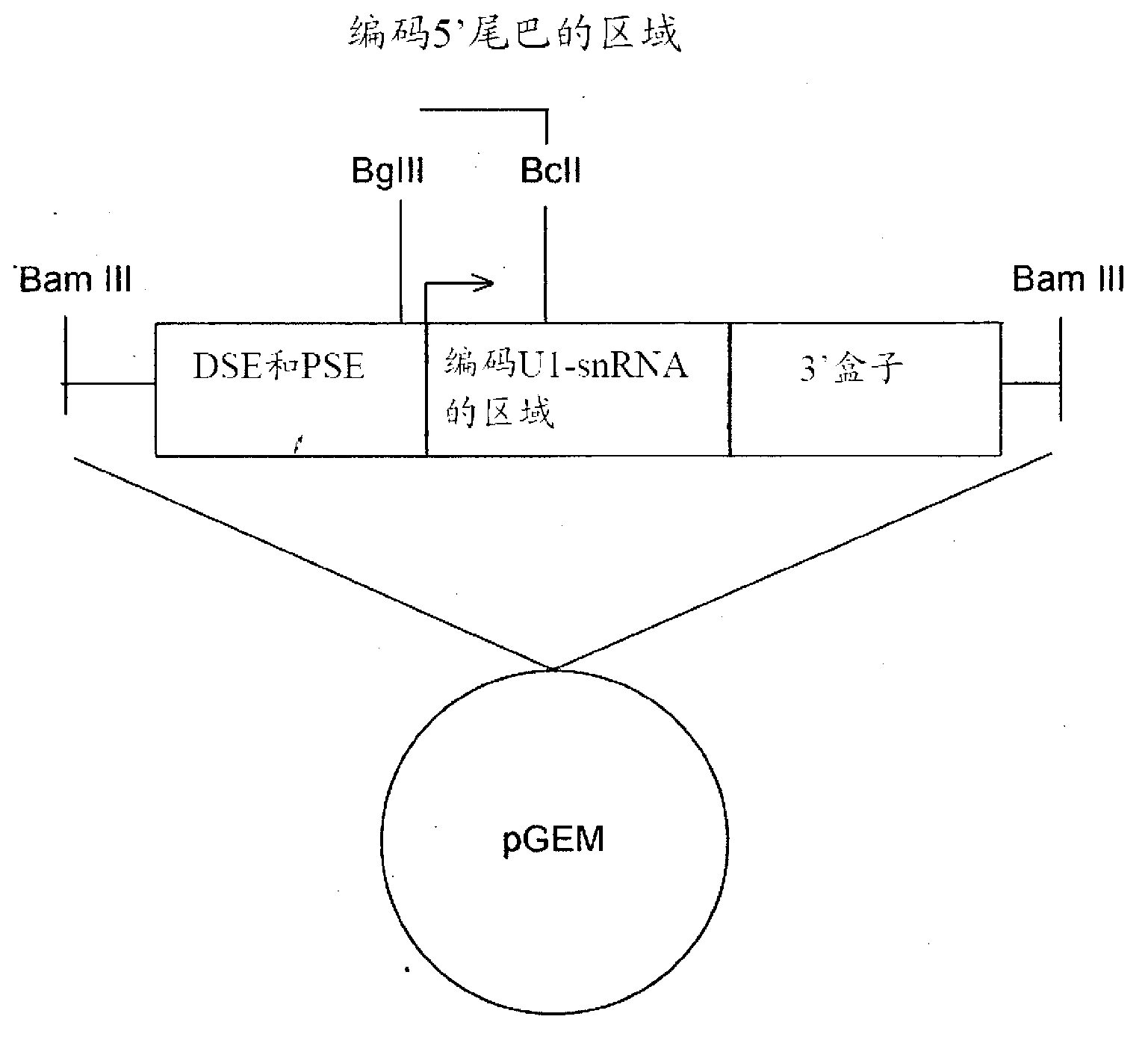
[0038] and, figure 2 A schematic diagram of U1snRNA gene elements is shown. The cloning strategy for preparing different modified U1snRNA is indicated. figure 2 It shows the U1snRNA gene inserted into the plasmid vector (pGEM) with the promoter elements DSE and PSE, the U1snRNA coding region (in the middle), and the 3'processing cassette. The transcription start site is indicated by an arrow. The sequence betw...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Transfection of microgenes into cultured cells and analysis of splicing products
[0044] The inclusion vector is inserted into the cell by transient transfection with Lipofectamine (Liposome). After extracting total cellular RNA with Trizol, RNA was analyzed by RT-PCR with specific primers.
[0045] The reaction takes place in two steps: reverse transcription of RNA into a cDNA strand by reverse transcriptase using random primers as a template, and amplification of the resulting cDNA by DNA polymerase.
[0046] The PCR reaction was performed in a final volume of 25μl of a mixture containing:
[0047] -5μl AMV / Tfl5x buffer, suitable for the above two enzymes to function correctly;
[0048] -1μl of 10mM dNTP mixture;
[0049] -50pmol forward primer and 50pmol reverse primer;
[0050] -2μl of 25mM MgSO 4 ;
[0051] -2μl of RNA extracted from cells;
[0052] -1μl AMV-RT (0.1μ / μl), 1μl Tfl DNA polymerase;
[0053] -Appropriate amount of ultrapure H 2 O
[0054] The reverse tra...
Embodiment 3
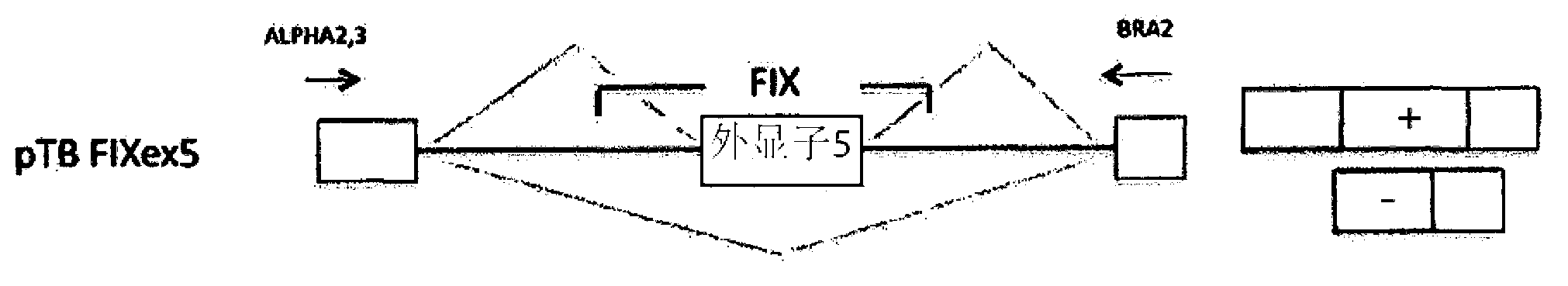
[0056] Example 3: Exons near the donor site of coagulation factor IX associated with hemophilia B Mutations and mutations in the polypyrimidine sequence upstream of the exon 5 receptor site
[0057] In the factor IX gene (F9), the mutation of exon at position -2 in the donor site, and the mutation at positions -8 and -9 in the acceptor site of exon 5 are the same as the type B Hemophilia is associated. It is interesting to note that the mutation at position-2 in the exon is a synonymous mutation and does not change the coding sequence, but causes the exon to be missed and therefore it is classified as a splicing mutation. Mutations at positions -8 and -9 in the receptor site also caused the omission of exon 5.
[0058] Table 2 shows the mutations in question, which were identified in patients with hemophilia B (Haemophilia B International Database). Nucleotides belonging to exon 5 are shown in capital letters, while those belonging to introns are shown in lower case. Each posi...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap