Teaching tool of from-to chart in logistics
An algorithm and logistics technology, which is applied in the field of teaching aids for logistics from to table algorithm, can solve the problems of cumbersome writing on the blackboard, large dependence on the blackboard, and high consumption of chalk, etc., and achieve the effects of short teaching time, no dust pollution, and simple use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
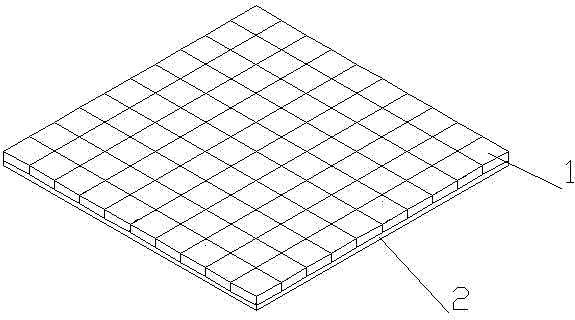
[0018] like figure 1 As shown, the teaching aid of the logistics from-to table algorithm in this embodiment includes several magnetic unit blocks 1 arranged on the magnetic pallet 2. The magnetic pallet 2 has certain magnetism and can absorb the magnetic unit blocks 1 tiled on it. , the magnetic unit block 1 is a square magnetic unit block of the same size, the back side is magnetic, and the front side can be written on with a pen. The magnetic unit block 1 tiled on it forms a matrix of magnetic unit block 1 from to (n+3)×(n+3), where the second magnetic unit block in the first row to the (n+1)th The first magnetic unit block and the second magnetic unit block to the (n+1)th magnetic unit block in the first column correspond to different devices from to the table, and the n+2th row (column) is the weight of a group of parts (the weight is equal to the weight product of each part), and the n+3th row (column) is the sum of the penalty points from the to table. During the calcu...
Embodiment 2
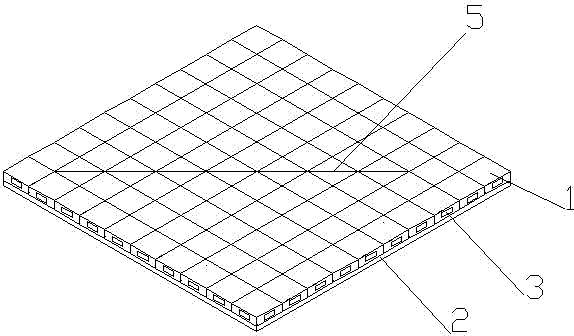
[0020] like Figures 2 to 3 Shown, the teaching aid of the logistics from to table algorithm of the present embodiment and figure 1 The structure of the teaching aid for the logistics from-to table algorithm shown is basically the same. The difference is that the magnetic unit block 1 is a hollow magnetic unit block, and the socket 3 is formed on the side of the magnetic unit block 1 . Preferably, the magnetic unit block 1 can be set as an inner cross hollow magnetic unit block, and four sockets 3 are formed on the four sides of the magnetic unit block 1, and the same direction sockets 3 of each magnetic unit block 1 are connected, and in the socket 3 It is provided with a cutting strip 4 that is longer than the edge of the magnetic pallet and has a smaller width than the width of the socket, which can be extracted at will. When in use, if a whole row or column of mobile magnetic unit blocks is required, the inserting strips only need to be inserted into the sockets of the m...
Embodiment 3
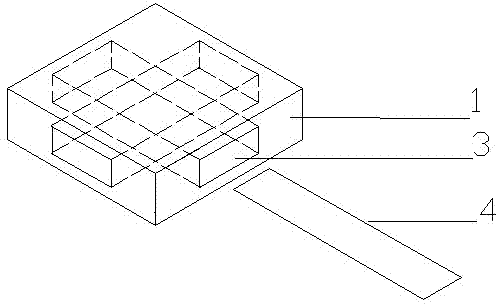
[0023] like Figure 4 As shown, the teaching aid of the logistics from-to table algorithm in this embodiment is basically the same in structure as the teaching aids of the first two kinds of logistics from-to table algorithms. The difference is that the teaching aid for the logistics from-to table algorithm also includes pallet handles arranged on the front side of the magnetic pallet 2 and the edges on the left and right sides. The edge of the supporting plate is composed of several blocking pieces 6, which are concave and convex. Each blocking piece 6 is arranged in the middle of two adjacent magnetic unit blocks 1, and the socket 3 of the magnetic unit block 1 is exposed outside the blocking piece 6. In addition, two corner stoppers 6 are provided at the front two corners of the magnetic pallet 1 . The magnetic unit block can be fixed on the magnetic supporting plate by setting the edge of the supporting plate to prevent the magnetic unit block from slipping.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com