Predication method for macroscopic effective properties of composite material with randomly distributed particles
A composite material, random distribution technology, used in particle and sedimentation analysis, particle size analysis, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as distortion of homogenization calculation results, and achieve the effect of eliminating particle overlap
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
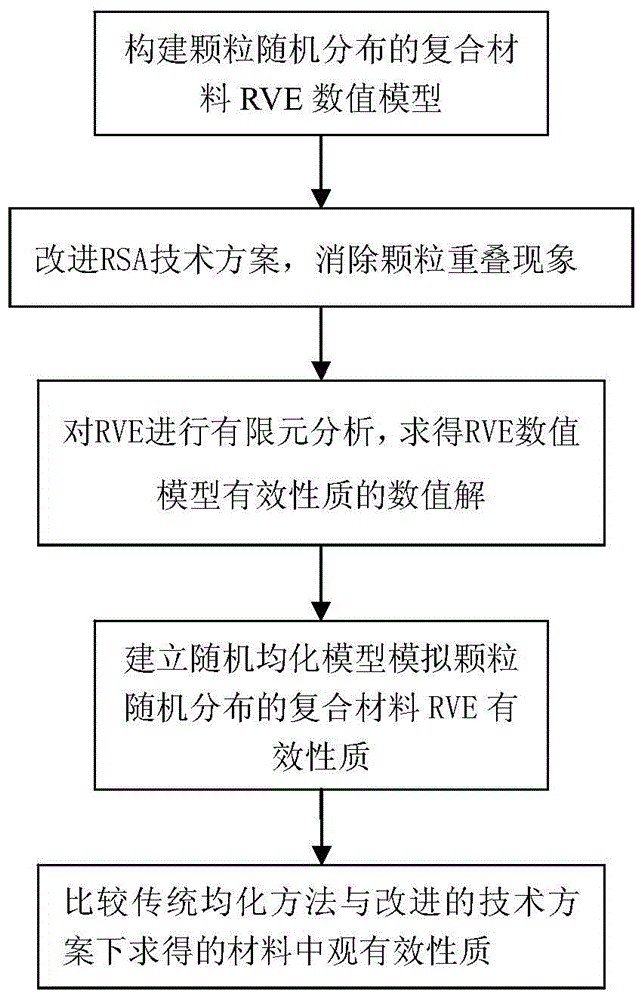
[0077] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Such as figure 1 Shown, the present invention has 5 main processes altogether:
[0078] 1. Construct a random RVE numerical model
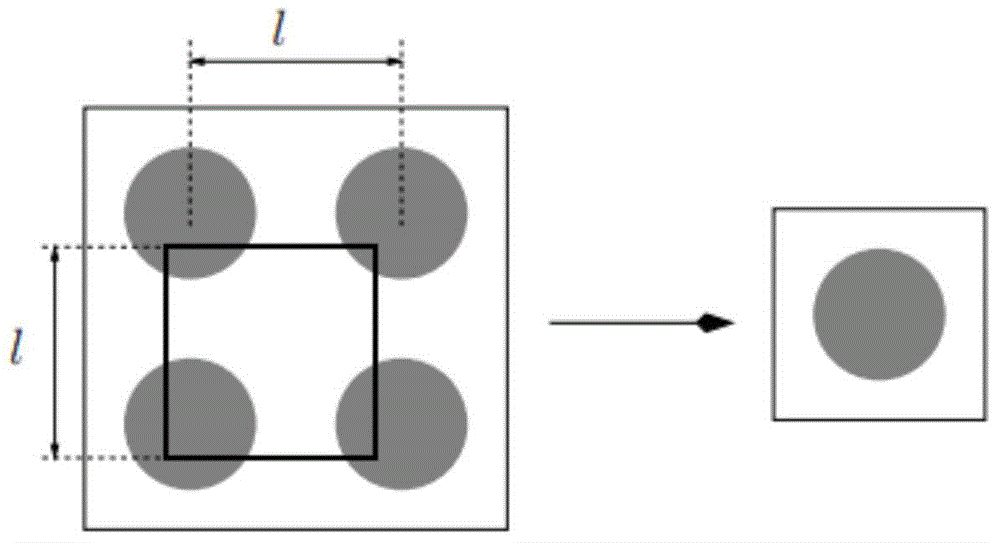
[0079] For a two-dimensional two-phase composite material composed of particles and matrix, the traditional homogenization method usually assumes that the particles are periodically distributed inside the RVE, thus further simplifying the periodic microstructure into a single-particle RVE, such as figure 2 shown. Although this simplified method greatly reduces the difficulty of calculation, it ignores the objective randomness of particle distribution.
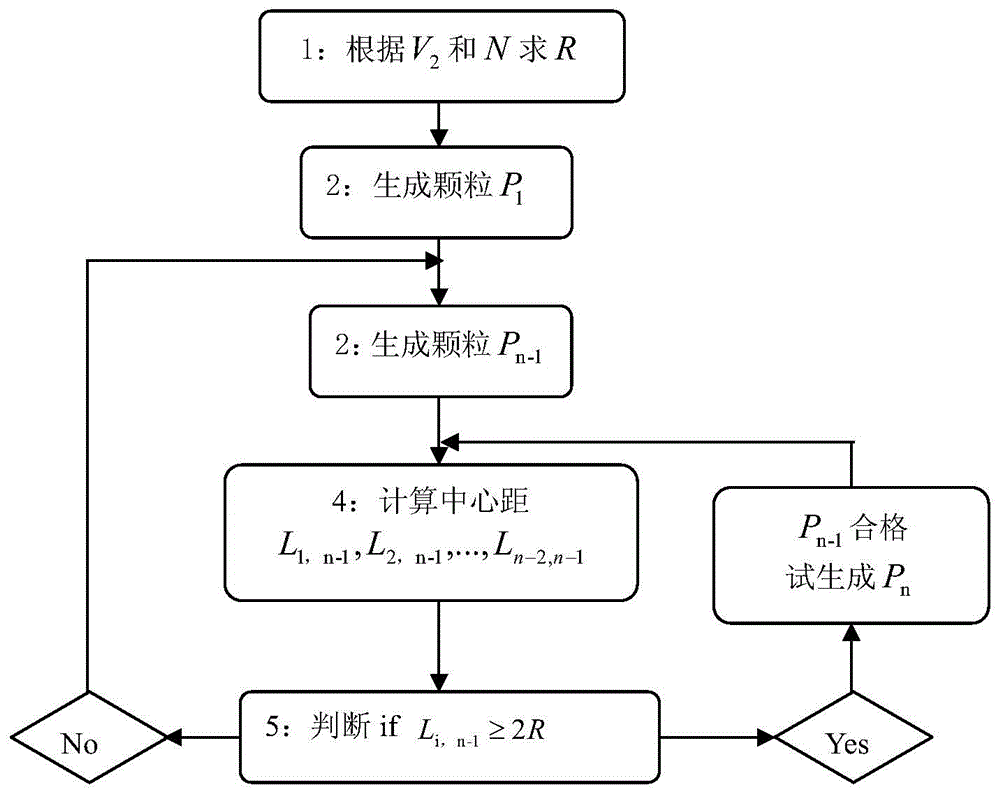
[0080] If the RSA method is used, the RVE with random distribution of particles can be generated, and the flow chart is as follows image 3 shown. The core idea and operation process of the traditional RSA method: generate particle inclusions one by one in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com