Method and device for choosing DNS (domain name server)
A technology for DNS server and domain name resolution request, which is applied in the field of DNS server selection device, which can solve problems affecting the user's Internet access speed, normal domain name resolution to phishing websites or hosts controlled by hackers, DNS hijacking, etc., so as to improve efficiency and safety effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] refer to figure 1 , shows a flowchart of steps of a method for selecting a DNS server according to an embodiment of the present invention, the method for selecting a DNS server may specifically include the following steps:
[0036] Step S101, determining N DNS servers to be selected, wherein N is a natural number greater than or equal to 2.
[0037] Step S102, sending domain name resolution requests to the N DNS servers to be selected, and obtaining the response time of the N DNS servers to the domain name resolution requests and the resolved IP addresses of the preset domain names carried in the domain name resolution requests.
[0038] Step S103, connect to the IP addresses resolved by the N DNS servers, and obtain the IP response time of the connected IP addresses.
[0039] In the specific implementation, because some sites have multiple servers, and different servers correspond to different IP addresses, different DNS servers may resolve different IP addresses for ...
Embodiment 2
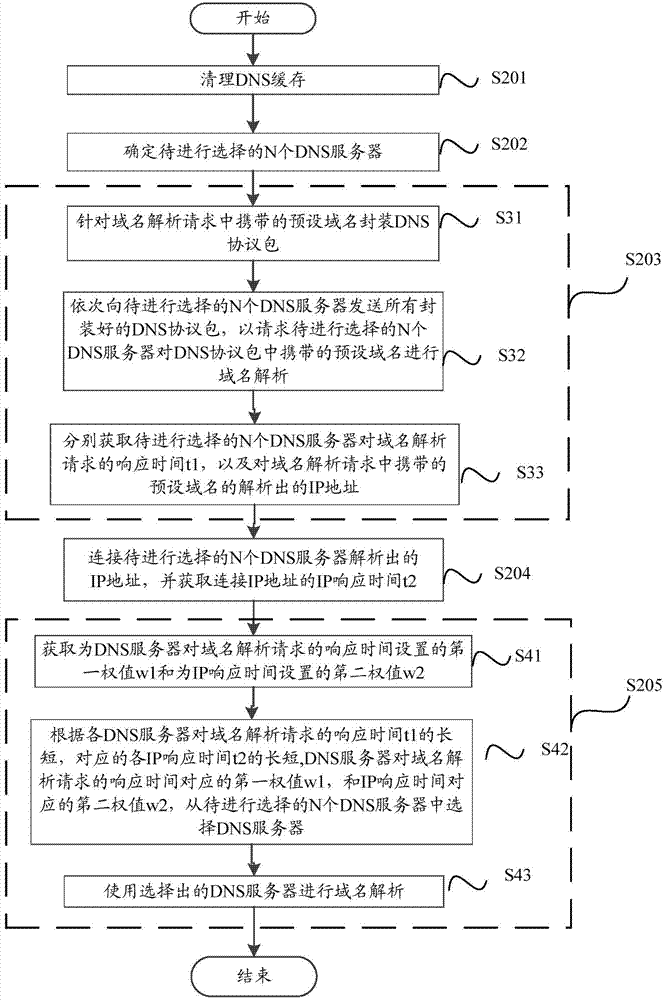
[0043] refer to figure 2 , shows a flowchart of steps of a method for selecting a DNS server according to an embodiment of the present invention, the method for selecting a DNS server may specifically include the following steps:
[0044] Step S201, network detection and repair.
[0045] In a specific implementation, the network detection and repair in step S201 may include one or more of the following three methods:
[0046] Method 1: Detect and repair the validity of the currently used DNS server.
[0047] The DNS server currently used by the user includes a preferred DNS server and an alternate DNS server, wherein the alternate server can be set to be different from the preferred server, the same, or not set. Once the preferred DNS server fails to perform domain name resolution, the backup DNS server will perform domain name resolution.
[0048] In a specific implementation, detecting the validity of the currently used DNS service is to detect whether there is a DNS hij...
Embodiment 3
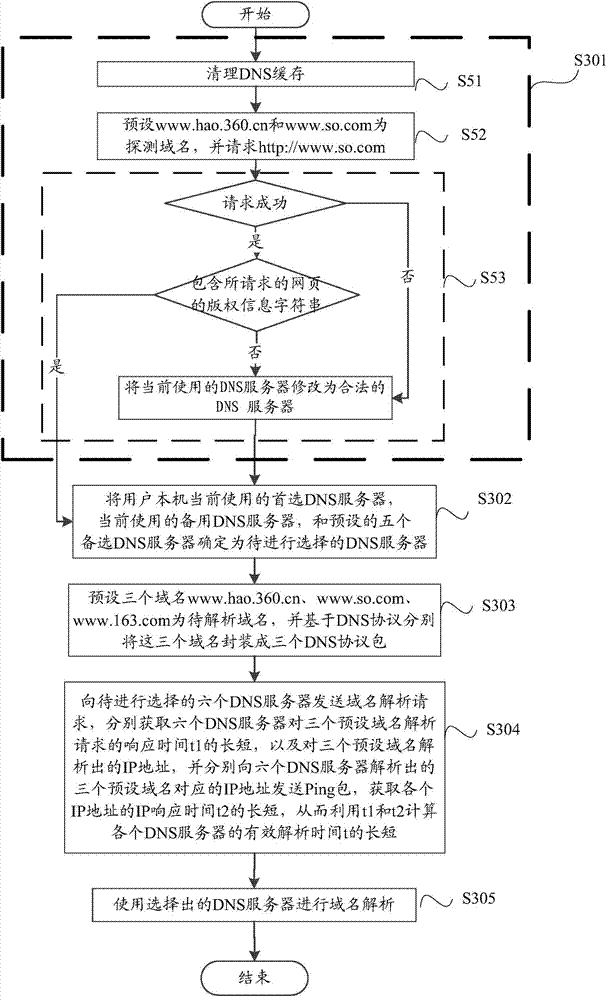
[0098] refer to image 3 , shows a flowchart of steps of a method for selecting a DNS server according to an embodiment of the present invention, the method for selecting a DNS server may specifically include the following steps:
[0099] Step S301, detecting the validity of the currently used DNS server.
[0100] Specifically, the following sub-steps are included:
[0101] Sub-step S51, clearing the DNS cache.
[0102] In sub-step S52, www.hao.360.cn and www.so.com are preset as detection domain names, and http: / / www.so.com is requested.
[0103] In sub-step S53, it is determined whether the currently used DNS server is valid according to the request result, and corresponding processing is performed.
[0104] include:
[0105] If the request fails, it is determined that the currently used preferred and alternate DNS servers are invalid, and the currently used DNS server is modified to a legal DNS server, for example, the currently used preferred DNS server is modified to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com