Method for quantitatively detecting welding spatter by utilizing acoustic emission signal energy equivalent of resistance spot welding process
A technology of acoustic emission signal and welding spatter, which is applied in the field of rapid detection of resistance spot welding quality, can solve the problems of lack of quantitative detection and evaluation methods, difficulty in detecting the quality of resistance spot welding solder joints, etc., and achieve low design and manufacturing costs and an evaluation method Simple, easy-to-achieve effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The workpiece to be welded is the overlapping joint of two galvanized steel sheet structures with a thickness of 1 mm. The main welding process parameters used are: welding current is 10000A, welding current duration is 8 cycles, and electrode pressure is 0.15MPa.
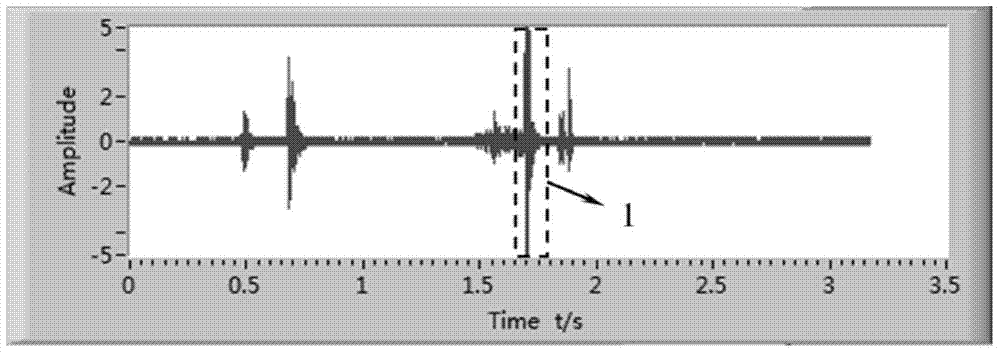
[0037] During welding, the structural load acoustic emission signal of the resistance spot welding process is collected in real time, and the dynamic curve of the structural load acoustic emission signal is drawn by the analysis software, as shown in figure 1 shown.
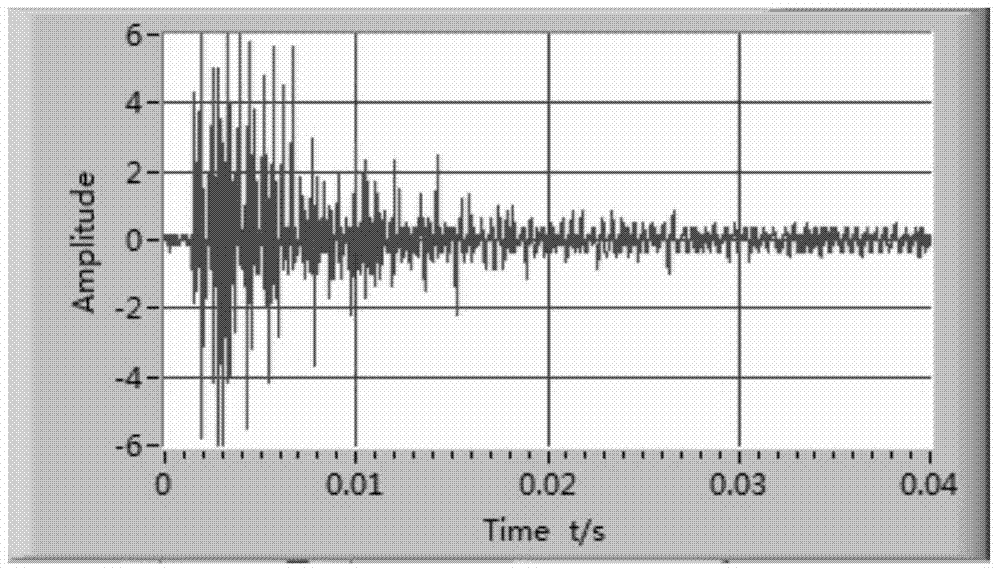
[0038] Different stages of the welding process can be identified from the waveform diagram, and the welding spatter signal 1 can be extracted, such as figure 2 shown. It can be seen that the mode of the welding spatter is a welding spatter event of a single acoustic emission event.
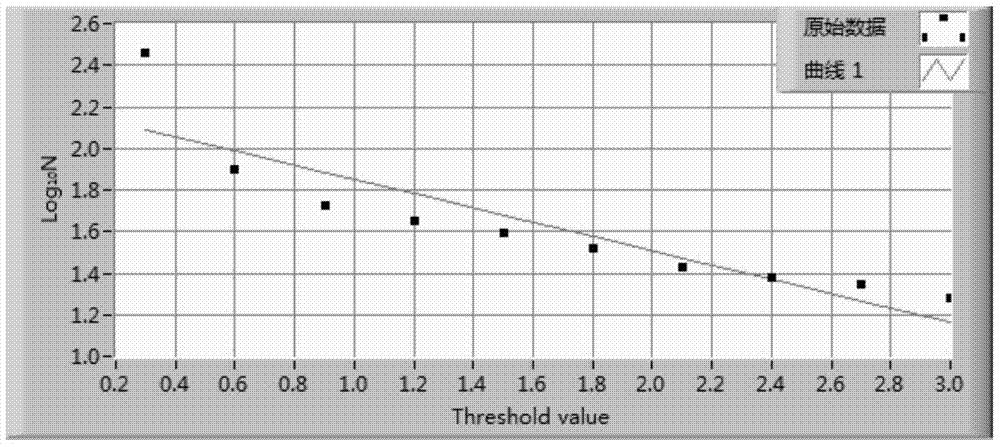
[0039] Statistics the amplitude distribution of welding spatter acoustic emission signal pulse. According to the distribution, the magnitude is divided into 10 ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The workpiece to be welded is the overlapping joint of two galvanized steel sheet structures with a thickness of 1 mm. The main welding process parameters used are: welding current is 11000A, welding current duration is 8 cycles, and electrode pressure is 0.15MPa.
[0045] During welding, the structural load acoustic emission signal of the resistance spot welding process is collected in real time, and the dynamic curve of the structural load acoustic emission signal is drawn by the analysis software, as shown in Figure 4 shown.
[0046] Different stages of the welding process can be identified from the waveform diagram, and the welding spatter signal 1 can be extracted, such as Figure 5 shown. It can be seen that the welding spattering mode is a welding spattering event composed of two acoustic emission events.
[0047] Statistics the amplitude distribution of welding spatter acoustic emission signal pulse. According to the distribution, the magnitude is divided i...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The workpiece to be welded is the overlapping joint of two galvanized steel sheet structures with a thickness of 1mm. The main welding process parameters used are: welding current is 10000A, welding current duration is 8 cycles, and electrode pressure is 0.15MPa.
[0053] During welding, the structural load acoustic emission signal of the resistance spot welding process is collected in real time, and the dynamic curve of the structural load acoustic emission signal is drawn by the analysis software, as shown in Figure 7 shown.
[0054] Different stages of the welding process can be identified from the waveform diagram, and the welding spatter signal 1 can be extracted, such as Figure 8 shown. It can be seen that the weld spatter pattern is a weld spatter event composed of three acoustic emission events.
[0055] Statistics the amplitude distribution of welding spatter acoustic emission signal pulse. According to the distribution, the magnitude is divided into 10 g...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com