A rapid identification method for hidden danger points of debris flow in strong earthquake area
An identification method, debris flow technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the need for rapid identification of debris flow hidden danger points in strong earthquake areas, misjudgment of mountain torrents as debris flow trenches, and difficult identification Debris flow hidden dangers and other issues are easy to obtain and calculate, reduce the probability of misjudgment of debris flow, and quickly identify the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be further described below.
[0020] Rapid identification of hidden danger points of debris flow was carried out for Longchi Town, Dujiangyan City, a strong earthquake area. Longchi Town is located in Dujiangyan City, Chengdu, Sichuan Province. It belongs to the humid subtropical climate zone in the Sichuan Basin. It has four distinct seasons, no extreme heat in summer, no severe cold in winter, abundant rainfall, fresh air, and pleasant climate. Not much, the annual average precipitation is 1134.8mm; it is only 10 kilometers away from Yingxiu, the epicenter of the 8.0-magnitude strong earthquake that occurred in Wenchuan on May 12, 2008, and the earthquake had a great impact on the area; after the Wenchuan earthquake, there were many outbreaks in this area Debris flows, such as the large-scale mass debris flows that broke out in this area in 2010.
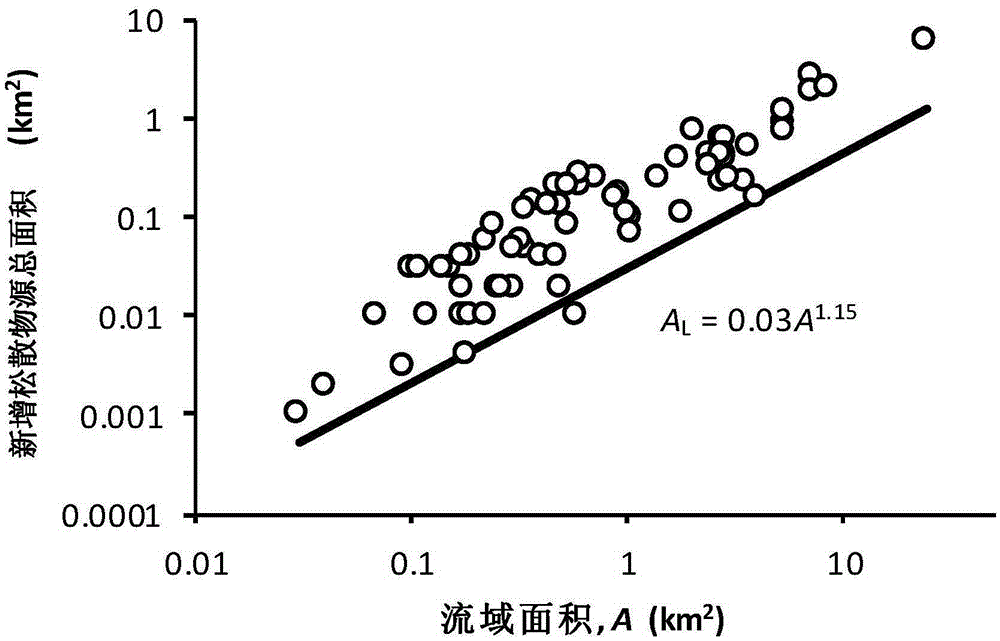
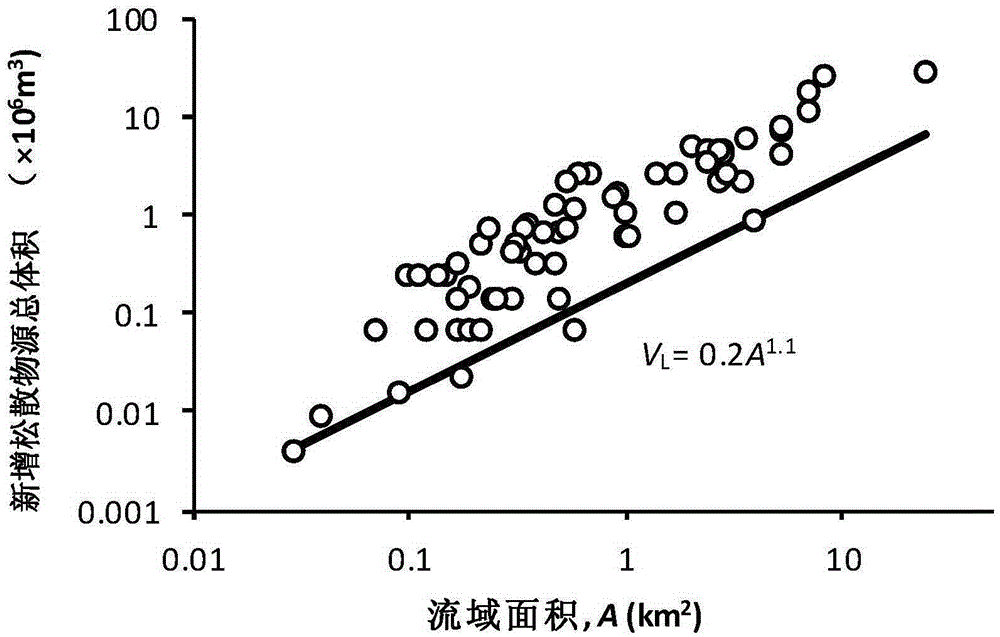
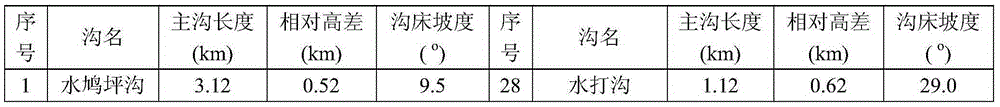
[0021] Through the ArcGIS software, the rapid identification met...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com