A method for identifying intra-individual SNPs in Sanger sequencing of diploid PCR products
A recognition method and diploid technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, biological neural network models, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to analyze sequencing files and unsuitable sequencing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0068] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples.
[0069] The method for identifying SNPs in individuals in the Sanger sequencing of diploid PCR products described in this embodiment is as follows:
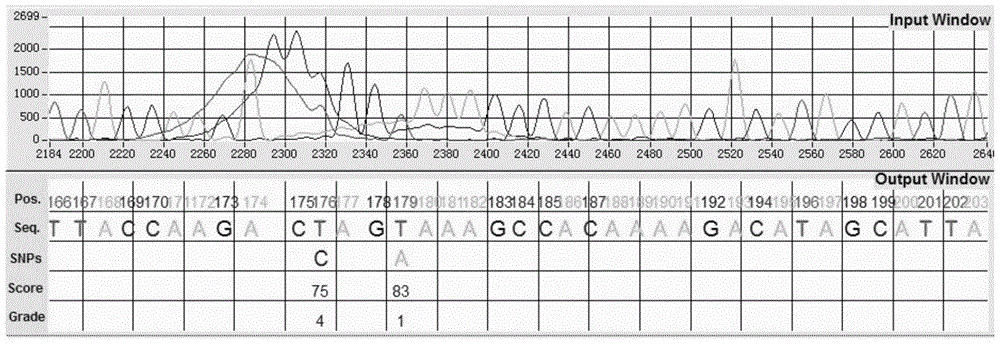
[0070] 1) Separating the fluorescence data of the four bases of adenine A, guanine G, cytosine C and thymine T from the chromatograms of diploid PCR product Sanger sequencing; the original data were sequencers from Applied Biosystems The generated sequencing chromatogram file with the extension .ab1 complies with the ABIF file format. Refer to the "Applied Biosystems Genetic Analysis Data File Format" released by the company in September 2009 to obtain the directory for storing file information. The directory contains The name of the file, the data type of the element, the number of elements and other related attributes can be used to separate the fluorescence data of A, G, T and C through information such as the element byte, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com