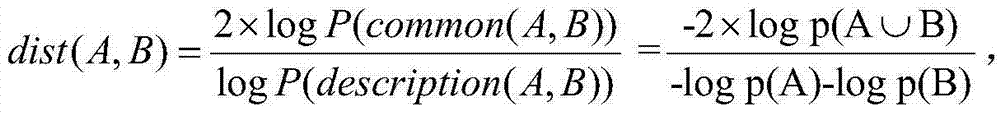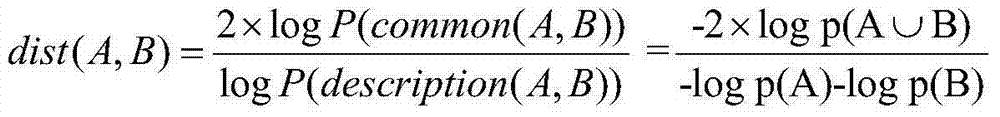Nearest neighbor filling method of non-fixed k values
A filling method and nearest neighbor technology, applied in neural learning methods, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as unreasonable distance calculations, and achieve an easy-to-implement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] First, various hybrid distance calculations. Divide common attributes in research into five categories: continuous, symmetric binary, asymmetric binary, disordered discrete, and ordered discrete. The distance of the present invention is defined as follows: in Represents whether there is missing phenomenon in case i and j, if there is, it is 0, otherwise it is 1. f is the attribute of the fth category among the five categories of attributes, n is the number of attributes, and d ij f That is, the distance between case i and j class f attributes.
[0025] A. Continuous value distance calculation
[0026] The distance calculation formula for two consecutive value instances: where n represents that there are n continuous attributes in cases i and j, A i,k is the attribute value of the kth attribute of case i, is the average of n consecutive attributes in case i.
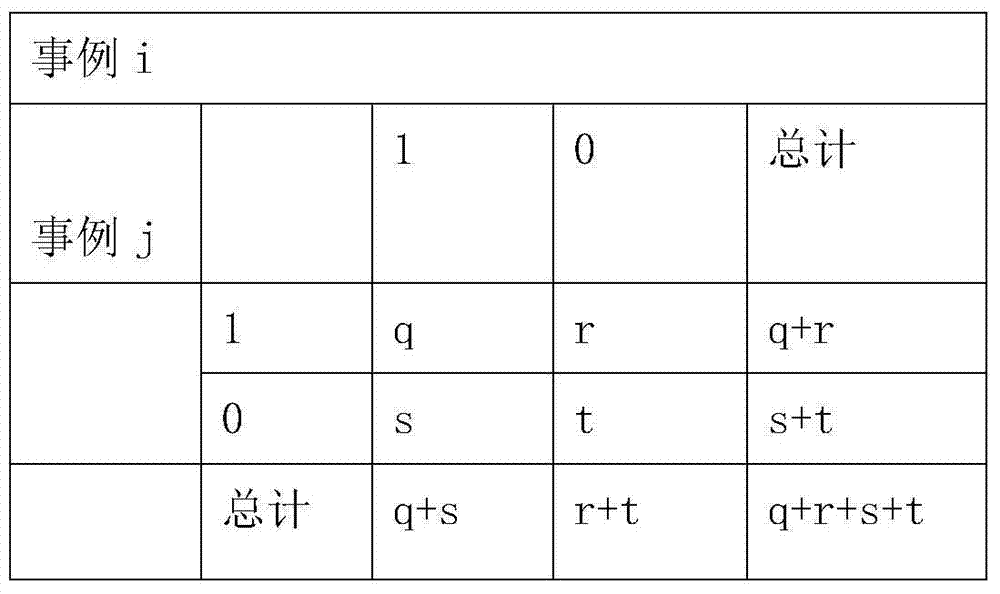
[0027] B. Symmetric Binary and Asymmetric Binary Attribute Distance Computation
[0028] If the di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com