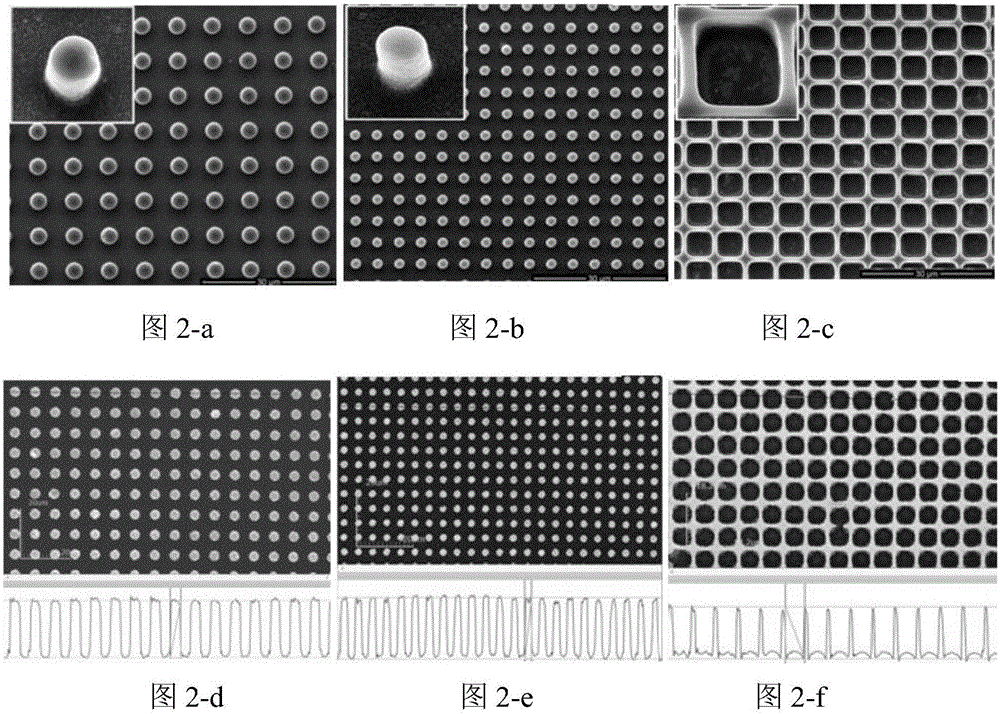
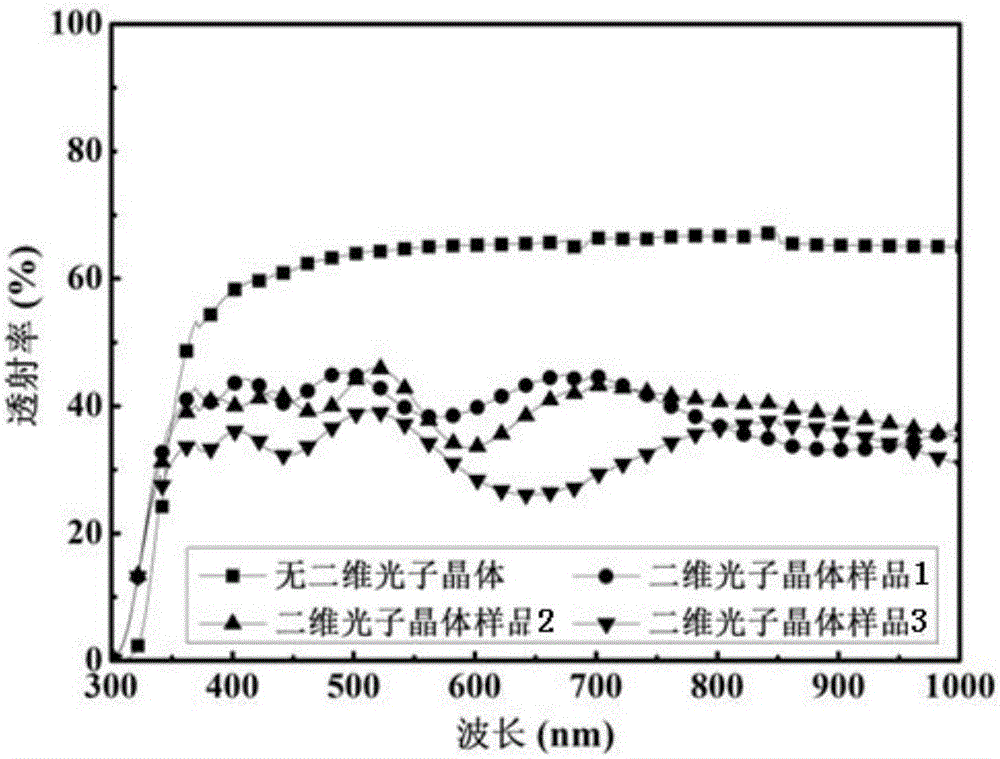
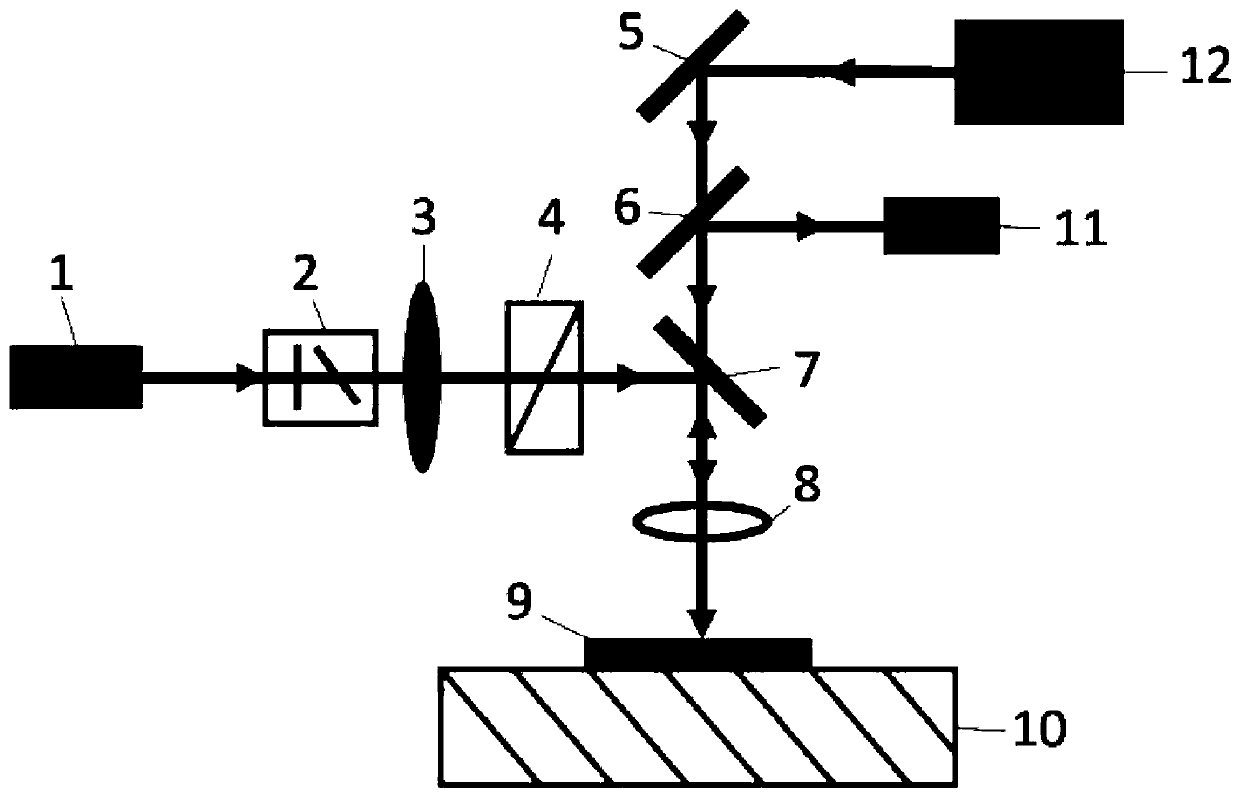
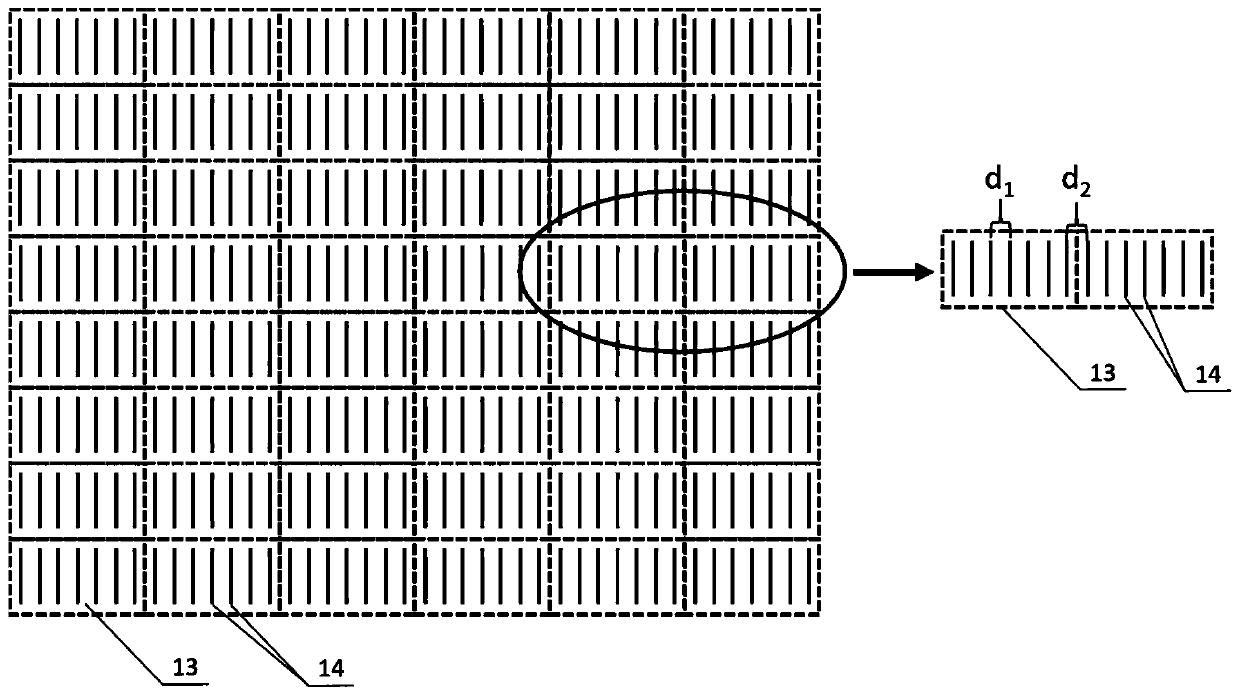
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Periodic microstructure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
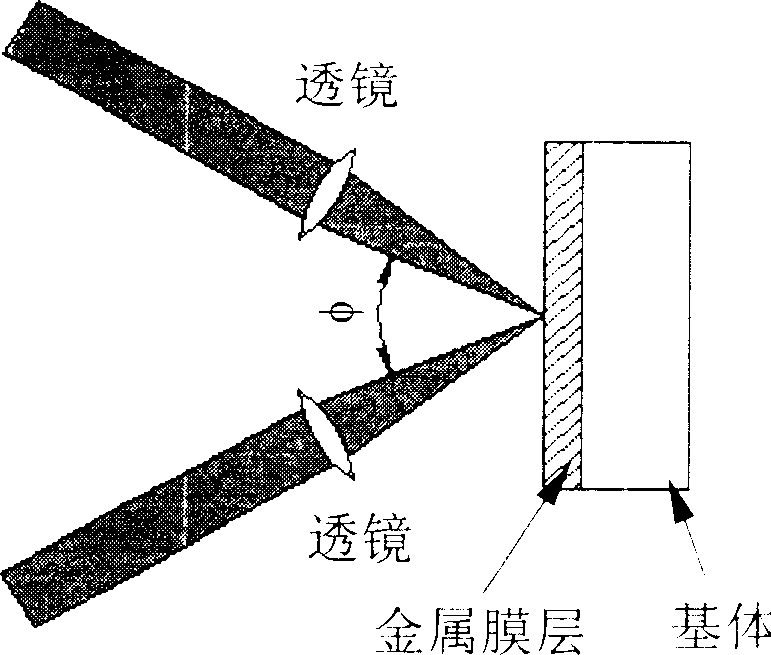
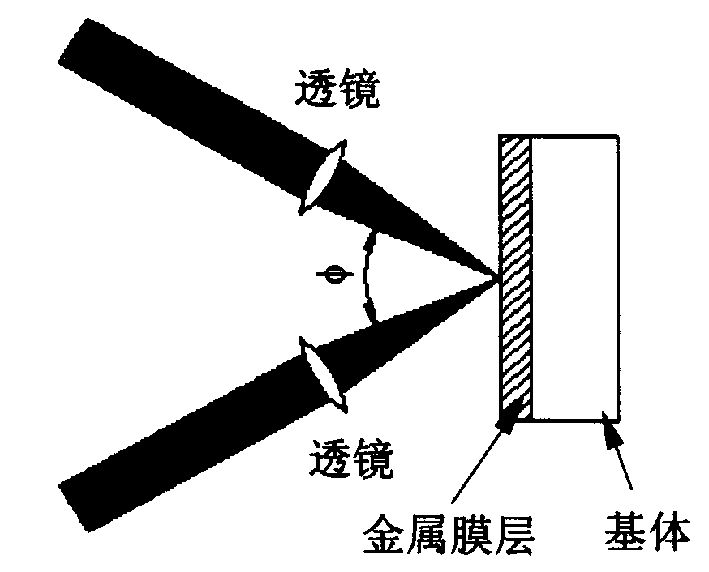
Method for preparing periodic microstructure on metallic film by femto second laser
InactiveCN1448755ASimple preparation processImprove efficiencyNon-linear opticsOptical elementsFemto second laserLaser beams
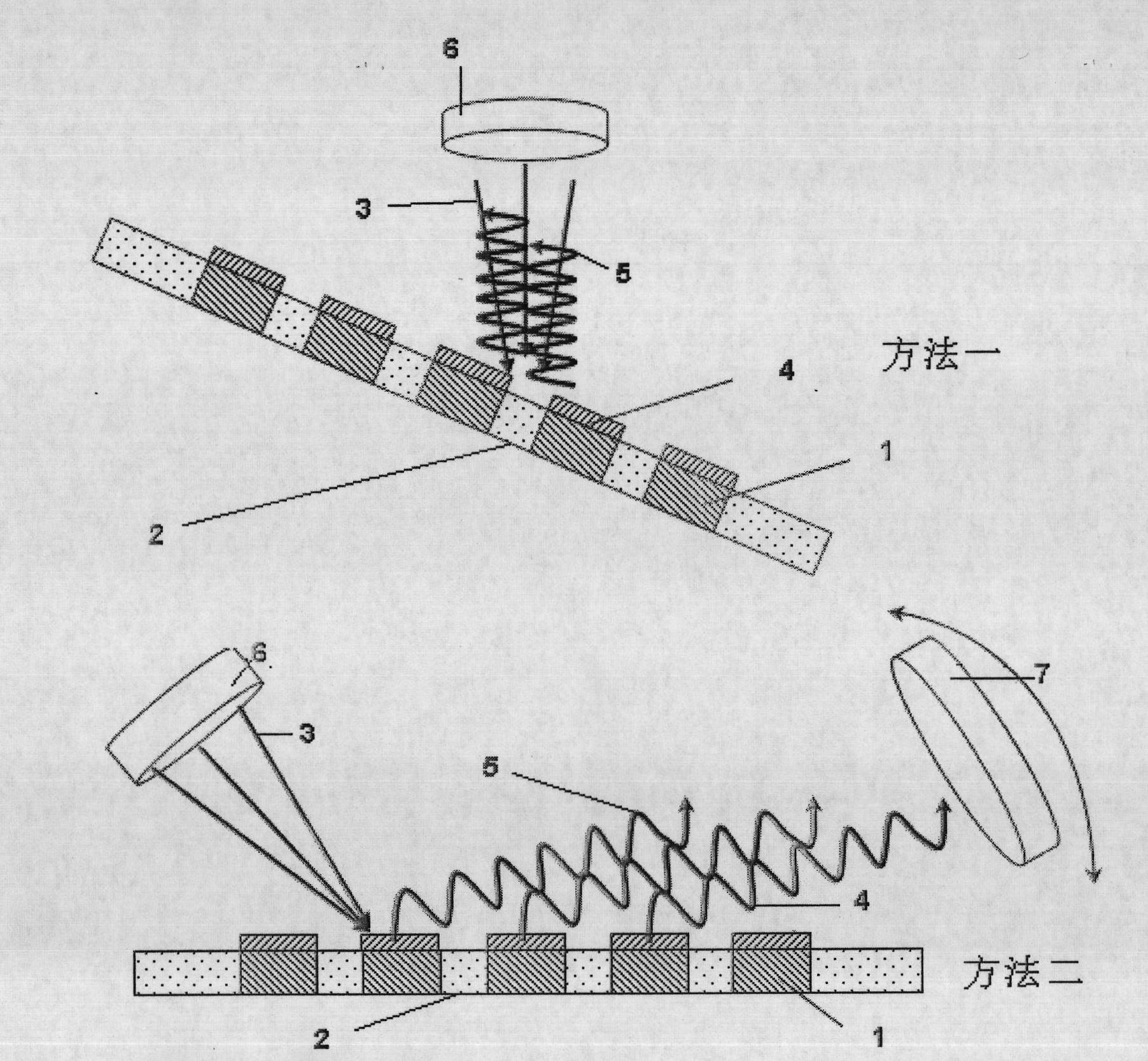
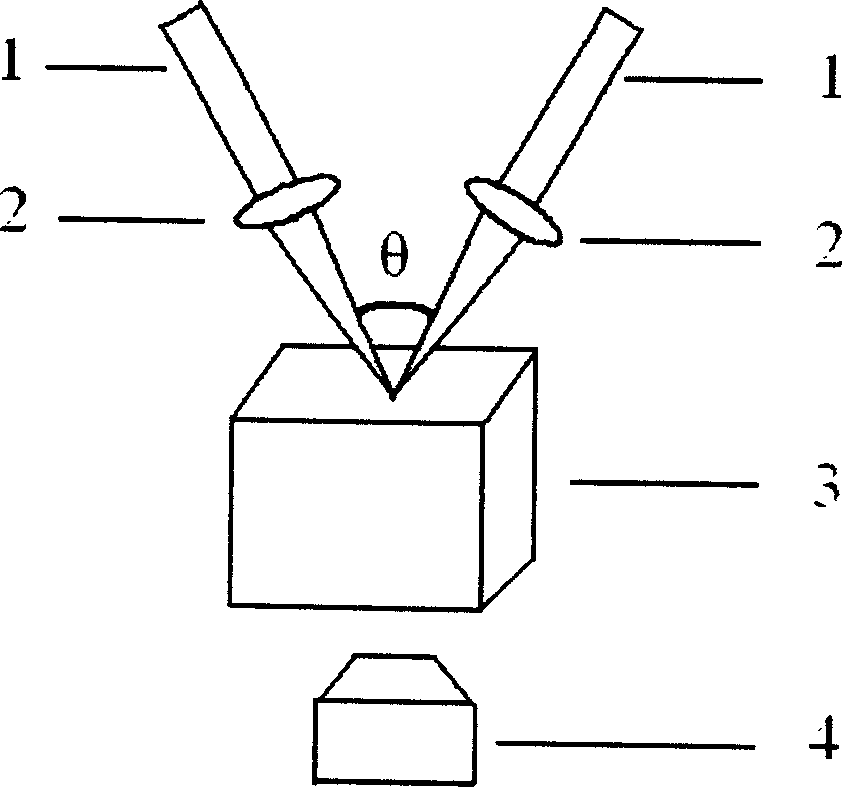
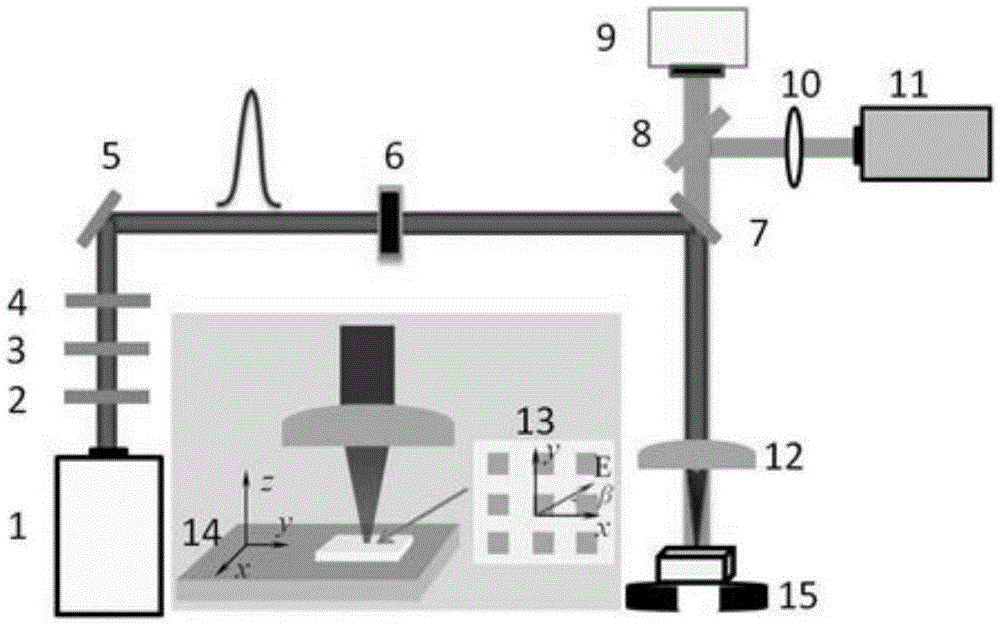
The laser beam produced by titanium jewel femto second laser is split into two beams and the two laser beams are focused by lenses to realize temporal and spatial coherent superposing before acting on metal film on quartz, common glass or silicon substrate. The laser pulse width, pulse frequency and single pulse energy are so controlled that the laser beam can burn out metal film and produce no damage of the substrate. The coherent laser beam is fixed and the sample on 3D platform is computer-controlled to move to prepare periodical microstructure of metal film.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for packaging LED (light emitting diode)
ActiveCN102005520AUniform pore sizeUnique optical propertiesSemiconductor devicesCooking & bakingEpoxy
The invention provides a method for packaging an LED (Light Emitting Diode), which belongs to the technical field of photoelectric devices. In the invention, an AAO (Anode Alumina Oxidation) template is used for preparing a periodic microstructure on epoxy resin in the process of packaging. The method comprises the following specific steps of: firstly, preparing the AAO template of the periodic microstructure matched with the wavelength of an LED chip to be packaged; secondly, uniformly spreading the AAO template on the inner surface of an LED packaging mould; lastly, casting the liquid epoxy resin in the mould; carrying out vacuum degassing; putting the mould in an oven for baking; and taking down the packaged device from the mould after the epoxy resin is solidified, wherein the outer surface of the epoxy resin of the LED device has the same periodic microstructure as the AAO mould. In the invention, the packaging mould which can be reused and has the periodic microstructure is further prepared by using the AAO mould. In the invention, the optical performance of the device is improved by transferring the periodic microstructure on the AAO template to the epoxy resin which is an LED packing material, and therefore light-extraction efficiency is improved.
Owner:SINO INNOV SEMICON (PKU) CO LTD
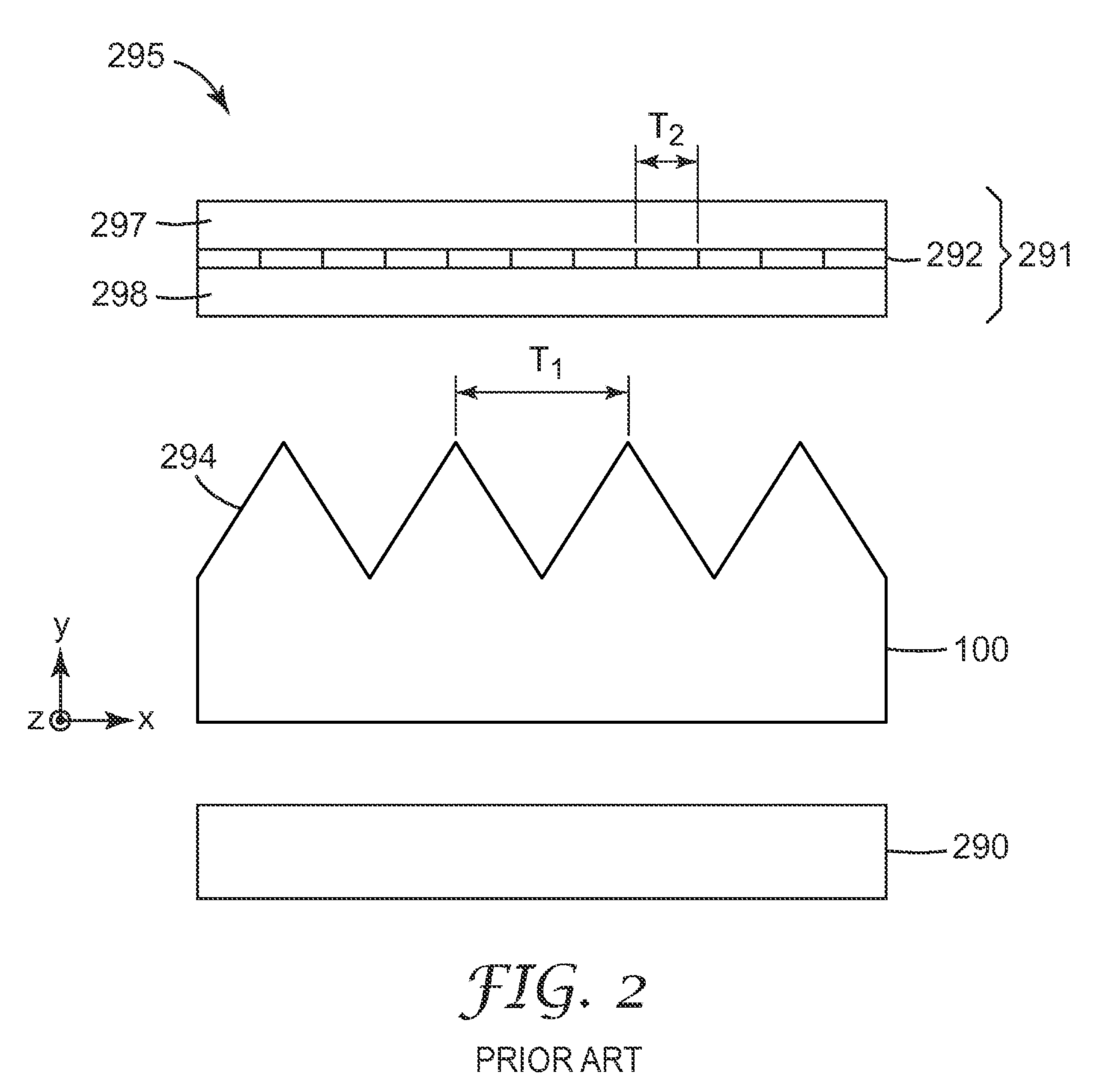
Method and apparatus for optically measuring the topography of nearly planar periodic structures
InactiveUS7321433B2Radiation pyrometryAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDiffraction orderMaxwell's equations
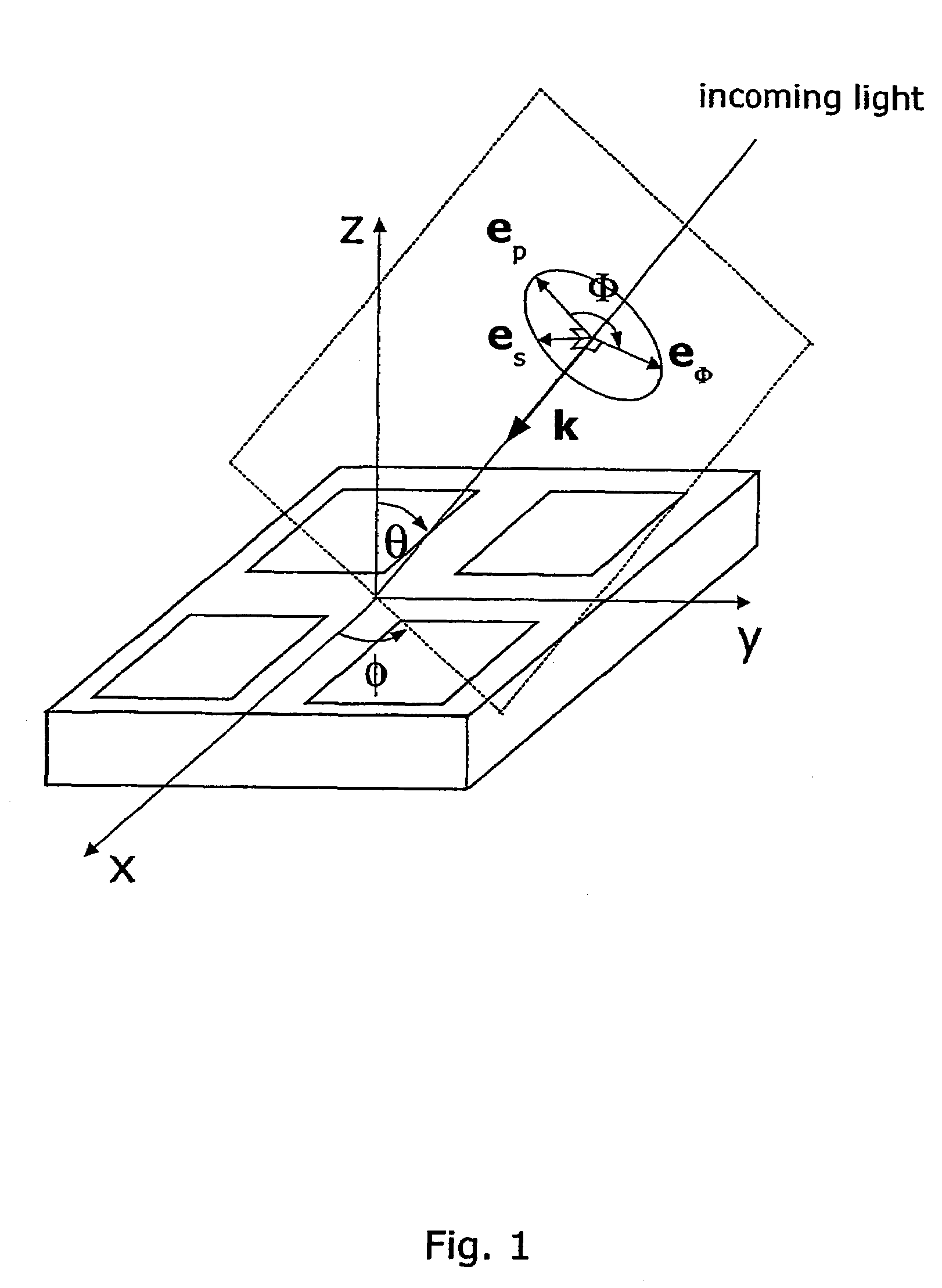
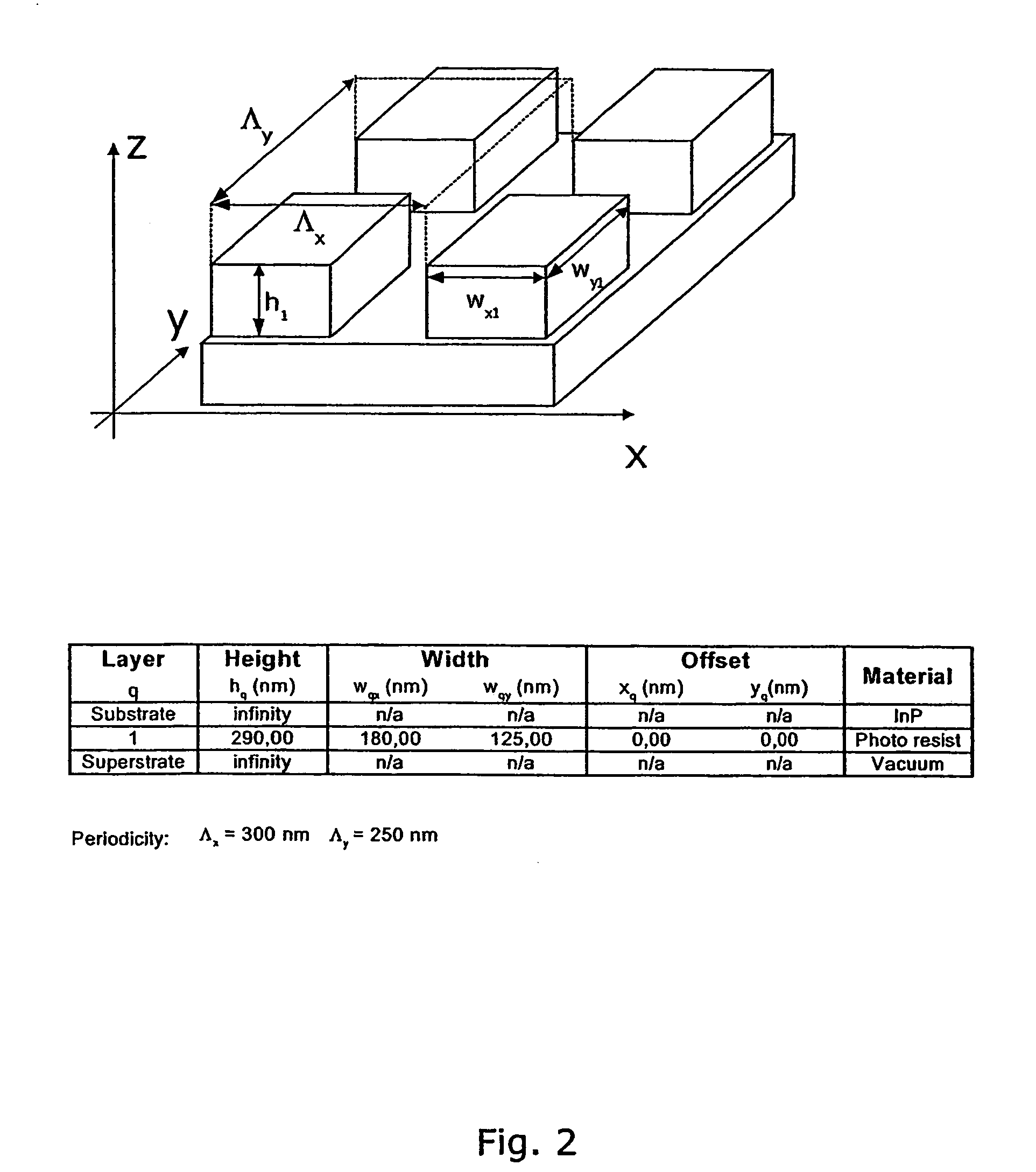
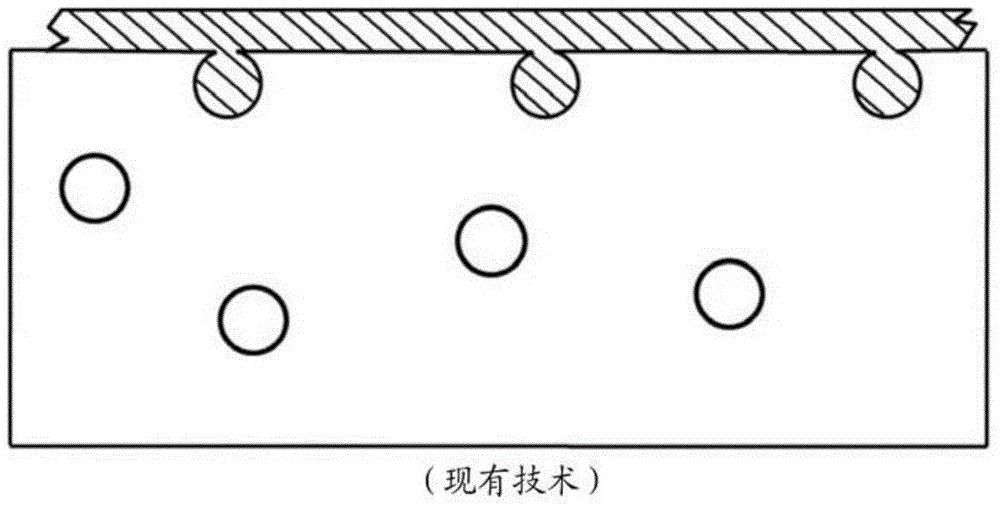
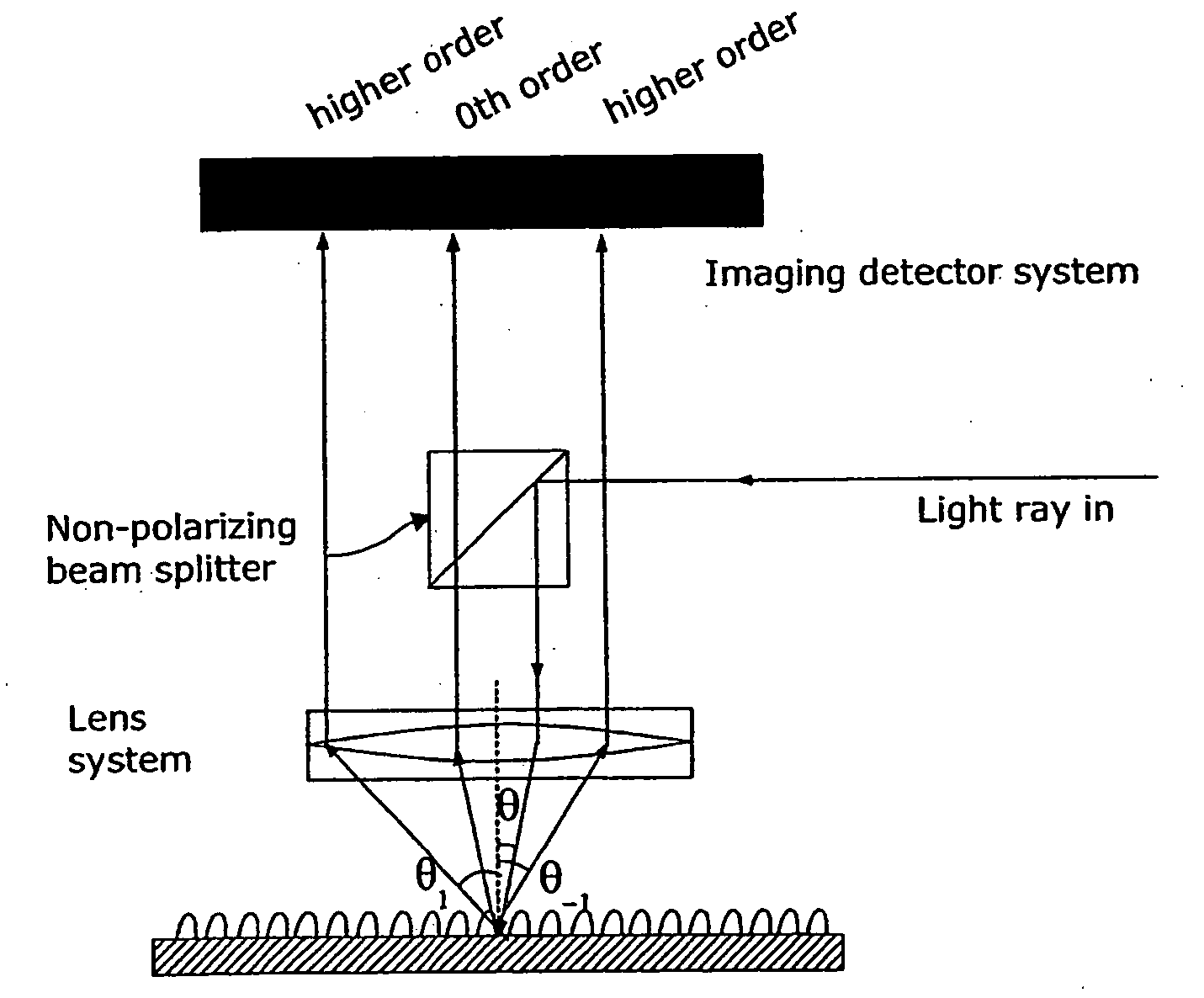
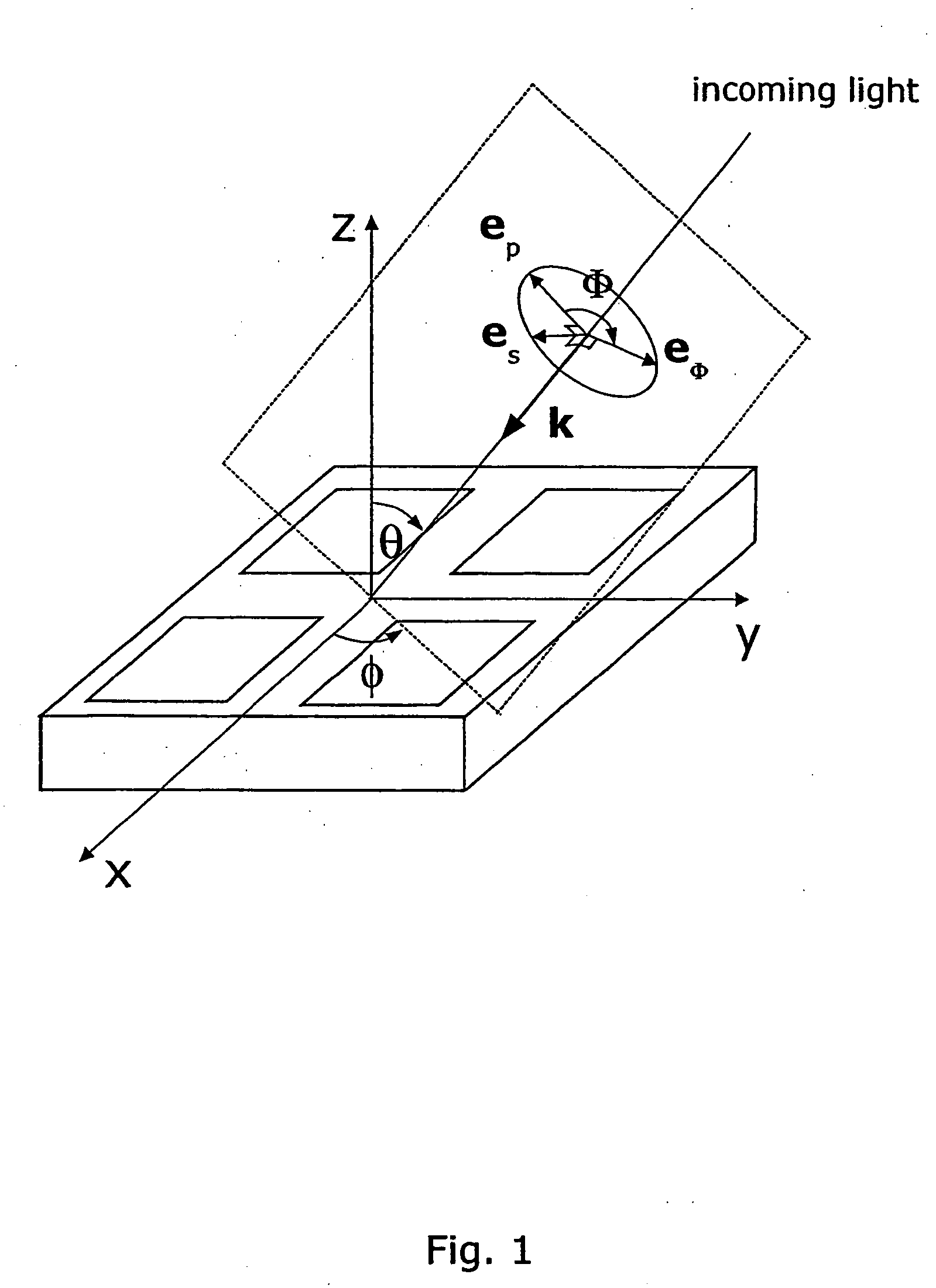
The present invention discloses a non-destructive method and apparatus for measuring the 3D topography of a sample having periodic microstructure deposited onto the surface, or deposited onto a film, or buried into the film or sample. In particular, the present invention relates to an optical system and method utilizing polarized light beam, diffracted from the repeated structure, to measure its spatial geometry giving parameters such as profile height, profile widths, sidewall angles, and arbitrary profile shape. The optical system employs a broadband or semi-monochromatic light source to produce a light beam that is polarized and focused onto the periodic structure being measured. The focused beam consists of a whole range of illumination angles that is provided to the structure simultaneously. Transmitted or reflected diffracted light generated by the interaction of the light with the periodic structure is collected by an imaging detector system. The detector records the diffraction light irradiance resolved into illumination angles, diffraction orders and wavelength. The data is applied to determine the geometrical profile of the periodic structure using a reconstruction algorithm that is based on comparisons between measured diffraction data and modeled diffraction irradiance of a profile model using Maxwell's equations. The reconstruction of the profile is performed by iterative adjustments of a profile seed model until the modeled diffraction irradiance matches the measured data within a predefined convergence tolerance.
Owner:DANSK FUNDAMENTAL METROLOGI
Method for preparation of polycrystalline silicon solar cell textile layer
ActiveCN101252155AFast productionLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesEtchingSolar cell
The present invention provides a polysilicon solar cell texture layer preparation method, relating to a solar cell, in particular to a polysilicon solar cell anti-reflection layer manufacturing process which utilizes a laser holographic method and is combined with a wet etching method. The present invention provides a polysilicon solar cell texture layer preparation method which is used for the fast manufacturing of large-area periodic microstructures, and has low cost as well as good anti-reflection effect. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: a polysilicon silicon chip is pretreated; holographic recording is carried out to a photoresist material on the surface of the polysilicon silicon chip for manufacturing two-dimensional periodic microstructure; with the photoresist as a structure template, a structure is manufactured into a silicon material by adopting acidic corrosive liquid.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for detecting surface enhanced raman spectrum based on interference and diffraction stimulation
InactiveCN101982762AHigh emission intensityImprove collection efficiencyScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringResonance angleSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The method for detecting a surface enhanced raman spectrum based on interference and diffraction stimulation of the invention belongs to the technical field of spectral analysis and detection. The method comprises the steps of: using a surface enhanced raman spectrum substrate having a periodic microstructure with a periodic size range from 0.05 to 50 microns, emitting the P polarized lasers with wavelength as same as the wavelength for stimulating the raman on the substrate which is absorbed with the sample from different angles, measuring the laser reflectivity of the base, using an incidence angle corresponding to the low reflectivity as the surface plasma incidence resonance angle with the stimulated raman wavelength, emitting the P polarized lasers under the incidence resonance angle on the base absorbed with the sample and receiving a raman signal along the reflection resonance angle. The method of the invention can efficiently stimulate the surface plasma and centrally emit the SERS signals under the resonance angle, therefore increasing the energy density of the signal and promoting the collecting effect of the light signals.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Light directing film
A light directing film and an optical system incorporating same are disclosed. The light directing film includes a first major surface and a microstructured second major surface. The microstructured second major surface has at least two periodic microstructured patterns. The first periodic pattern is arranged along a first direction. The second periodic pattern is arranged along a second direction different from the first direction.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Process for preparing conductive polymer periodic microstructure
The process of preparing periodical conducting polymer micro structure on the surface of various substrate with fs laser interference field includes the following steps: 1) splitting one fs laser beam into two laser beams focused separately with two lenses and intersected at the focus to realize time and space interference; 2) preparing conducting polymer film conventionally on the surface of the substrate; 3) controlling the output energy density of the laser to make the energy density in the interference points higher than that to melt while lower than the damage threshold of the substrate; and 4) acting the laser interference field onto the conducting polymer film and controlling the laser acted area on the film to form serial points with periodical micro structure of the conducting polymer. Thus formed micro structure has resolution up to submicron or even nanometer size and is expected to be applied in microelectronics and sensor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for the metallation of a workpiece and a layer structure made up of a workpiece and a metal layer
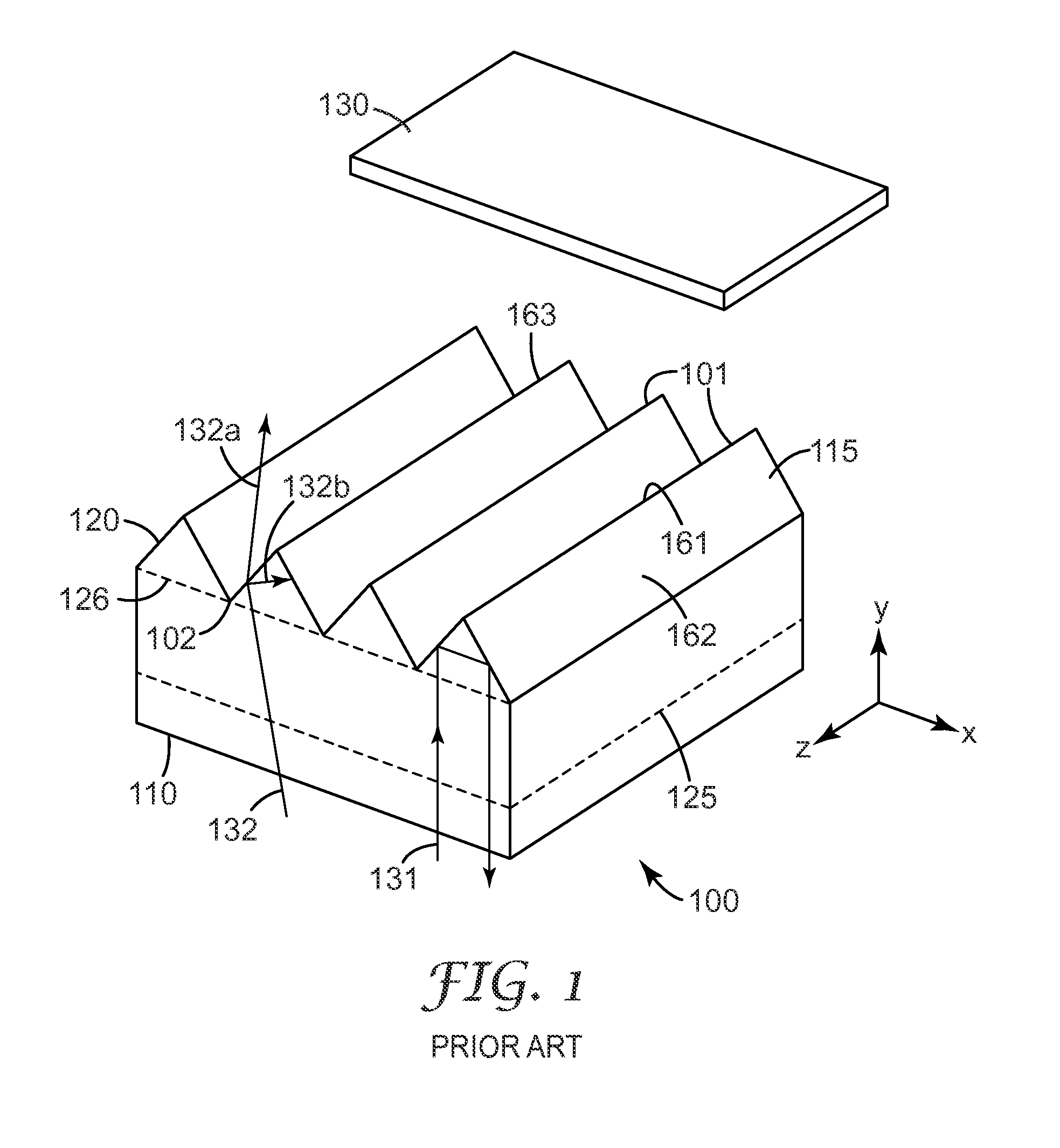
The invention relates to a method for the metallation of a workpiece surface. The workpiece surface is provided, in the regions to be metallized, with periodic microstructures (6) that are preferably transfered to the workpiece surface by forming or molding a tool (2) microstructured by means of laser radiation (5). Then at least the microstructured regions of the workpiece surface are metallized in an adhesive manner in order to produce the layer structure.
Owner:LPKF LASER & ELECTRONICS
Method and apparatus for optically measuring the topography of nearly planar periodic structures
InactiveUS20060176493A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDiffraction orderMaxwell's equations
The present invention discloses a non-destructive method and apparatus for measuring the 3D topography of a sample having periodic microstructure deposited onto the surface, or deposited onto a film, or buried into the film or sample. In particular, the present invention relates to an optical system and method utilizing polarized light beam, diffracted from the repeated structure, to measure its spatial geometry giving parameters such as profile height, profile widths, sidewall angles, and arbitrary profile shape. The optical system employs a broadband or semi-monochromatic light source to produce a light beam that is polarized and focused onto the periodic structure being measured. The focused beam consists of a whole range of illumination angles that is provided to the structure simultaneously. Transmitted or reflected diffracted light generated by the interaction of the light with the periodic structure is collected by an imaging detector system. The detector records the diffraction light irradiance resolved into illumination angles, diffraction orders and wavelength. The data is applied to determine the geometrical profile of the periodic structure using a reconstruction algorithm that is based on comparisons between measured diffraction data and modeled diffraction irradiance of a profile model using Maxwell's equations. The reconstruction of the profile is performed by iterative adjustments of a profile seed model until the modeled diffraction irradiance matches the measured data within a predefined convergence tolerance.
Owner:DANSK FUNDAMENTAL METROLOGI
Method for generating two-dimensional high-volume-fraction earth-rock mixed material geometric model
PendingCN114048663ARaise the upper limitImprove production efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationComputational physicsContact model
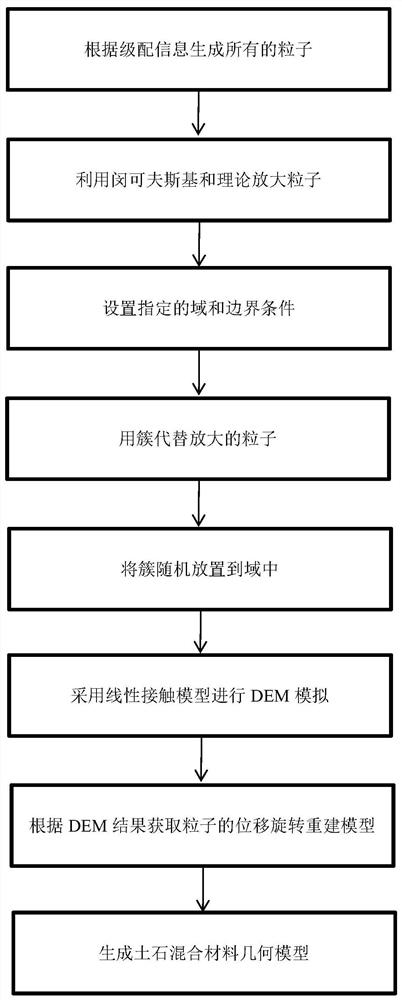
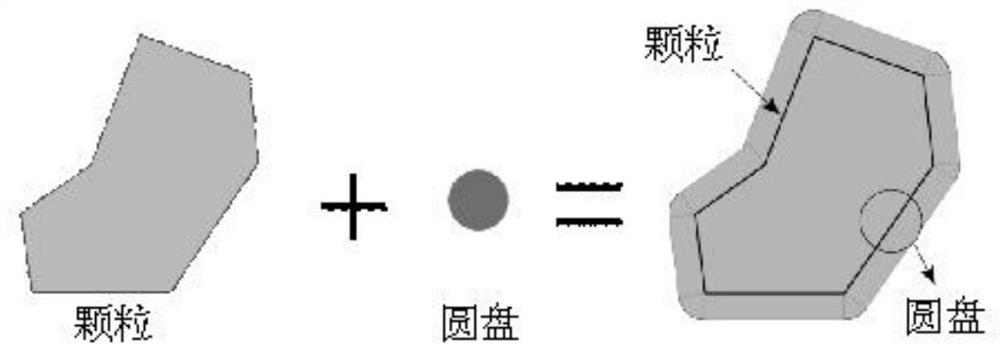
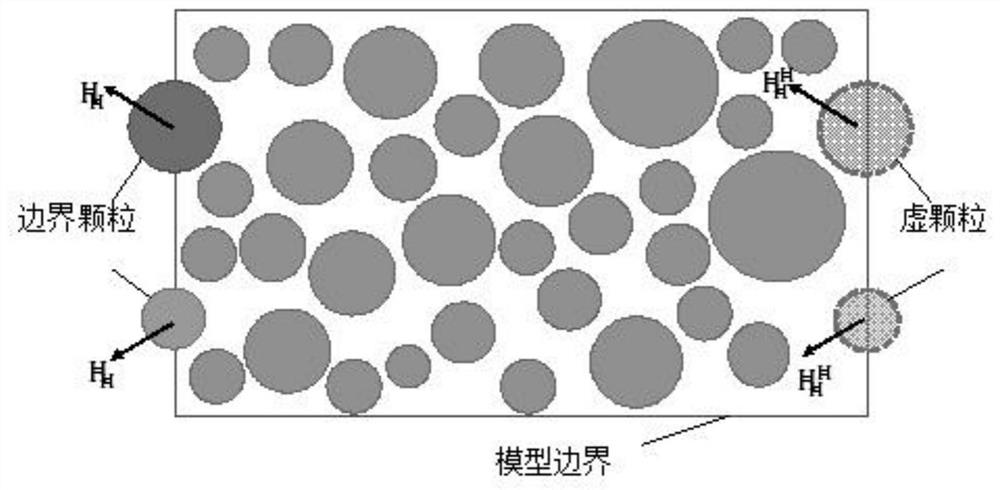
The invention discloses a method for generating a geometric model of a two-dimensional high-volume-fraction earth-rock mixed material, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, generating randomly distributed particles in any shape according to a grading curve; performing Minkowski sum operation on the particles, and controlling the minimum gap between the adjacent particles; achieving transition from particles to clusters by an overlapped discrete element cluster method, and randomly placing the particles in a certain area; assigning a linear contact model, performing DEM simulation, separating overlapped clusters, and recording initial positions, displacement and rotation of the clusters; and finally, reconstructing the model based on the displacement and rotation information. The theoretical maximum volume fraction of any particle shape is easy to obtain, meanwhile, the boundary distribution problem of the particles and the contact problem between the particles are solved, in addition, the periodic boundary condition in the DEM provides a simple implementation method for the periodic microstructure, the generated model better conforms to the actual situation. Reliability of a subsequent numerical method test research result can be improved, and the method has relatively high application significance.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Preparation method for pile face black silicon material
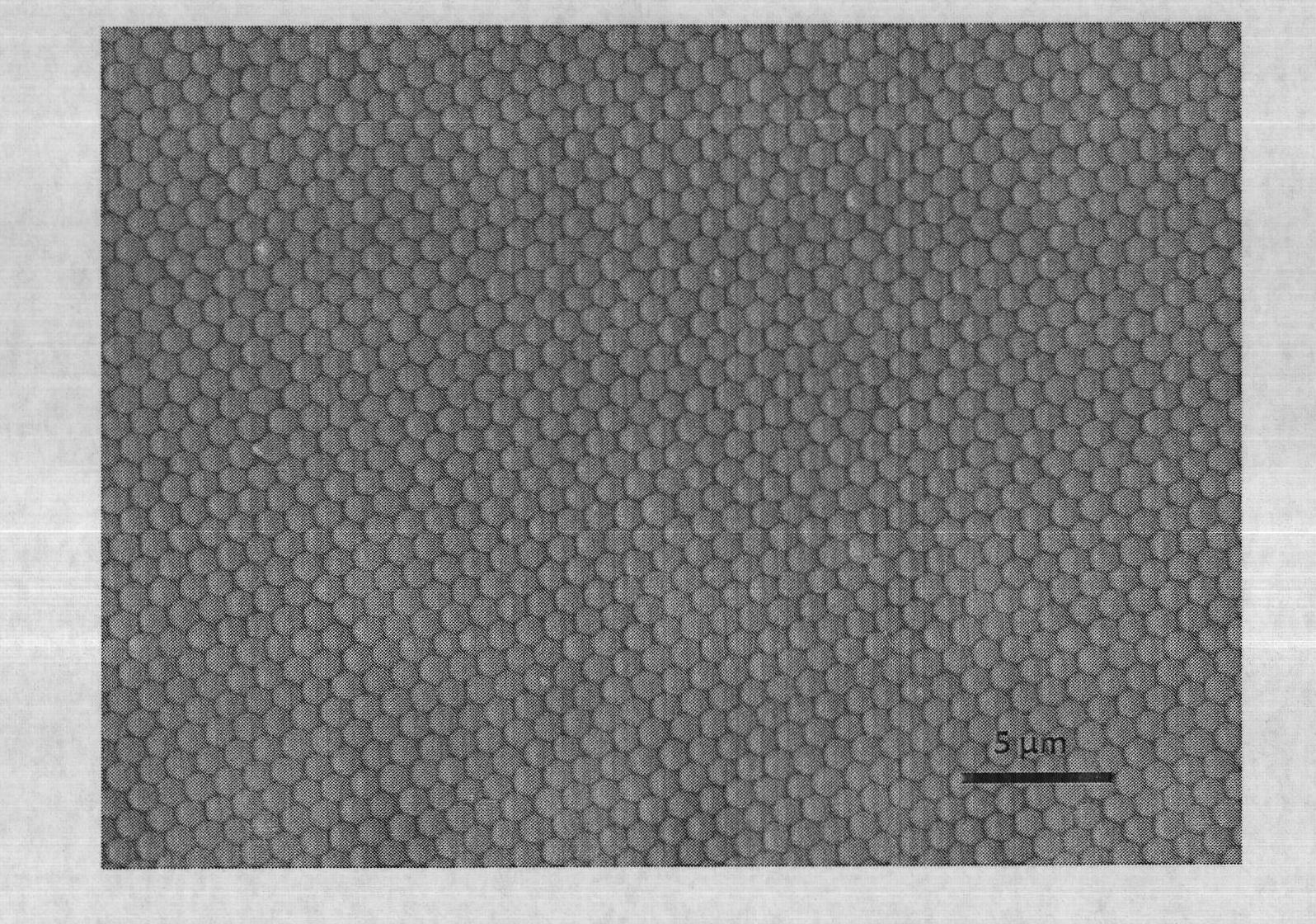
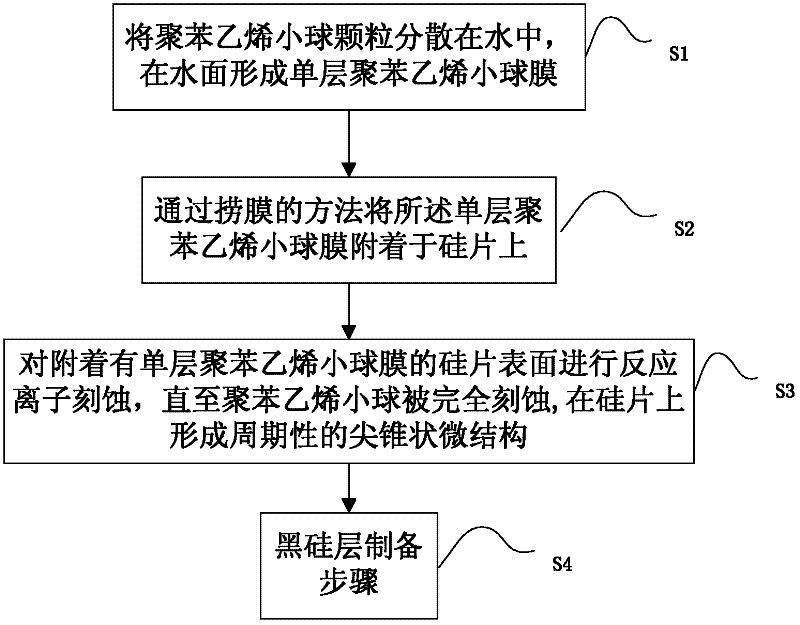
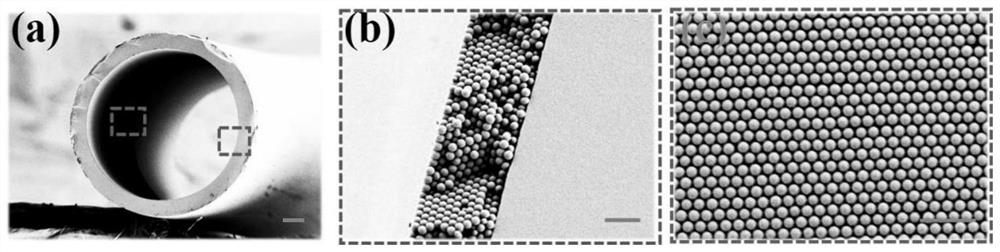
The present invention provides a preparation method for a pile face black silicon material, comprising a rough technology step and a next black silicon layer preparation step, wherein the rough technology step comprises: dispersing polystyrene particle beads in the water to form a single layer bead membrane on the water surface; attaching the single layer bead membrane onto a silicon chip by the film salvaging method; implementing the reactive ion etch on the surface of the silicon chip attached with the single layer polystyrene bead membrane to form a periodic microstructure on the silicon chip. Based on the preparation method of the invention, the black silicon material of the pile face structure can be obtained on the silicon substrate, and can be wildly used in the preparation of a solar cell or photoelectric elements.
Owner:江苏顶洁医疗器械有限公司
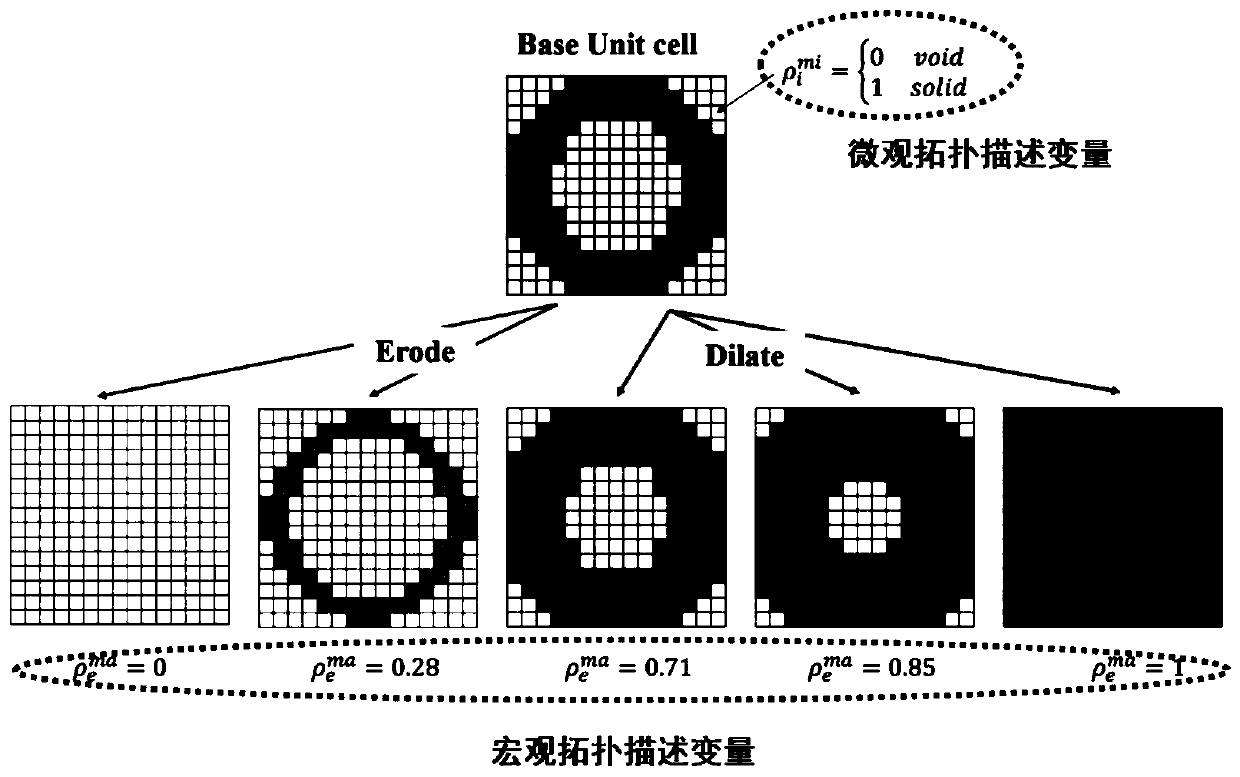
Quasi-periodic hierarchical structure topology optimization method based on corrosion-diffusion operator
PendingCN110751729ASimple math listIncrease stiffnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing data aquisition/processingMacroscopic scaleAlgorithm
The invention discloses a quasi-periodic hierarchical structure topological optimization method based on a corrosion-diffusion operator. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a structure model; performing corrosion-diffusion operation on the microstructure to obtain a quasi-periodic microstructure library; predicting the equivalent elastic tensor of the microstructure in the alignment period microstructure library by using an asymptotic homogenization method; based on the obtained elasticity modulus of the microstructure database, establishing an explicit function relationshipbetween the microstructure elasticity modulus and the volume fraction ratio by adopting B spline function fitting, and establishing an optimization model; according to the optimization model, calculating the sensitivity of a flexibility function of the structure relative to two design variables, namely a macroscopic topology variable and a microcosmic topology variable; according to the obtainedsensitivity information, iteratively updating a design variable to finish collaborative optimization design of the microcosmic unit density and the macrocosmic unit density; and reconstructing macroscopic and microscopic optimization results obtained by the optimization model to obtain a geometric model of the whole heterogeneous structure.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
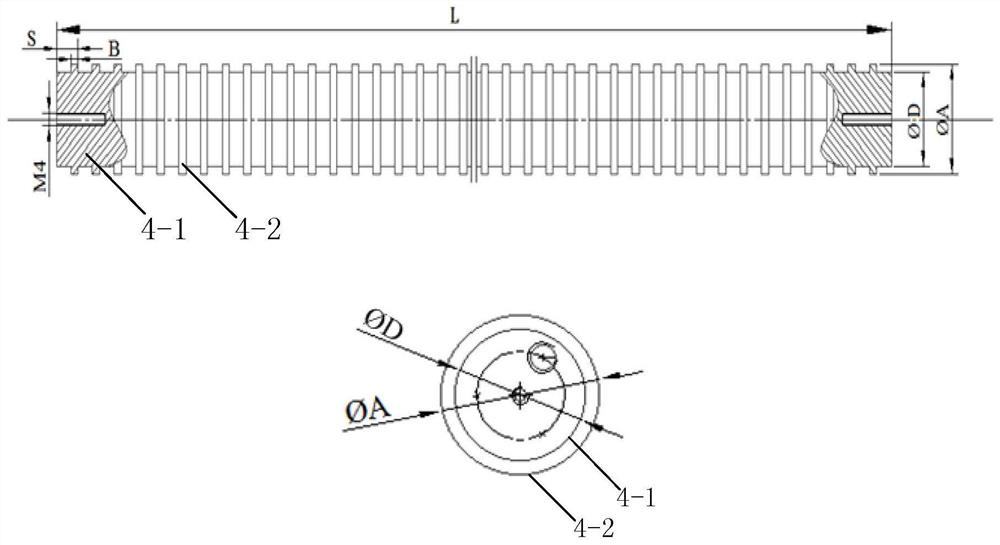
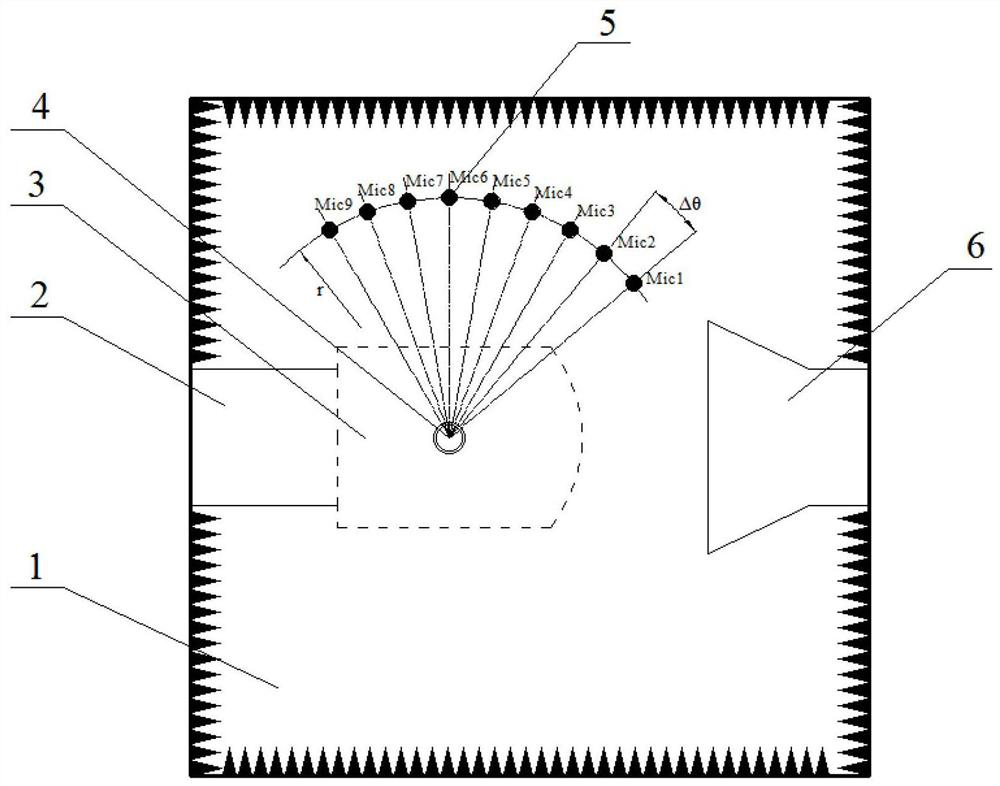
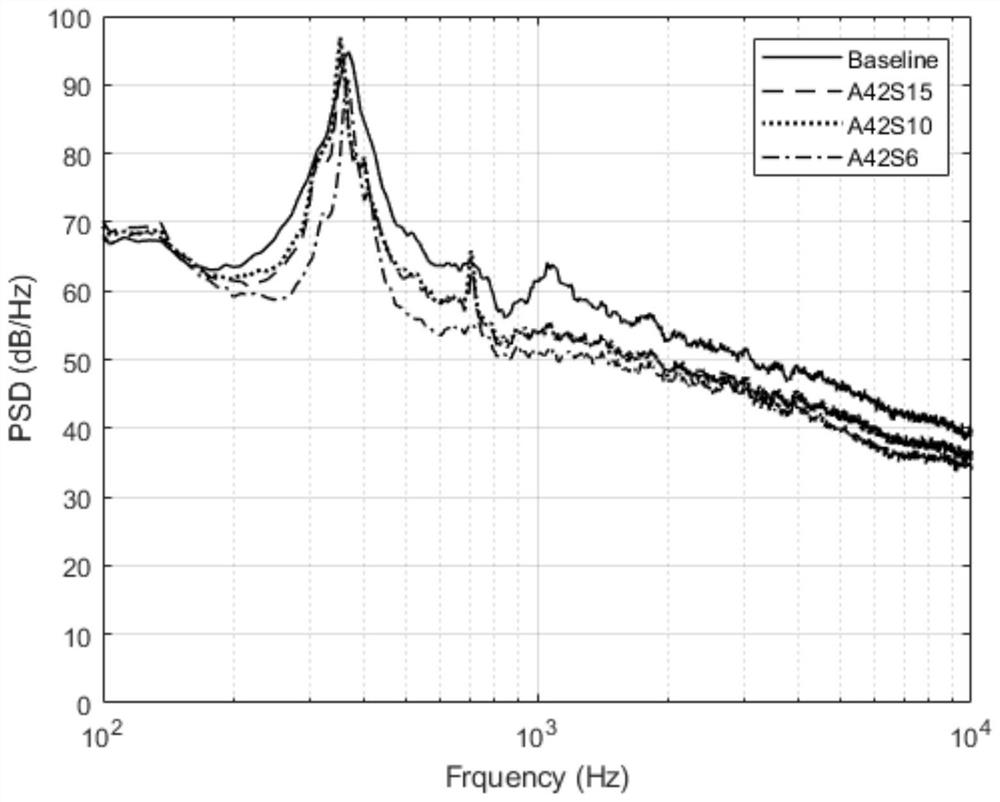
Periodic microstructure noise reduction device and noise suppression test system and method
The invention discloses a periodic microstructure noise reduction device and a noise suppression test system and method. The test system comprises a silencing wind tunnel, noise sensors and a model test piece. The model test piece adopts a periodic microstructure noise reduction device and is arranged in the silencing wind tunnel; the periodic microstructure noise reduction device comprises a reference cylinder, radial protruding structures are periodically arranged on the reference cylinder in the axial direction, the diameter of the reference cylinder is D, the length of the reference cylinder is L, the setting period is S, the outer diameter of each radial protruding structure is A, and the thickness of each radial protruding structure is B; and the plurality of noise sensors are arranged in the silencing wind tunnel in an arc-shaped array manner along the airflow direction by taking the center of the model test piece as a circle center. According to the test system provided by the invention, the noise generated by the airflow on the model is acquired through the plurality of noise sensors, and the change of a noise single-tone signal and an overall broadband signal is analyzed, so that a research basis is provided for noise suppression.
Owner:LOW SPEED AERODYNAMIC INST OF CHINESE AERODYNAMIC RES & DEV CENT
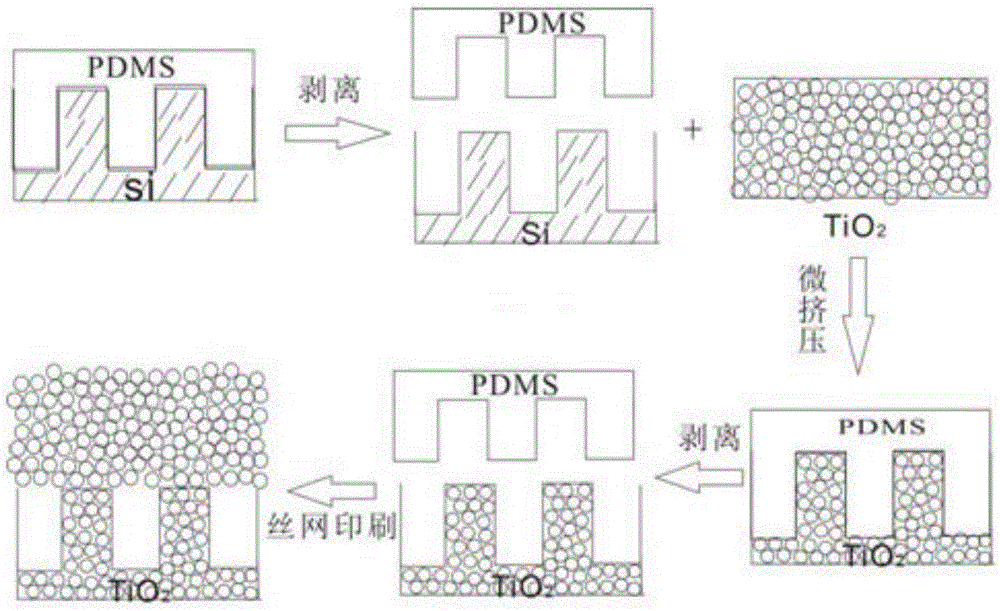
Photoanode containing two-dimensional nano-crystal photonic crystal light-scattering layer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105118675AClear patternThickness is easy to controlLight-sensitive devicesScreen printingPhotonic crystal
The invention discloses a photoanode containing a two-dimensional nano-crystal photonic crystal light-scattering layer, wherein a compact layer, a two-dimensional nano-crystal photonic crystal light-scattering layer and a mesoporous nanocrystalline layer are successively arranged on an FTO glass substrate from bottom to top. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the photoanode containing the two-dimensional nano-crystal photonic crystal light-scattering layer. According to the method, firstly, a nanocrystalline colloidal film is formed through the micro extrusion process on a PDMS soft template, and structurally integrated two-dimensional nano-crystal photonic crystals of periodic microstructures are prepared. Secondly, a nanocrystalline film is prepared on the two-dimensional nano-crystal photonic crystals through the silk-screen printing process. After the high-temperature annealing step, a mesoporous nanocrystalline photoanode provided with the two-dimensional photonic crystal light-scattering layer is obtained. Based on the above manufacturing method, structurally integrated, macroscopically large-area and thickness-controllable photonic crystals can be prepared. The method is simple and low in cost. The photoanode prepared by the method is higher in photoelectric conversion efficiency and battery efficiency.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of large-size nano periodic grating
ActiveCN111007586ALow environmental requirementsAchieve outputDiffraction gratingsFaculaPeriodic microstructure
The invention discloses a preparation method of a large-size nano periodic grating. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: establishing an optical path system, adjusting the laser energy density, preparing a grating crack structure of a laser spot on the surface of a processed sample, and obtaining a distance d1 between two adjacent laser-induced surface periodic microstructures in a grating crack structure; moving the processing sample for multiple times along the Y direction through a three-dimensional moving platform; moving the processing sample for a set distance along the X direction through the three-dimensional moving platform, so that the structural distance d2 between the grating crack structure of the current laser spot prepared on the surface of theprocessing sample and the grating crack structure of the previous laser spot equals the structural distance d1; and repeating the steps to prepare the nano periodic grating with any length and width on the surface of the processed sample. According to the method, the large-size nano periodic grating can be directly prepared only by controlling the laser energy density and the moving platform, theprocess is simple, the requirement for the environment is extremely low, and implementation is convenient.
Owner:中国工程物理研究院上海激光等离子体研究所
A Method for Dynamically Controlling the Periodic Micro-Nano Structure of Crystalline Silicon Surface Based on Square Hole Assisted Electrons
ActiveCN104625416BLower ablation thresholdEfficient and precise designLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoNano structuring
The invention relates to a method for electronic dynamic control of crystal silicon surface periodic micro-nano structures based on square hole assistance and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method is based on local transient electronic excitation dynamic control, and femtosecond laser linear polarization is focused through an objective lens and then is focused on the surface of a material through a square hole copper wire mesh to achieve various precise control of different surface periodic micro-nano structures; by controlling laser scanning speed and pulse energy, ablation of strip-shaped surface corrugated structures and multi-point array micro-nano structures is achieved; by controlling the relative positions of the laser polarization direction and the direction (x axis) of the edge of a square hole, direction control of the periodic micro-nano structures can be achieved; by effectively adjusting the included angle between the linear polarization laser direction and the direction (x axis) of the edge of the square hole, selective ablation of the crystal silicon surface periodic micro-nano structures is achieved. Compared with existing methods, the method has the advantages that surface processing precision and efficiency are improved effectively, and efficient and accurate form control of the surface periodic micro-nano structures is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
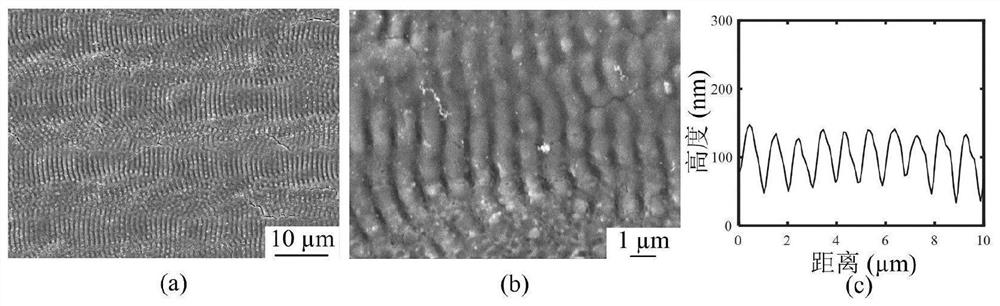
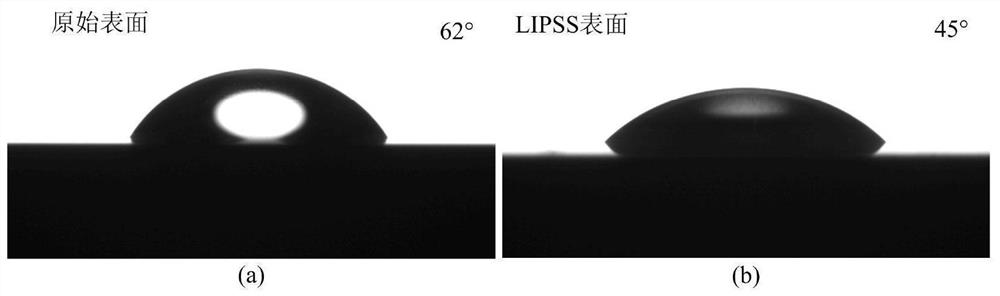
Method for preparing periodic microstructure on surface of titanium alloy through nanosecond laser irradiation
ActiveCN113118633AIncreased durabilityEasy to operateLaser beam welding apparatusNitrogen gasTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a method for preparing a periodic microstructure on the surface of a titanium alloy through nanosecond laser irradiation, and belongs to the field of laser surface modification. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the surface of the titanium alloy is pretreated, a pretreated titanium alloy sample is placed in a gas cavity, nitrogen is conveyed through a gas inlet, the gas cavity is filled with the nitrogen, and the nitrogen flow is 1-20 L / min; 2, after 10-15 seconds of gas pre-supply, a nanosecond fiber laser device is turned on, and a focused laser beam is vertically irradiated on the surface of the titanium alloy sample through silicon dioxide glass; and 3, the periodic microstructure is prepared on the surface of the titanium alloy by controlling laser parameters, and meanwhile, the laser nitriding effect is achieved. According to the method, the wettability of the surface of the titanium alloy can be improved, and the regulation and control of the surface color can be realized; and in addition, due to the action of laser nitriding, the hardness and the wear resistance of the titanium alloy surface after laser irradiation are improved. The method for preparing the periodic microstructure is simple and good in repeatability, and the prepared structure has excellent durability.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Grating element
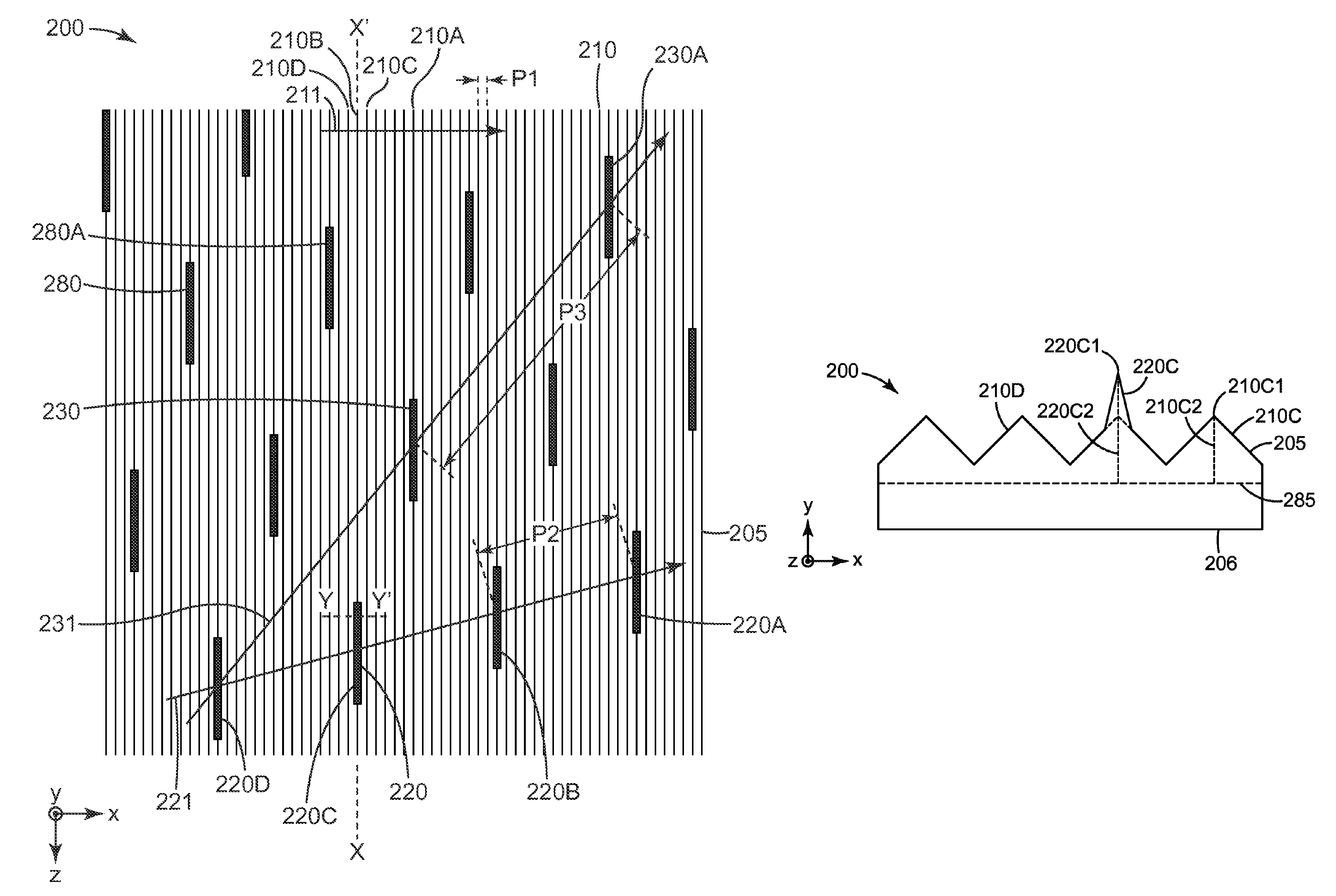
A grating device includes an optical material layer; a channel type optical waveguide region provided in the optical material layer; extension regions provided on the outsides of the channel type optical waveguide region, respectively; a Bragg grating provided in the channel type optical waveguide region; and periodic microstructures provided in the extension regions, respectively. The periodic microstructures are provided in 50 percent or larger of a total of areas of the extension regions.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
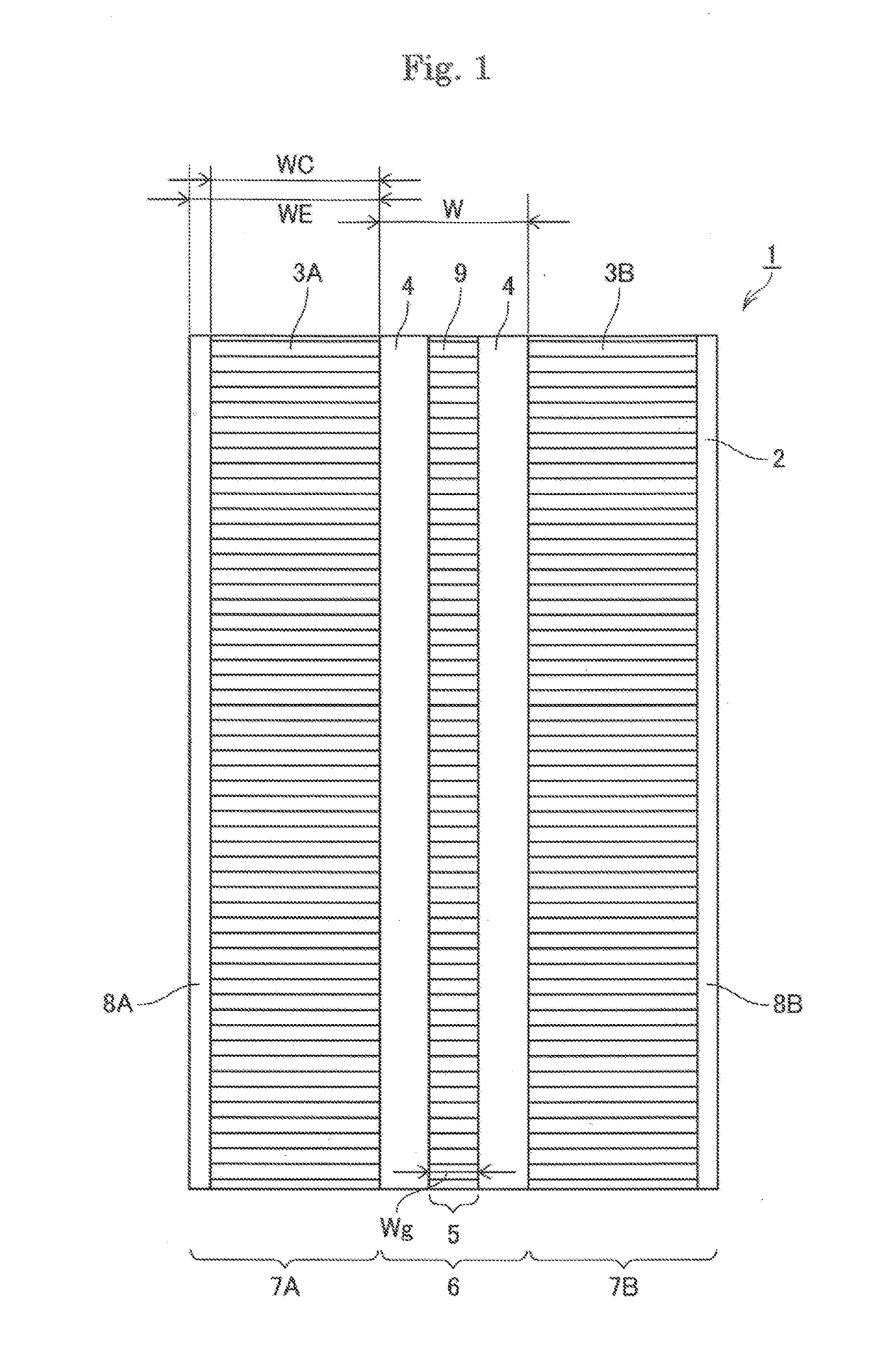
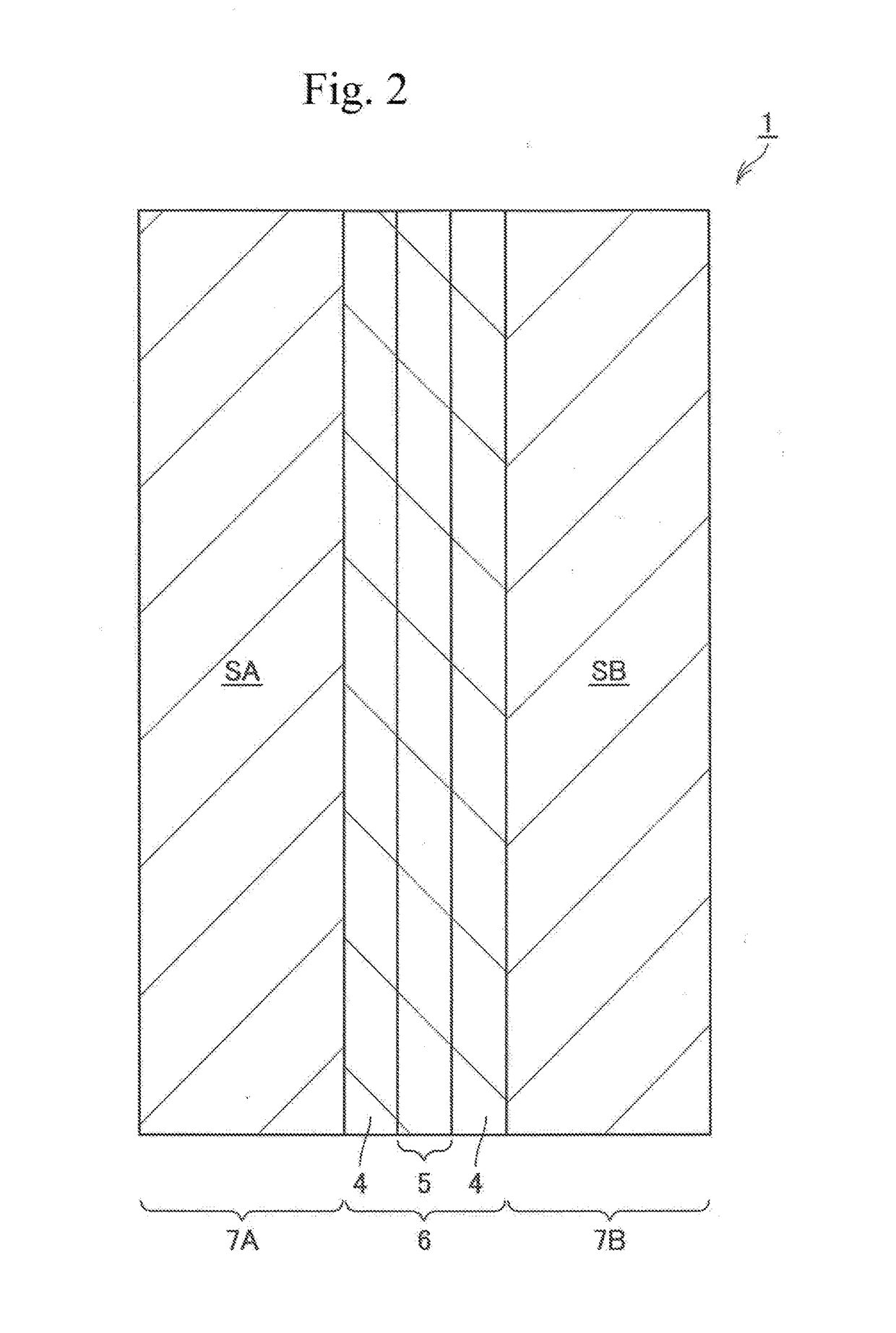
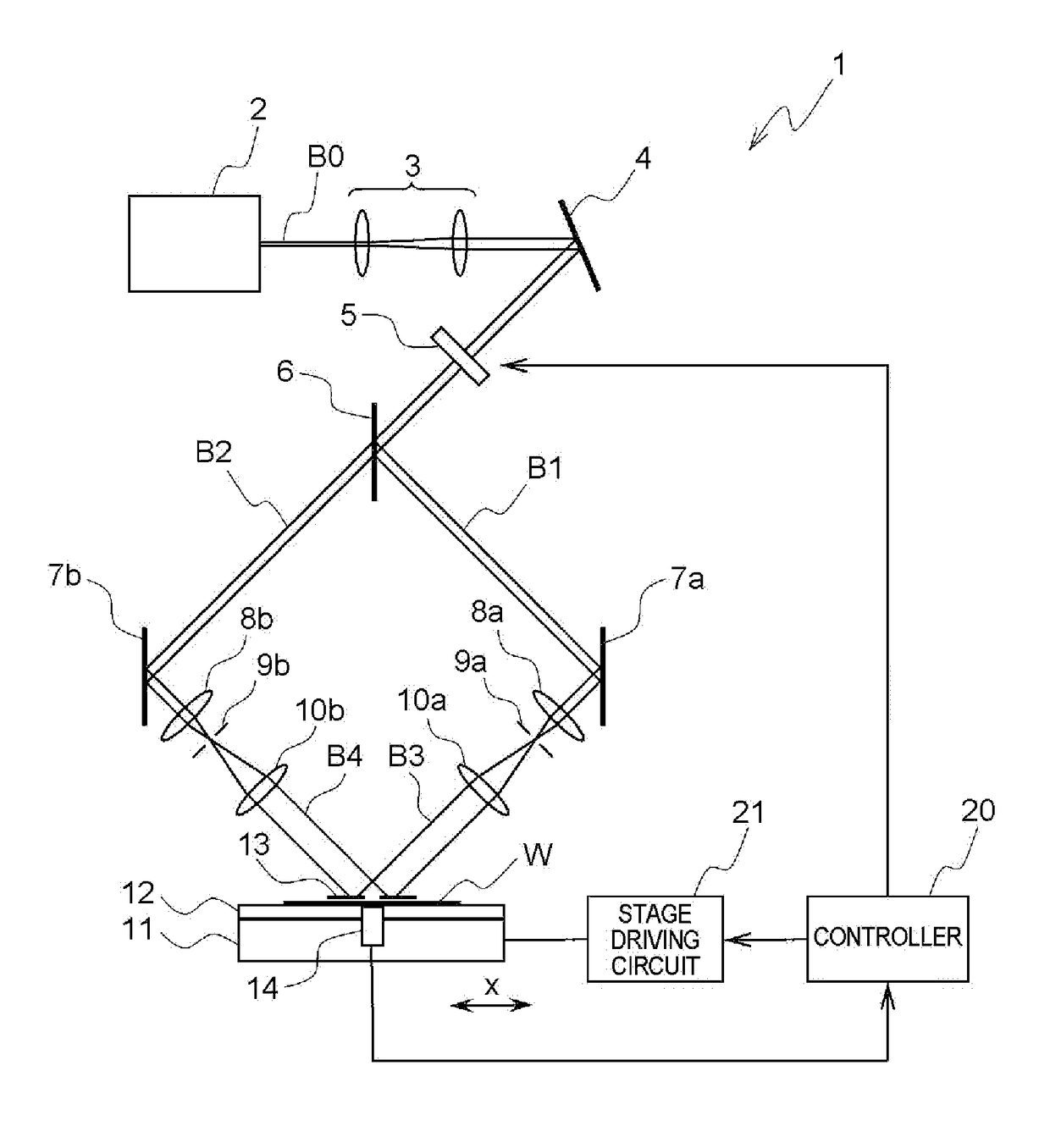
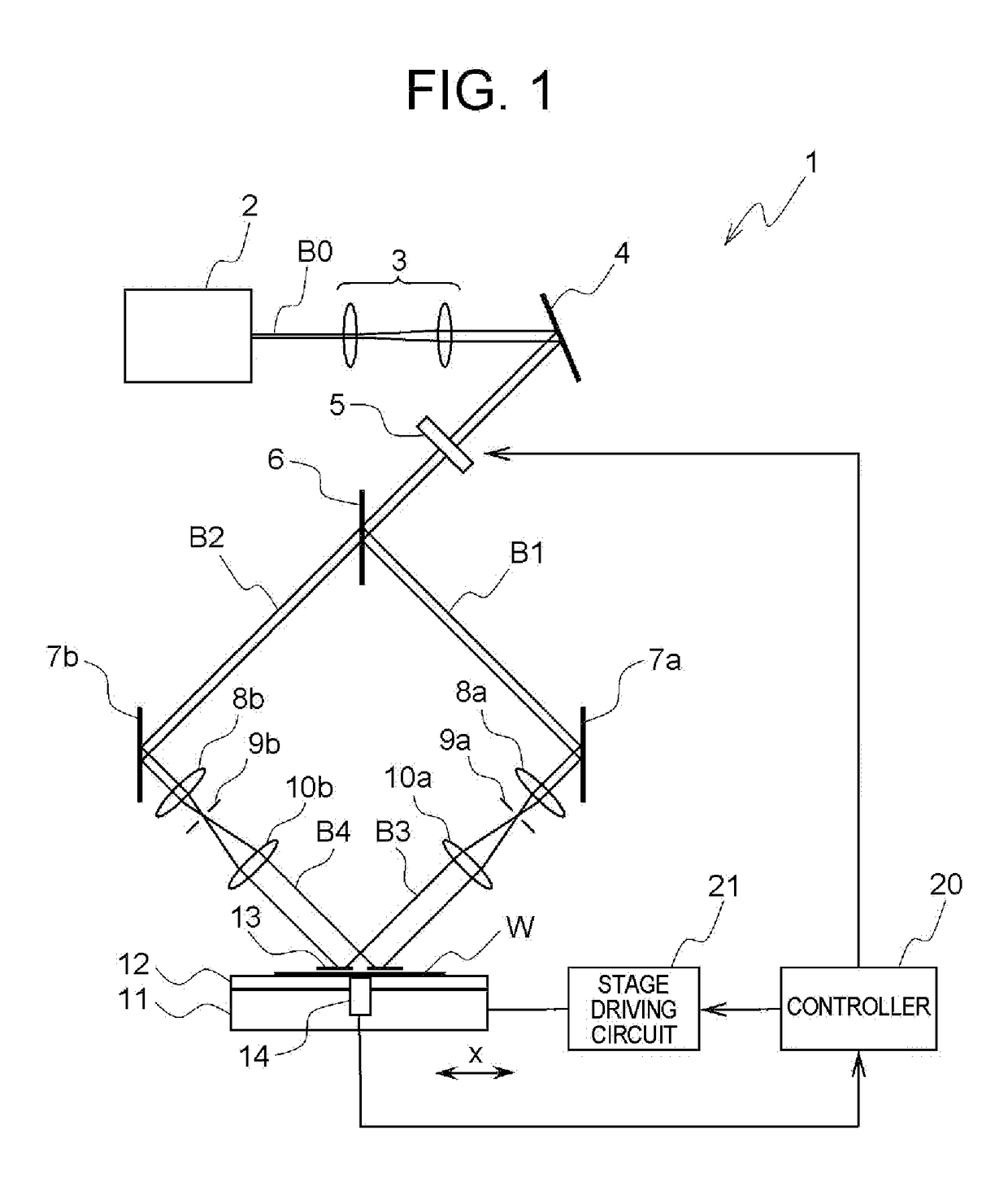
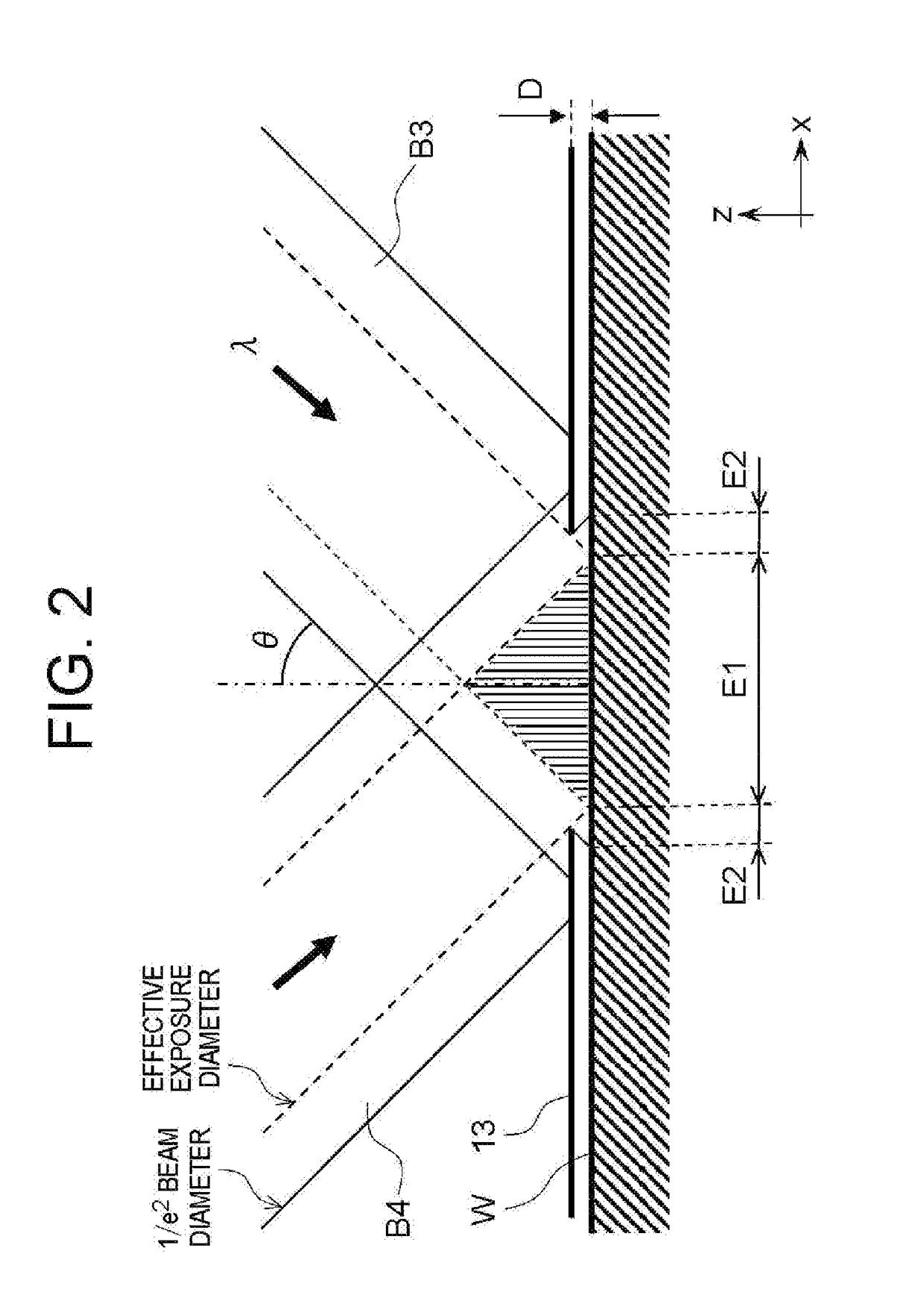
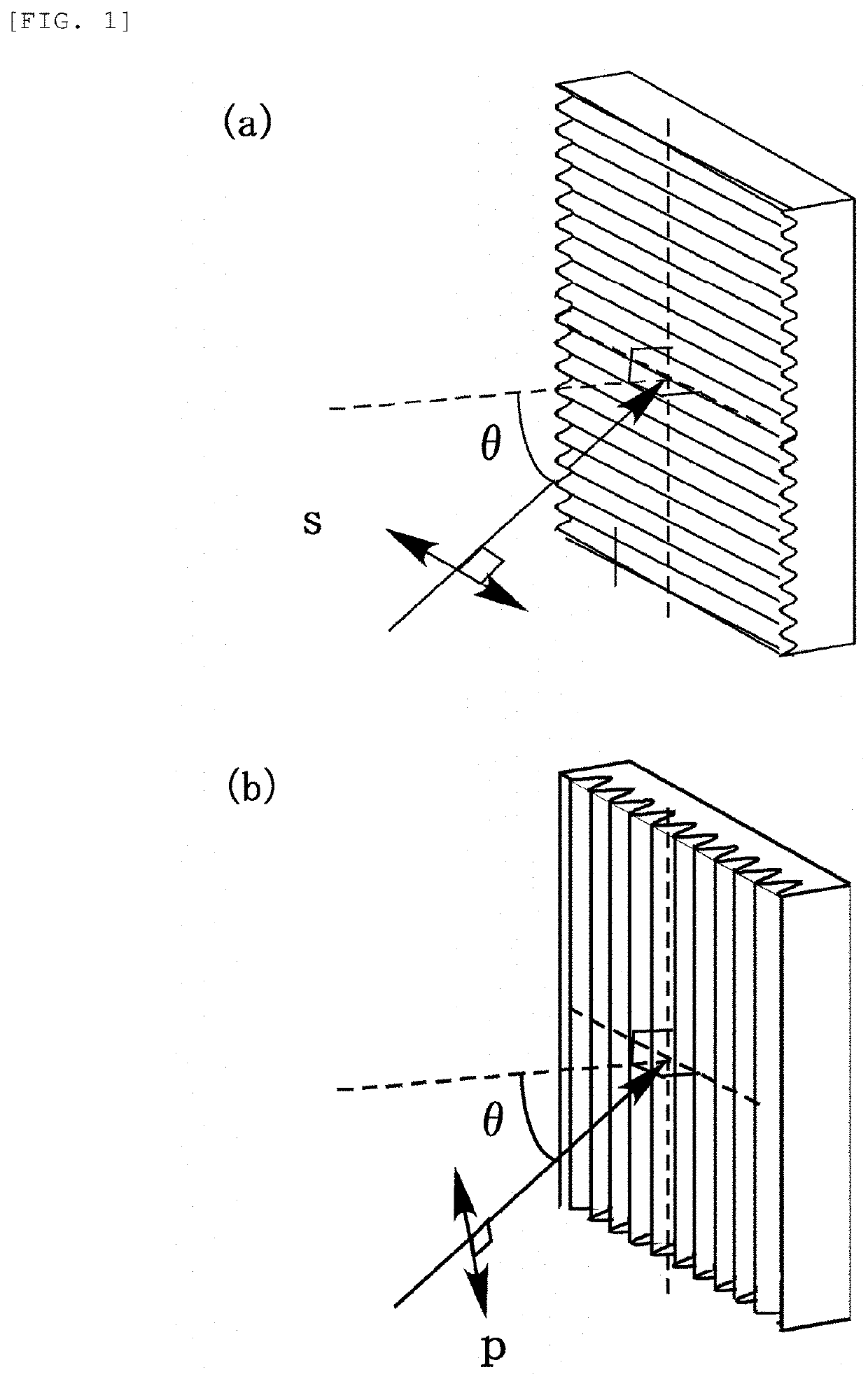
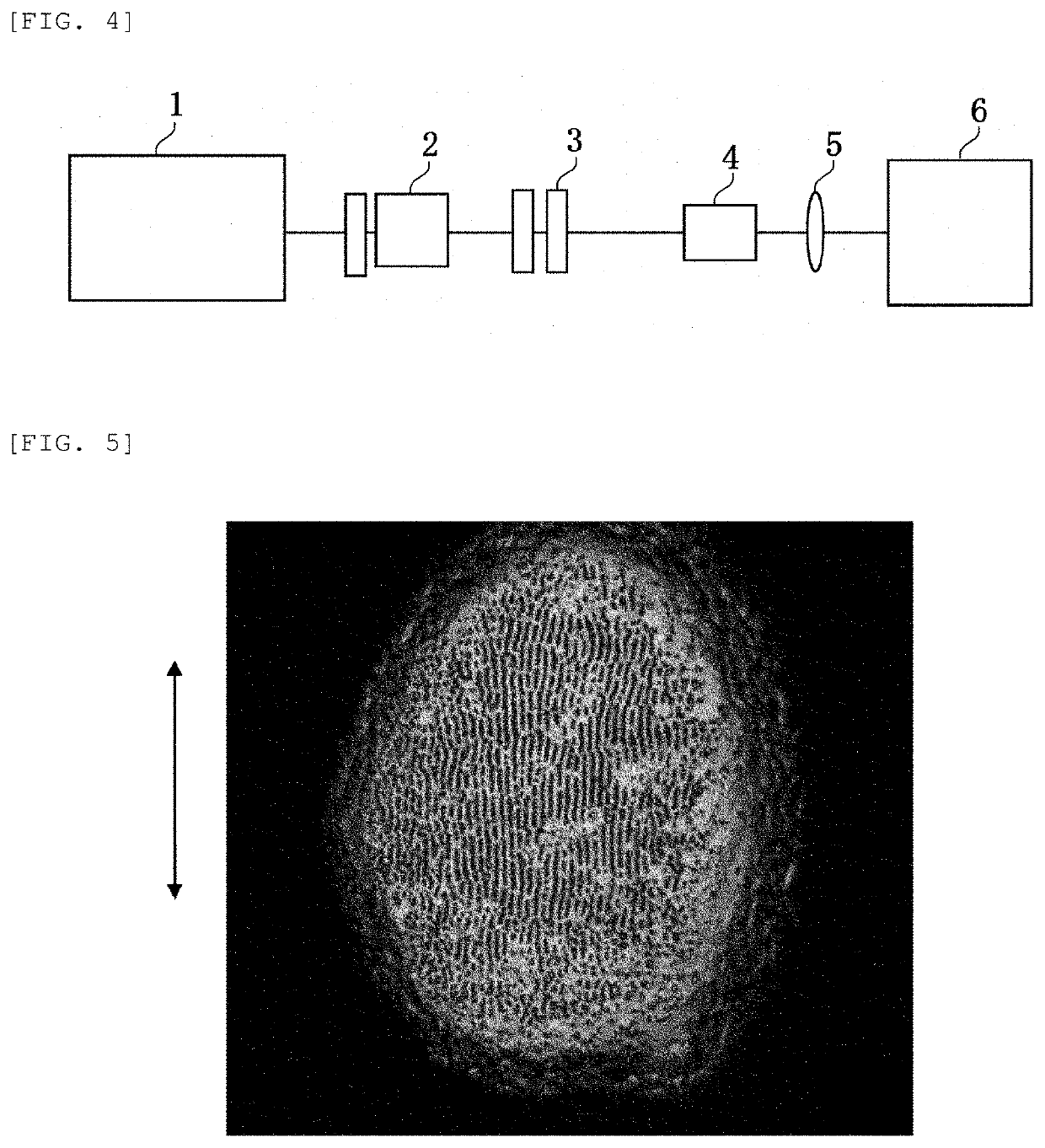
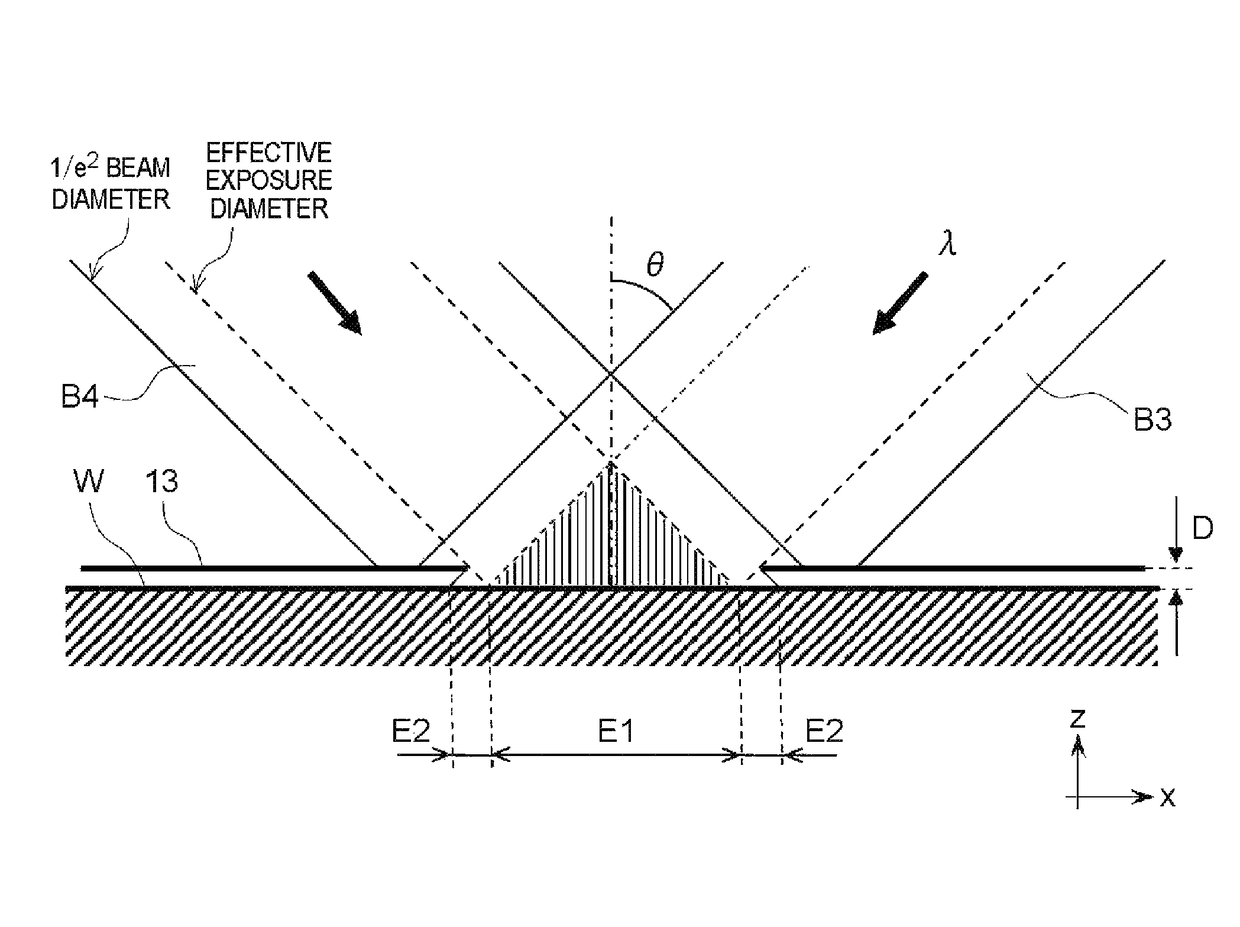
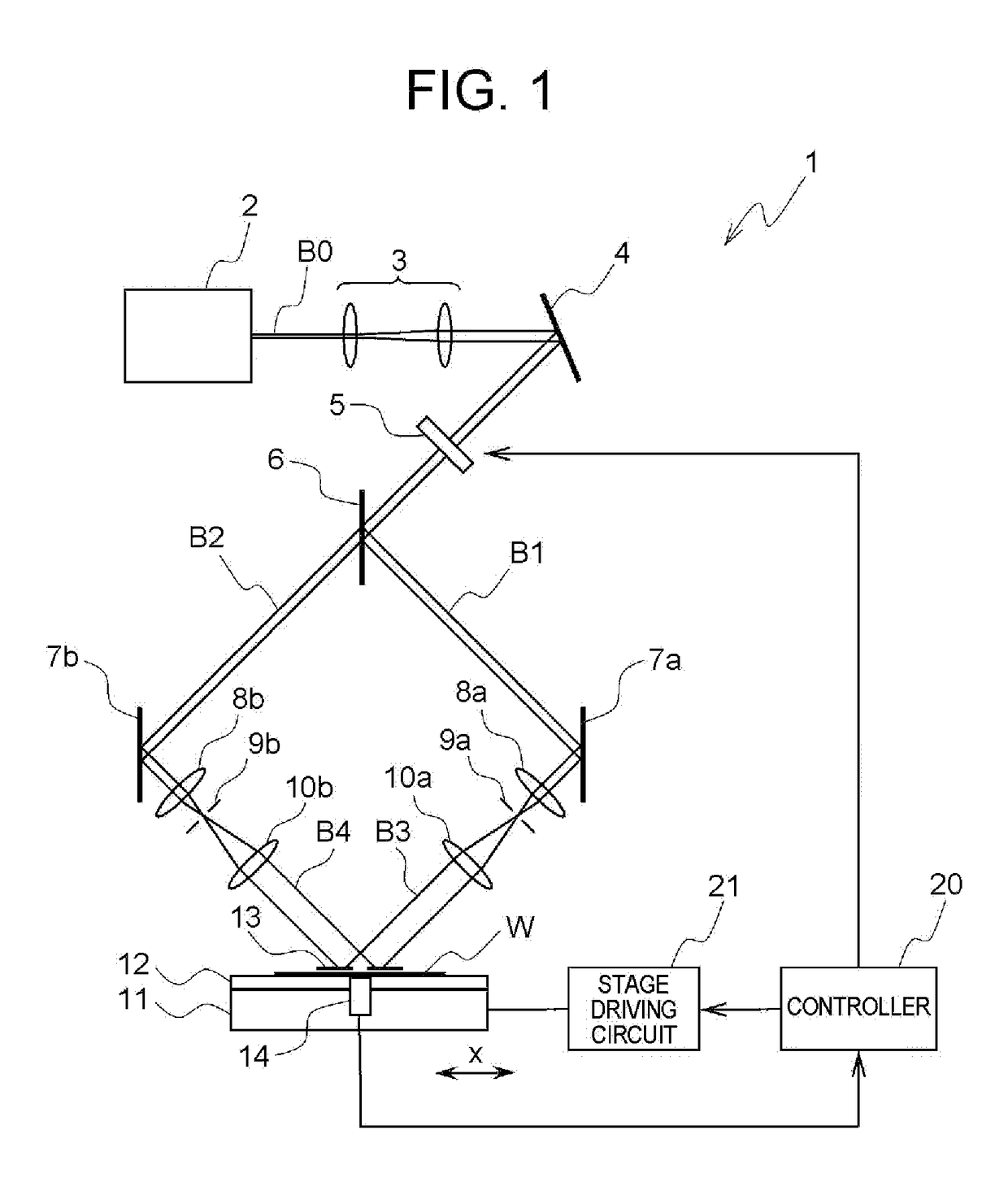
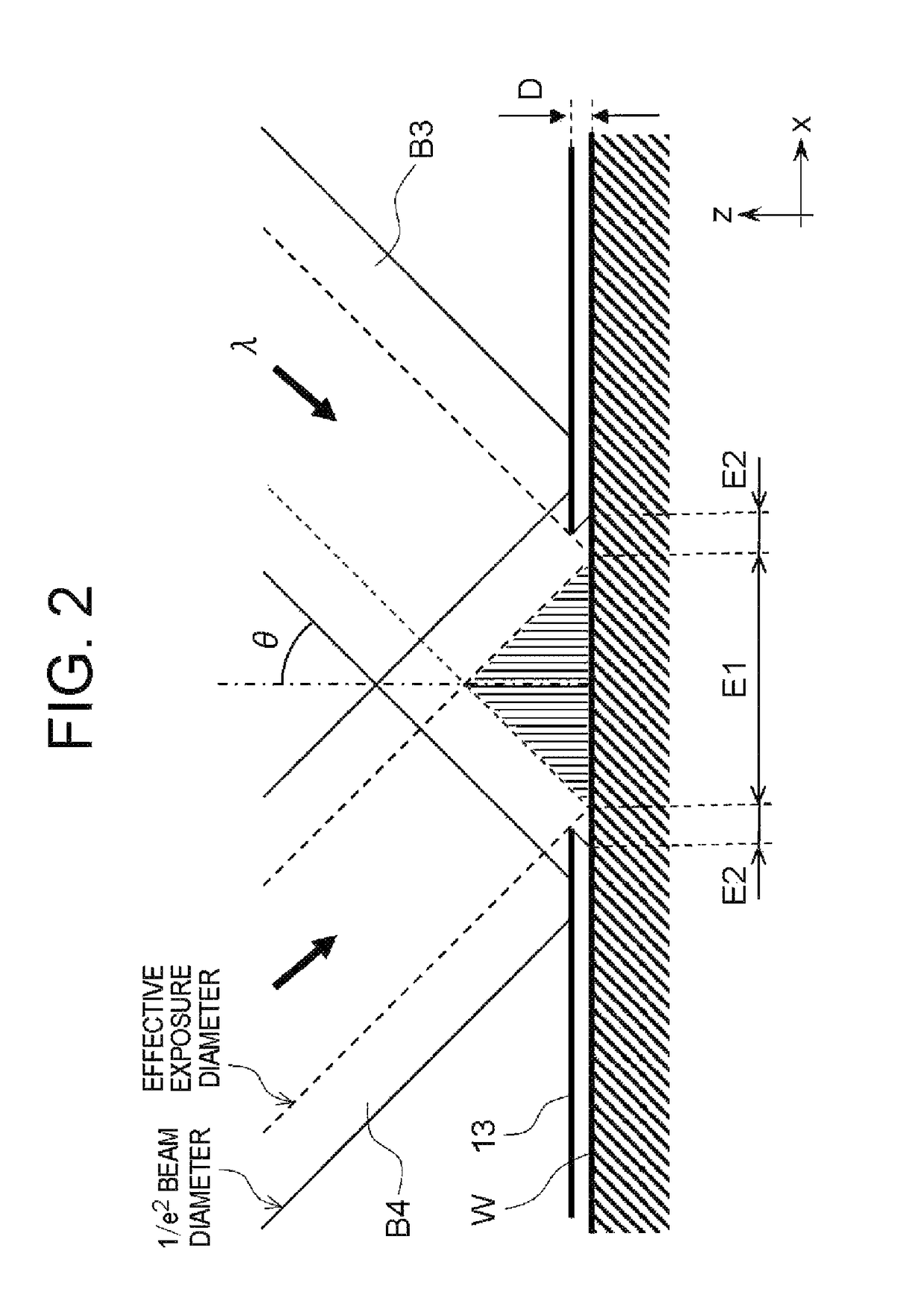
Exposure method, method of fabricating periodic microstructure, method of fabricating grid polarizing element and exposure apparatus
ActiveUS20170261847A1Small sizeLow costPhotomechanical apparatusOptical elementsLight irradiationLight beam
Disclosed herein an exposure apparatus capable of implementing a microfabrication onto a work with a higher throughput and a lower cost. The exposure apparatus generates interfering light by crossing two or more branched light beams branched from output light from a coherent light source at a predetermined interfering angle, and exposes the substrate by repeating an irradiation onto the substrate with the interfering light and a conveyance of the substrate. At this moment, the exposure apparatus shapes in interfering light irradiation region on the substrate onto which the interfering light is irradiated into a predetermined shape. Then, the exposure apparatus disposes a plurality of the interfering light irradiation regions in successive shots to be located adjacent to each other on the substrate in a direction of conveying the substrate without the interfering light irradiation regions being overlapped when exposing the substrate while conveying the substrate in a stepwise manner.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Light guide plate and backlight module group employing same
ActiveCN107102396AImprove convergence characteristicsReduce crosstalkPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsLight guidePeriodic microstructure
The invention discloses a light guide plate and a backlight module group employing the same. The light guide plate comprises a light incoming surface, a transmission layer, and a light outgoing surface. The transmission layer is provided with an optical wave conducting layer which enables the propagation direction of at least a part of light entering from the light incoming surface to be perpendicular to the light outgoing surface. The light outgoing surface is provided with a periodic microstructure. Through the above mode, the light guide plate can improve the convergence characteristic of light entering the light guide plate, reduces the crosstalk of optical paths of all sections, and achieves the superthin small-crosstalk display of 1D segmentation effect.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Solar concentrating method and device based on periodic microstructure
InactiveCN102201477AAvoid life shorteningImprove cooling effectRoof covering using slabs/sheetsRoof covering using tiles/slatesDiffraction orderGrating
The invention relates to a solar concentrating method and device based on a periodic microstructure, and particularly relates to a solar concentrator. The device comprises a transparent medium substrate and solar batteries, wherein a transparent thin film covers the upper surface of the transparent medium substrate; a periodic microstructure is prepared on the transparent thin film; and the solarbatteries are arranged on two sides of the transparent medium substrate, which are parallel to the direction of a grating slot line on the transparent thin film. When sunlight is incident to the transparent thin film of the solar concentrating device based on the periodic microstructure, the diffraction order with a diffraction angle exceeding the total reflection angle of the medium substrate spreads inside the medium substrate and finally arrives at the solar battery on the sidewalls of the medium substrate; and the diffraction order not forming the total reflection in the medium substrate and the zero order of the incident sunlight play the lighting role through the transparent medium substrate. The solar concentrating device has the advantages of small size, simple structure, low cost, no tracking, large receiving angle, high concentrating uniformity, and the like, and is particularly suitable for any buildings and vehicles with glass windows.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
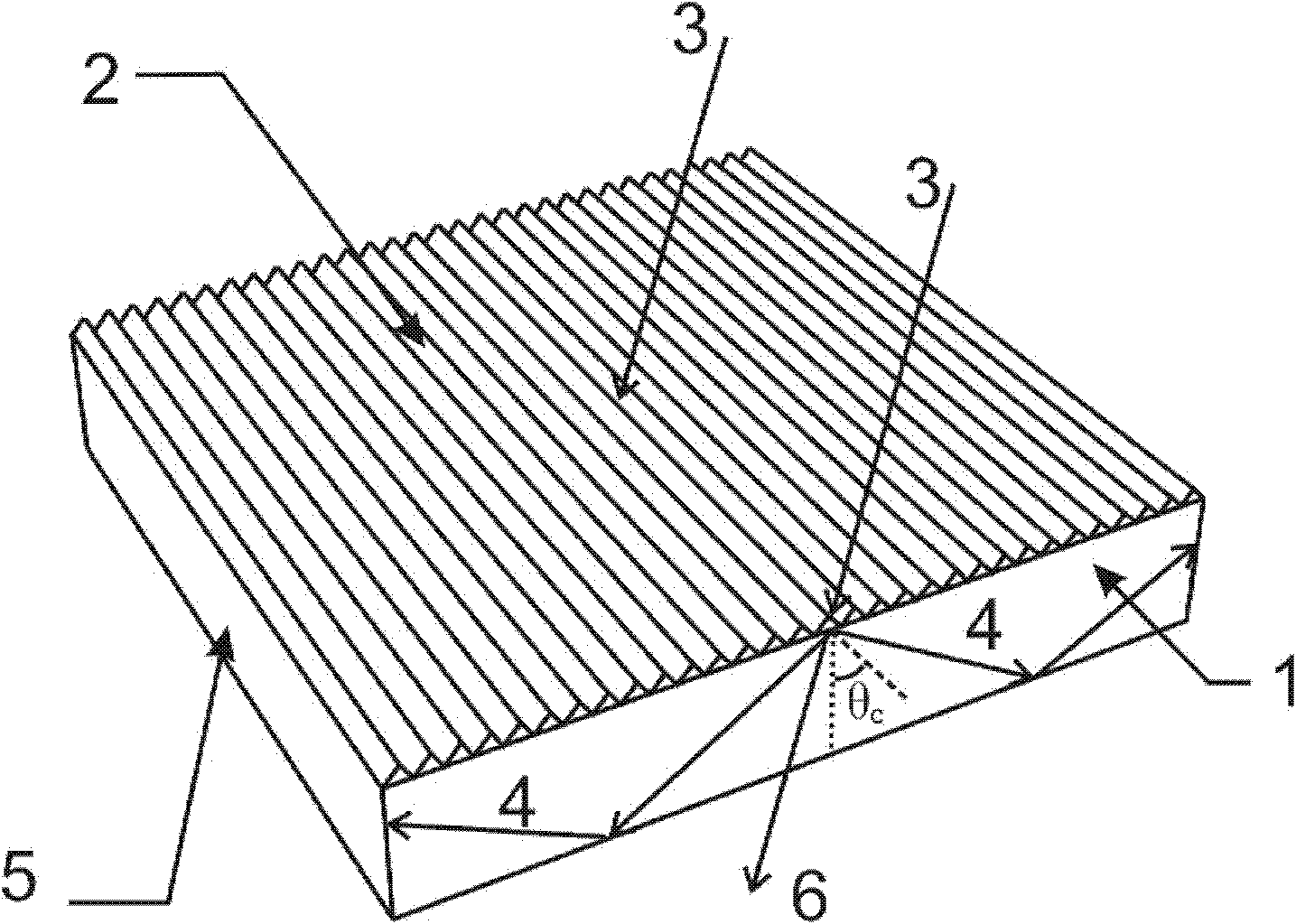
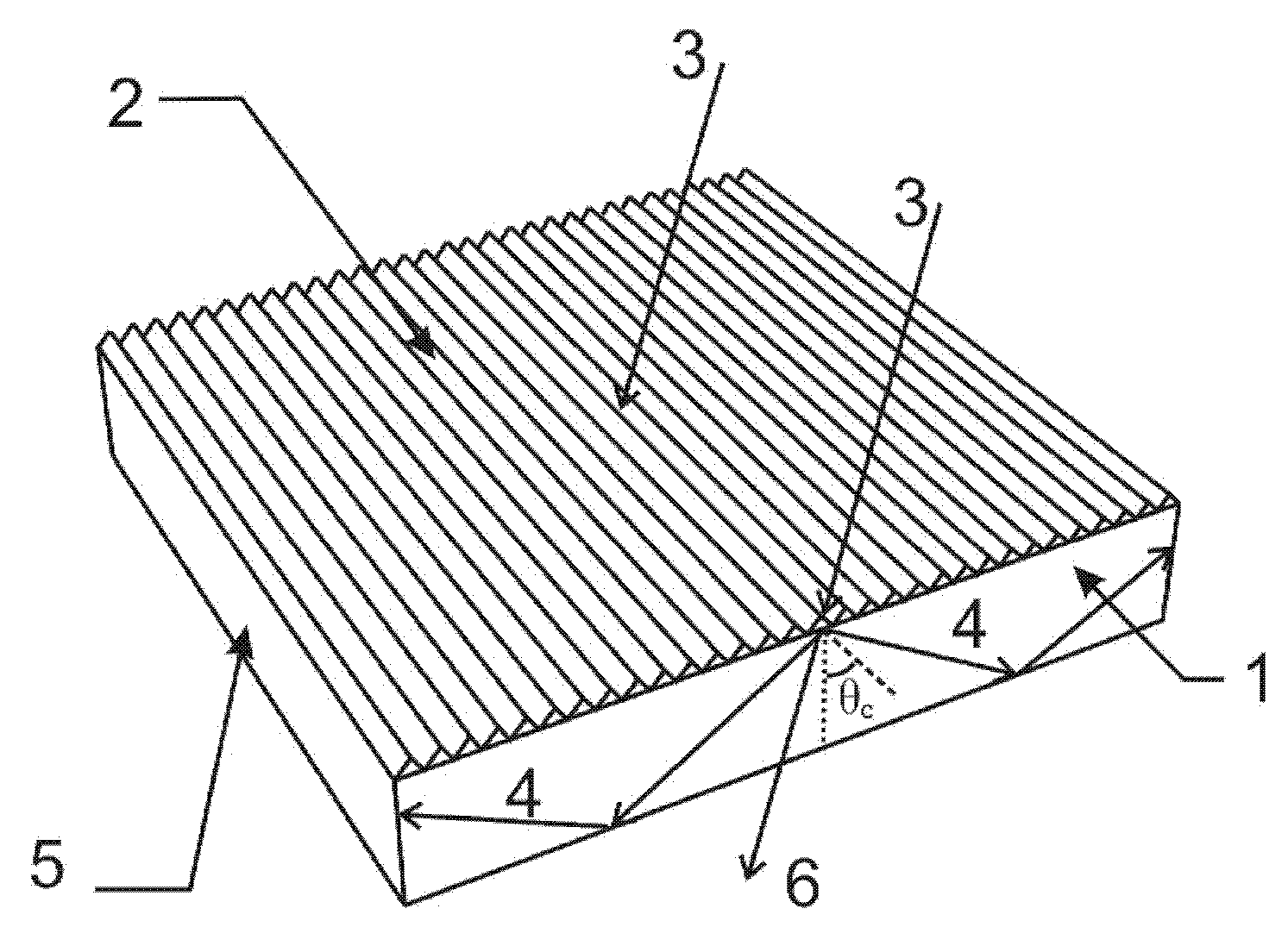
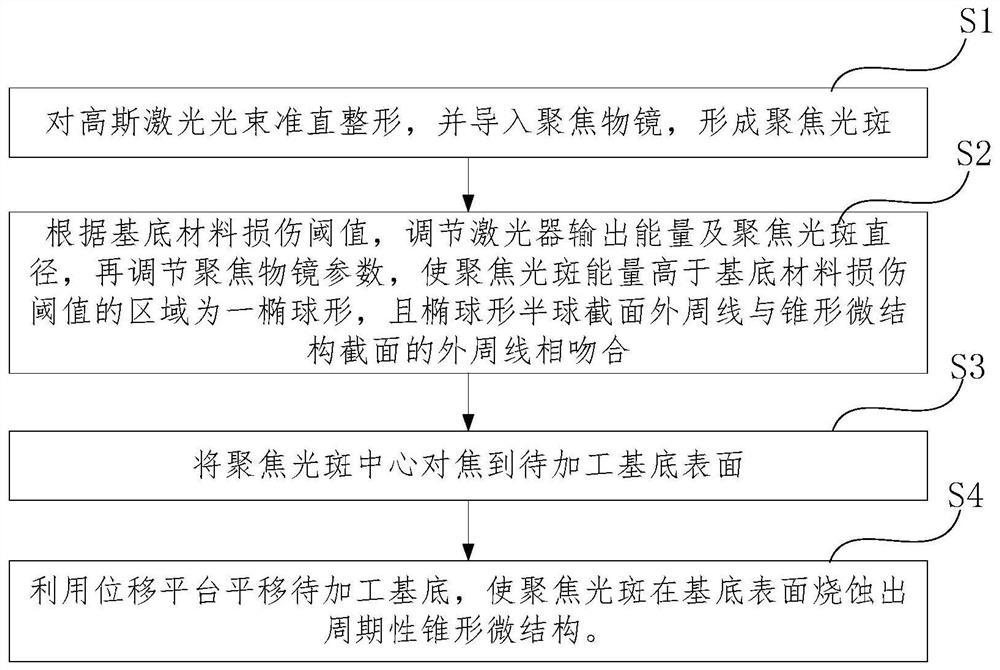
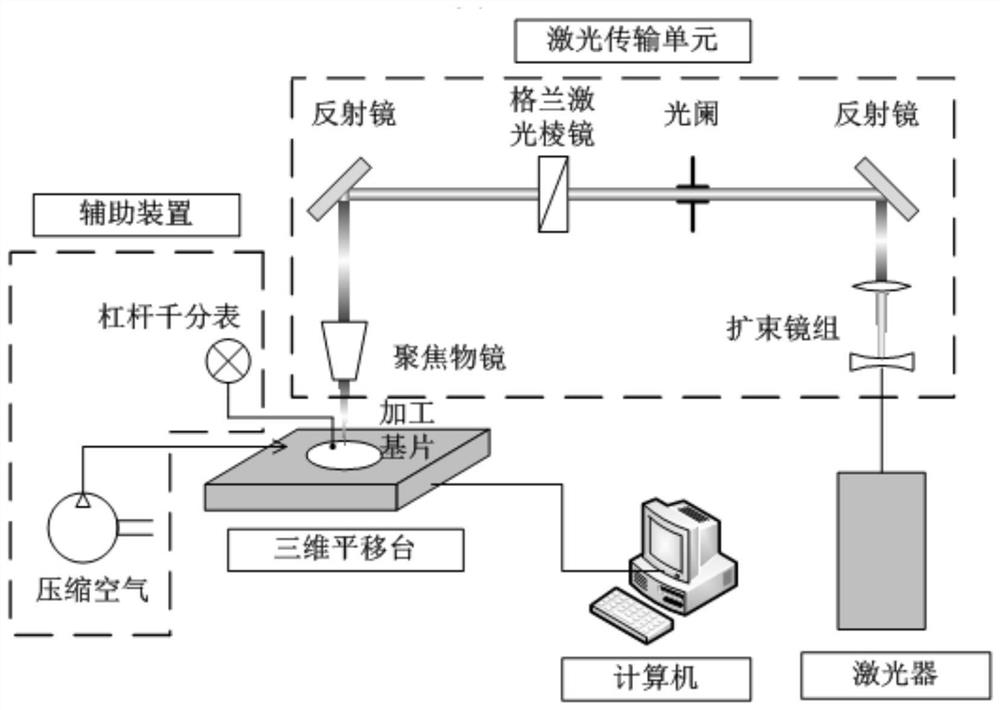
Processing method of surface periodic conical microstructure based on Gaussian beam focusing direct writing
The invention provides a processing method of a surface periodic conical microstructure based on Gaussian beam focusing direct writing, and aims to solve the problem of low processing efficiency of alarge-area surface periodic conical microstructure in the prior art. The processing method of the surface periodic conical microstructure comprises the following steps of: firstly, importing a Gaussian laser beam into a focusing objective lens to form a light spot; then, adjusting relevant parameters according to a substrate material damage threshold value, so that an area, of which the focusing light spot energy is higher than the substrate material damage threshold value, is ellipsoidal; and after the light spot is focused to a substrate processing surface, translating a substrate to be processed by utilizing a displacement platform, so that the focusing light spot ablates the periodic conical microstructure on the surface of the substrate. According to the processing method, high-precision focusing is not needed, the conical periodic microstructure is directly formed on the surface of the substrate by utilizing the energy distribution gradient of the Gaussian beam after focusing andthrough a scanning motion form, and the processing of a fine three-dimensional structure is completed at one time, so that the speed is high, the efficiency is high, the process flow is simple, and high-precision continuous non-planar processing can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG INST OF TECH PHYSICS
Surface structure forming method for zirconia-based ceramics, and zirconia-based ceramics
ActiveUS10774003B2Improve adhesionIncrease resistanceDental implantsJoint implantsCrystallographyLaser beams
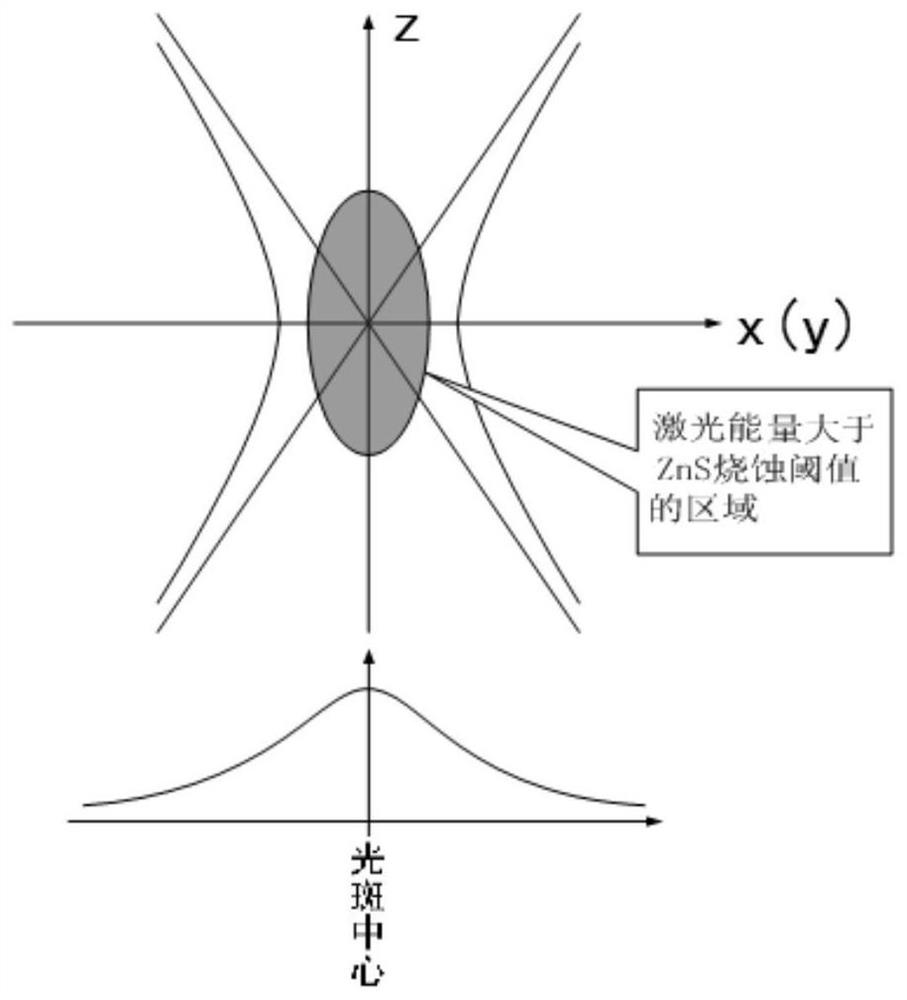
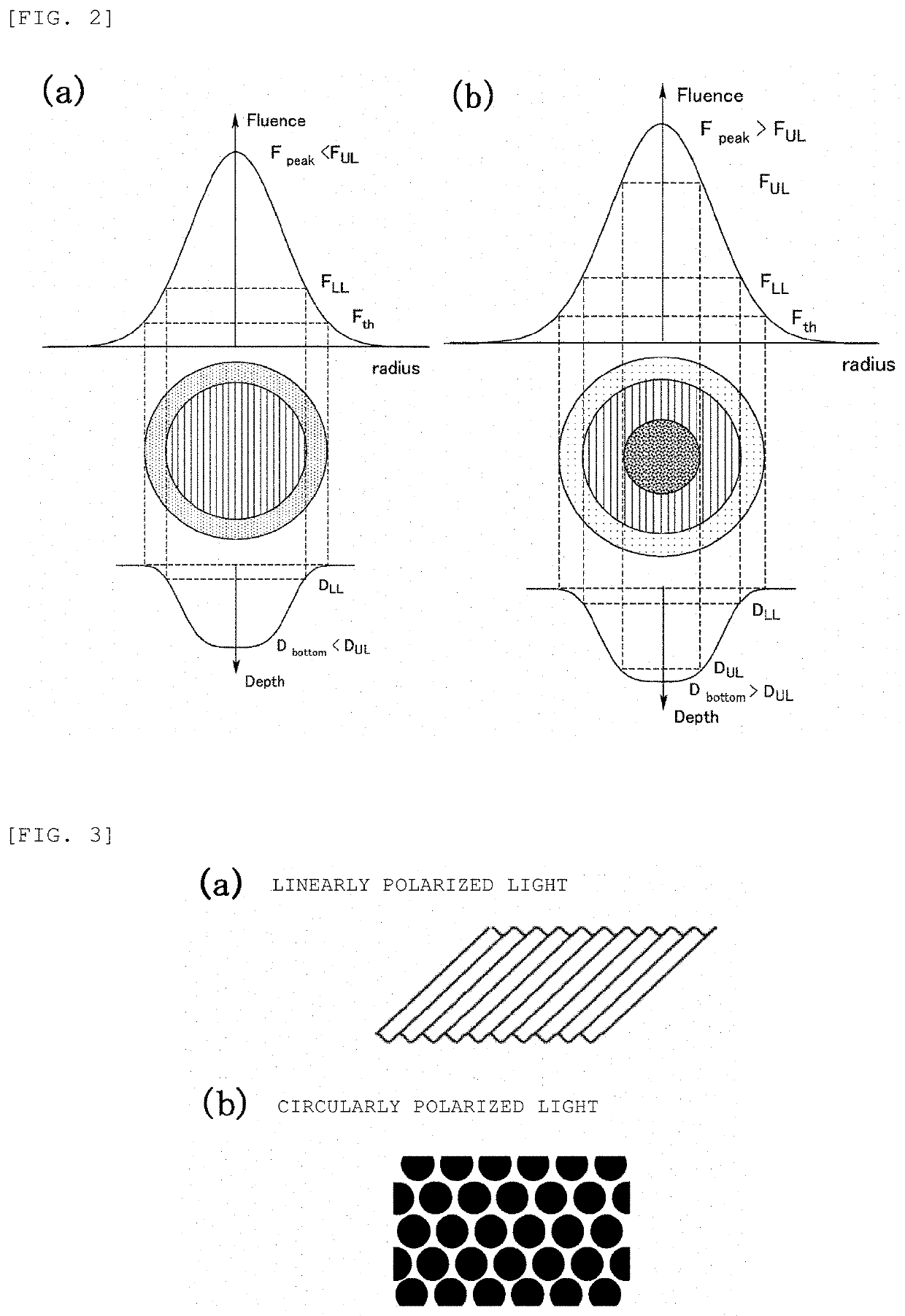
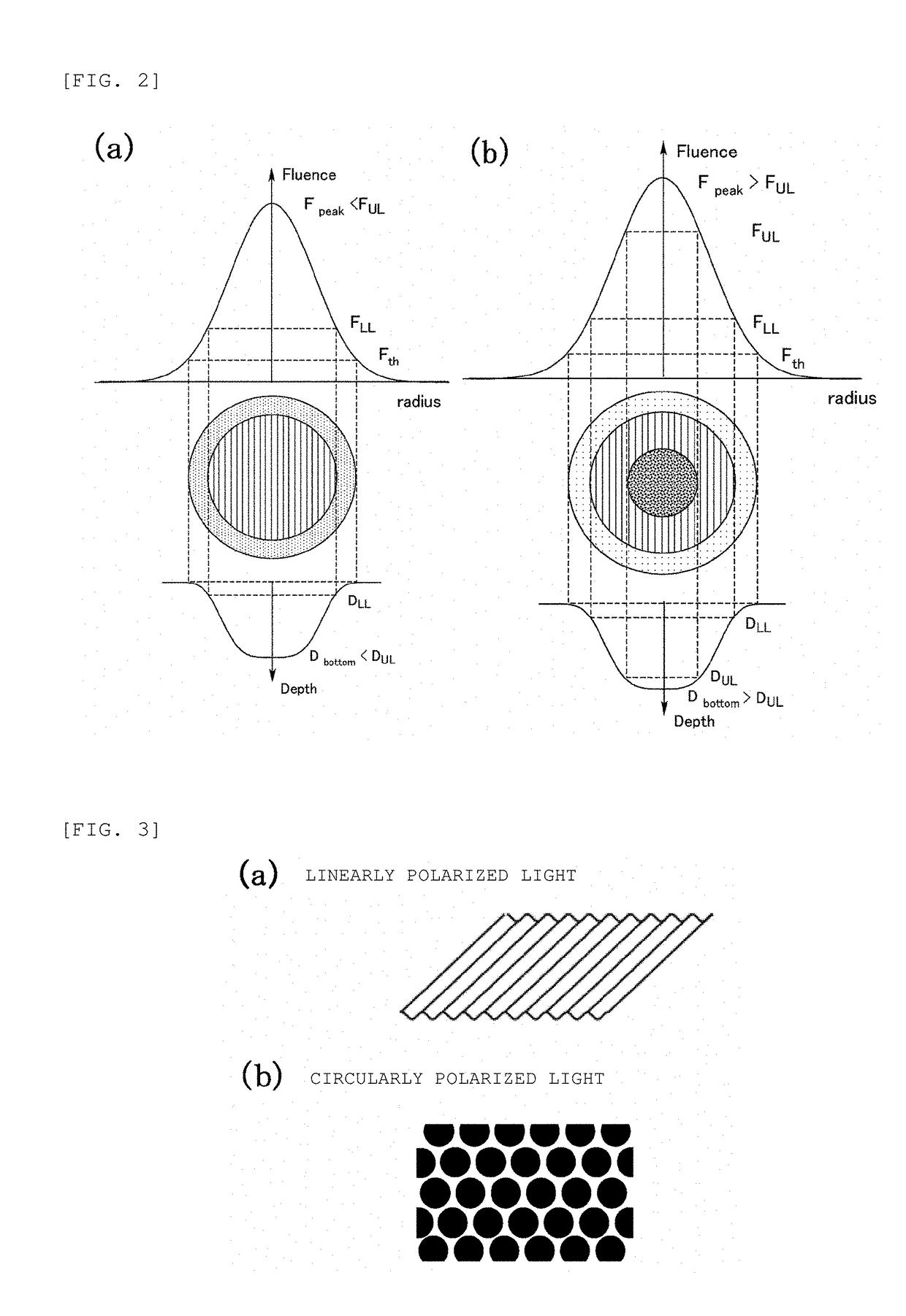
Provided herein is a method for forming a periodic microstructure on a surface of zirconia-based ceramics, which are not easily mechanically workable, without causing thermal adverse effects. A zirconia-based ceramic having a surface periodic microstructure is also provided. A linearly or circularly polarized laser beam is irradiated to a zirconia-based ceramic surface, and periodic irregularities are formed in a spot of the laser beam. Stripe-pattern irregularities parallel to the direction of polarization can be formed in a spot of a laser beam by irradiating a linearly polarized ultrashort pulsed-laser beam to a zirconia-based ceramic surface. A mesh-like raised region and a dot-like recessed region can be periodically formed by irradiating a circularly polarized ultrashort pulsed-laser beam to a ceramic surface.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
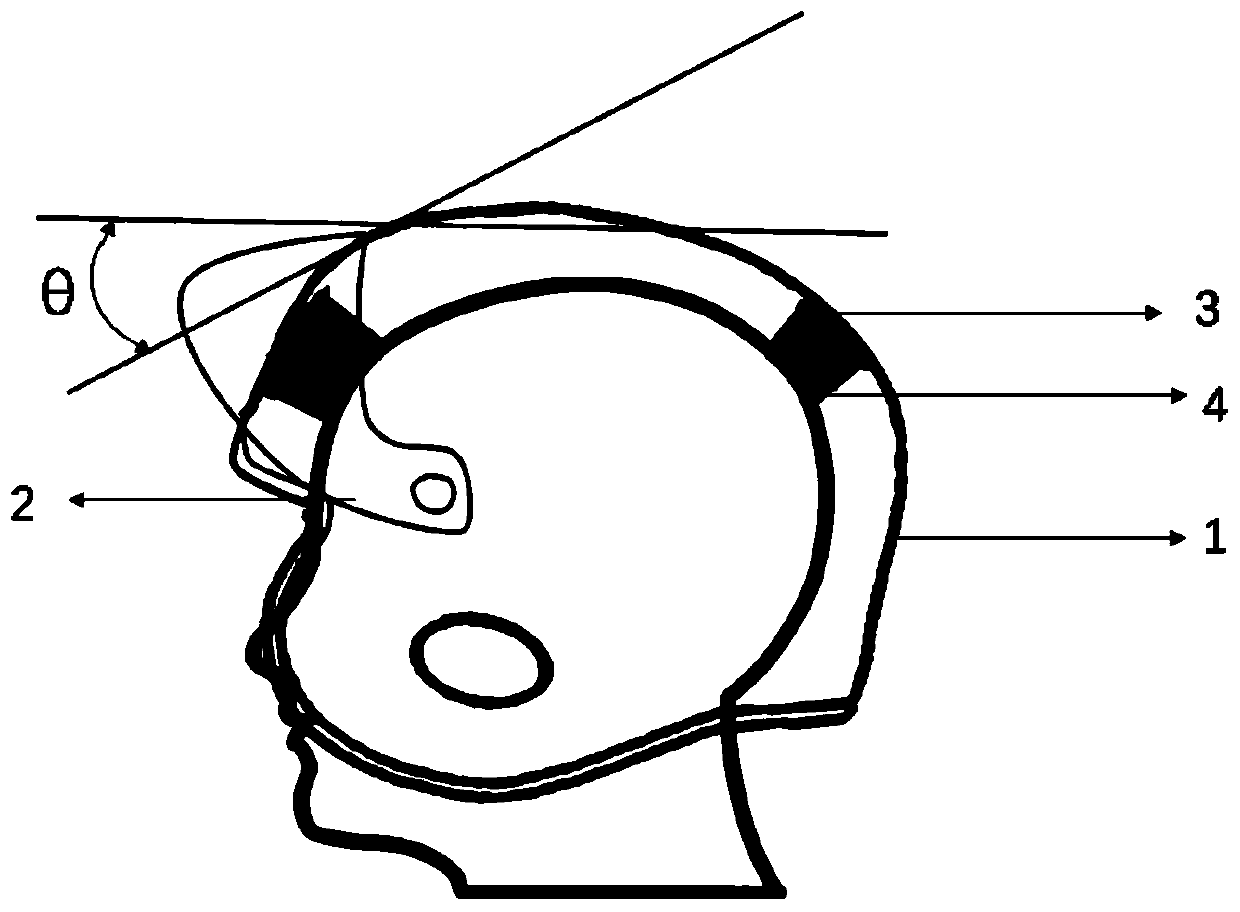
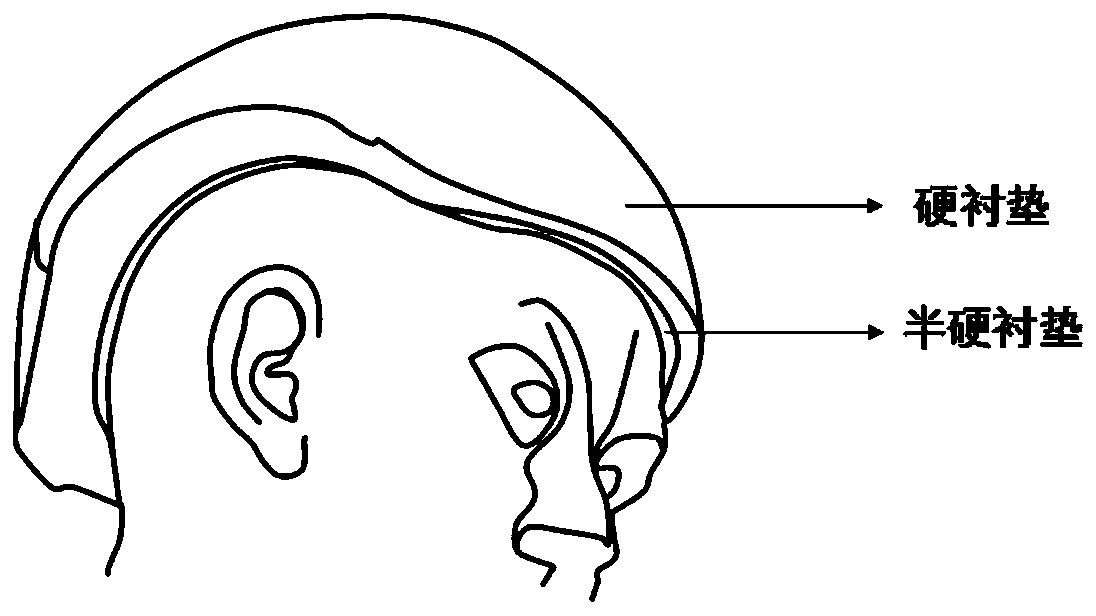
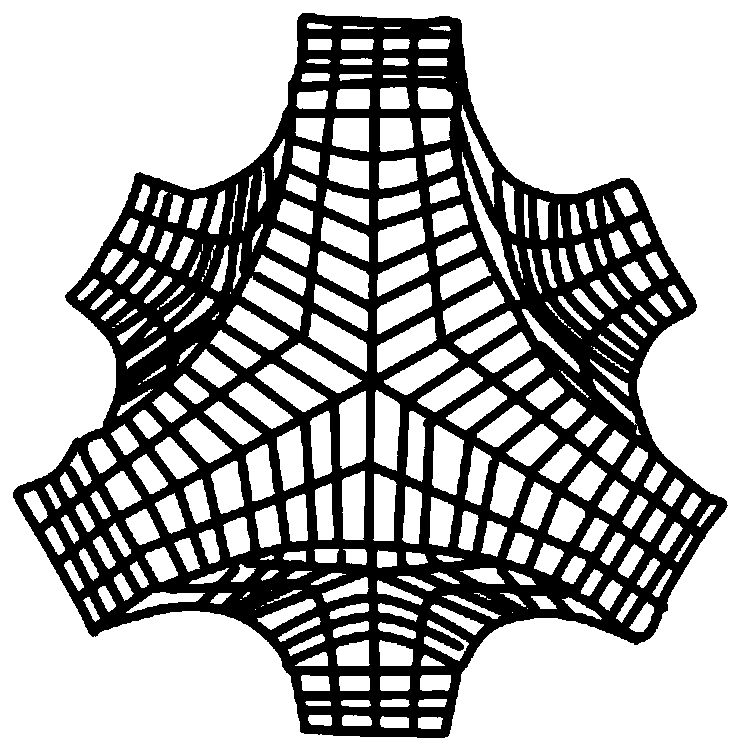
Protective helmet with negative Poisson's ratio effect liner and design method thereof
PendingCN109977487ANegative Poisson's ratio effect is betterMeet comfort requirementsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsProtective glassesEngineering
The invention discloses a protective helmet with a negative Poisson's ratio effect liner and a design method thereof. The key of the protective helmet with the negative Poisson's ratio effect liner isthat the liner part is matched with a shell, a buffer layer and a pair of protective glasses. The designed protective helmet can be customized and has better protective performance. The method comprises the steps of firstly determining the head type of a user and the type of a selected helmet, determining the size of each component, and then combining the designed periodic microstructure with 3Dprinting for preparation according to different use requirements of the hard liner and the semi-hard liner; and finally, all the components are mutually combined for preparation, and the use requirements are met. The manufactured helmet is lighter and thinner while reducing weight, the helmet can be customized according to personal head type differences, wearing is more comfortable, and the requirements for protection, functions and comfort are met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Exposure method, method of fabricating periodic microstructure, method of fabricating grid polarizing element and exposure apparatus
ActiveUS10101652B2Small sizeReduce in quantityPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight irradiationLight beam
Disclosed herein an exposure apparatus capable of implementing a microfabrication onto a work with a higher throughput and a lower cost. The exposure apparatus generates interfering light by crossing two or more branched light beams branched from output light from a coherent light source at a predetermined interfering angle, and exposes the substrate by repeating an irradiation onto the substrate with the interfering light and a conveyance of the substrate. At this moment, the exposure apparatus shapes in interfering light irradiation region on the substrate onto which the interfering light is irradiated into a predetermined shape. Then, the exposure apparatus disposes a plurality of the interfering light irradiation regions in successive shots to be located adjacent to each other on the substrate in a direction of conveying the substrate without the interfering light irradiation regions being overlapped when exposing the substrate while conveying the substrate in a stepwise manner.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
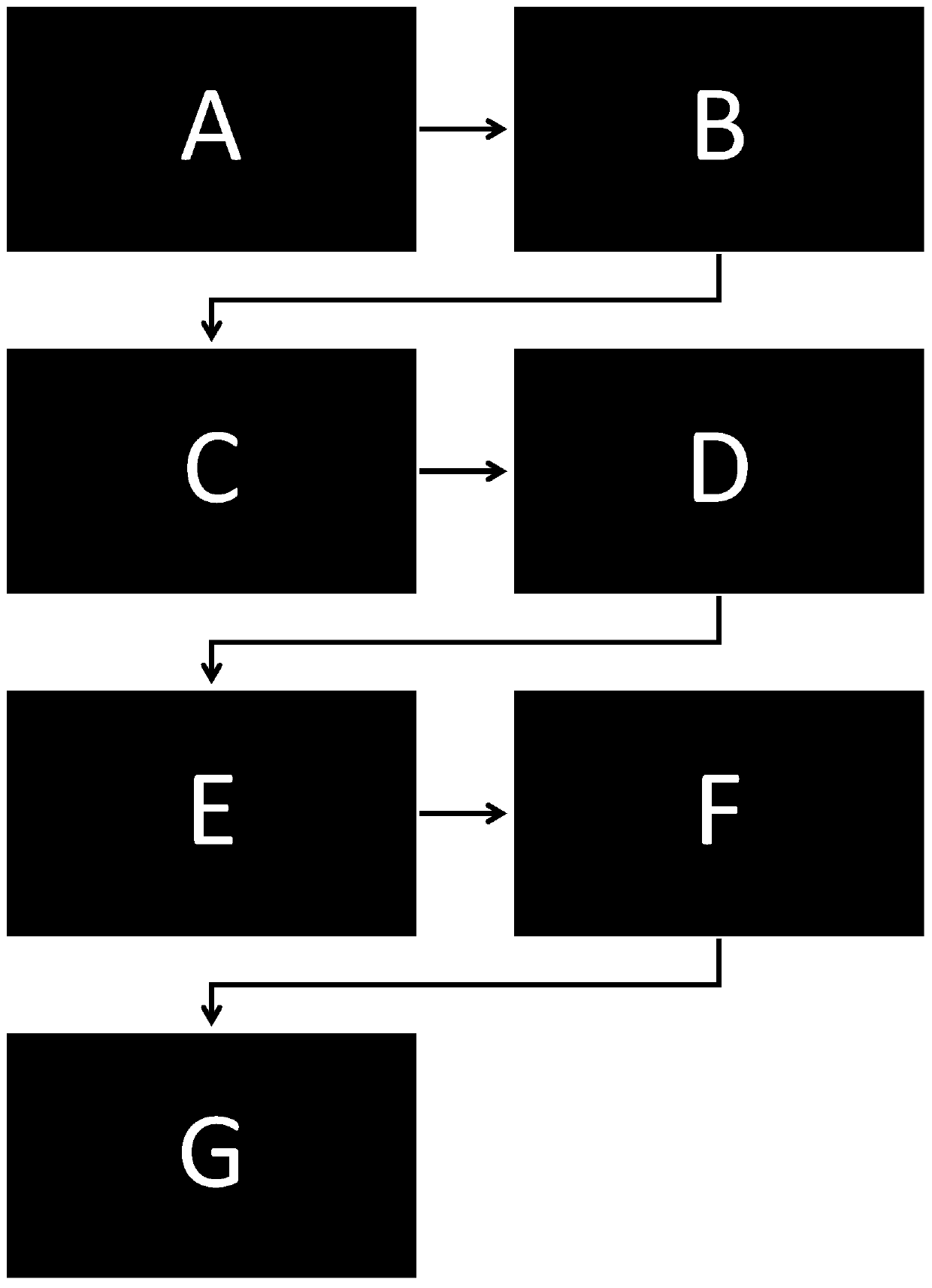
Filter for carbon ion terahertz characteristic spectral line detection and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110021802AImprove reliabilityEasy to integrateResonatorsPhotoresistPeriodic microstructure
The invention discloses a filter for carbon ion terahertz characteristic spectral line detection and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of terahertz and semiconductor micro-processing. The filter for carbon ion terahertz characteristic spectral line detection comprises a main transverse shaft, a secondary transverse shaft, and a longitudinal shaft, wherein the longitudinal shat penetrates through the middle of the main transverse shaft and the secondary transverse shaft. A resonance unit is a metal hollow-out layer; a substrate is polyimide with the thickness of 25 microns; and the metal layer of the resonance unit is a 200 nm gold layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of step A, putting the polyimide substrate subjected to laser processing into deionized water; carrying out other steps; and step G, clamping a product by using ceramic tweezers, slowly shaking in an acetone solution, and stripping the extra metal layer after the photoresist is corroded by acetone, and forming a hollowed-out Orthodox-type cross type resonance unit which is consistent with the design pattern on one side of the periodic microstructure. The method hasthe advantages of simple process, convenient operation and low cost. High adhesion can be obtained without annealing, so that the reliability and the integration of the device are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Photonic crystal based on laser etching graphene film stack and processing method
ActiveCN111880261ABy blockingQuick tuneOptical light guidesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingPhotonic crystal
The invention provides a photonic crystal based on laser etching graphene film stacking, which comprises a plurality of double-layer crystal structures stacked together, each double-layer crystal structure comprises a glass substrate and a graphene film, and a periodic microstructure pattern is arranged in an area, corresponding to the hollow part of the annular glass substrate, on the graphene film. A graphene film layer and an air layer are formed on the double-layer crystal structure, and the thickness of the air layer can be adjusted by changing the thickness of the glass substrate; the periodic microstructure pattern on the graphene film is manufactured by adopting a laser etching method according to a design pattern. The invention further provides a processing method of the photoniccrystal based on laser etching of the graphene film stack. According to the method, the photonic crystal can be rapidly prepared, the process is simple and easy to implement, parameters such as the size of the designed micro-periodic structure and an etching pattern can be rapidly adjusted, finally, control over propagation of light with different frequencies in the photonic crystal is achieved, and the method has excellent design flexibility and parameter adjustability.
Owner:温州大学平阳智能制造研究院
Preparation method and application of responsive structural color micro-pipeline
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a responsive structural color micro-pipeline. According to the method, a vertical deposition method is utilized to obtain a tubular colloidal crystal template; a glass rod is inserted into the tubular colloidal crystal template; a hydrogel pre-polymerization solution is injected into a gap between the tubular colloidal crystal template and the glass rod; the template is removed after the solution is solidified, and the responsive structural color micro-pipeline is obtained after reduction reaction. The responsive structural color micro-pipeline prepared by the method of the invention can generate shape change under certain stimulation, can be applied to a microfluidic system, is used for controlling the flow speed and the flow direction of fluid, inherits a periodic microstructure of the colloidal crystal template, has intuitive structural color change during deformation, and provides a real-time visual sensing analysis function. The structural color micro-pipeline based on the responsive hydrogel has the advantages of being simple in preparation method, convenient to operate, low in production cost and the like, and is high in practicability.
Owner:NANJING DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL
Surface structure forming method for zirconia-based ceramics, and zirconia-based ceramics
ActiveUS20170260100A1Improve heat resistanceHigh mechanical strengthDental implantsJoint implantsLight beamPulsed laser beam
Provided herein is a method for forming a periodic microstructure on a surface of zirconia-based ceramics, which are not easily mechanically workable, without causing thermal adverse effects. A zirconia-based ceramic having a surface periodic microstructure is also provided. A linearly or circularly polarized laser beam is irradiated to a zirconia-based ceramic surface, and periodic irregularities are formed in a spot of the laser beam. Stripe-pattern irregularities parallel to the direction of polarization can be formed in a spot of a laser beam by irradiating a linearly polarized ultrashort pulsed-laser beam to a zirconia-based ceramic surface. A mesh-like raised region and a dot-like recessed region can be periodically formed by irradiating a circularly polarized ultrashort pulsed-laser beam to a ceramic surface.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Microstructural on-chip light source device based on straight waveguide total reflection coupling connection and production method of microstructural on-chip light source device
PendingCN108521073AAchieve controllable optical power outputReduce lossLaser optical resonator constructionCouplingWaveguide
The invention relates to technical field of design of photoelectronic devices and particularly relates to a microstructural on-chip light source device based on straight waveguide total reflection coupling connection and a production method of the microstructural on-chip light source device. The microstructural on-chip light source device is characterized by comprising a substrate, a straight waveguide interlinking cavity and an output waveguide section, wherein the substrate is used for bearing functional devices and injecting current and comprises a lower metal layer, a substrate material layer, an insulating layer and an upper metal layer which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top; the straight waveguide interlinking cavity is used for generating laser oscillation, is arranged on the substrate material layer and comprises four strip-shaped straight waveguide cavity subsections which are interlinked through right angles, a total-reflection mirror is arranged on the outer sidesurface of a joint of each two adjacent straight waveguide cavity subsections, and periodic microstructures are distributed on one straight waveguide cavity subsection; and the output waveguide section is arranged on the substrate material layer, and one end of the output waveguide section is connected to the end part of one straight waveguide cavity subsection. According to the microstructural on-chip light source device, the low-loss loop oscillation can be realized, and the power of the device is adjustable.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAXING LASER TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com